Approach for modulating regulatory t cells and inhibiting tumor growth
A regulatory, tumor technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, anti-tumor drugs, anti-growth factor immunoglobulins, etc., can solve problems such as hindering the application of Treg targeting methods and limiting the therapeutic potential of Treg targeting methods.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0099] Example 1: This example describes the materials and methods to be used in subsequent examples.
[0100] mice. C57BL / 6 / J, FoxP3 YFP-Cre , Rag1 – / – (B6.129S7-Rag1 tm1Mom / J) Mice were purchased from Jackson Laboratories. CD36fl / fl mice were generated as previously described (Son, N.H. et al. J Clin Invest 128, 4329-4342 (2018).). PPARγ was produced as described by Dammone, G et al. fl / fl and PPARβ fl / fl Mice (Dammone, G. et al. International journal of molecular sciences 19 (2018)). Dankort et al. (Dankort et al. Nature Genetics volume 41, pages 544-552 (2009)) describe BRafCA; Tyr::CreER; Ptenlox4-5 (Braf / Pten). K-ras in NSCLC is described by DuPage et al. (DuPage et al. Nature Protocols Vol. IV, pp. 1064–1072 (2009)) LSL-G12D / + / p53 fl / fl Conditioned mouse model. Animals were maintained at the Specific Pathogen Free Facility of the University of Lausanne and all experimental studies were approved and performed in accordance with the guidelines and regulations ...
Embodiment 2
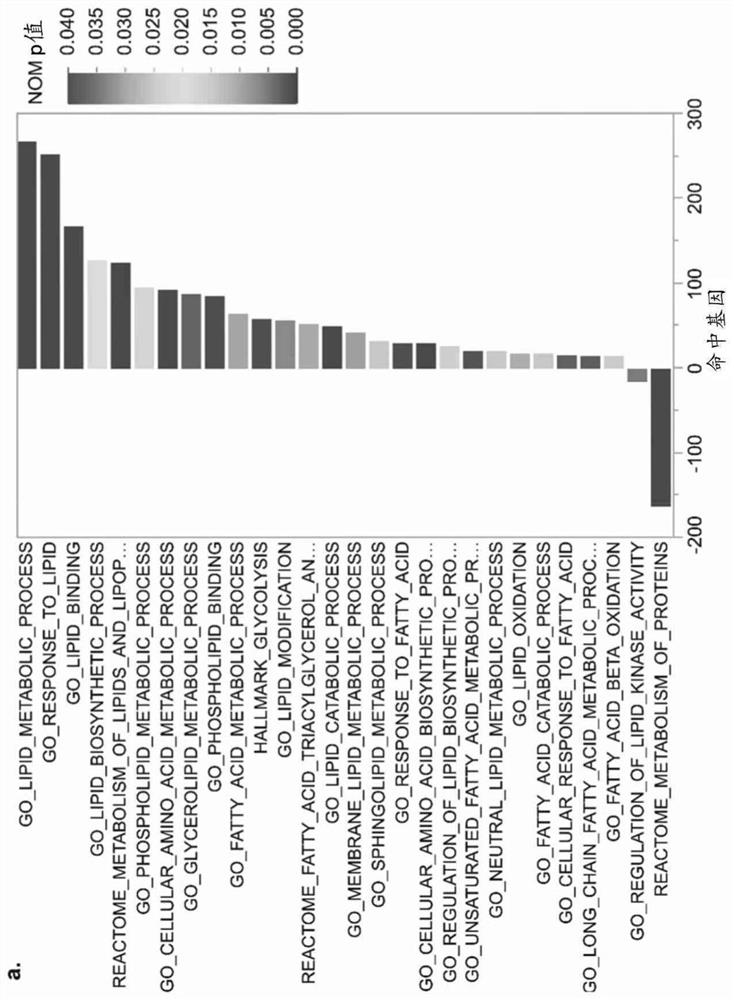
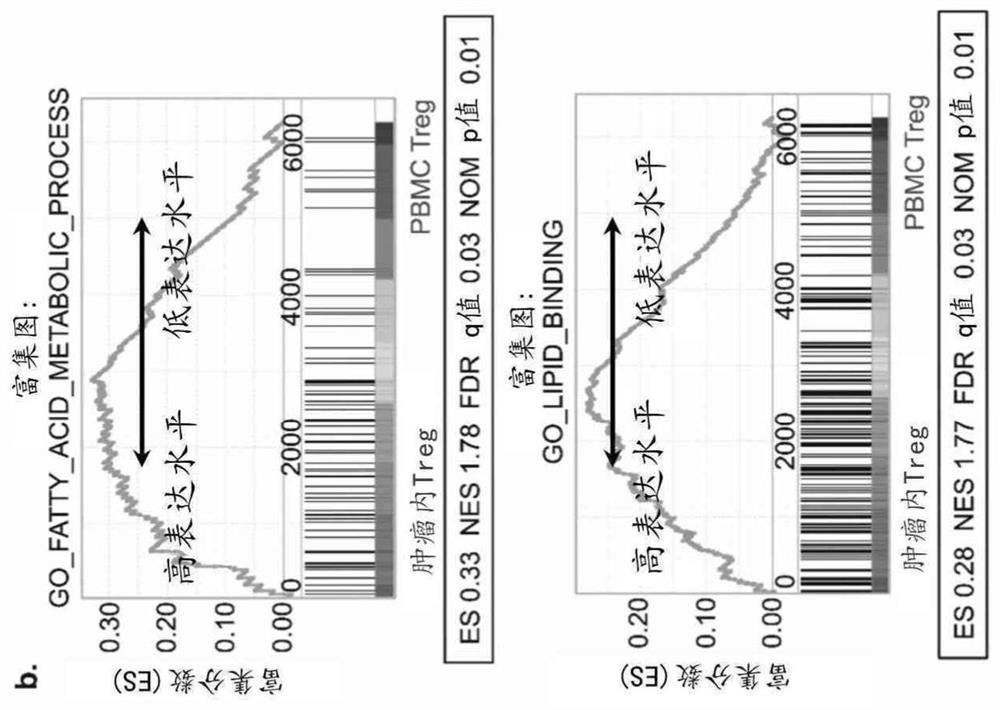
[0116] Example 2: Intratumoral Treg increases lipid metabolism and CD36 expression
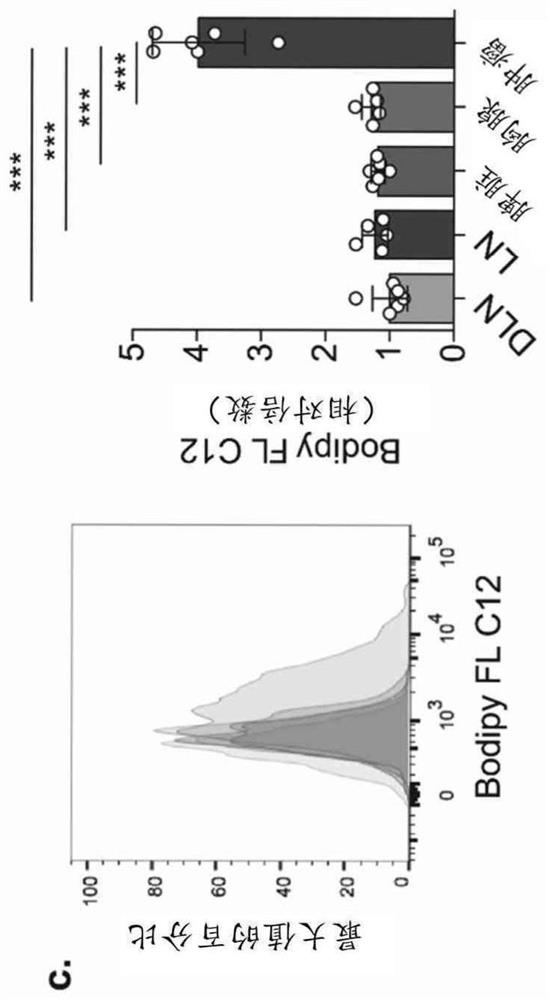
[0117] To elucidate whether intratumoral Tregs preferentially participate in specific metabolic pathways, in a previously published study, RNA sequencing results of intratumoral Tregs and circulating Tregs obtained from breast cancer patients were first analyzed (Plitas, G. et al. Immunity 45, 1122 -1134). Gene pathway analysis, with a particular focus on metabolic pathways, revealed that intratumoral Tregs highly expressed metabolic genes responsible for lipid metabolism compared with circulating Tregs ( Figure 1a and 1b), suggesting that intratumoral Tregs may increase their lipid metabolism. Indeed, a comparison between peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and intratumoral Tregs revealed that intratumoral Tregs internalized higher amounts of the green fluorescent fatty acid, Bodipy FL C12, and contained Higher neutral lipid cont...
Embodiment 3
[0118] Example 3: CD36 controls the accumulation of Treg in the tumor and inhibits its function
[0119] To investigate whether CD36 expression regulates Treg behavior in tumors, CD36 fl / fl mice with Foxp3 YFP-Cre Mice were crossed to generate Treg-specific CD36-deficient mice (termed Treg CD36- / - ). Given that genetic ablation of key regulators in Tregs could lead to systemic activation of T lymphocytes and autoimmunity due to impairment of Treg suppressive function, we first examined whether CD36 deficiency in Tregs affects immune homeostasis. found that in both sexes, older Treg CD36- / - Mice (21-23 weeks) showed a strong association with Foxp3 YFP-Cre Mice (referred to as wild-type mice throughout the study) were of comparable body weight. Compared with WT mice, Treg CD36- / - CD4 + and CD8 + A similar proportion of effector or memory populations (CD44 hi CD62L lo ). In addition, Treg CD36- / - Mice showed neither abnormal infiltration of lymphocytes and myeloid cel...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com