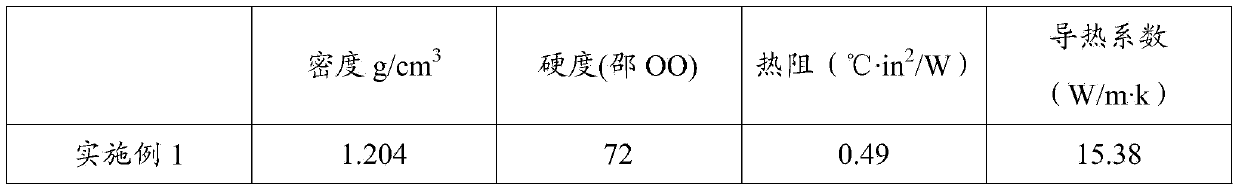
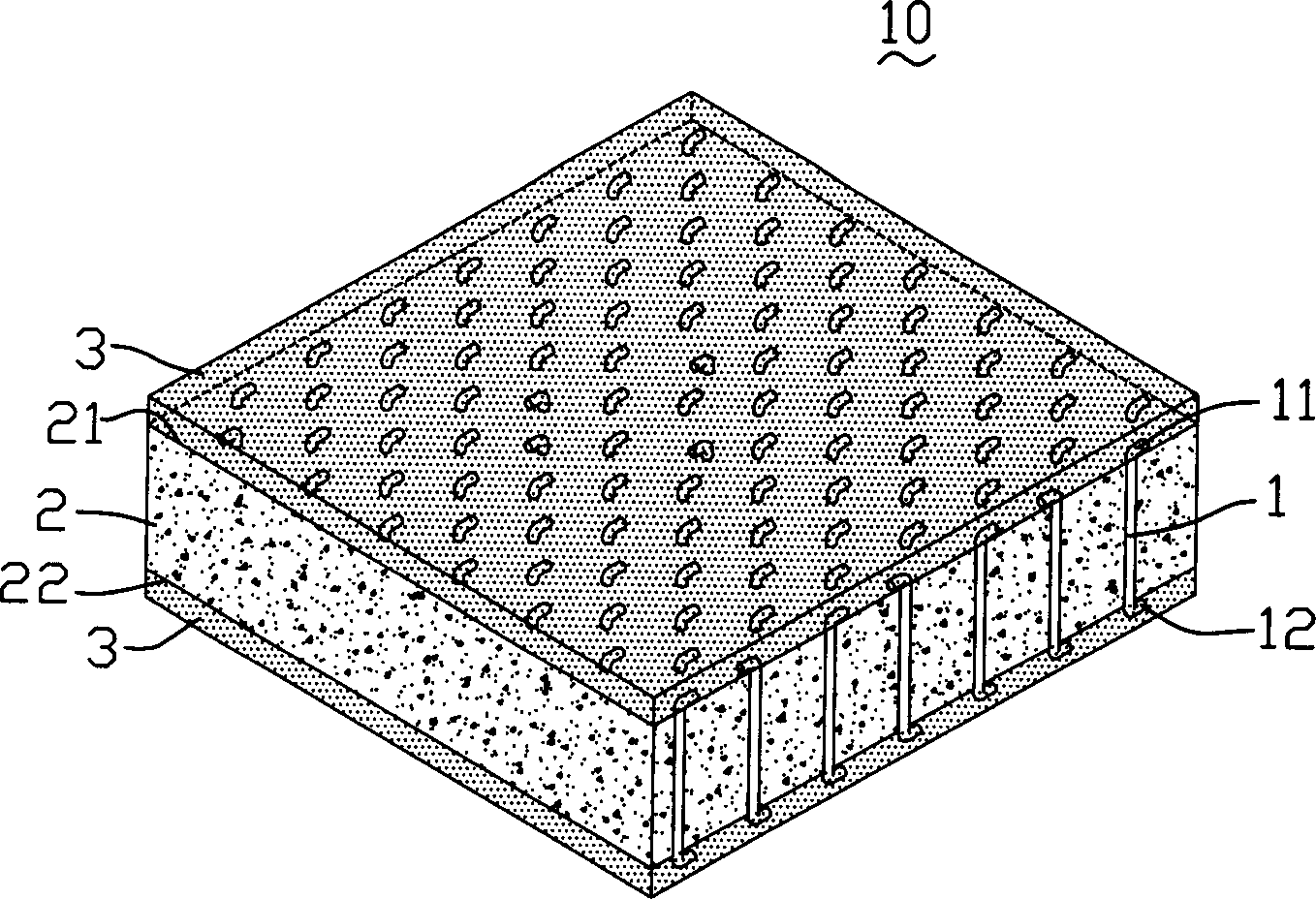
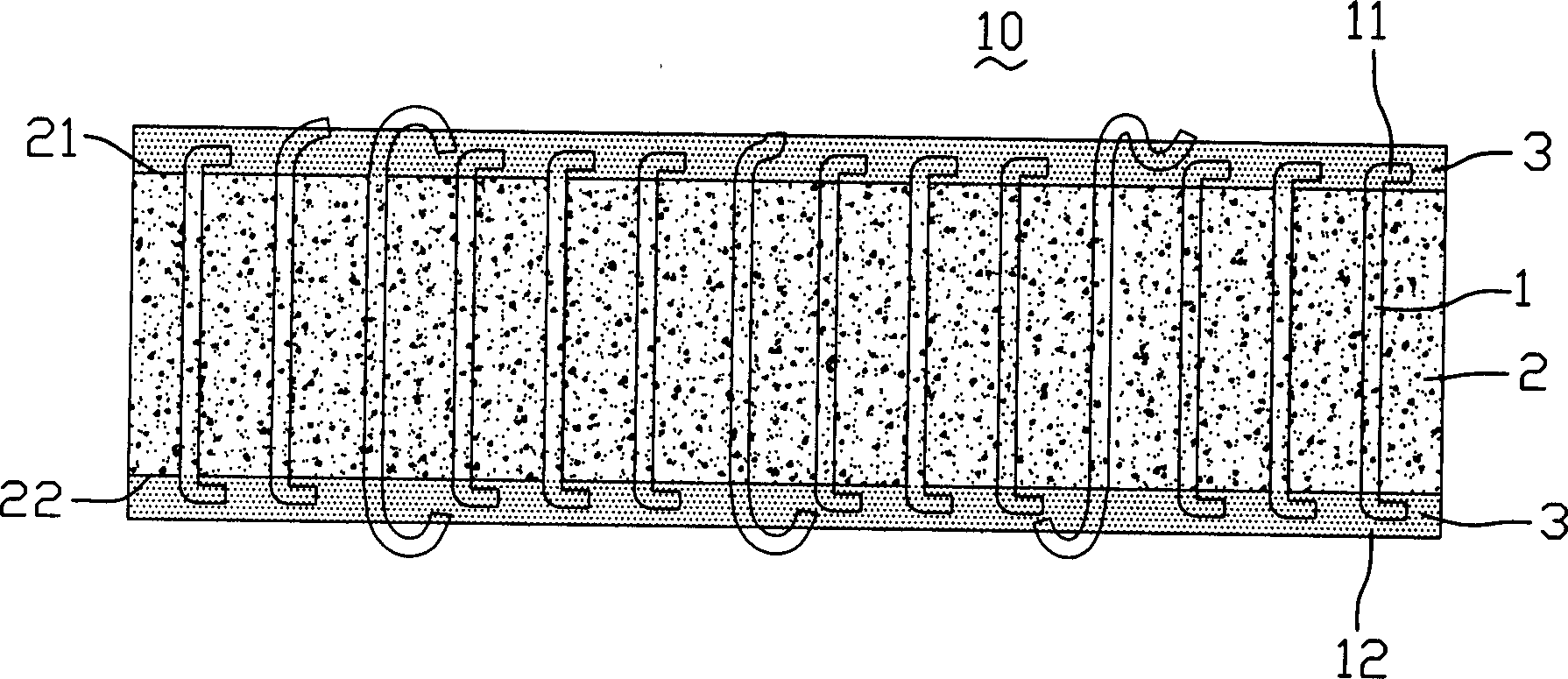
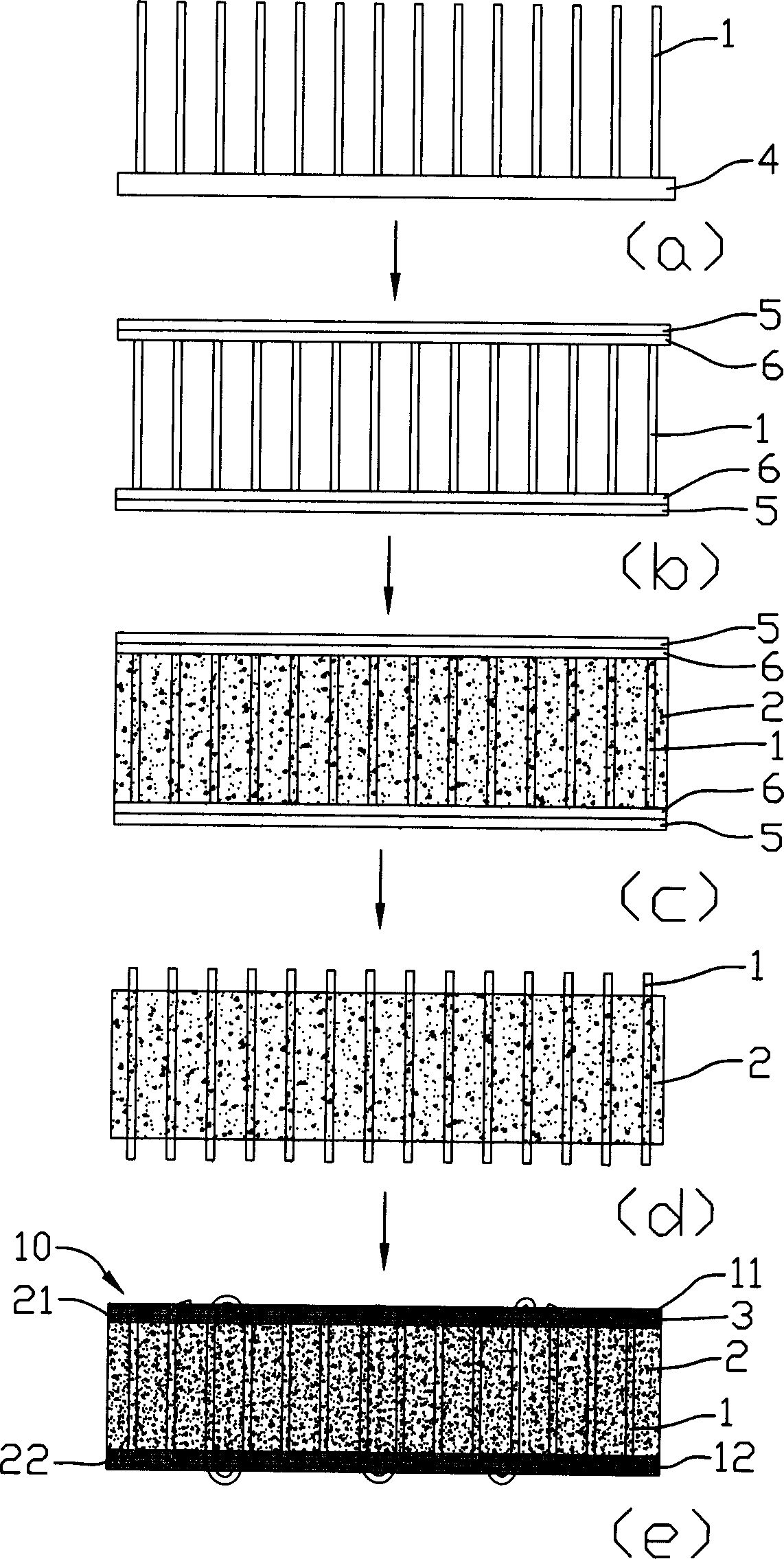
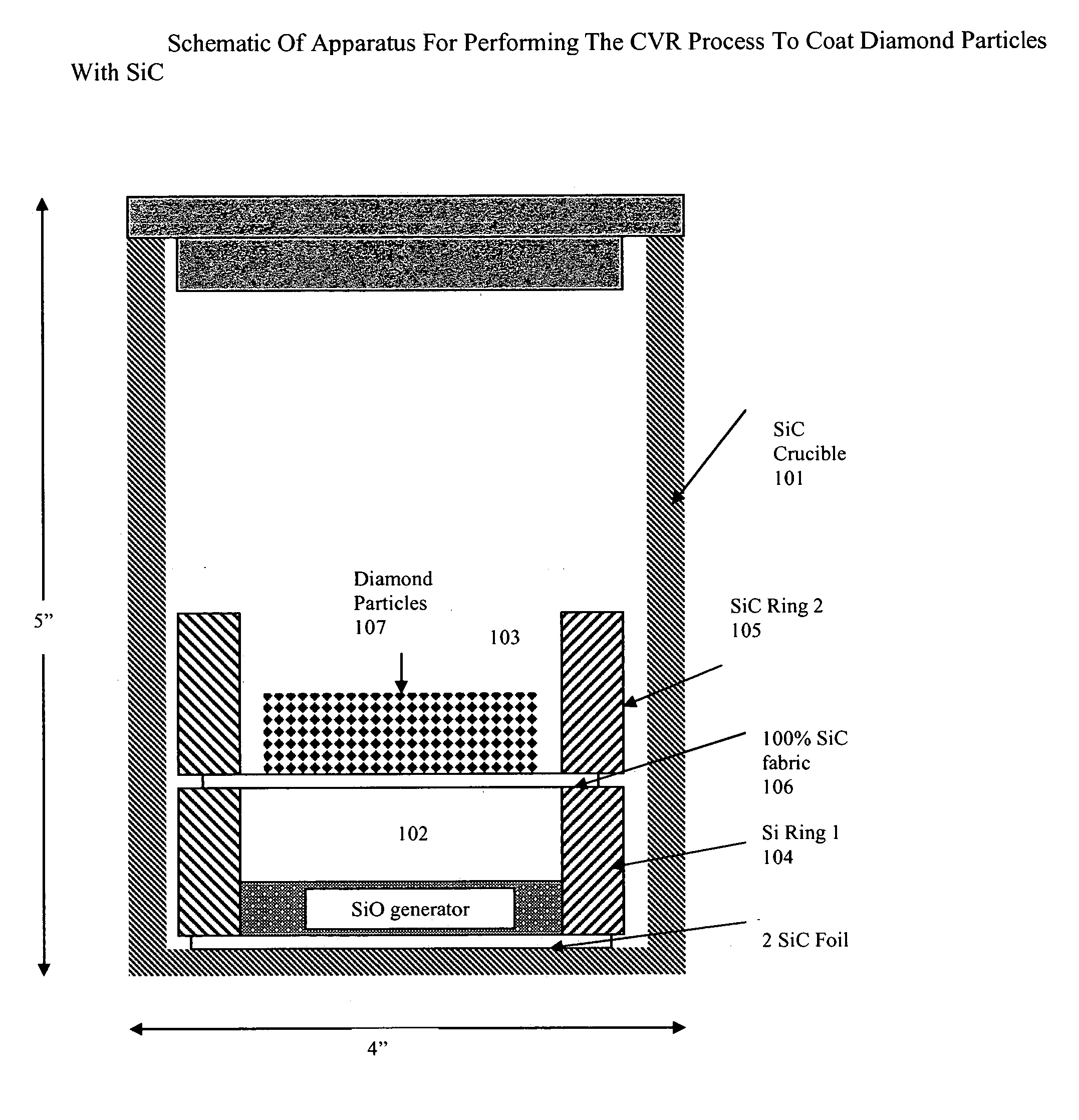
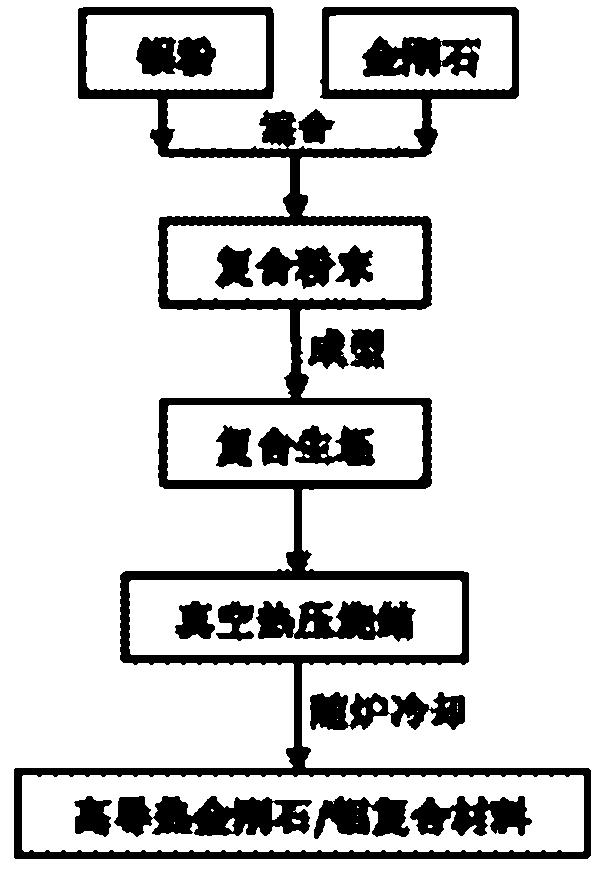
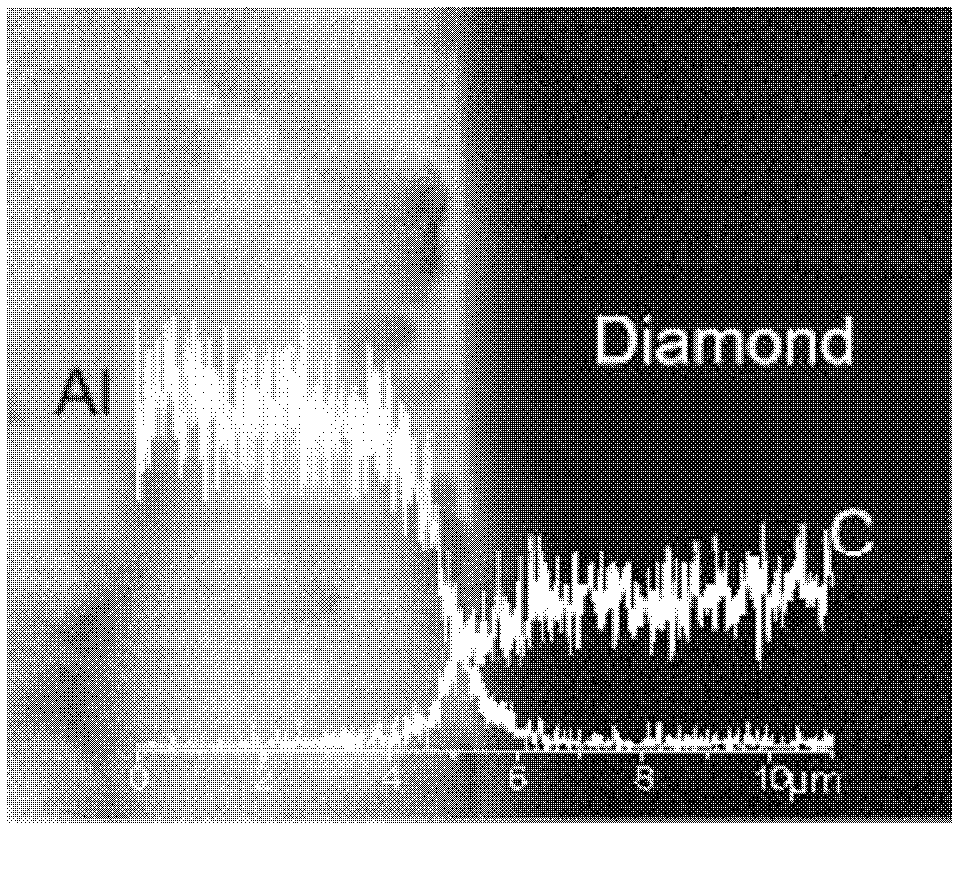
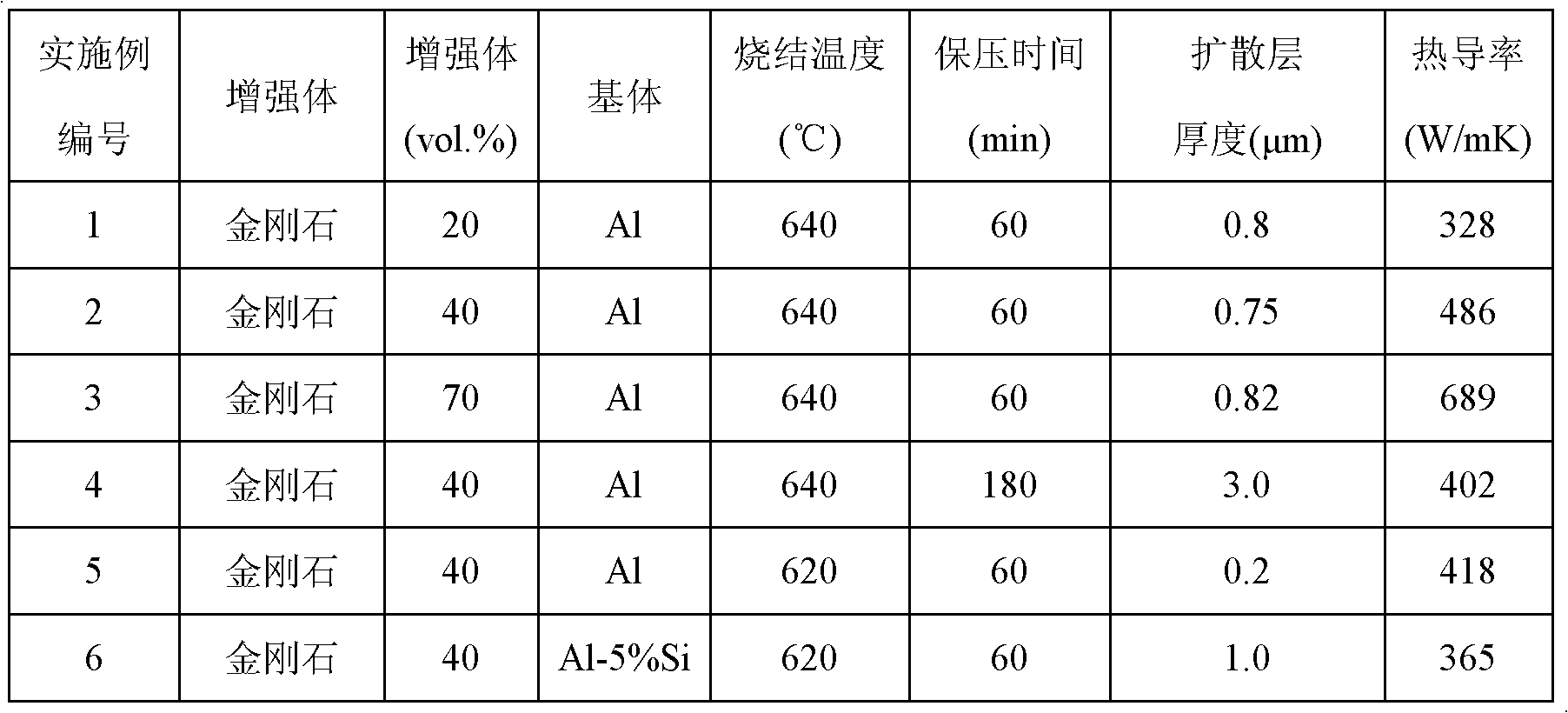
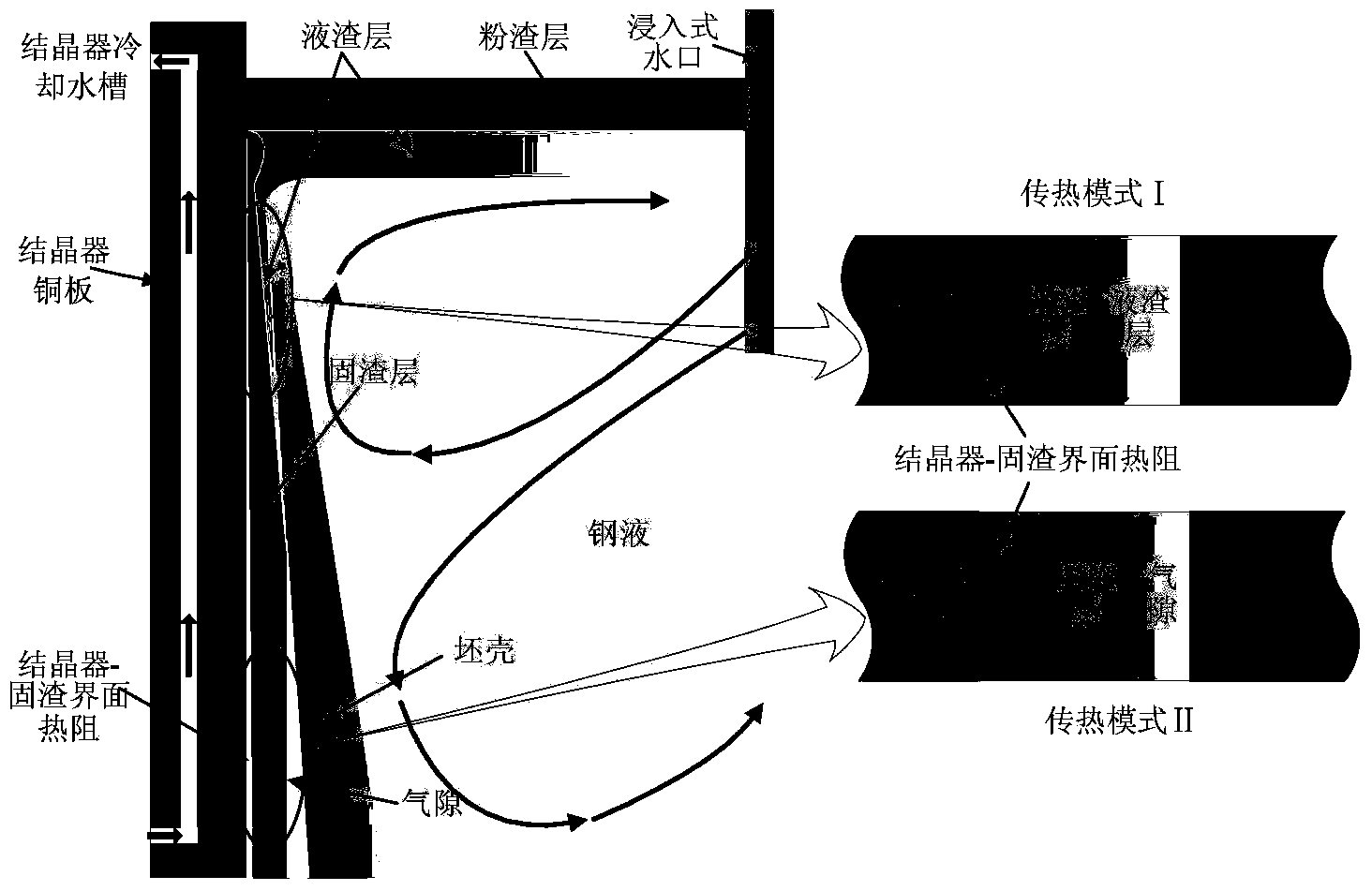
Patents
Literature
222 results about "Interfacial thermal resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interfacial thermal resistance, also known as thermal boundary resistance, or Kapitza resistance, is a measure of an interface's resistance to thermal flow. This thermal resistance differs from contact resistance (not to be confused with electrical contact resistance) because it exists even at atomically perfect interfaces. Owing to differences in electronic and vibrational properties in different materials, when an energy carrier (phonon or electron, depending on the material) attempts to traverse the interface, it will scatter at the interface.
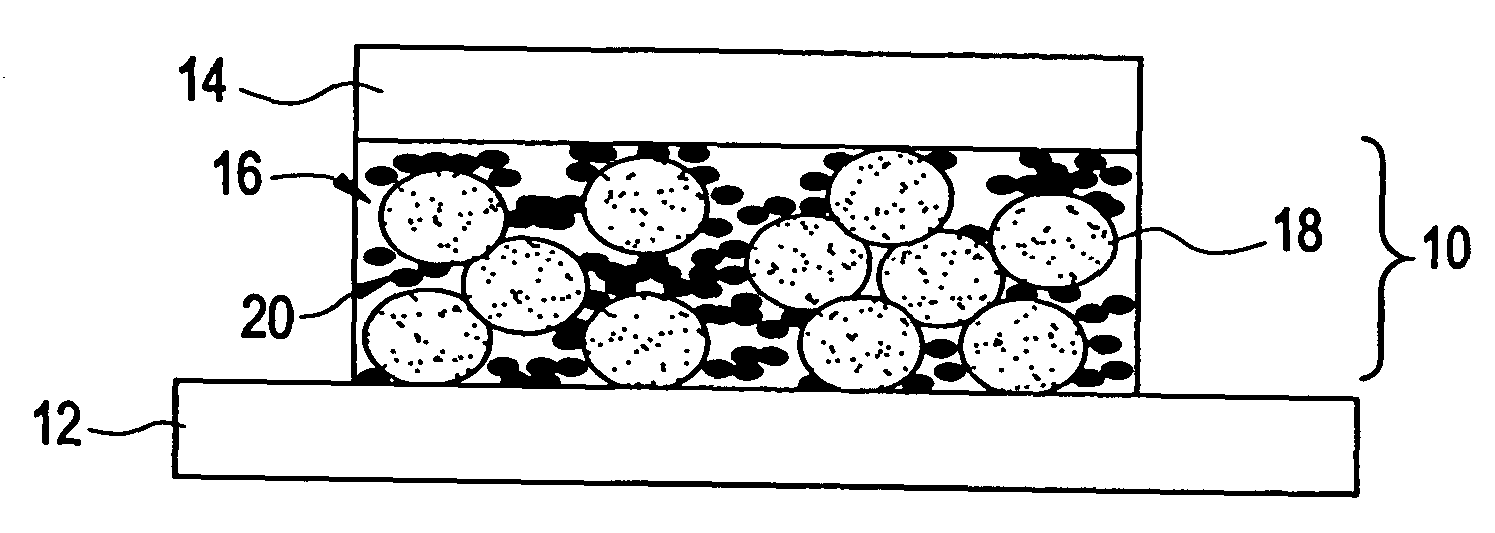
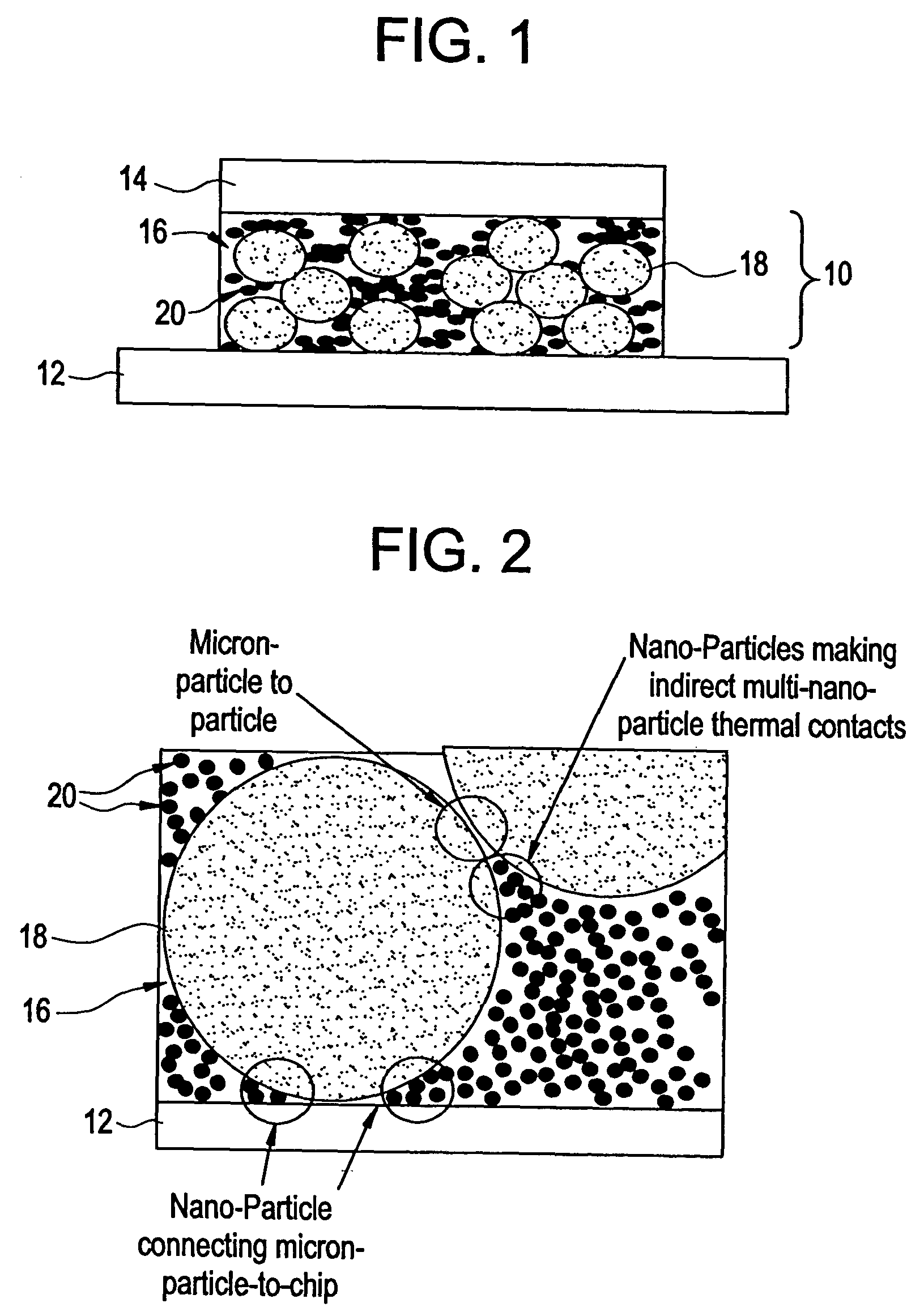
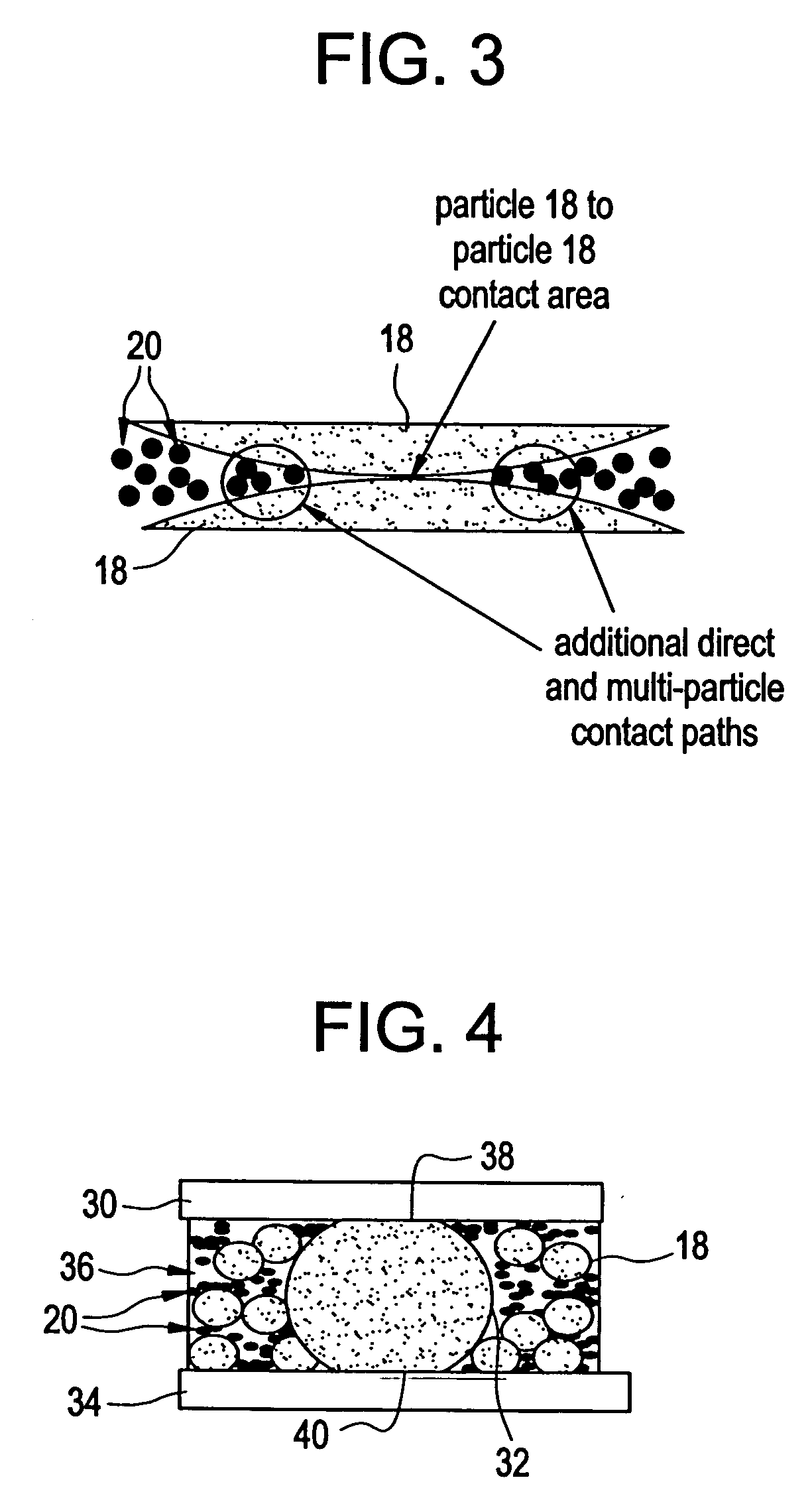
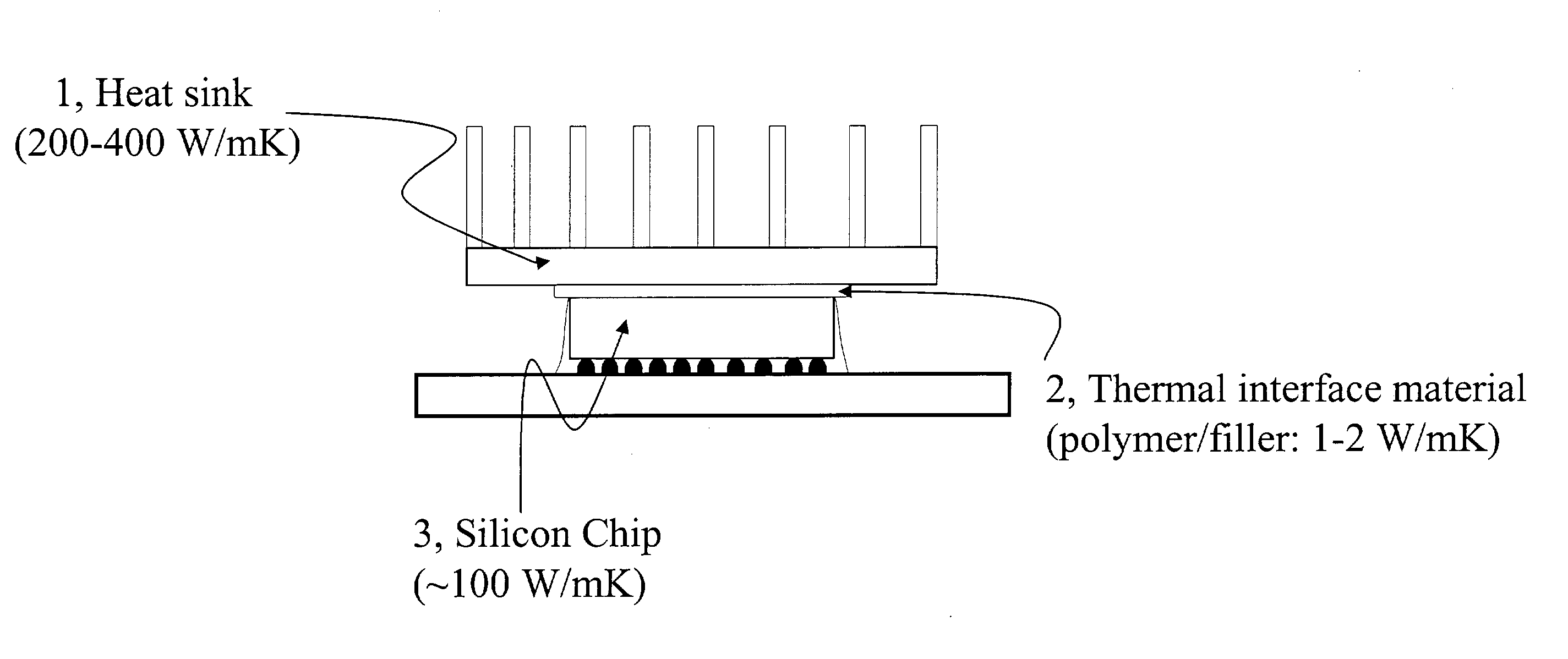
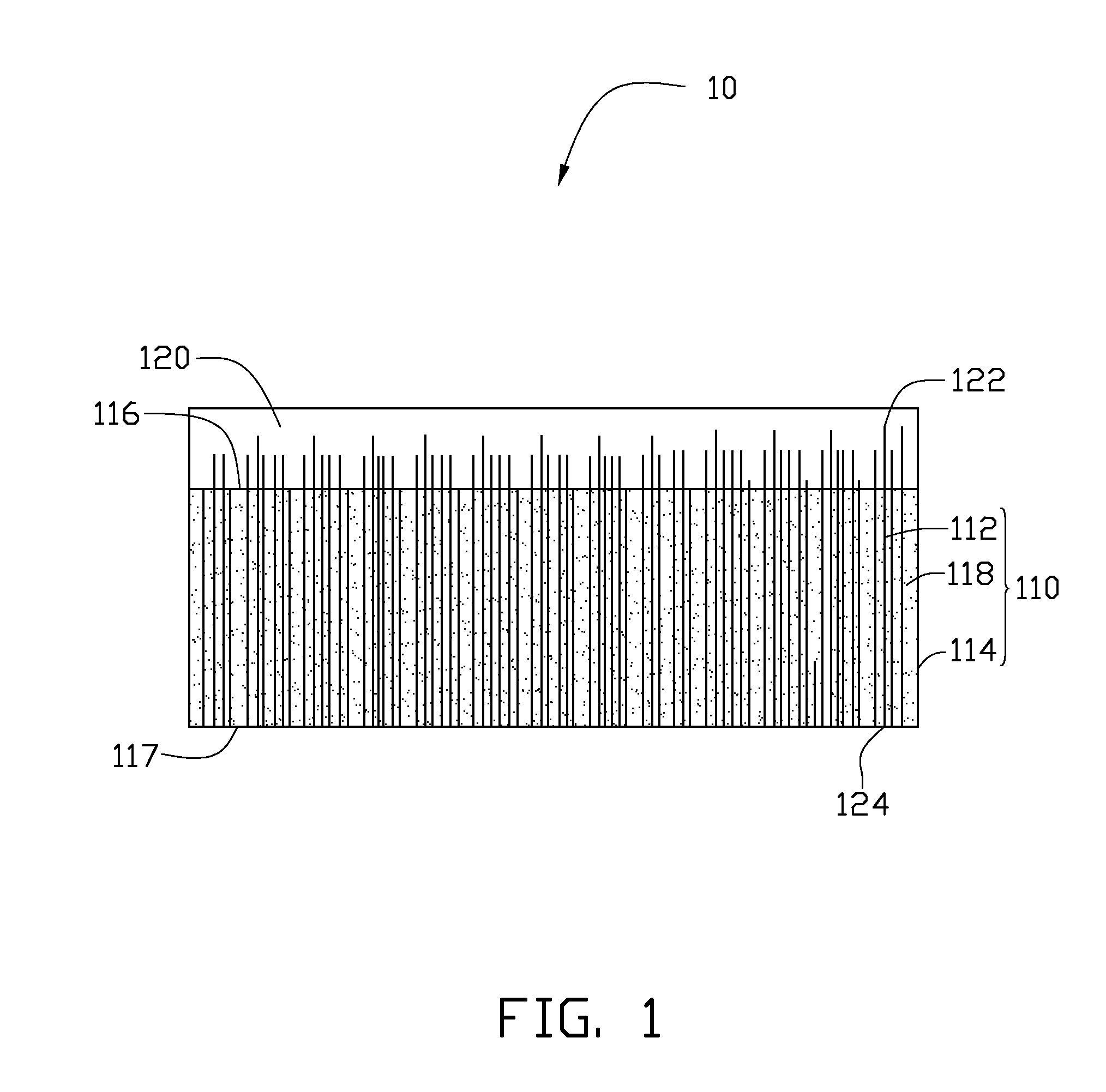
Thermal conductive material utilizing electrically conductive nanoparticles
ActiveUS20050045855A1Improve heat transfer efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsConductive materialNanoparticleInterfacial resistance
Thermal interface compositions contain both non-electrically conductive micron-sized fillers and electrically conductive nanoparticles blended with a polymer matrix. Such compositions increase the bulk thermal conductivity of the polymer composites as well as decrease thermal interfacial resistances that exist between thermal interface materials and the corresponding mating surfaces. Such compositions are electrically non-conductive. Formulations containing nanoparticles also show less phase separation of micron-sized particles than formulations without nanoparticles.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
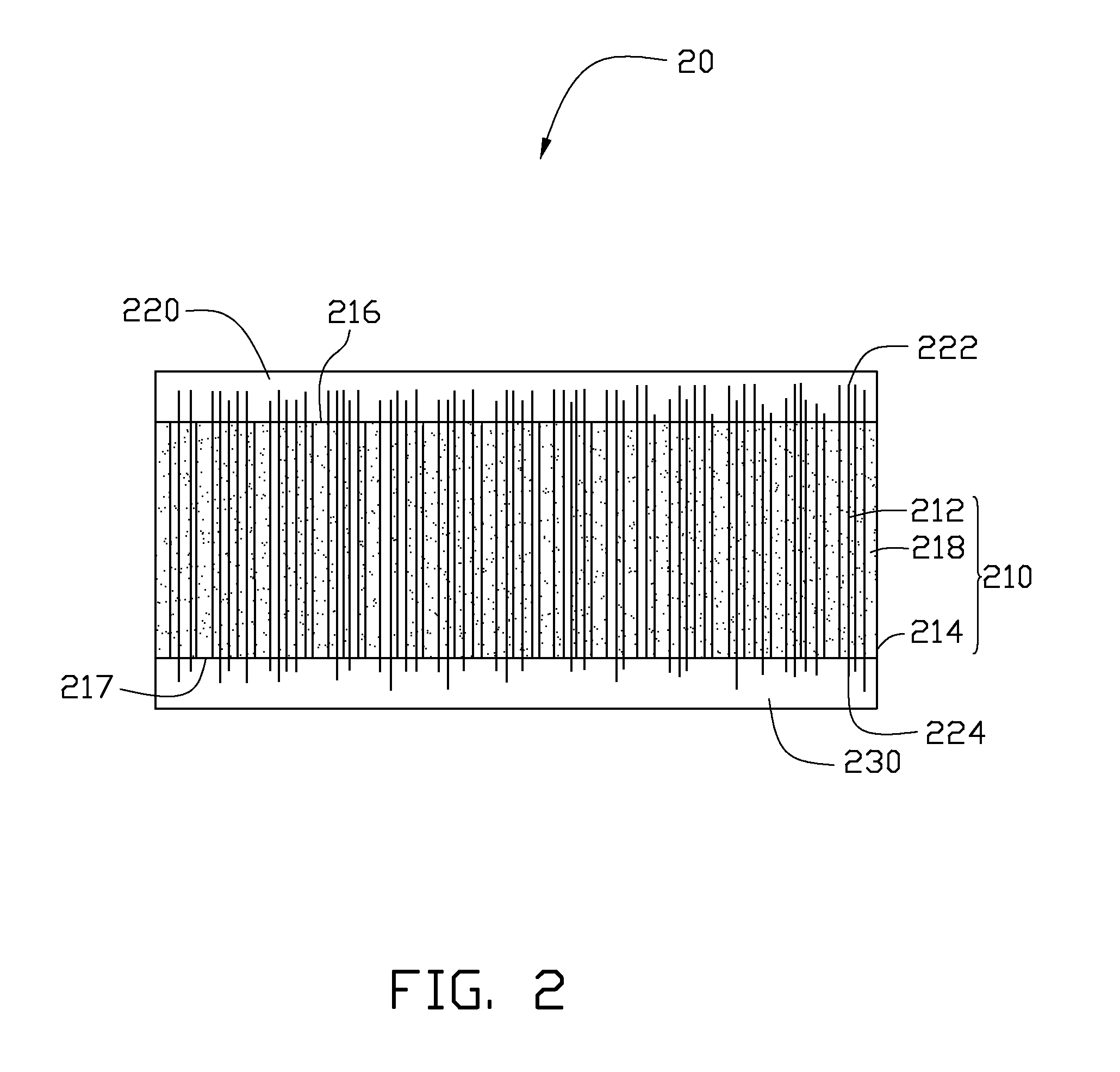
Organic matrices containing nanomaterials to enhance bulk thermal conductivity
InactiveUS20050161210A1Improve heat transfer efficiencySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNanoparticleInterfacial resistance
Thermal interface compositions contain nanoparticles blended with a polymer matrix. Such compositions increase the bulk thermal conductivity of the polymer composites as well as decrease thermal interfacial resistances that exist between thermal interface materials and the corresponding mating surfaces. Formulations containing nanoparticles also show less phase separation of micron-sized particles than formulations without nanoparticles.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Double heat flux gauge steady state method for measuring material heat conductivity
InactiveCN101126729AOvercoming Difficulties of Inaccurate MeasurementsMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentHeat flowHeat flux
The utility model relates to a material thermal conductivity measuring method of double heat-flux meter steady-state method, belonging to the technical field of material heat conduction performance testing. Based on the analysis of one-dimensional heat conduction in multilayer flat plate, the utility model proposes the adoption of the method of double heat-flux meter and samples with different thickness for heat conduction measurement, and gives quantitative criterion of one-dimensional heat conduction. The utility model adopts multi-point temperature measurement in heat-flux meter, calculates the average heat flux density with one-dimensional heat conduction formula of multi-layer flat plate, overcomes the difficulty of inaccurate heat flux density measurement, and makes alignment-fitting calculation for the actual thermal conductivity coefficient and the interface thermal resistance with test data of samples with different thickness. In addition, the utility model can test not only the thermal conductivity of solid material, but also the thermal conductivity coefficient of film material.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Heat conducting composite material and heat conducting composite sheet prepared by applying same
InactiveCN103146198ASpeed up heat dissipationLower interface thermal resistanceHeat-exchange elementsHeat conductingMetallurgy
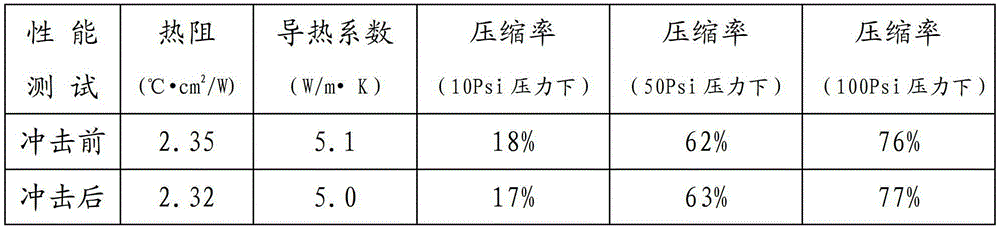
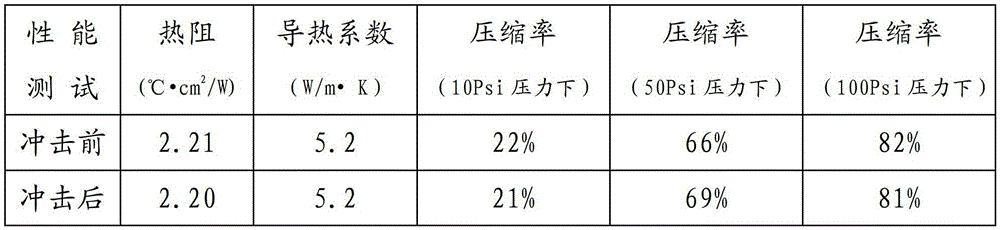
The heat conducting composite material provided by the invention is formed by mixing silicone oil and heat conducting powder, and various functional assistants are selectively added according to demands. The heat conducting coefficient of the heat conducting composite material is greater than 5.0W / m.K, and the material can be flexibly compressed at the environmental temperature of -40 to 200 DEG C and is not hardened, so that the material can be applied to filling gaps between various heating elements and radiating elements so as to reduce interface thermal resistance, shorten the heat conducting path and increasing the radiating speed of the elements. A heat conducting composite sheet provided by the invention is formed by mould pressing or rolling the heat conducting composite, and the compression ratio is high ( the compression ratio reaches over 40% at 50Psi). The heat conducting composite sheet can be directly attached to the components and has the characteristics of simple preparation process, convenience in use and the like.
Owner:SHENZHEN BORNSUN INDAL
Oriented flexible heat conduction material as well as forming technology and application thereof
InactiveCN103740110AImprove thermal conductivityGood flexibilitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesNuclear engineeringPliability
The invention provides an oriented flexible heat conduction material. Main components of the oriented flexible heat conduction material are silicon rubber and anisotropism heat conduction packing. A plurality of heat conduction paths which are parallel to each other and continuous are formed in the oriented flexible heat conduction material by linearly and continuously arranging the anisotropism heat conduction packing filled in the silicon rubber in heat conduction path directions. The oriented flexible heat conduction material has good heat conduction property in a particular direction and good flexibility, can form good contact with an interface, is low in interface resistance and can be used for improving a heat dissipation effect very well. The embodiment of the invention also provides a forming technology and an application of the oriented flexible heat conduction material.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD +2
High heat-conducting copper-based composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101831584ALow densitySmall coefficient of thermal expansionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingInterfacial thermal resistanceThermal expansion
The invention relates to a high heat-conducting copper-based composite material and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of electronic packaging materials. The copper-based composite material consists of 50-80 percent by volume of electroplated diamond particles and 20-50 percent by volume of copper. The electroplated diamond particles and a caking agent are mixed according to the volume ratio of 1:1-4:1 and are produced into a diamond prefabricated part by using an injection forming process of the prefabricated part; and a copper matrix is directly placed on the diamond prefabricated part or is melt and poured on the diamond prefabricated part to be produced into the high heat-conducting copper-based composite material by using a pressure infiltration process. The copper-based composite material has higher heat conductivity ratio than that of an aluminum-based composite material; by plating the surface of diamond, the interface bonding of the matrix copper and the diamond can be improved and the interface heat resistance can be reduced; in addition, the material has low density and small thermal expansion coefficient and meets the requirement for light quality of packaging materials.
Owner:GENERAL RESEARCH INSTITUTE FOR NONFERROUS METALS BEIJNG
Aqueous heat dissipation coating and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104804618AImprove cooling effectHigh thermal conductivityEpoxy resin coatingsBoron nitrideSlurry
The invention discloses an aqueous heat dissipation coating and a preparation method thereof. The aqueous heat dissipation coating comprises an aqueous dispersoid containing a base resin, nanometer carbon material-coated boron nitride composite powder and optional auxiliary materials. The composite powder comprises boron nitride and a boron nitride-coating nanometer carbon material. The preparation method comprises carrying out grinding dispersion on the aqueous dispersoid containing a base resin and the optional auxiliary materials to obtain dispersive slurry, at least adding slowly the composite powder into the dispersive slurry, carrying out high speed stirring and carrying out standing defoaming. The nanometer carbon material-coated boron nitride composite powder is used as a coating filler so that excellent thermal conductivity of the nanometer carbon material and boron nitride and conductive infrared radiation characteristics of the nanometer carbon material are fully utilized, interface thermal resistance of the nanometer carbon material and boron nitride is reduced, and the coating has the advantages of high thermal conductivity, high infrared radiation rate, construction convenience, safety, environmental friendliness and wide application prospect.
Owner:芜湖海泰科新材料有限公司
Heat interface material and its making process
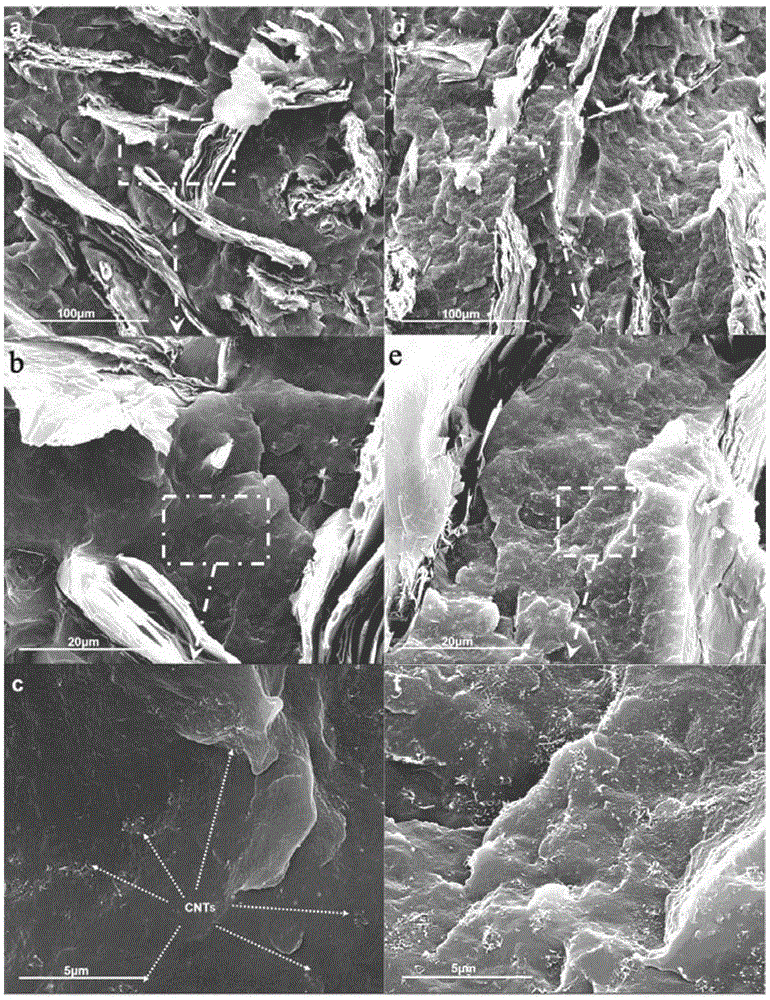
ActiveCN1846983AIncrease contactImprove thermal efficiencyNanotechLayered productsHeat resistanceCarbon nanotube
The heat interface material includes one base body and carbon nanotubes distributed inside the base body. The base body includes one first surface and one opposite second surface, and the carbon nanotubes extend from the first surface to the second surface and extend beyond at least one surface to bend elastically inside a phase change material layer formed in the surface. The present invention also provides the making process of the heat interface material. Owing to the carbon nanotubes with at least one end elastically bending in the phase change material, the heat interface material has good heat interface contact, low heat resistance and high heat conducting efficiency.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
High thermal conductivity metal matrix composites
ActiveUS20050074355A1Improve thermal conductivitySemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesParticulatesSurface layer
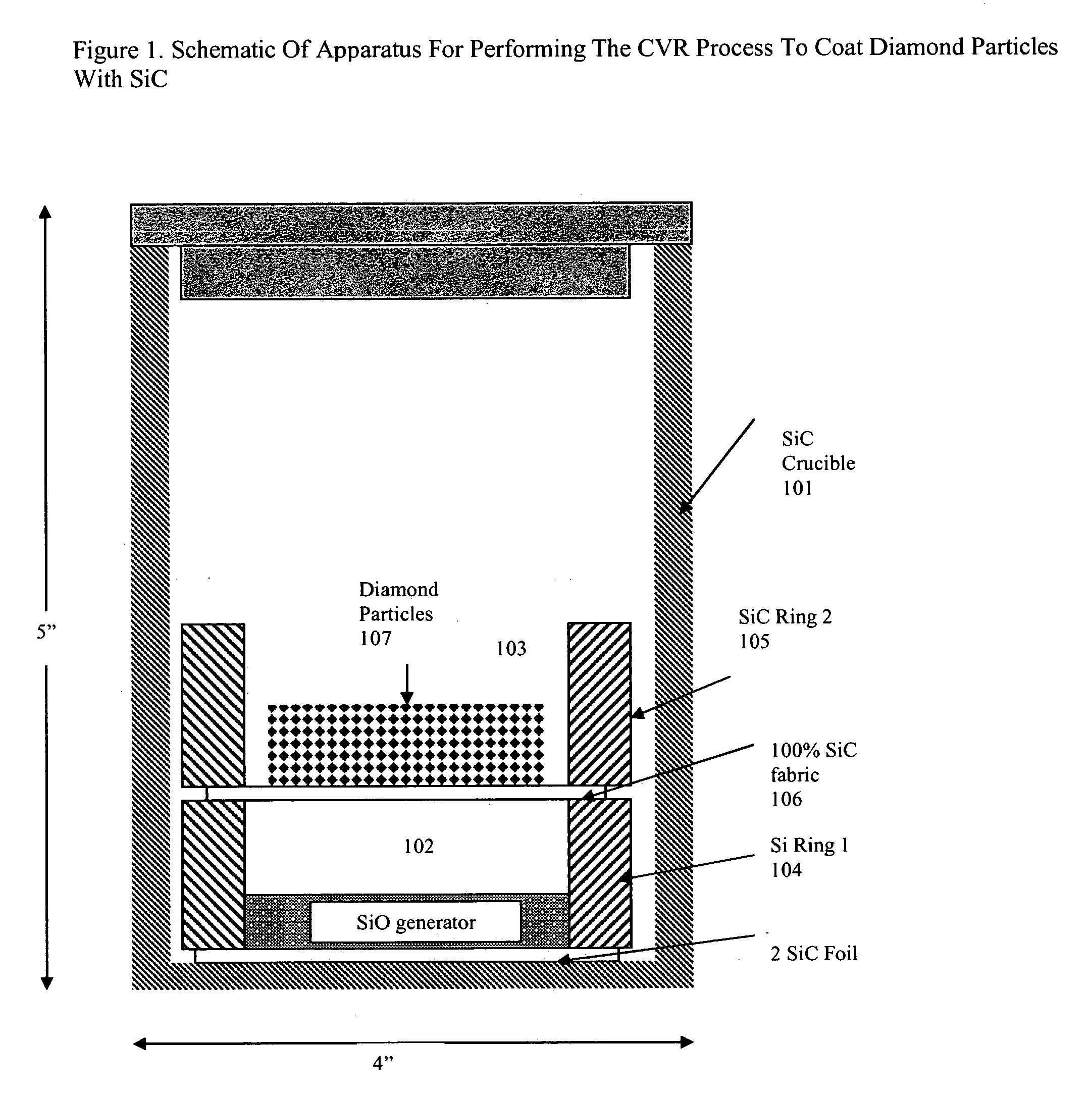
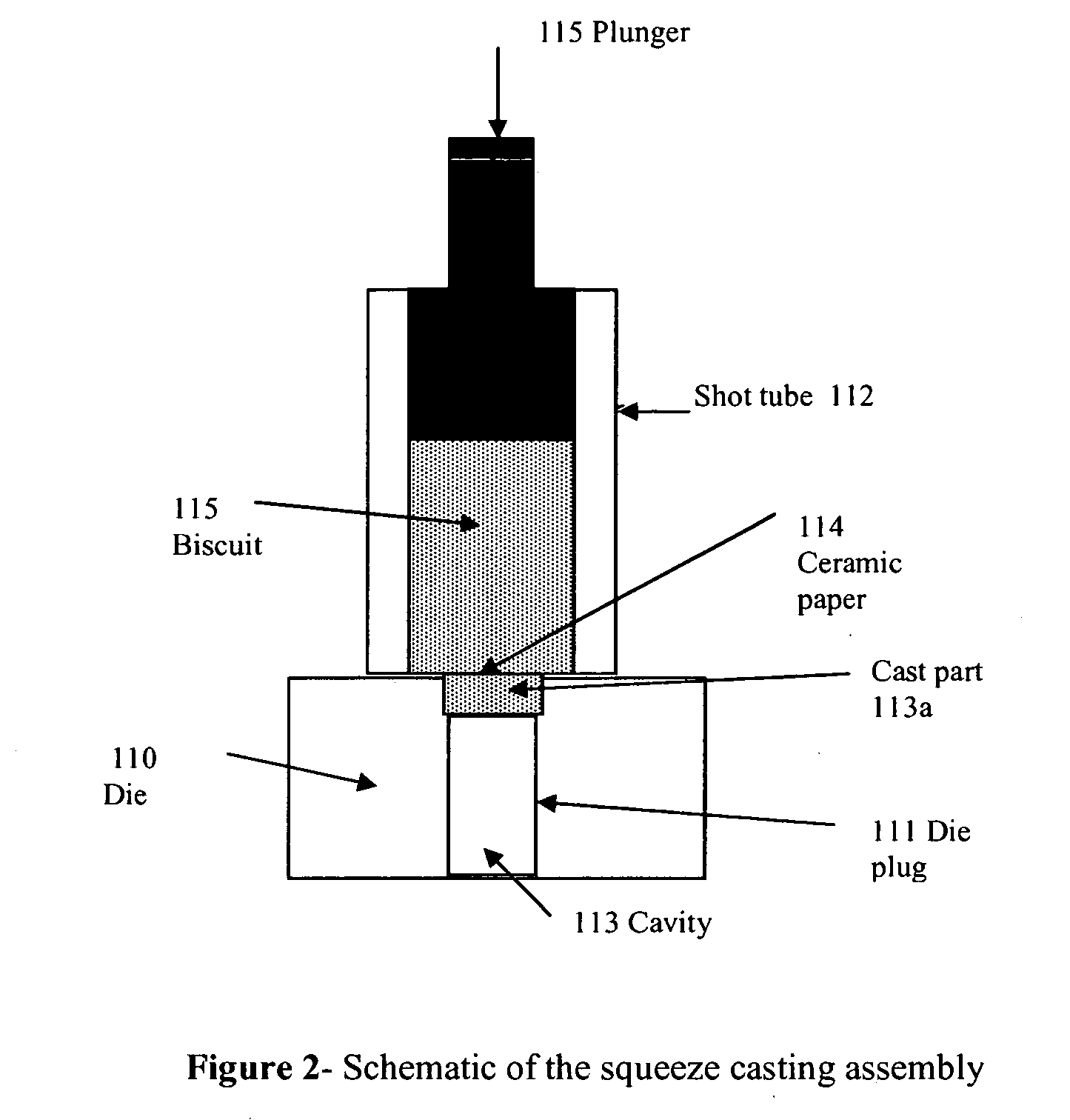
Discontinuous diamond particulate containing metal matrix composites of high thermal conductivity and methods for producing these composites are provided. The manufacturing method includes producing a thin reaction formed and diffusion bonded functionally graded interactive SiC surface layer on diamond particles. The interactive surface converted SiC coated diamond particles are then disposed into a mold and between the particles and permitted to rapidly solidify under pressure. The surface conversion interactive SiC coating on the diamond particles achieves minimal interface thermal resistance with the metal matrix which translates into good mechanical strength and stiffness of the composites and facilitates near theoretical thermal conductivity levels to be attained in the composite. Secondary working of the diamond metal composite can be performed for producing thin sheet product.
Owner:MATERIALS & ELECTROCHEM RES
High-heat-conductive composition, preparation method and heat-conductive gasket thereof
InactiveCN105419345AHigh surface energyImprove surface activityHeat-exchange elementsMicron scaleHeat resistance
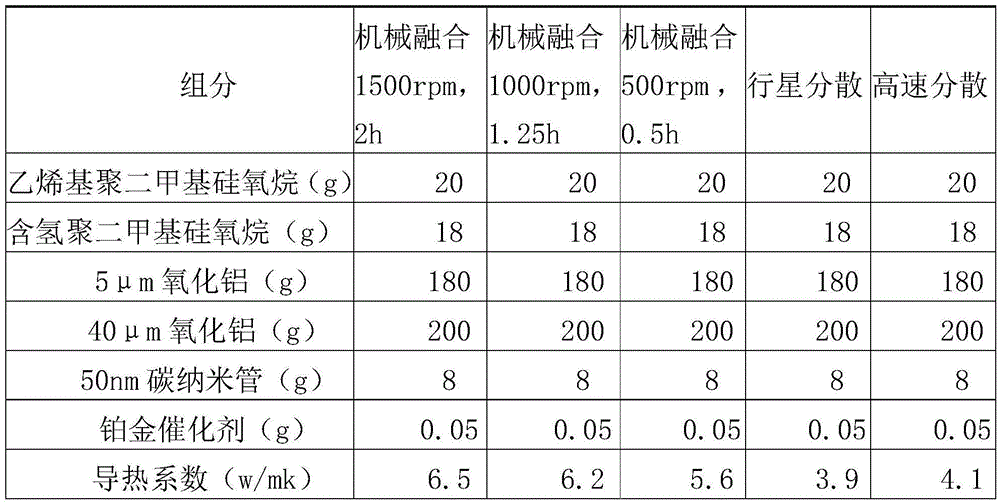
The invention relates to a high-heat-conductive composition, which includes a polysiloxane substrate and a composite heat-conductive filling material which is prepared through a mechanical fusion method. The composition is prepared through fusion and stirring. The high-heat-conductive composition is prepared from the polysiloxane substrate, and the composite heat-conductive filling material which is prepared through the mechanical fusion method and includes a micron-scale heat-conductive powder, a nano-scale heat-conductive powder and / or a submicron-scale heat-conductive powder, wherein the nano-scale heat-conductive powder and the submicron-scale heat-conductive powder are large in surface area, high in surface energy and high in surface activity. By means of the mechanical fusion method, the nano-scale heat-conductive powder is fused with the micron-scale heat-conductive powder to prepare the composite heat-conductive filling material. The micron-scale heat-conductive powder and the nano-scale heat-conductive powder are fully dispersed and meanwhile interface heat resistance therebetween is greatly reduced. The heat-conductive performance of the nano-scale heat-conductive powder is fully achieved so that the high-heat-conductive composition is better in the heat-conductive performance.
Owner:PINGHU ALLIED IND
Heat dissipation structure and heat dissipation system adopting the same
InactiveUS20110030938A1Semiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCarbon nanotubeInterfacial thermal resistance
A heat dissipation structure includes a thermal interface material and a transition layer. The thermal interface material includes a matrix and a plurality of carbon nanotubes dispersed in the matrix. The thermal interface material has a first surface and a second surface opposite to the first surface. The transition layer is positioned on one of the first surface or the second surface of the thermal interface material. A thickness of the transition layer is in a range from about 1 nanometer to about 100 nanometers. The transition layer is in contact with the carbon nanotubes of the thermal interface material. An interface thermal resistance between the transition layer and the heat source is less than that between the plurality of carbon nanotubes and the heat source. The present application also relates to a heat dissipation system adopting the heat dissipation structure.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
Phase change alloy thermal interface composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105838333AImprove thermal conductivityLower interface thermal resistanceHeat-exchange elementsMolten stateInterfacial thermal resistance
The invention relates to a phase change alloy thermal interface composite material. Raw materials used for preparing the phase change alloy thermal interface composite material include low-melting point alloy and a heat conduction filler, and the heat conduction filler accounts for 5-85% of the total mass of the low-melting point alloy; and the low-melting point alloy includes two or above meltable metals. The low-melting point phase change alloy thermal interface composite material is in a molten state after a low melting point is reached, has extremely lower viscosity and better fluidity than heat conduction pastes, further fills gaps in the interface, greatly reduces the interface thermal resistance, and is an extremely good thermal interface material; and the low-melting point alloy is used as a dispersant, and the high conduction filler is added to the low-melting point alloy, so the composite material has dual characteristics of high heat conductivity and low interface thermal resistance.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Heat conduction type aramid nano insulation paper and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108978328AHigh strengthImprove insulation performancePlastic/resin/waxes insulatorsSynthetic cellulose/non-cellulose material pulp/paperNanofiberDiameter ratio
The invention discloses heat conduction type aramid nano insulation paper and a preparation method thereof. According to the heat conduction type aramid nano insulation paper and the preparation method thereof, disclosed by the invention, aramid nano fiber with high strength, high modulus, high length-diameter ratio, good temperature resistance and good insulativity is utilized as a matrix, and good mechanical performance, good insulativity, good temperature resistance and good flexibility are given to aramid nano insulation paper; hydroxylated nano boron nitride is used as heat conduction filler and is dispersed in the aramid nano fiber matrix so as to be used for a main carrier for heat conduction, so that interface bonding is optimized, interface thermal resistance is reduced, high heatconductivity is given to the aramid nano insulation paper, and meanwhile, the insulavitity of the aramid nano insulation paper cannot be influenced; the problems that since the heat conductivity of aramid insulation paper at present is low, electrical insulation equipment is poor in heat dissipation and short in service life are solved; meanwhile, the problems that since a heat conduction composite resin impregnation technology is utilized, insulation paper is hard and crispy, the technology is complicated and the like are avoided.
Owner:宝鸡科达特种纸业有限责任公司
Method for preparing high-heat-conductivity diamond copper-base composite material through super-high-pressure sintering
InactiveCN102586641AShort preparation timeIncrease productivityVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingHeat resistanceInterfacial thermal resistance
The invention discloses a method for preparing a high-heat-conductivity diamond copper-base composite material through super-high-pressure sintering and belongs to the field of heat sink materials. The volume percentage of copper powder used as a base body is 30 to 70 percent, and the volume percentage of a wild phase coated diamond is 30 to 70 percent. The process method for preparing the composite material comprises the following steps of: performing micro evaporating on the coated diamond under vacuum to improve the wettability of the coated diamond with the copper powder so as to reduce interface heat resistance; reducing the copper powder; and blending the modified diamond and the copper powder in a certain proportion, cold-pressing and forming, filling into a pyrophyllite mold, and sintering on a hexahedral press at high temperature under high pressure to obtain the diamond copper-base composite material. The diamond / copper-base composite material with high heat conductivity and low expansion coefficient can be used as a plasma part oriented heat sink material in a fusion reactor and can also be applied to other radiating material fields of electronic packaging materials and the like, and has very good development prospect.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Polymer composite material with double-network structure and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a polymer composite material with a double-network structure and a preparation method thereof. The composite material contains fillers A and fillers B, wherein the size of the fillers A is 30 to 500 microns and the size of the fillers B is 1.0 to 20 microns; the size ratio of the fillers A to the fillers B is at least 20; the fillers A and the fillers B are uniformly distributed in a polymer base material, are in mutual overlap joint and penetrate through to form a conductive and heat-conducting access with a staggered network structure; the fillers B with the smaller size are distributed in grids of a loose network structure formed by the fillers A with the large size and are in mutual overlap joint to form a relatively dense network, and the inner part of the obtained composite material has a double-network structure which is good for moving electrons and reducing interface heat resistance, so that the conductive and heat-conducting performances are greatly improved at the same time. A method for constructing double networks by using the size difference of the two types of fillers has an ingenious concept and an operation method is simple; existing high molecular material modified machining equipment is used for realizing production; the method has low cost and is easy to popularize and apply.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Method for establishing temperature field model of steel box beam bridge road system under high-temperature asphalt concrete paving
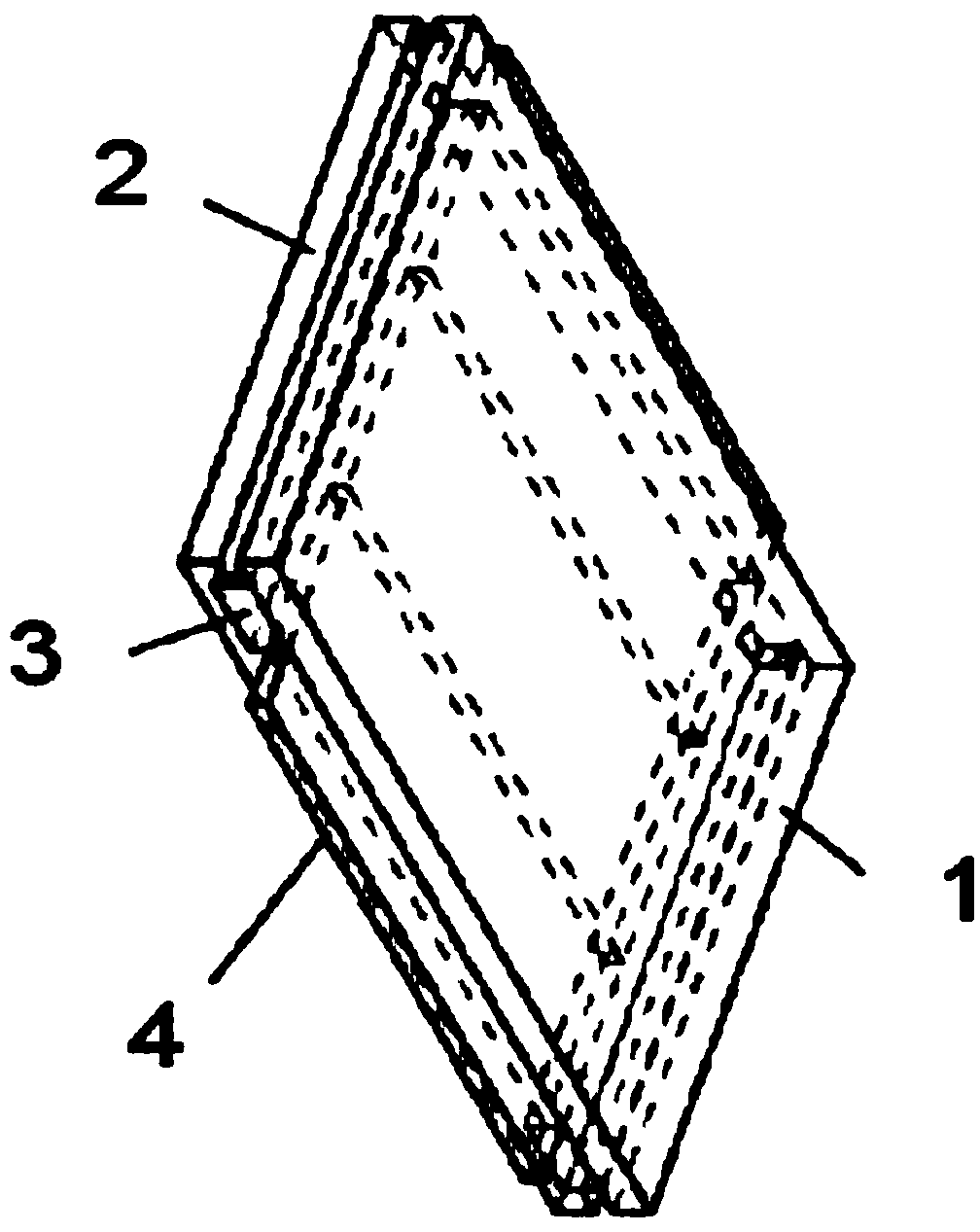
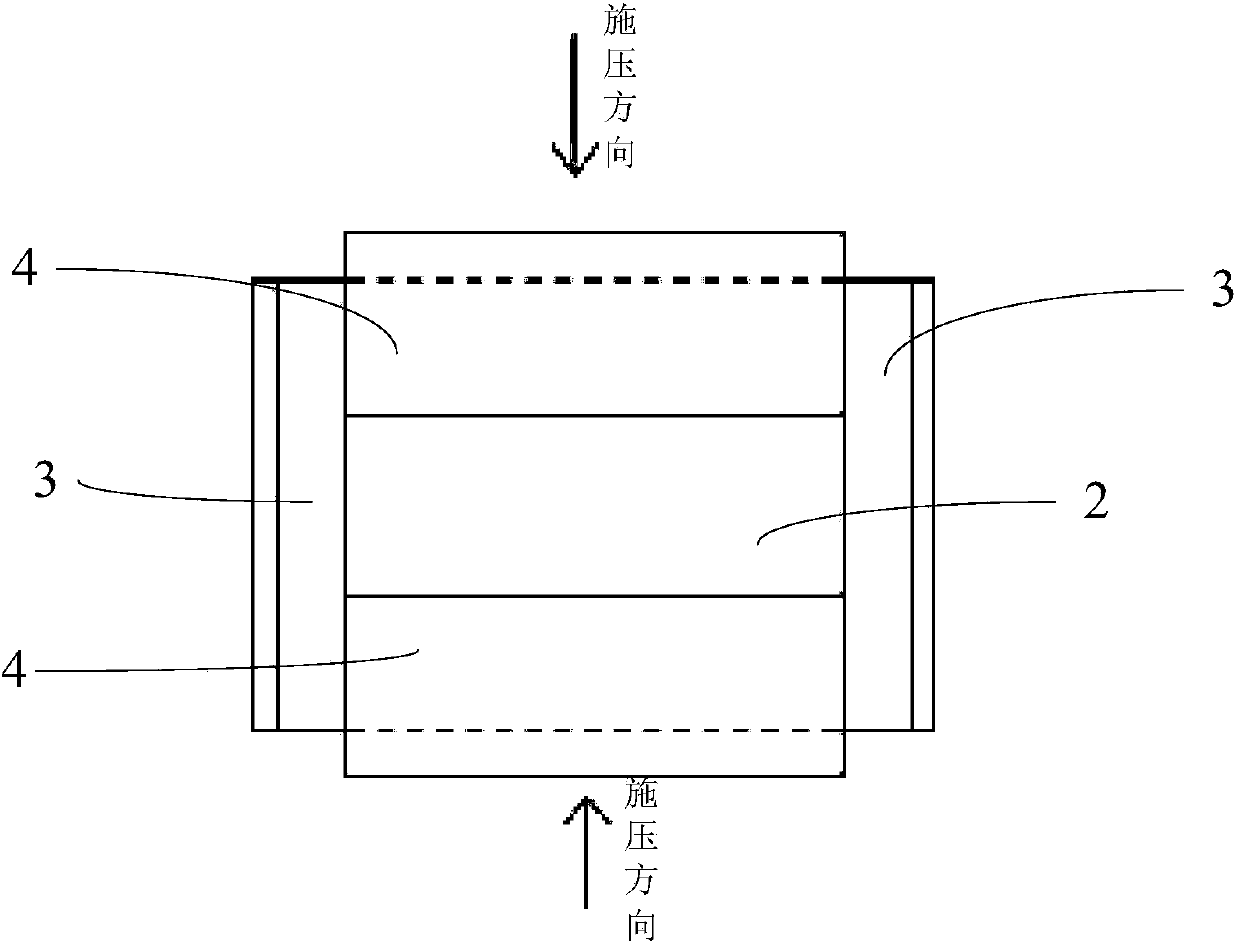
ActiveCN103726434AReflect the temperature field distributionIncrease reflectionBridge structural detailsRoads maintainenceThermal insulationInterfacial thermal resistance
The invention provides a method for establishing a temperature field model of a steel box beam bridge road system under high-temperature asphalt concrete paving. The model comprises a paving layer (1), a steel bridge panel (2), U-shaped ribs (4) and diaphragm plates (5). An interface thermal resistor (3) is arranged between the paving layer (1) and the steel bridge panel (2) and is used for reflecting a barrier effect of an adhesive layer in an adhesive layer-paving composite structure on temperature transfer. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the optimal interface thermal resistance by using a test-numerical simulation mixed parameter analysis method and combining a numerical optimization technology; establishing an actual bridge numerical model, setting a movable temperature load (6) to simulate the paving construction process, and calculating and analyzing the temperature field distribution condition of the steel box beam bridge road system. The method mainly depends on finite element modeling, a thermal insulation effect of the adhesive layer can be well reflected, and the paving construction process can be really simulated. Compared with field measurement, the method is simple and feasible, different working conditions can be simulated, and the temperature field distribution condition of the steel box beam bridge road system can be accurately reflected.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for preparing diamond enhanced copper based composite with high volume fraction
InactiveCN102071332AEvenly distributedImprove thermal conductivityInterfacial thermal resistanceVacuum evaporation
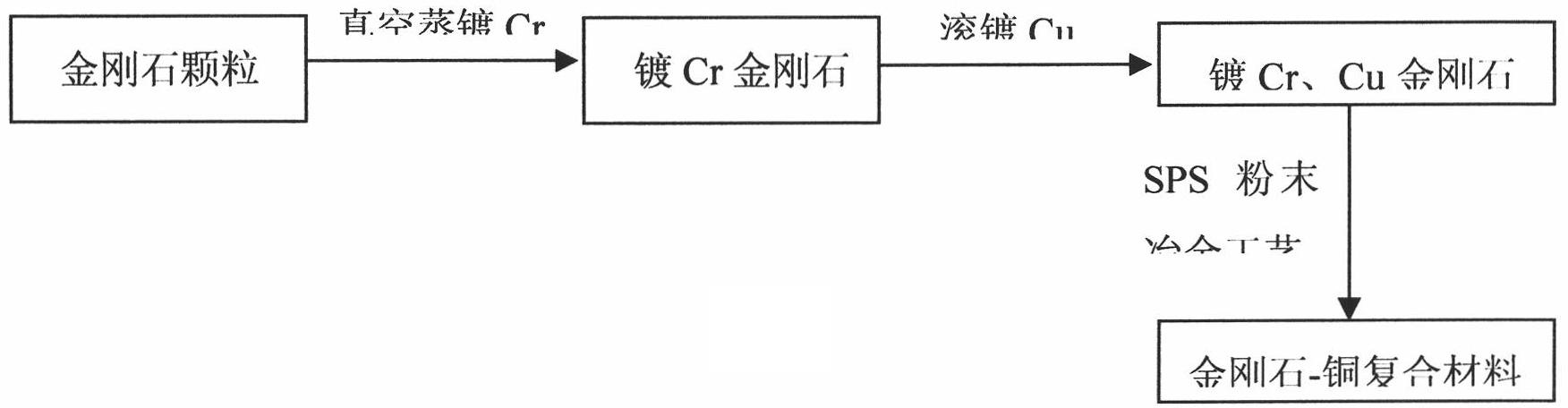
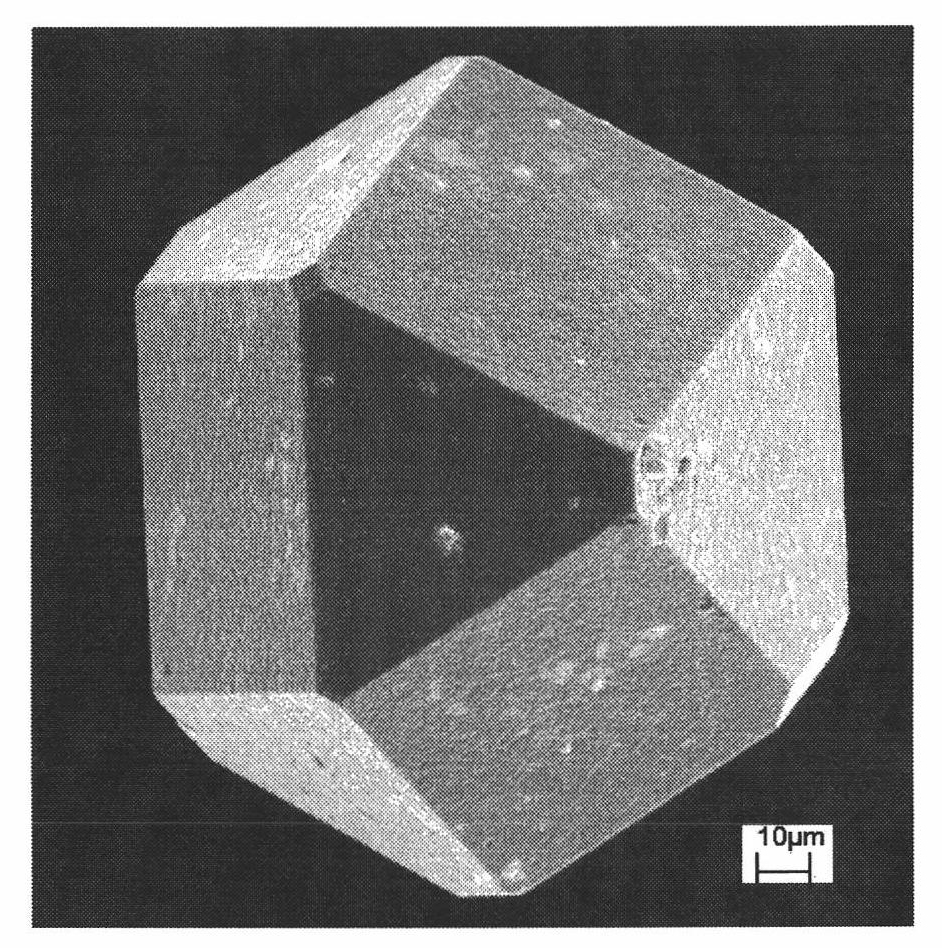
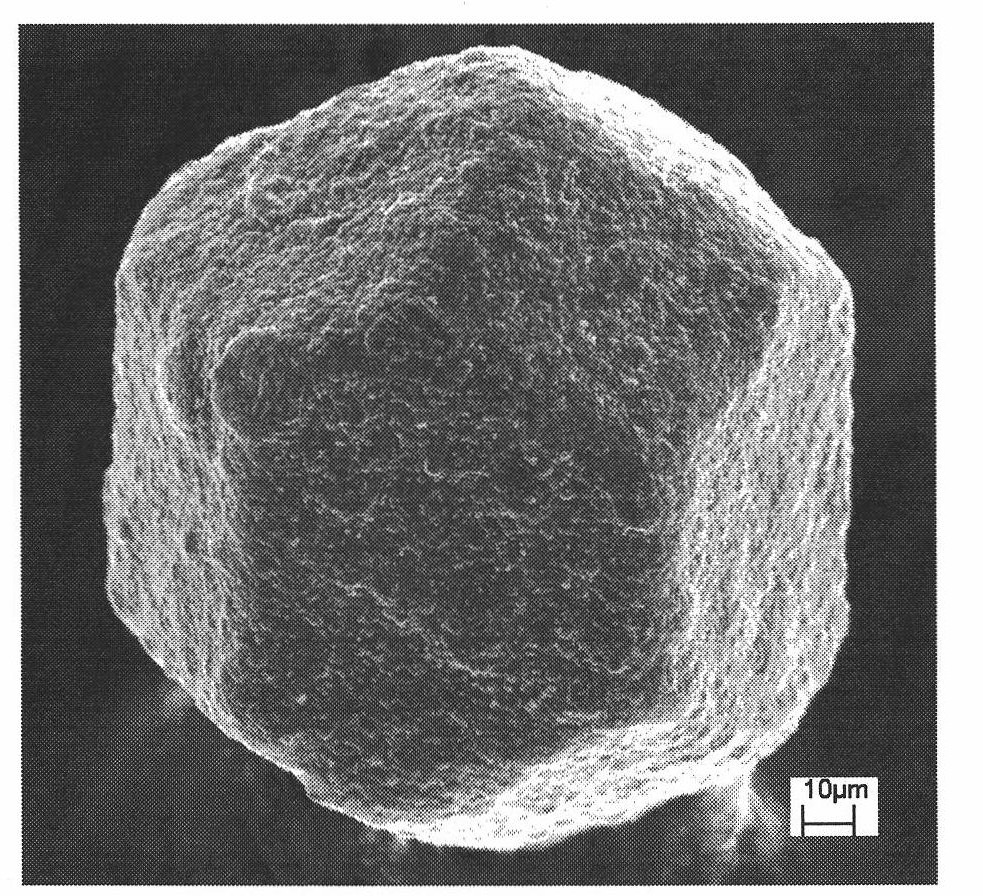
The invention relates to a diamond enhanced copper based composite and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the metal based composite field. In the composite of the invention, the volume ratio of diamond to copper is 40-70:60-30 and the particle size of diamond is 38-212mu m. The preparation method comprises the following steps: plating a 0.1-2mu m of Cr layer on the surface of diamond through vacuum evaporation after the surface pretreatment of diamond; placing the diamond plated with Cr in a barrel to perform copper element barrel plating and thickening, wherein the copper coating on the surface of diamond is 7-20mu m in thickness and the weight of the obtained diamond is increased by 100%-170%; and directly placing the obtained diamond in a spark plasma sintering (SPS) furnace to prepare the diamond-copper composite. The method of the invention directly uses the thicker copper coating on the surface of diamond as base material, thus avoiding the problem that diamond is not mixed uniformly with copper powder so as to cause the additional interfacial thermal resistance; and all kinds of composites with different diamond contents can be obtained by changing the increased weight of diamond, thus the maneuverability is high and the technology is simple. The composite has higher thermal conductivity and can be used in the fields such as electronic packaging.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Method for preparing high conductivity diamond/aluminum composite material
ActiveCN102534331AEnhanced interface bindingHigh thermal conductivityMicrometerInterfacial thermal resistance
The invention discloses a method for preparing a high conductivity diamond / aluminum composite material. The method comprises the following steps of: uniformly mixing diamond and aluminum powder to obtain diamond / aluminum composite powder; performing cold pressing or cold isostatic pressing to obtain a diamond / aluminum powder compact; performing vacuum hot pressed sintering on the compact, and ensuring that an atomic diffusion layer with proper thickness is generated at a diamond / aluminum interface by controlling the sintering temperature and time; and cooling to obtain the high conductivity diamond / aluminum composite material. The atomic diffusion layer with the thickness of 0.01-5.0 micrometers is formed at the diamond / aluminum interface by controlling the temperature and time of the vacuum hot pressed sintering, so that good interface bond can be achieved, low interface thermal resistance can be achieved, and the high conductivity composite material is obtained. The method is simple and feasible, low in production cost and suitable for preparing large-size composite materials.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
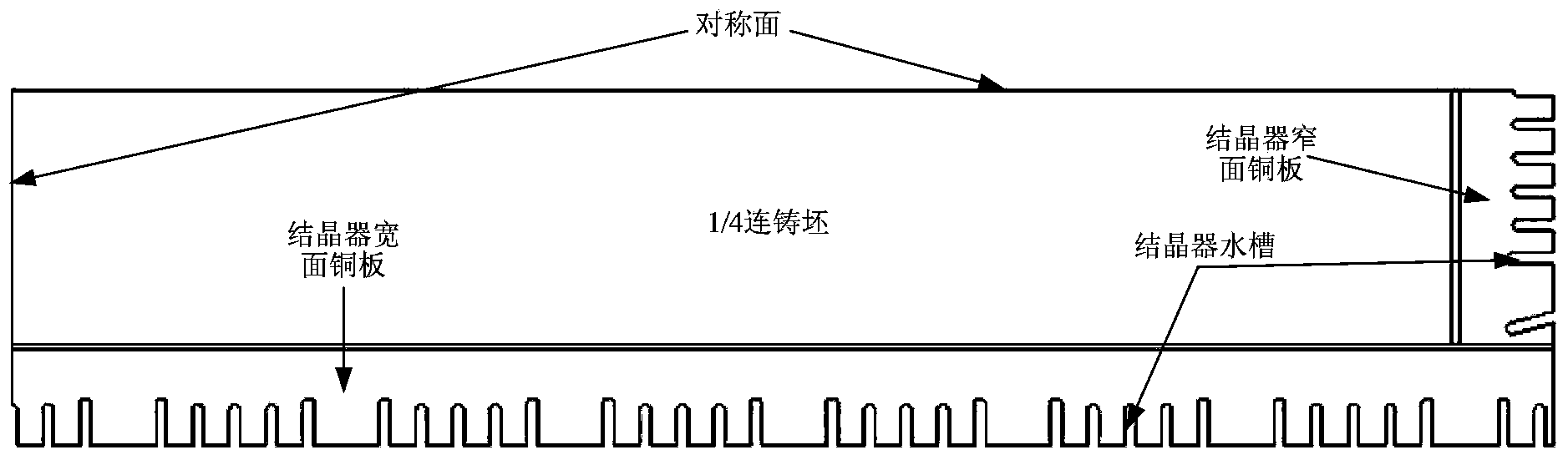
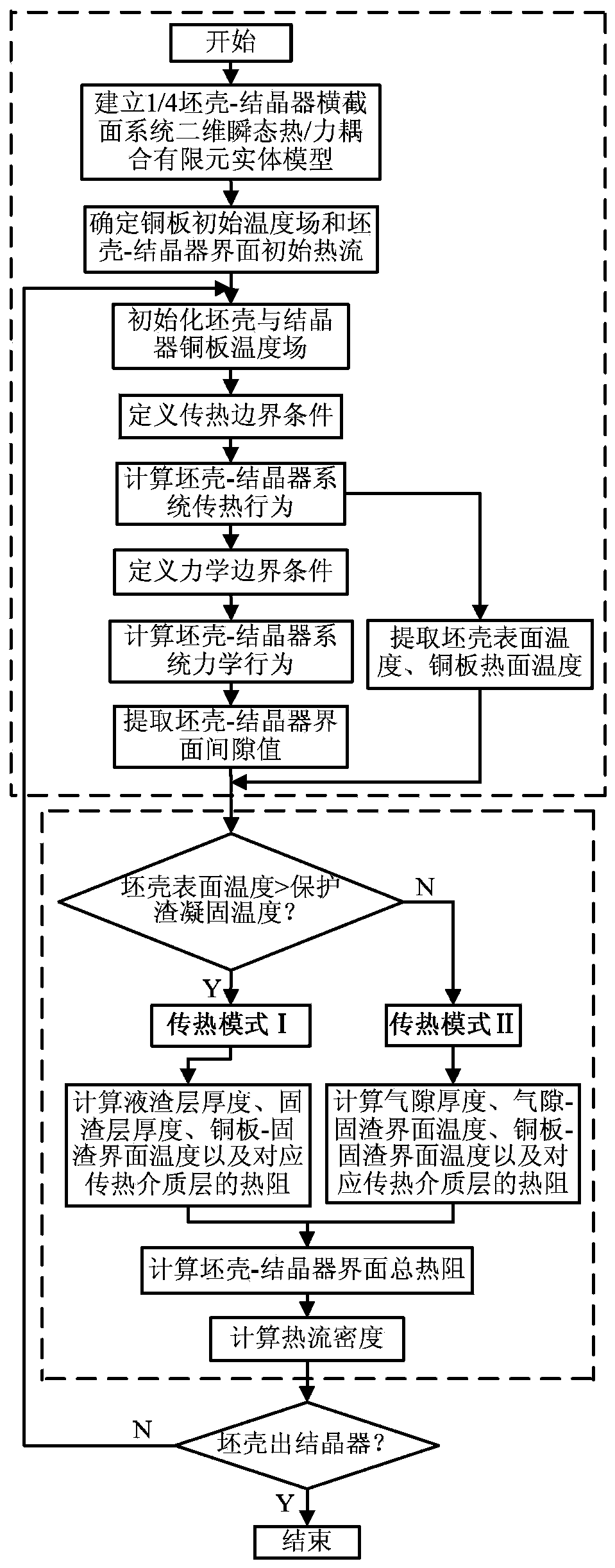
Method for determining heat flux density of continuous casting crystallizer based on flux film and air gap dynamic distribution
InactiveCN103433448AEasy to getImprove universalityCasting parameters measurement/indication devicesElement modelHeat flux
The invention belongs to the field of metallurgy continuous casting process numerical analog simulation, and discloses a method for determining heat flux density of a continuous casting crystallizer based on flux film and air gap dynamic distribution. According to a crystallizer copper plate structure and the size of the section of a continuous casting, a two-dimensional transient heat / force coupling finite element model with a 1 / 4 blank shell-crystallizer cross section system as a computation object is built, and the temperature of the surface of the blank shell, the temperature of the hot surface of a copper plate and the width of the clearance of a blank shell-crystallizer interface are determined. If the temperature of the surface of the blank shell is higher than the solidification temperature of casting powder, the heat resistor of the blank shell-crystallizer interface is formed by connecting a melt cinder layer, a solidification slug layer and a crystallizer-solidification slug interface heat resistor in series. If the temperature of the surface of the blank shell is smaller than or equal to the solidification temperature of the casting powder, the heat resistor of the blank shell-crystallizer interface is formed by connecting an air gap layer, a solidification slug layer and a crystallizer-solidification slug interface heat resistor in series. The method has good universality, and is suitable for determining the heat flux density of all existing continuous casting machine types and sectional crystallizers.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
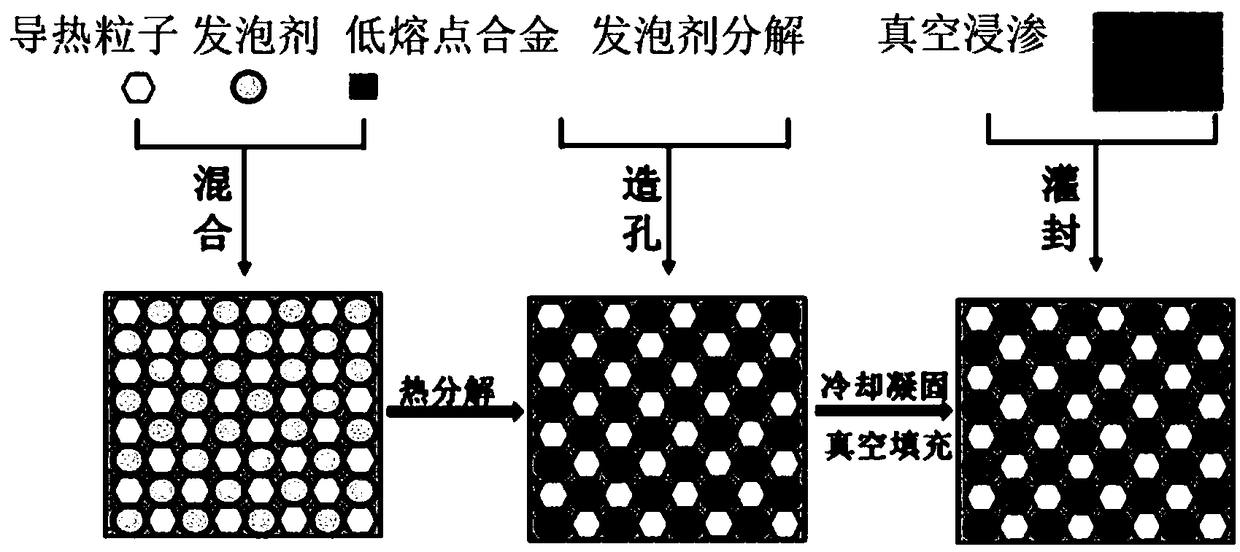
Thermal interface material based on composite thermal-conduction network of low-melting-point metals and thermal-conduction particles, and preparation method of thermal interface material
The invention discloses a thermal interface material based on a composite thermal-conduction network of low-melting-point metals and thermal-conduction particles, and a preparation method of the thermal interface material, and belongs to the technical field of thermal interface materials. The material is prepared by taking low-melting-point metals, thermal-conduction particles, a foaming agent, and a high-molecular polymer as raw materials and adopting the technical processes of metallurgical interconnection of the low-melting-point metals and the thermal-conduction particles, high-temperaturedecomposition and pore-forming of the foaming agent, vacuum impregnation of the high-molecular polymer, and the like. The material is provided with an extremely high thermal conductivity through high-efficiency three-dimensional thermal-conduction channels constructed by the low-melting-point metals and the thermal-conduction particles; high elasticity and softness of the material are ensured through the use of the high-molecular polymer and the low-melting-point metals; in a use process, metallurgical interconnection is formed at the interface of the low-melting-point metals and a metal substrate, and the high-molecular polymer has an adhesive effect with the substrate, so that the two connection mode provide extremely low interface resistance and restrict the overflow problem of the low-melting-point metals.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and Apparatus for Evaluation and Improvement of Mechanical and Thermal Properties of CNT/CNF Arrays
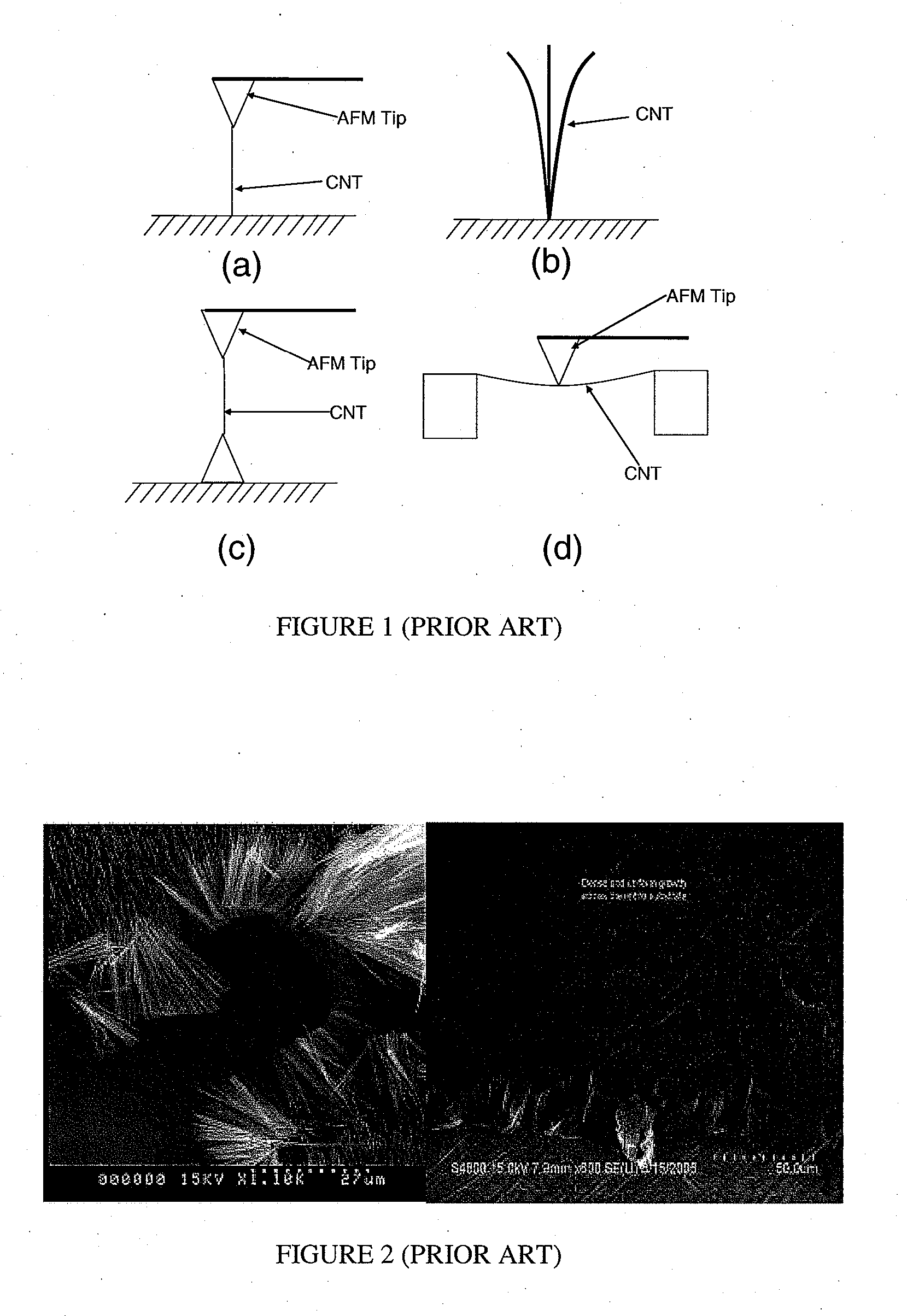
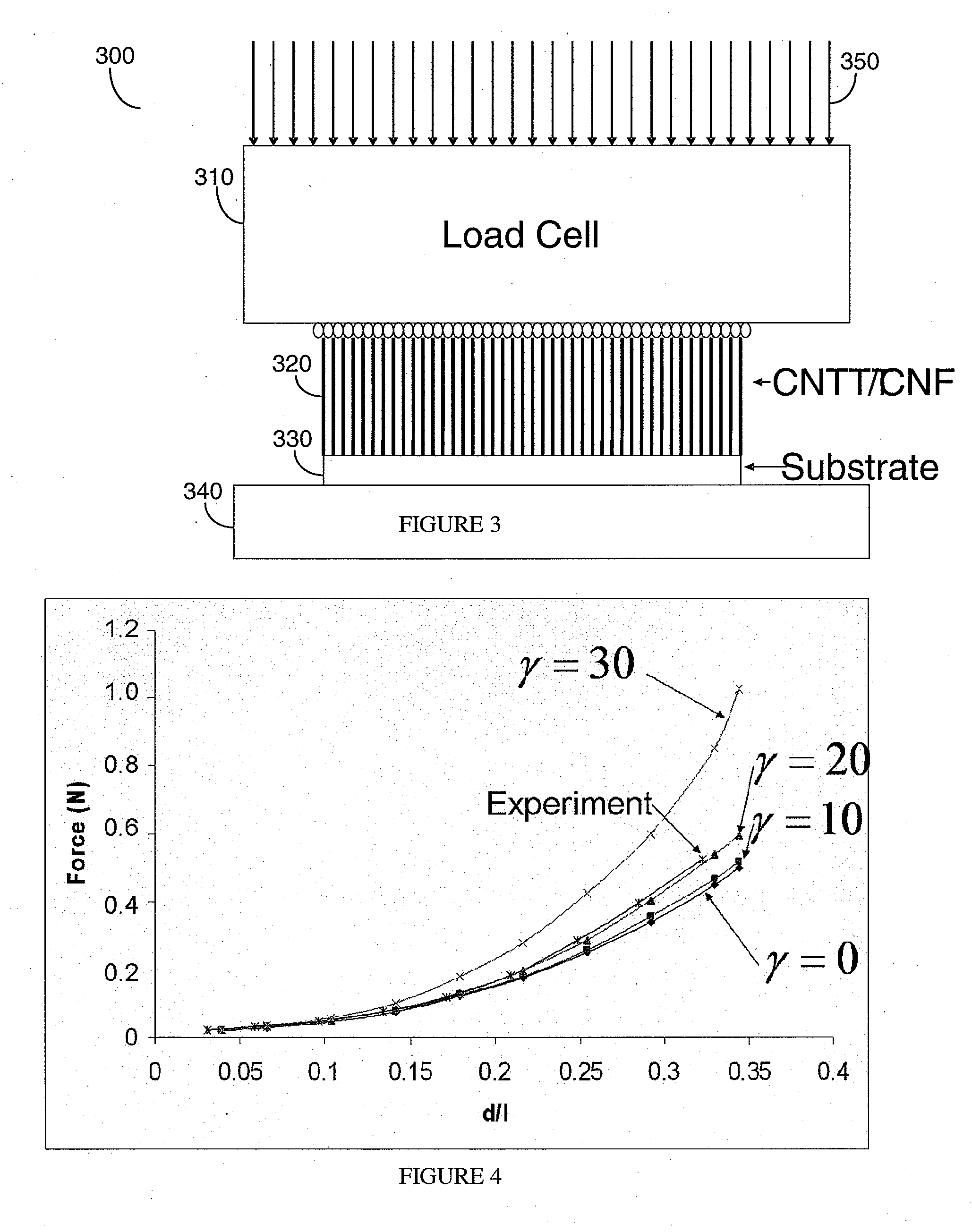
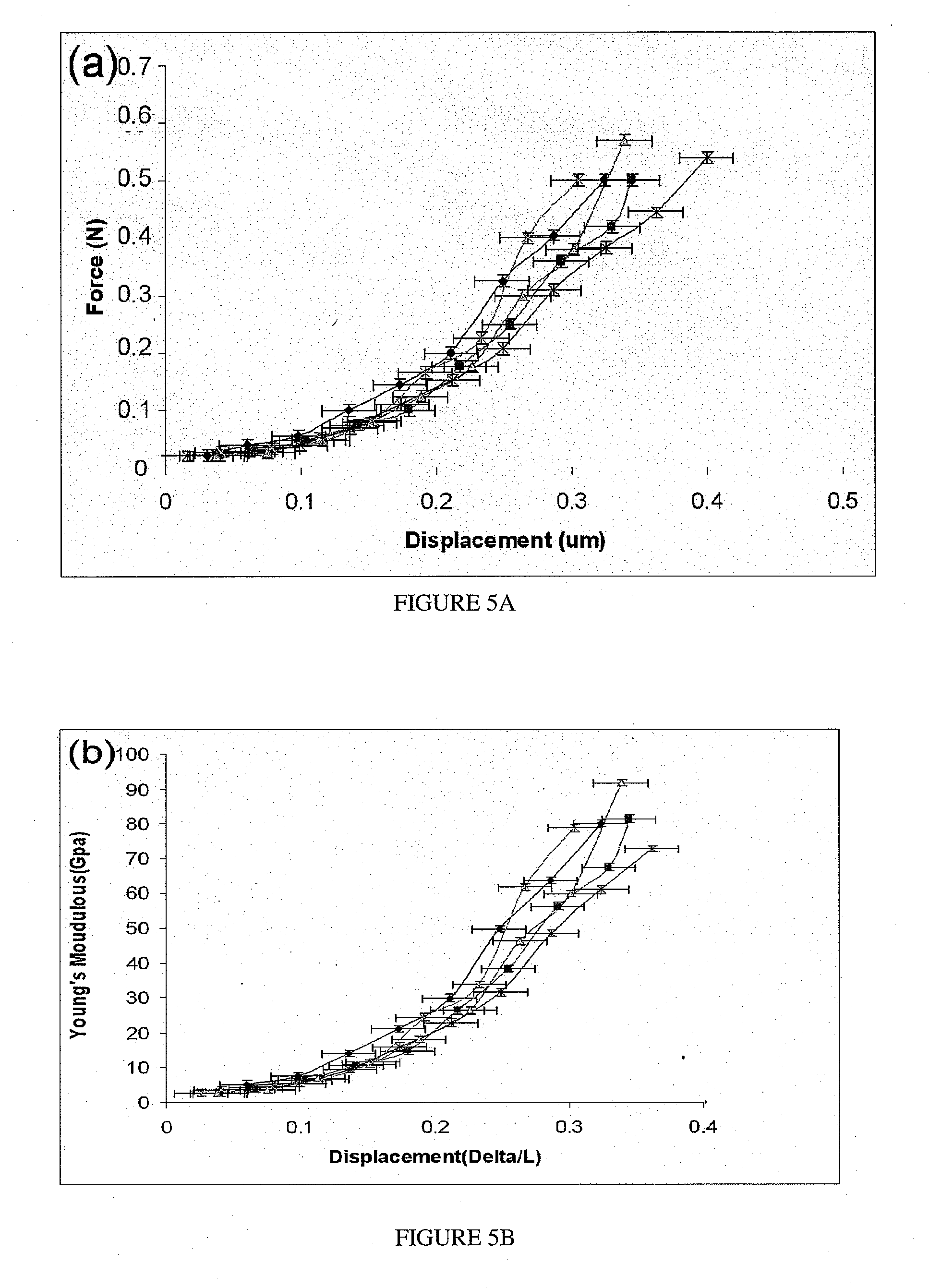
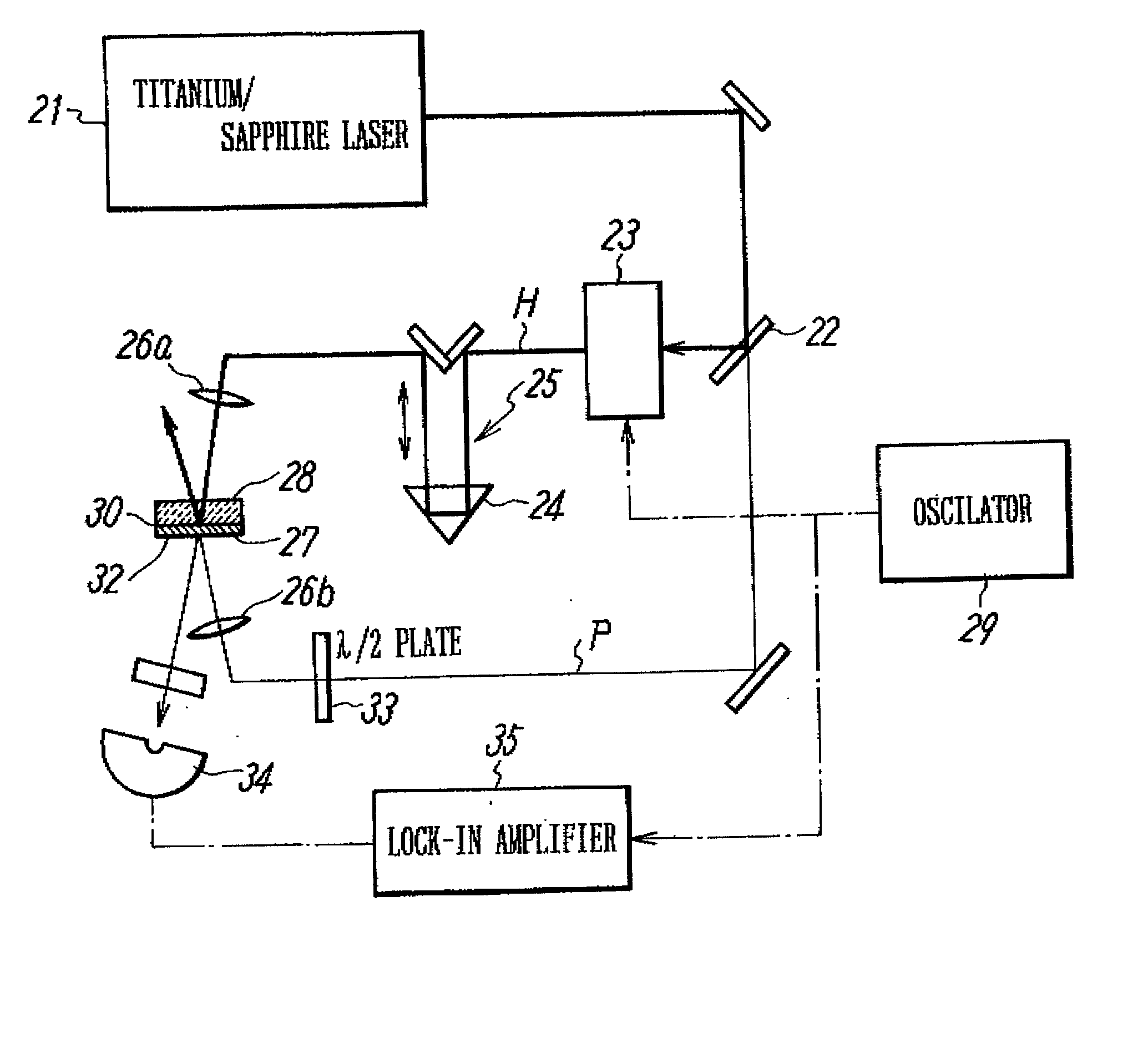
ActiveUS20080096293A1Increasing of Young 's modulusReduce thermal resistanceMaterial nanotechnologySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementInterfacial thermal resistanceCarbon nanofiber
A method and apparatus for the evaluation and improvement of the mechanical and thermal properties of carbon-nanotube (CNT) and carbon nanofiber (CNF) arrays grown on a substrate is disclosed. The Young's modulus of a CNT / CNF material is measured by applying an axial compressive force on the CNT / CNF array and measuring the applied forces and the induced displacements. Also disclosed are the evaluation of the nonlinear stress-strain relationship of the CNT / CNF material, increasing of the Young's modulus and decreasing the thermal resistance by application of a compressive load, the application of rapid thermal annealing to improve the quality of the CNT / CNF material and to reduce the interfacial thermal resistance, improvement of the bonding strength of the CNT / CNF array to a substrate, evaluation of the bonding strength of the CNT / CNF array to a substrate, evaluation of the shearing force at failure, and an analytical stress model that enables one to predict the interfacial shearing stress from the measured force.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method for measuring thermal diffusivity and interface thermal resistance
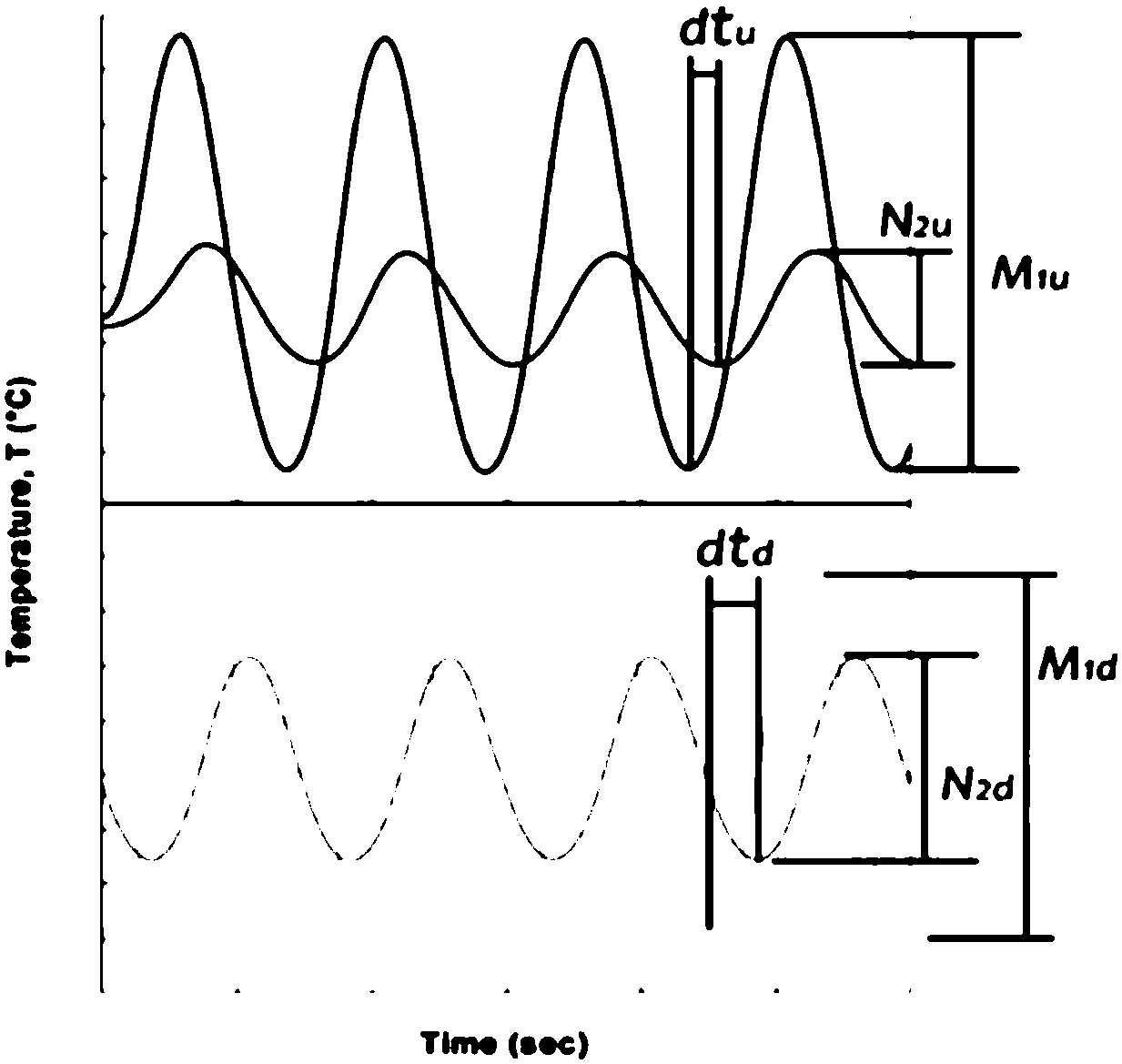
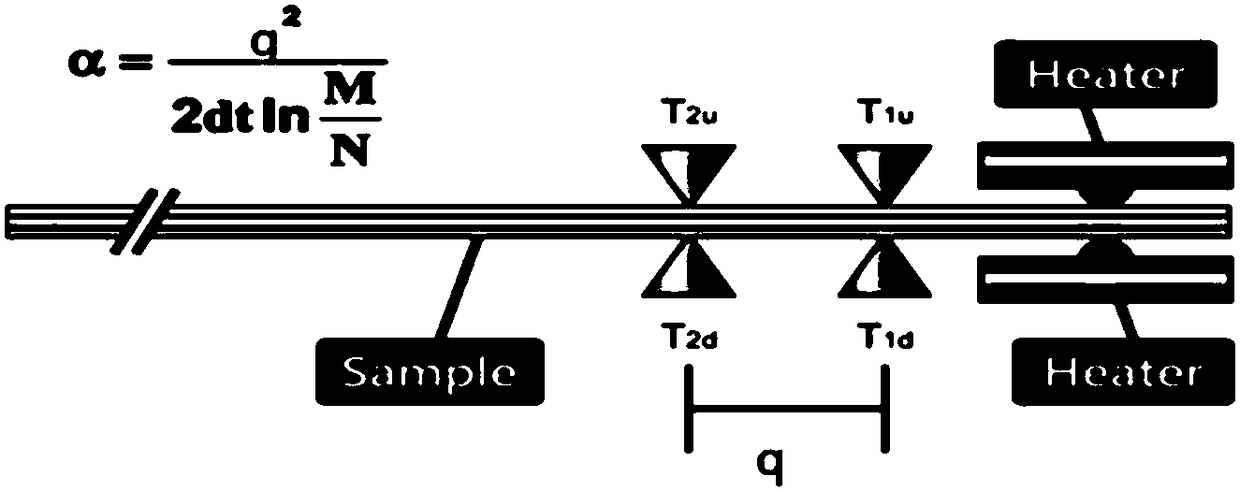
InactiveUS20020080850A1Material thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentThermal forceThermal diffusivity
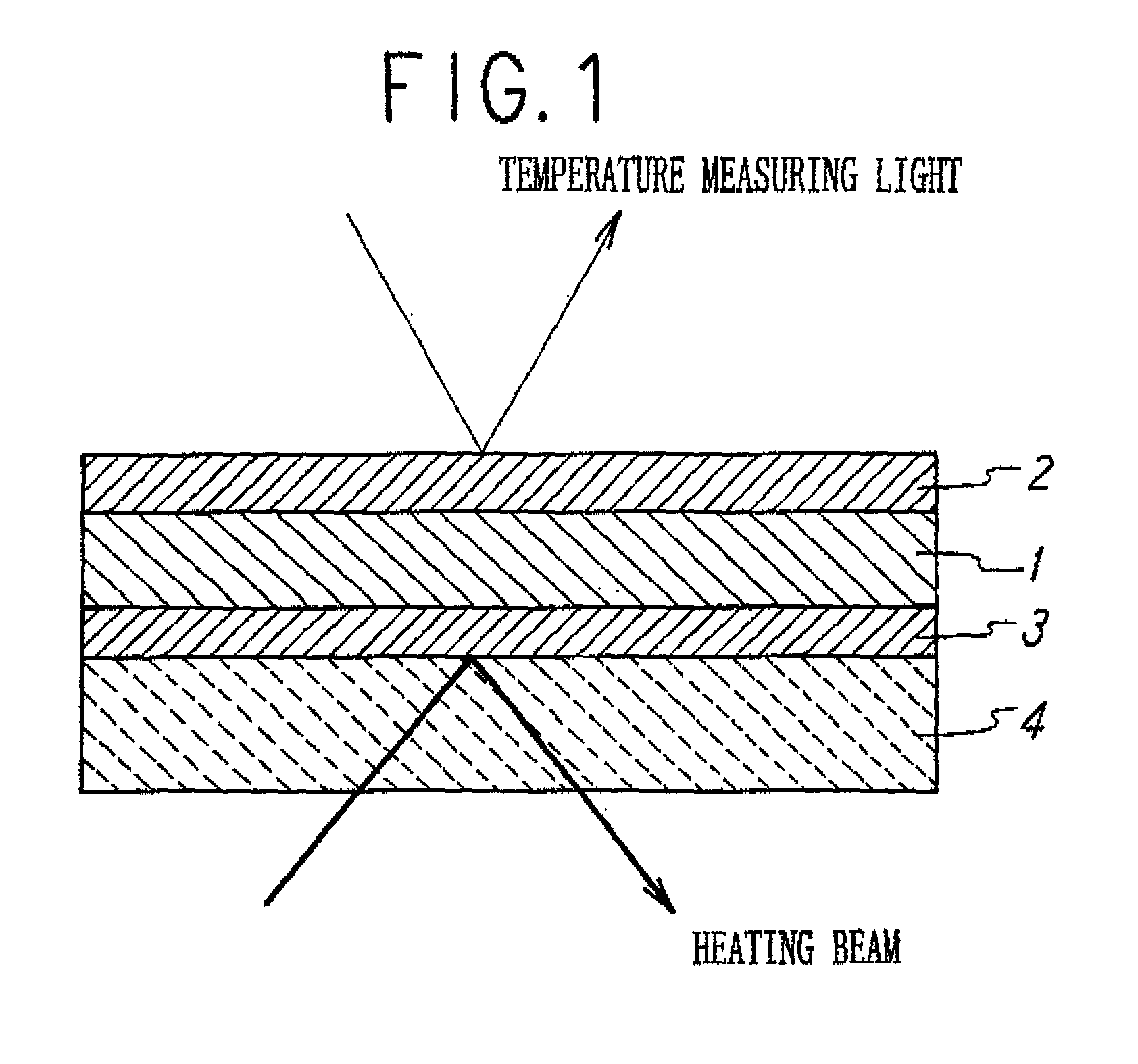
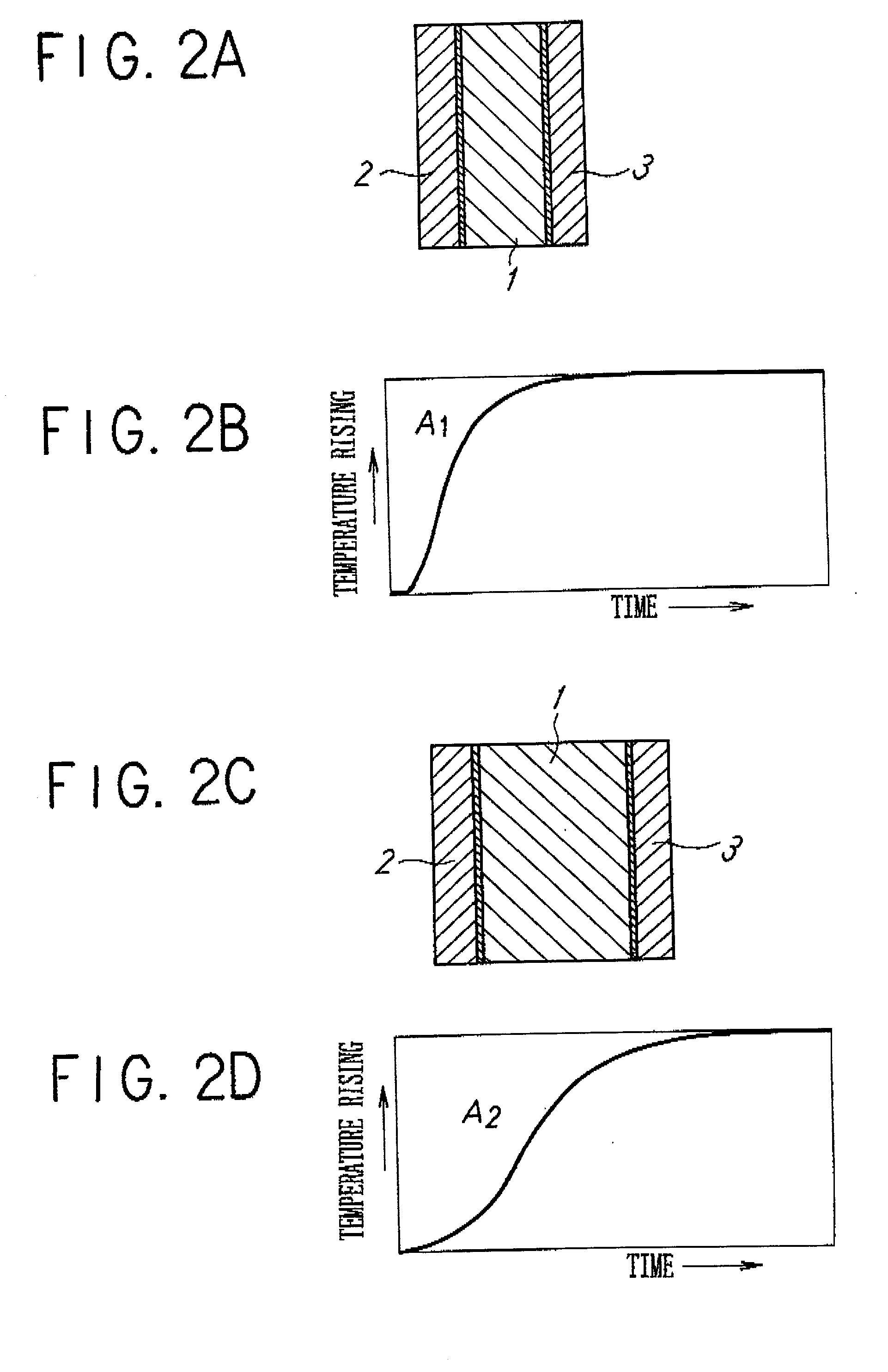
An object of the invention is to make it possible to correctly and easily measure a thermal diffusivity within a three-layer substance containing an non-metal substance. A non-metal film 1 whose thermophsical properties are unknown is disposed between a first metal film 2 and a second metal film 3, thereby forming a sample having a three-layer structure. The metal films 2 and 3 have predetermined known thermophsical properties, belong to the same sort of substance and have the same thickness. The three-layer substance is disposed on a transparent substrate 4 and is heated from below the second metal film 3, using a picosecond light pulse coming from below and passing through the transparent substrate 4. The light pulse used in the irradiation is converted into a heat in the second metal film 3 during only one picosecond, with such heat diffusing through interface / non-metal film layer / interface and thus arriving at the first metal film 2. By measuring a temperature change on the surface of the first metal film 2, it is possible to perform correct measurement by using the thermoreflectance method formerly suggested in a patent application by the inventors of the present invention.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Preparation method of low thermal resistance thermal interface
InactiveCN101609802AIncrease chance of contactHigh bonding strengthSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCarbon nanotubeInterfacial thermal resistance
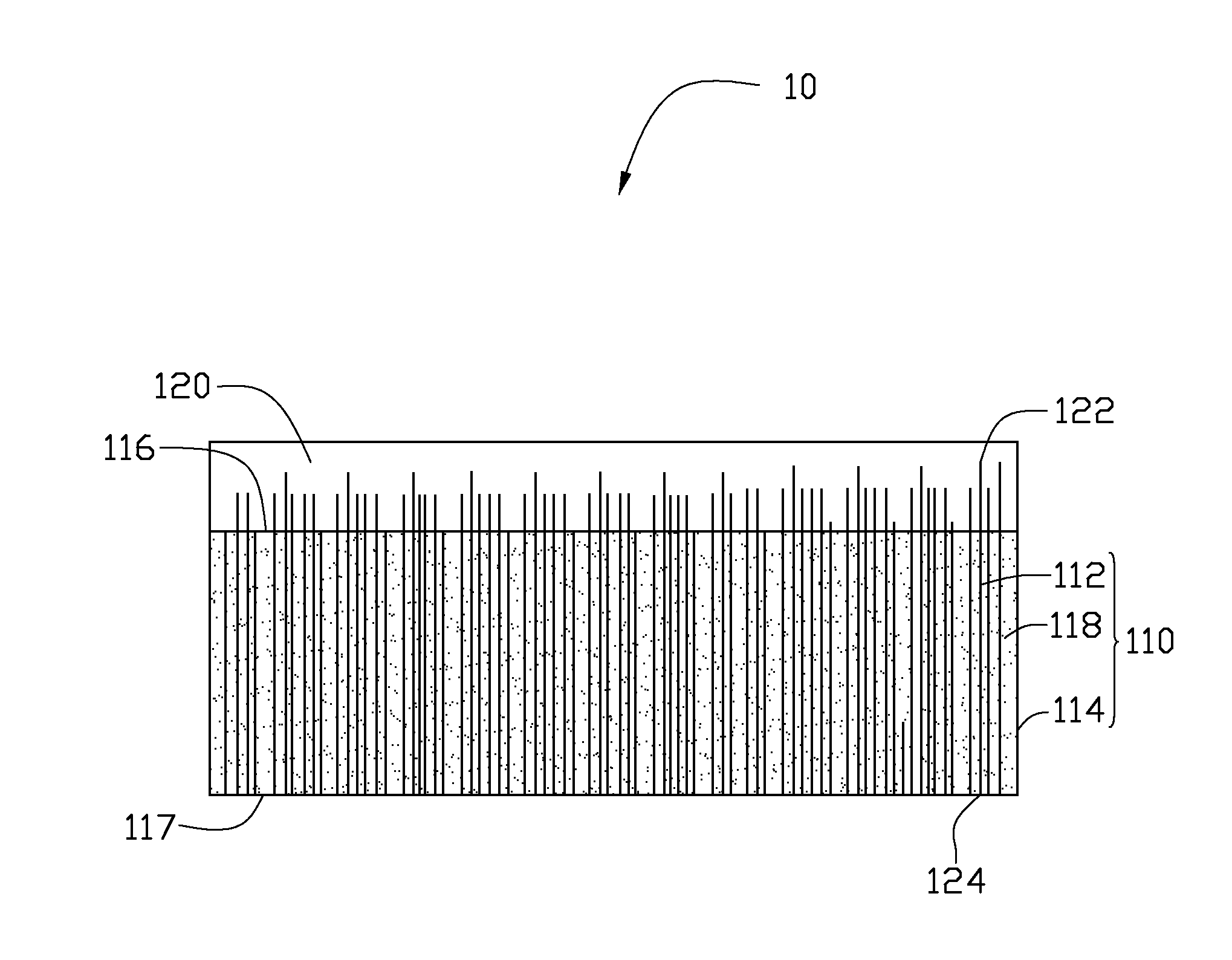
The invention provides a preparation method of low thermal resistance thermal interface. Firstly a vertically aligned carbon nano tube (VACNT) is prepared on a substrate, then the VACNT is modified and magnetized, and then contact probability between the VACNT and a target substrate is improved by magnetic aiming, and finally bonding between the VACNT and the target substrate is realized by bonding technology. Owing to the combined action of magnetic force and pressure, conformal contact is formed between the VACNT and the target substrate, thus effectively reducing interface contact thermal resistance. The invention solves the difficult problem that the VACNT is directly used as thermal interface material, provides a new way for research and development of nano encapsulation and interconnection and low thermal resistance encapsulation technology, and promotes the research of optoelectronic integration technology and the research and development of power devices.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Non-contact vibrationless low-temperature solid interface thermal resistance testing arrangement
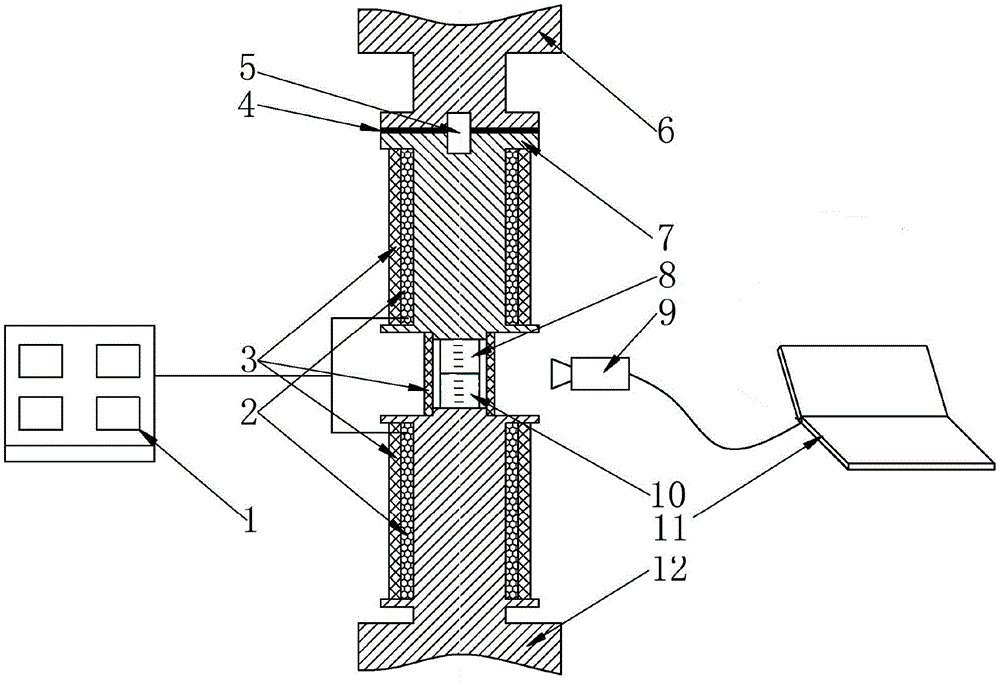
InactiveCN104634811AInsulate the influenceShorten the timeMaterial heat developmentVacuum pumpingEngineering
The invention discloses a low-temperature solid interface thermal resistance testing arrangement. An upper end of a lower bellows and a lower end of an upper bellows are fixed in a sealed manner at an opening of an upper end of a vacuum cap; a seal cover covers the upper end of the upper bellows; the upper surface of the lower end of the lower bellows is connected to a lower surface of a bottom of a sample holder through a flexible cold guide structure; the lower end of the lower bellows contacts an upper surface of a cold head of a refrigerating machine; the upper end of the upper bellows, the upper end of the sample holder and the seal cover are tightly fixed to a vibration isolation support; and an enclosed space is formed by the upper bellows, the lower bellows and the seal cover, and is internally provided with a sample clamp, which is arranged at the bottom of the sample support and is used for mounting a sample to be detected. According to the structure in the invention, a vacuum environment can be formed in the enclosed space for the air in the enclosed space can be quickly pumped out; vacuum-pumping time and cooling time are reduced during sample replacement; and an experimental period is shortened. The upper end of the sample support is tightly connected to the vibration isolation support, and the bottom of the sample support is connected to the lower end of the lower bellows through the flexible cold guide structure, so that influence of cold head vibration on the sample support when the refrigerating machine works is avoided.
Owner:NAVAL UNIV OF ENG PLA
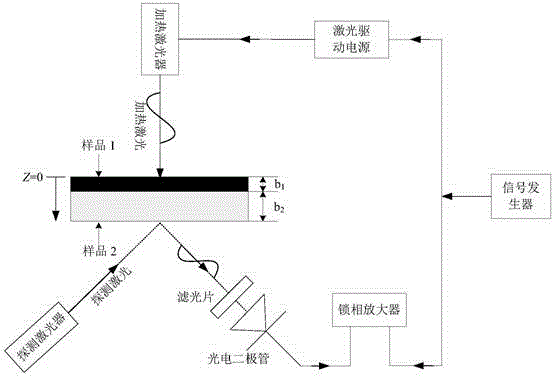
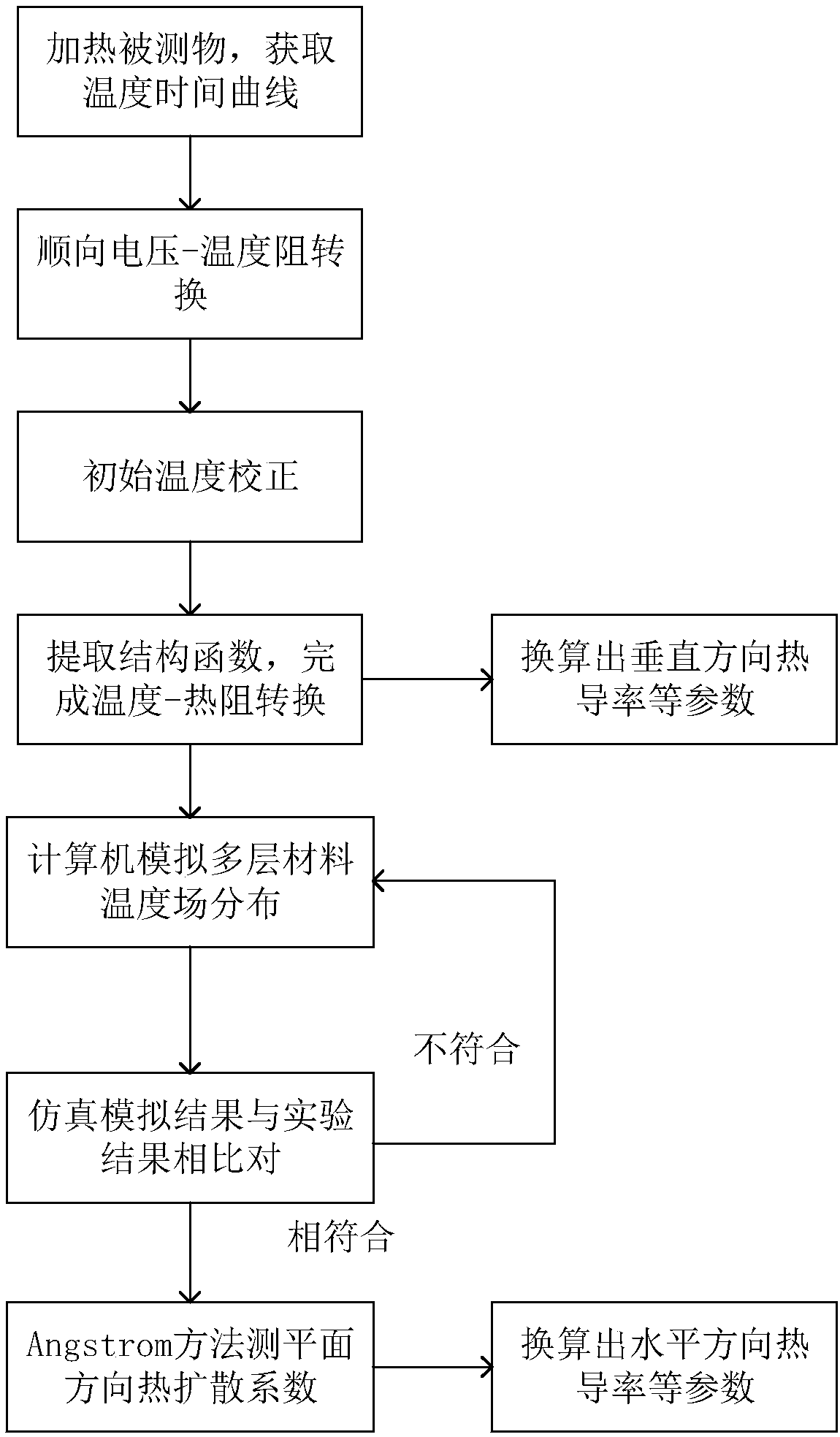
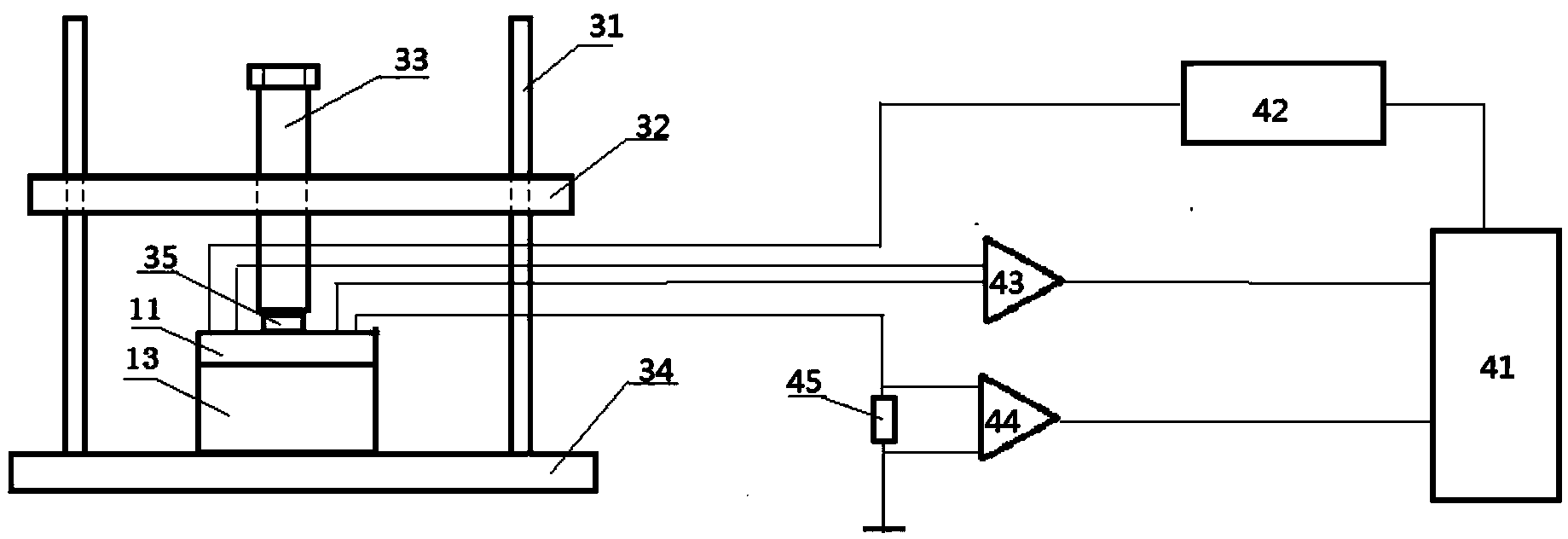
Test method and system for thermophysical parameters based on multilayer composite material
ActiveCN108614005AShort measurement timeImprove anti-interference abilityMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentHeat flowThermal diffusion coefficient
The invention discloses a test method for thermophysical parameters based on a multilayer composite material, wherein the method comprises the following steps: heating a multilayer composite materialtested object by the system, and measuring the time-temperature curve T (t) of the tested object; calculating to obtain thermal resistance and interface thermal resistance of various layers of materials in the vertical direction of the multilayer composite material tested object by the system; carrying out analogue simulation by the system, to obtain heat transfer disturbance between the layers ofmaterials; and measuring planar thermophysical parameters via an Angstrom method by the system, and converting into related thermophysical parameters. A test system for the thermophysical parametersbased on the multilayer composite materials includes a time-temperature curve obtaining module, a thermal resistance conversion module, a system analogue simulation and a thermophysical parameter calculation module. The method can measure the vertical-direction thermal resistance and the horizontal-direction thermal diffusion coefficient of the multilayer composite material, and simulates the thermal crosstalk direction of heat flow among multiple layers of materials. The method can be widely applied in the field of material heat testing.
Owner:JIEYAO PRECISION HARDWARE SHENZHEN
Contact thermal resistance modeling method considering elasticoplastic deformation of micro-bulge and thermal resistance of air medium
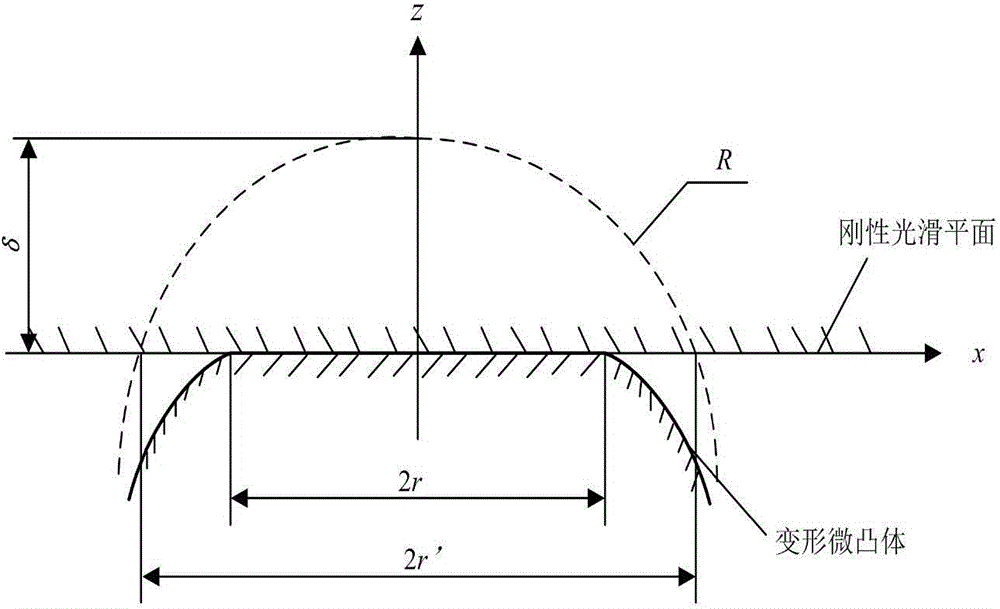
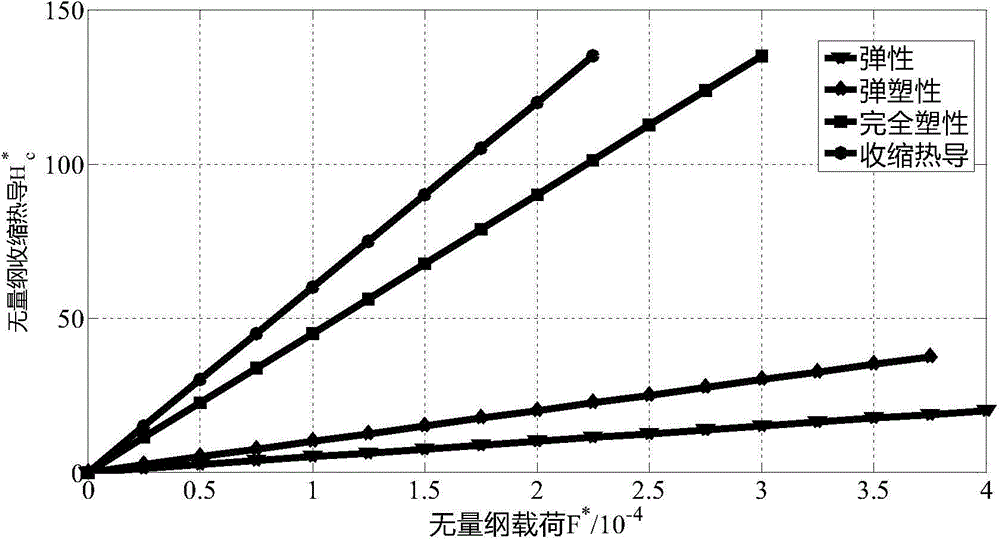
ActiveCN104978465AAccurate calculationSpecial data processing applicationsThermal stateHeat resistance
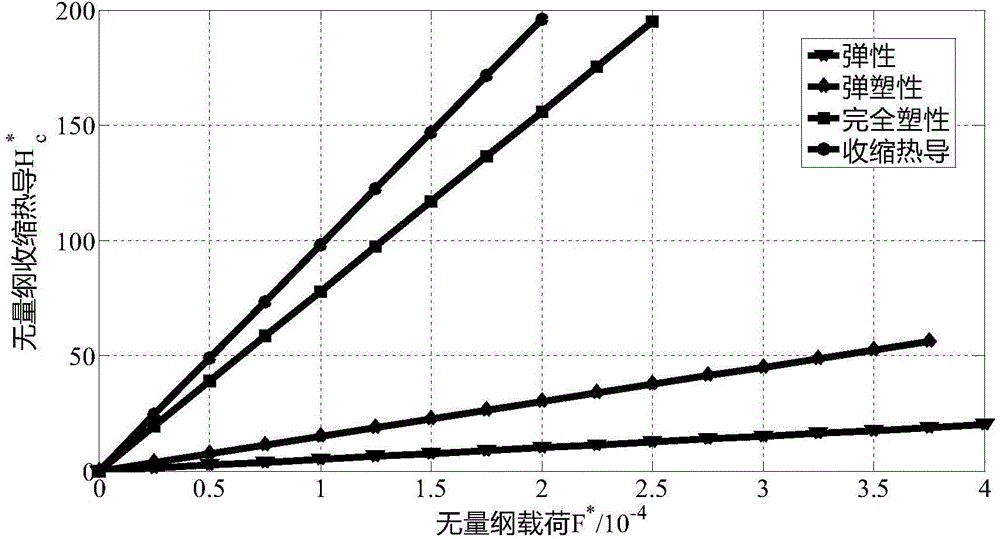
The invention discloses a contact thermal resistance modeling method considering elasticoplastic deformation of a micro-bulge and thermal resistance of an air medium, wherein influence of the elasticoplastic deformation of the micro-bulge and the heat resistance of the air medium on the contact thermal resistance is considered. The method comprises: according to elastic deformation, elasticoplastic deformation and fully-plastic deformation of the micro-bulge, computing an actual contact area and contact load of a joint surface; then, respectively computing thermal constriction resistance and the heat resistance of the air medium, and computing total contact thermal resistance by virtue of combination of the thermal constriction resistance and the heat resistance of the air medium,; and finally, obtaining a relationship between the contact thermal resistance and the load by using a Matlab writing and computing program. The contact thermal resistance modeling method is characterized in that the influence of the elasticoplastic deformation of the micro-bulge and the heat resistance of the air medium is considered; the thermal constriction resistance, generated by elasticoplastic deformation, accounts for 15% of the total thermal constriction resistance; and when the load is relatively small, the influence of the heat resistance of the air medium is relatively large and cannot be ignored. The method provided by the invention can provide theoretical basis for computing the contact thermal resistance of boundary conditions for electro-spindle thermal state analysis.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Interface thermal resistance measuring method in dissimilar metal compound molding process
InactiveCN104359942ARealize measurementMeasurable dynamic changesMaterial heat developmentInterfacial thermal resistanceThermocouple
The invention provides an interface thermal resistance measuring method in a dissimilar metal compound molding process, relates to the technical field of heating in metal material plastic processing, and aims to solve the problems that a contact thermocouple is easily loosened, even broken and cannot applied to interface thermal resistance measurement in dissimilar metal formation by adopting an existing interface thermal resistance measuring method because a material is deformed under large load. According to the scheme, the method comprises the following steps: firstly, establishing a temperature field molded by compounding of a dissimilar material; secondly, measuring and collecting information of the temperature field; thirdly, plastically deforming the dissimilar metal material; fourthly, dissolving the interface thermal resistance. The method is used for measuring the interface thermal resistance in the dissimilar metal compound molding process.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for testing contact thermal resistance among thin-layer materials based on 3-omega method
ActiveCN104034749ALow geometry requirementsAvoid derivationMaterial heat developmentContact pressureFast measurement
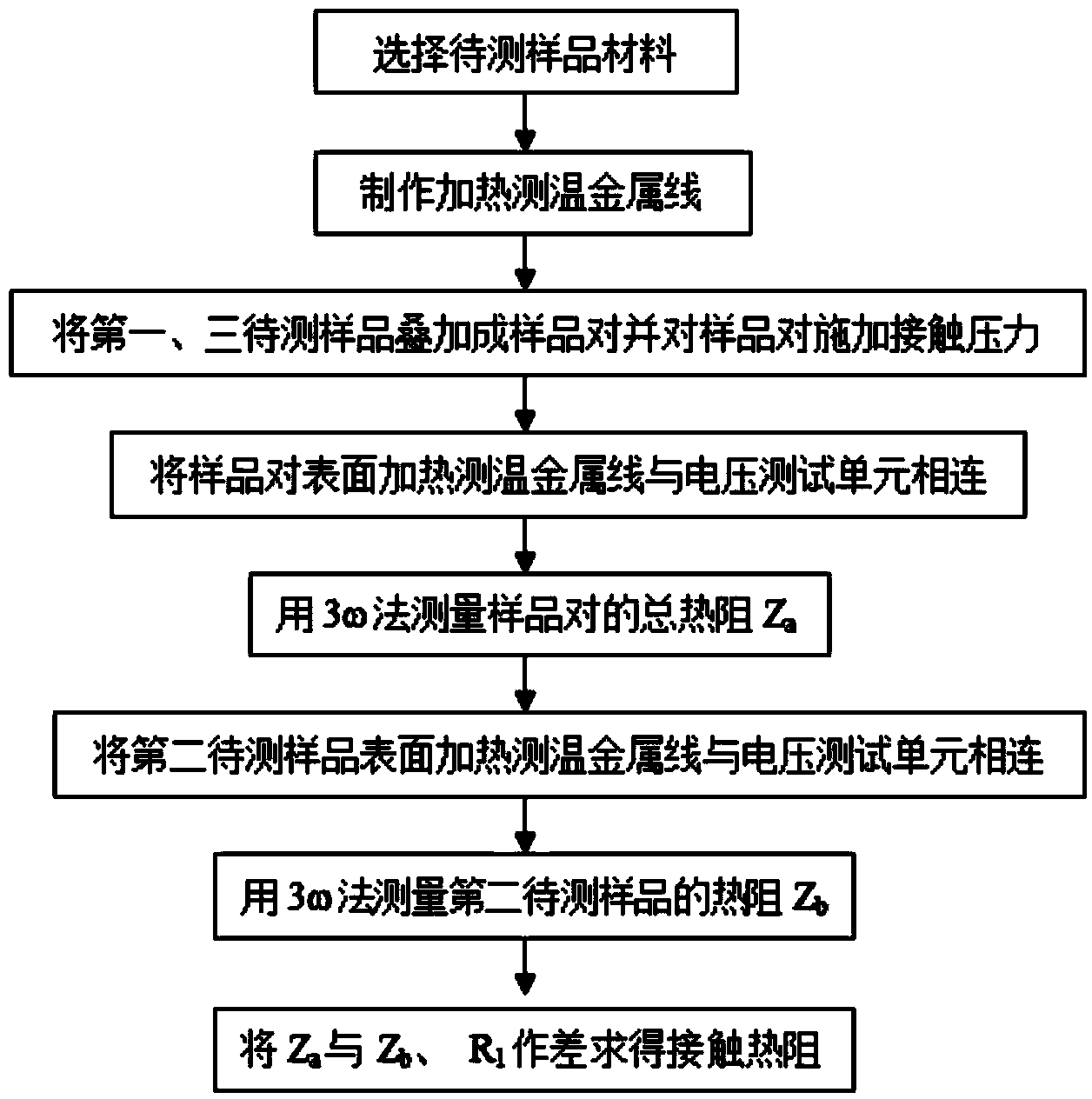
The invention provides a method for testing contact thermal resistance among thin-layer materials based on a 3-omega method. According to the method, the total thermal resistances of a to-be-measured sample pair and a contrast sample are respectively measured by virtue of the 3-omega method, and then the contact thermal resistance is calculated by virtue of a subtraction manner. The method comprises the following steps: overlapping a first to-be-measured sample and a third to-be-measured sample, so as to form the contact-thermal-resistance to-be-measured sample pair; taking a second to-be-measured sample as a contrast object; regulating the size of contact pressure between the first to-be-measured sample and the third to-be-measured sample by virtue of a pressure loading device; connecting a voltage testing unit with heating temperature-measuring metal wires on the surfaces of to-be-measured samples, measuring the total thermal resistances of the to-be-measured sample pair and the second to-be-measured sample, and finally carrying out subtraction so as to obtain the contact thermal resistance. The method has the advantages that the contact thermal resistance among the thin-layer materials can be rapidly measured, and a measurement principle is relatively simpler than the measurement principles of other transient methods.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Heat radiation backboard for photovoltaic assembly
ActiveCN105140327AEffective isolationImprove electrical insulation strengthPhotovoltaic energy generationSemiconductor devicesFiberAlkali free
The invention relates to a heat radiation backboard for a photovoltaic assembly. The backboard is composed of a metal heat conduction layer, an insulated bonding layer at one side of the metal heat conduction layer and a weather resistant layer at the other side of the metal heat conduction layer, wherein the insulated bonding layer is added with an alkali-free glass fiber powder filling material, the thickness of the bonding layer is 20-50 micrometer, the thickness of the metal heat conduction layer is 50-200 micrometer, and the thickness of the weather resistant coating layer is 8-20 micrometer. Addition of alkali-free glass fiber powder enables high electrical insulation performance of the bonding layer, and when the bonding layer is combined with the metal layer, requirements for insulation performance of the backboard material can be satisfied, and the problem that a traditional resin backboard is low in heat radiation performance is sovled. Compared with a present metal backboard, a common method, in which an insulated high molecular film layer is pasted, is replaced, and the interface thermal resistance is effectively reduced. Compared with the prior art, the whole temperature of the assembly is effectively reduced, and the power generating efficiency of the assembly is improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU FIRST APPLIED MATERIAL CO LTD
Boron nitride-silver/cellulose composite material and preparation method thereof
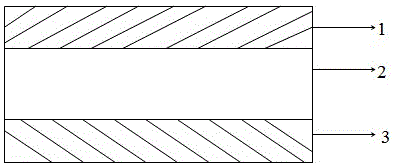
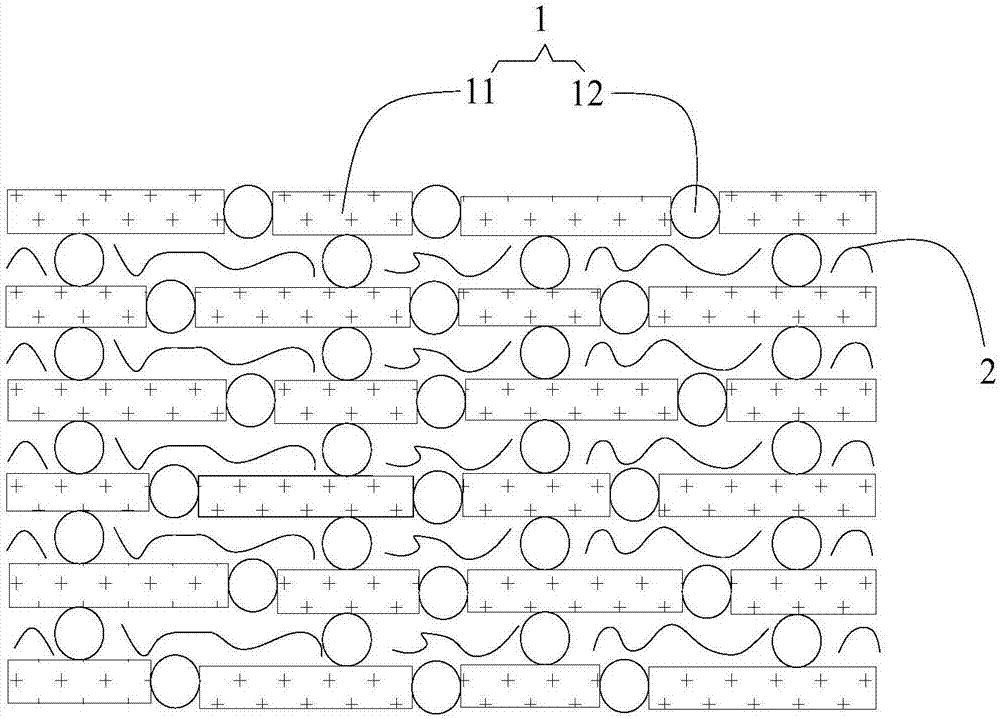
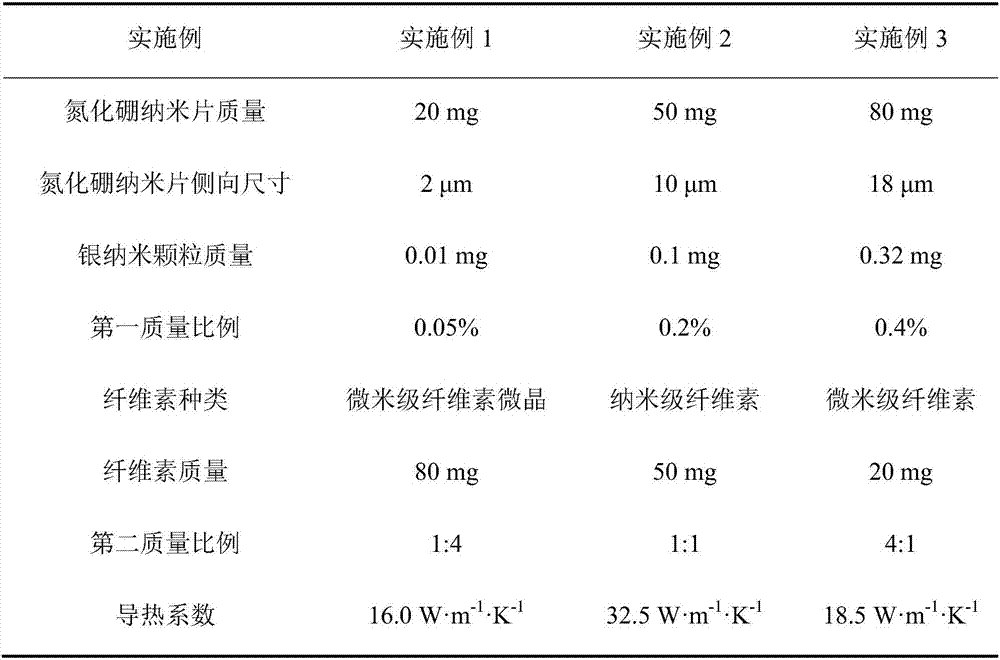
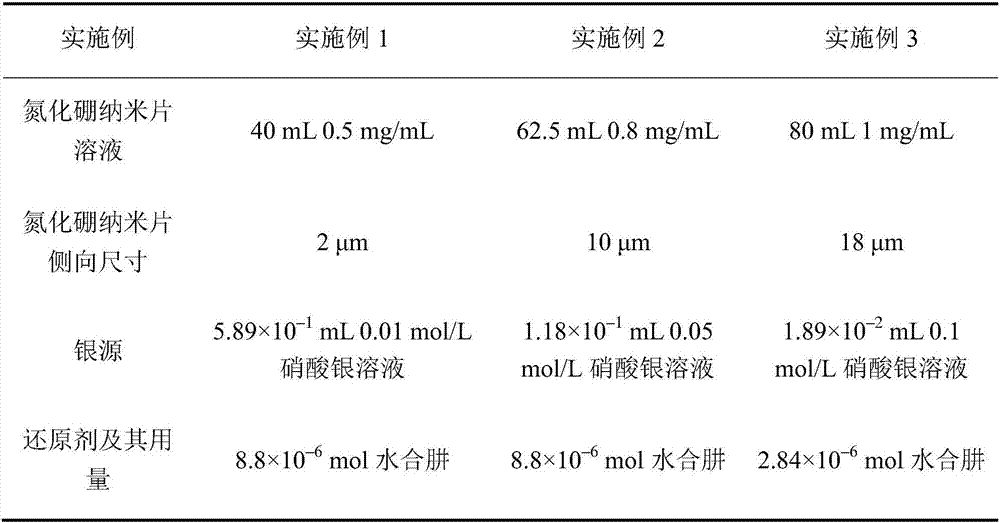
ActiveCN106977771ALower interface thermal resistanceImprove mechanical propertiesCelluloseElectric machinery
The invention discloses a boron nitride-silver / cellulose composite material, which is prepared from boron nitride nanosheets, cellulose and silver nanoparticles, wherein the silver nanoparticles are bridged with the at least two boron nitride nanosheets along the horizontal directions of the boron nitride nanosheets, so that boron nitride-silver hybrid filler is formed; the cellulose isolates the two adjacent layers of stacked boron nitride-silver hybrid filler. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the boron nitride-silver / cellulose composite material. According to the boron nitride-silver / cellulose composite material provided by the invention, the interface thermal resistance in boron nitride is effectively reduced by means of the bridging action of the silver nanoparticles, so that high heat-conducting property is realized; furthermore, the boron nitride-silver / cellulose composite material also has excellent flexibility, thus having a better application effect in the fields such as micro-electronics, electrical machinery and electric appliances.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com