Thermal interface material based on composite thermal-conduction network of low-melting-point metals and thermal-conduction particles, and preparation method of thermal interface material
A low-melting-point metal and thermal interface material technology, applied in the field of thermal interface materials, can solve the problems of poor thermal conductivity and difficult to meet the heat dissipation requirements of high-performance electronic components, and achieve high thermal conductivity, low interface thermal resistance, good elasticity and The effect of softness
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
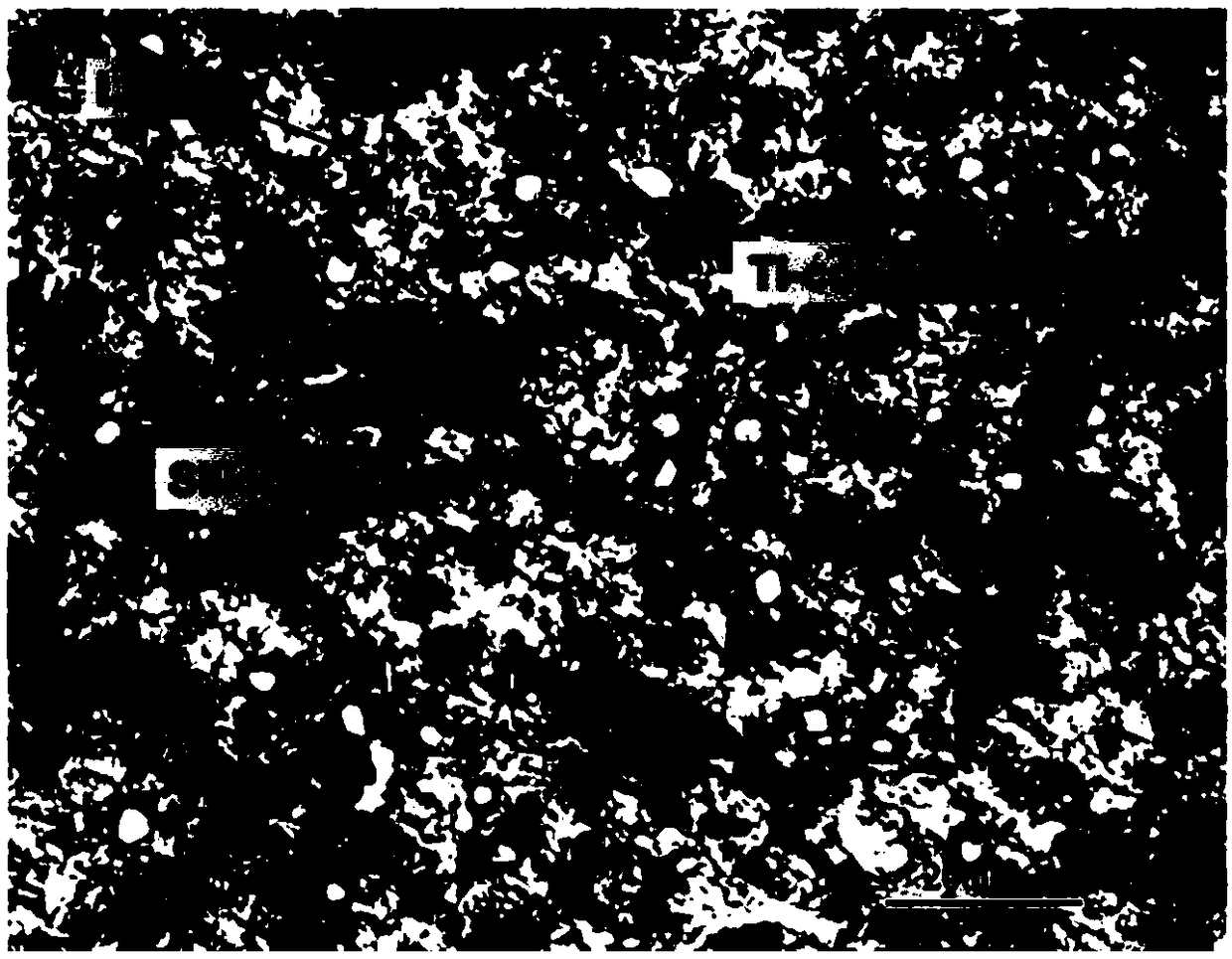
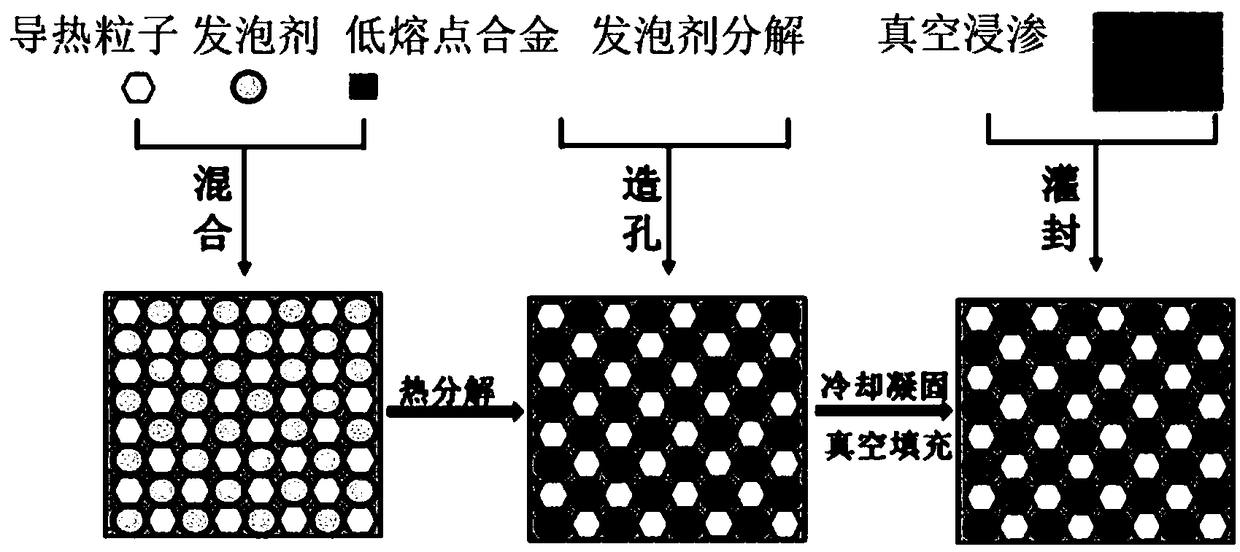
[0029] The preparation principle of the thermal interface material in this example is as follows: figure 1 As shown, the specific process is as follows:
[0030] (1) Preparation of low-melting point alloy: mix gallium (purity 99.99%) and titanium powder (1600 mesh, purity 99.99%) according to the mass ratio of 99:1, fully stir, and place in a constant temperature furnace at 200°C for 2 hours to obtain a low melting point alloy. Melting point alloy - gallium titanium alloy.
[0031] (2) Take titanium-coated diamond particles (325 mesh, vacuum-evaporated titanium) and mix them with gallium-titanium alloy according to the mass ratio of 1:1.6, and place them in a mortar, grind and stir repeatedly for 15 minutes, so that the gallium and titanium-coated diamond particles are completely Wet and mix thoroughly, and keep it in a constant temperature furnace at 200°C for 2 hours to form a stronger metallurgical bond between gallium and titanium.
[0032] (3) Making foaming agent: Grin...
Embodiment 2
[0039] (1) Mix low-melting-point gallium metal (purity 99.99%) and thermally conductive copper particles (150 mesh, purity 99.99%) at a mass ratio of 1:2, stir well, and keep warm at 50°C for 10 minutes. Production of foaming agent: Grind ammonium bicarbonate into fine particles, pass through stainless steel standard sieves of different meshes, and sieve to obtain ammonium bicarbonate particles with a particle size of 34-50 μm.
[0040](2) Add the prepared foaming agent to the mixture prepared in the first step according to the mass ratio of 5%, fully mix, and then place the mixture in the mold, with 1.16×10 6 The pressure of Pa compacts and shapes the material.
[0041] (3) Place the sample prepared in the third step in a holding furnace, first heat it at 80°C for 8 hours, and then hold it at 120°C for 2 hours to ensure that the ammonium bicarbonate is completely decomposed, thereby obtaining a three-dimensional network structure material with continuous pores.
[0042] (4) ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] The preparation process of the thermal interface material in this embodiment is as follows:
[0047] (1) Electroless copper plating on the surface of boron nitride (particle size ≈ 5 μm, purity 99.9%), boron nitride particles with low melting point metal gallium (purity 99.99%) and metallization (copper-coated boron nitride) Mix according to the mass ratio of 1:1, stir well, and keep warm at 50°C for 10min.
[0048] (2) Making foaming agent: Grinding ammonium bicarbonate into fine particles, passing through stainless steel standard sieves with different meshes, sieving to obtain ammonium bicarbonate particles with a particle size of 34-50 μm.
[0049] (3) Add the prepared foaming agent to the mixture prepared in the first step according to the mass ratio of 5%, fully mix, and then place the mixture in the mold, with 1.16×10 6 The pressure of Pa compacts and shapes the material.
[0050] (4) Place the sample prepared in the third step in a holding furnace, first heat i...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thermal diffusivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com