Wheeled leg robot and driving method thereof
A wheel-legged robot and thigh technology, which is used in motor vehicles, transportation and packaging, etc., can solve the problems of low effective energy utilization rate of robots, large throttling power loss, hydraulic components and seal damage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
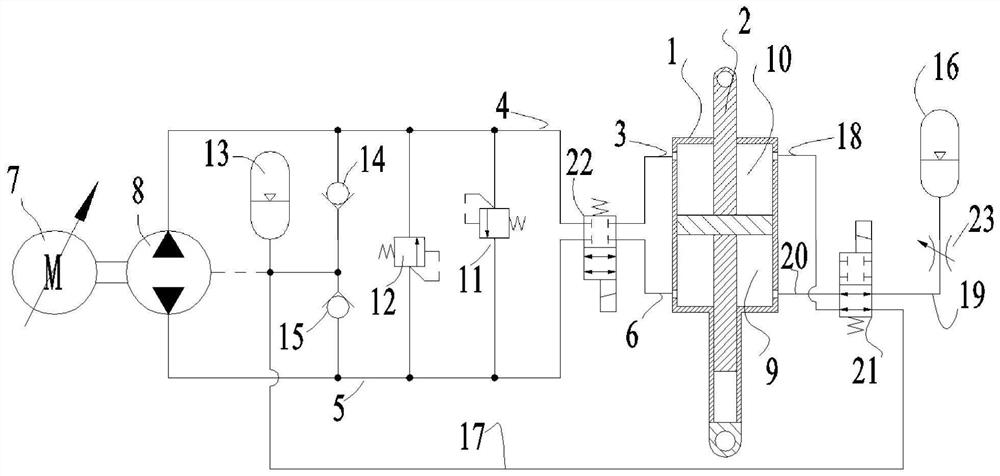
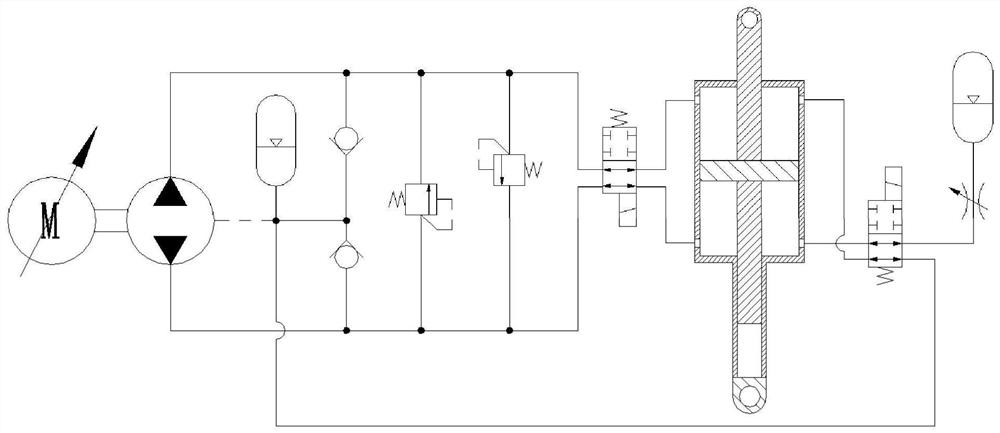
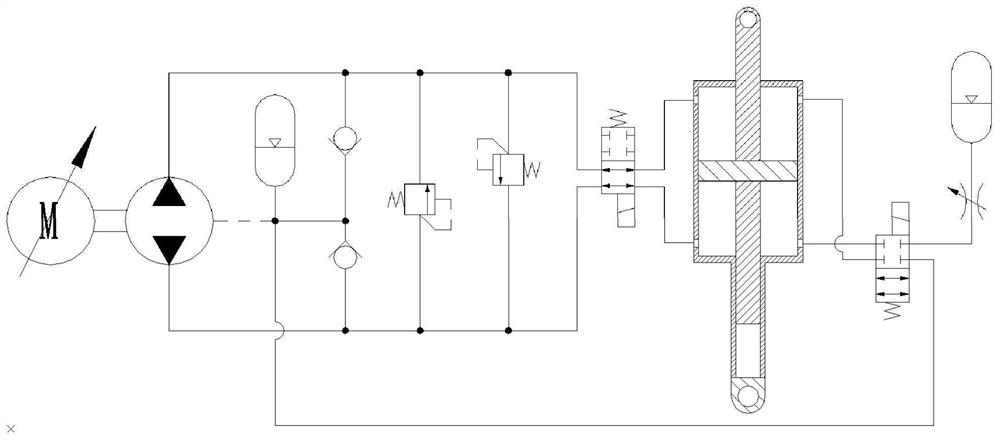
[0029] See attached Figure 1~5. A wheel-legged robot comprises a car body 35, a thigh 36, a calf 37, a wheel 38 and two hydraulic control systems; one end of the thigh 36 is hinged to the car body 35, and the other end of the thigh 36 is hinged to one end of the calf 37; the calf The other end of 37 is provided with wheel 38; two hydraulic control systems respectively control the size of the included angle between the car body 35 and the thigh 36, and the size of the included angle between the thigh 36 and the shank 37; the hydraulic control system includes hydraulic cylinder 1, Piston rod 2, oil supplement accumulator 13, high-pressure accumulator 16, high-pressure oil circuit and low-pressure oil circuit; the hydraulic cylinder 1 is provided with a bearing chamber 9 and a non-bearing chamber 10; the piston rod 2 separates the bearing chamber 9 and the non-bearing chamber 10; the outlet of the charge accumulator 13 communicates with the non-bearing chamber 10 through a low-...
Embodiment 2
[0031] See attached Figure 1~5 . On the basis of the first embodiment, the hydraulic control system further includes a second solenoid valve 21; the low-pressure oil circuit includes the fifth oil circuit 17 and the sixth oil circuit 18; the high-pressure oil circuit includes the seventh oil circuit 19 and the eighth oil circuit 20; the second electromagnetic valve 21 is a two-position four-way electromagnetic switch valve; the second electromagnetic valve 21 includes a2 port, b2 port, c2 port and d2 port; the fifth oil circuit 17 Both ends of the sixth oil passage 18 are respectively connected to the b2 port and the non-bearing chamber 10; both ends of the seventh oil passage 19 are respectively connected to the c2 port and the high-pressure accumulator device 16; both ends of the eighth oil passage 20 are respectively connected to the d2 port and the bearing chamber 9; when the second solenoid valve 21 is in the off-potential state, except that the a2 port is connected to ...
Embodiment 3
[0039] See attached Figure 1~5. A method for driving a wheel-legged robot, using the wheel-legged robot described in Embodiment 1, including a passive vibration reduction step; the passive vibration reduction step specifically includes: driving the wheel-legged robot to drive when the wheel 38 touches the ground and rotates; The low-pressure oil circuit is conducted, and the outlet of the charge accumulator 13 communicates with the non-bearing chamber 10 through the low-pressure oil circuit; the high-pressure oil circuit is conducted, and the outlet of the high-pressure accumulator 16 passes through the high-pressure oil circuit and the bearing chamber 9 communication; the hydraulic oil between the bearing chamber 9 and the non-bearing chamber 10 is not exchanged; when the wheel-legged robot is driving on a flat ground, the load force borne by the hydraulic cylinder 1 and the piston rod 2 has no fluctuation, the car body 35 has no vibration, and the piston The relative elong...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com