Quasi-zero stiffness electromagnetic vibration isolator suitable for ultralow-frequency vibration reduction and isolation
A quasi-zero stiffness, vibration isolator technology, applied in the direction of shock absorber, shock absorber-spring combination, spring/shock absorber functional characteristics, etc., can solve the problem of low dynamic stiffness and air gap of electromagnet negative stiffness mechanism Too big etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
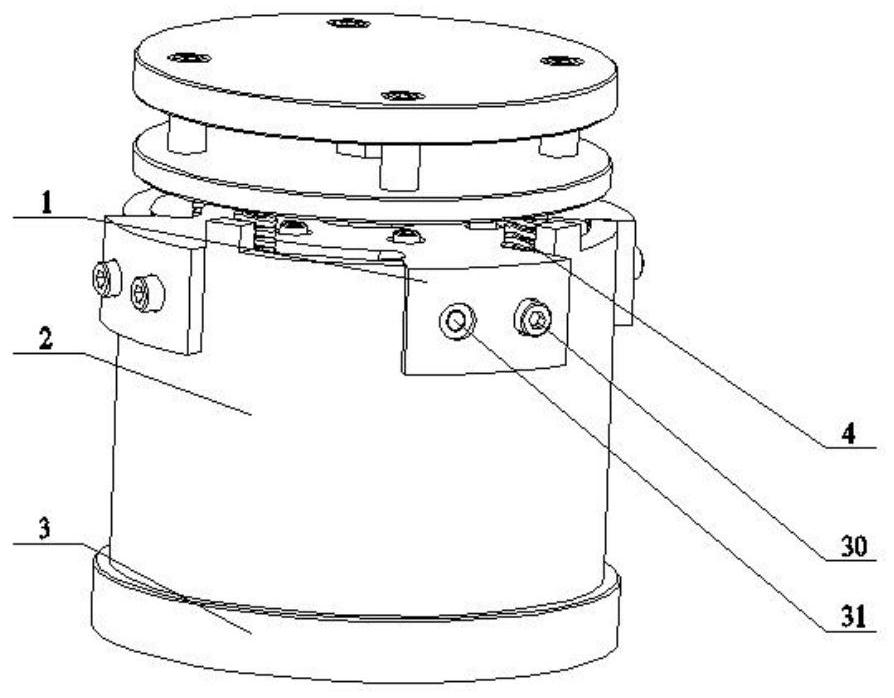
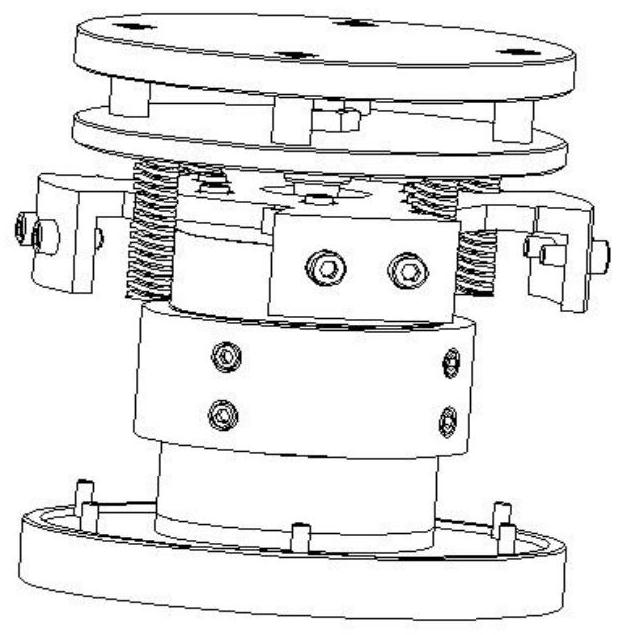
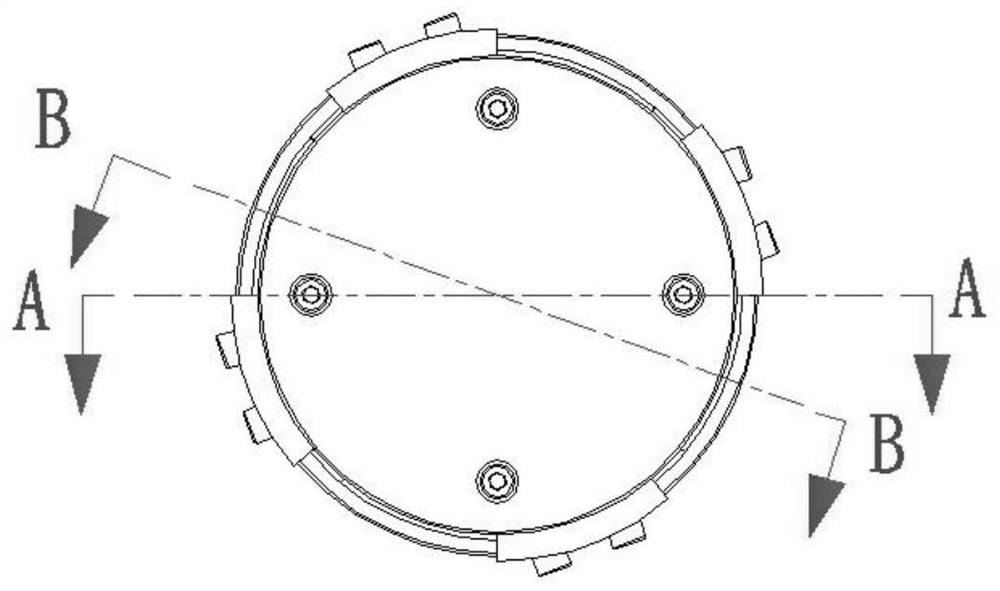
[0039] according to Figure 1 to Figure 15 As shown, the present invention provides a kind of quasi-zero stiffness electromagnetic vibration isolator suitable for ultra-low frequency vibration reduction and isolation, a kind of quasi-zero stiffness electromagnetic vibration isolator suitable for ultra-low frequency vibration reduction and isolation, which includes a stator mounting plate 1, The housing composed of the vibration isolator cover 2 and the base 3, and the mover assembly, the upper stator assembly and the lower stator assembly etc. located inside the housing. The lower stator assembly is installed on the base 3, the vibration isolator cover 2 is installed on the base 3, the stator mounting plate 1 is installed on the vibration isolator cover 2, the upper stator assembly is installed on the stator mounting plate 1, and the spring 4 is installed on the moving Between the subassembly and the vibration isolator cover 2, the movable subassembly is placed on the spring 4...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com