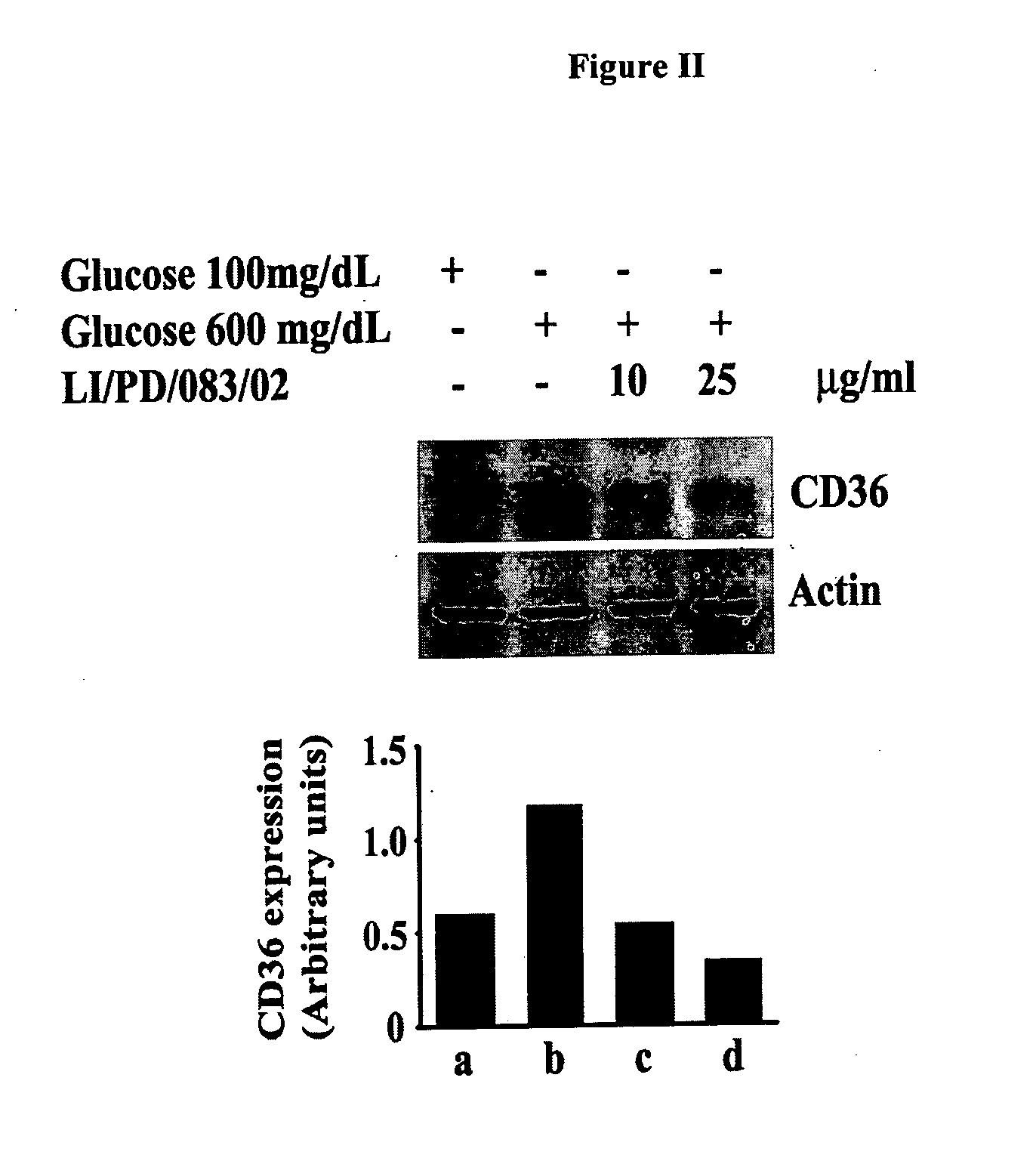
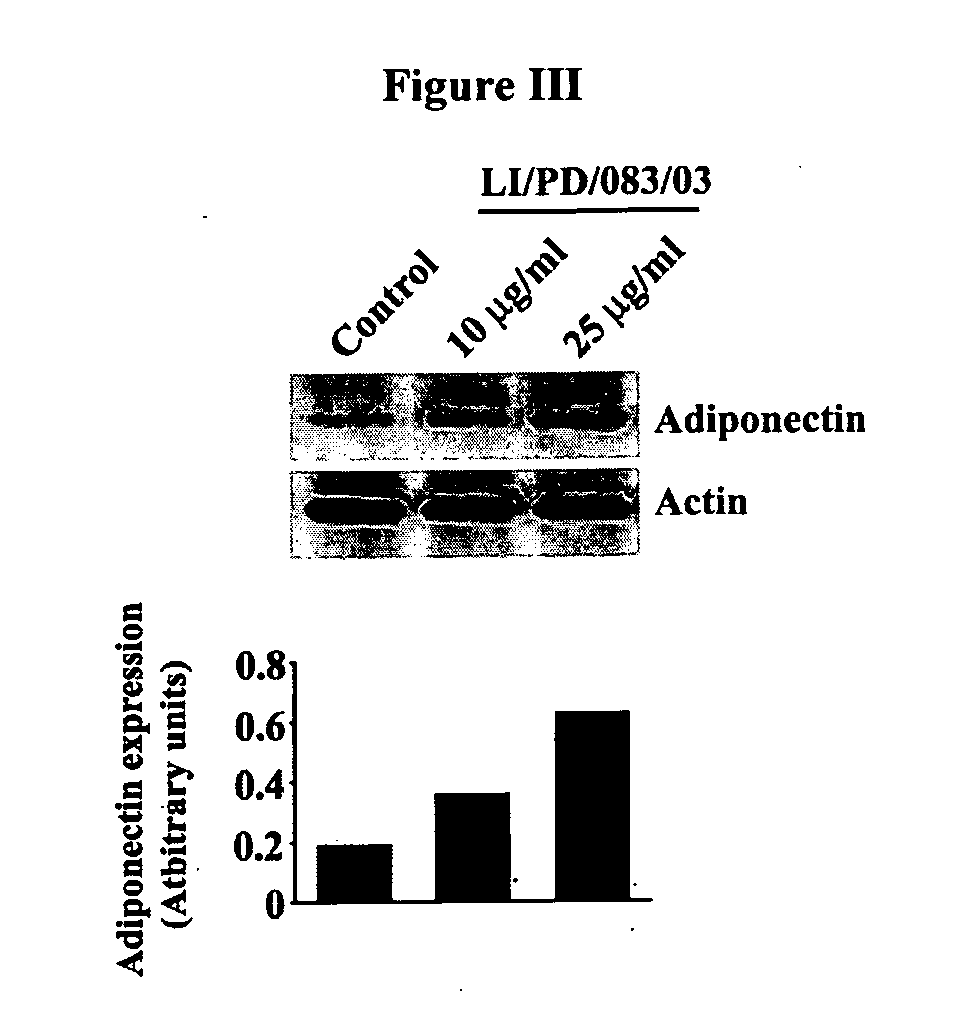
Patents
Literature
91 results about "CD36" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
CD36 (cluster of differentiation 36), also known as platelet glycoprotein 4, fatty acid translocase (FAT), scavenger receptor class B member 3 (SCARB3), and glycoproteins 88 (GP88), IIIb (GPIIIB), or IV (GPIV) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CD36 gene. The CD36 antigen is an integral membrane protein found on the surface of many cell types in vertebrate animals. It imports fatty acids inside cells and is a member of the class B scavenger receptor family of cell surface proteins. CD36 binds many ligands including collagen, thrombospondin, erythrocytes parasitized with Plasmodium falciparum, oxidized low density lipoprotein, native lipoproteins, oxidized phospholipids, and long-chain fatty acids.
Immunotherapeutic methods for extracorporeal modulation of CD36 and its ligands
InactiveUS20020086276A1Easy to identifyCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsOther blood circulation devicesImmunotherapyCD36
The present invention relates to methods for modulating an immune response in a patient by modulating the circulating levels of CD36 ligands. In particular, an extracorporeal apheresis method is described which can be used to modulate the levels of CD36 ligands in the bloodstream of a patient in need of immunotherapy.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT HEALTH CENT
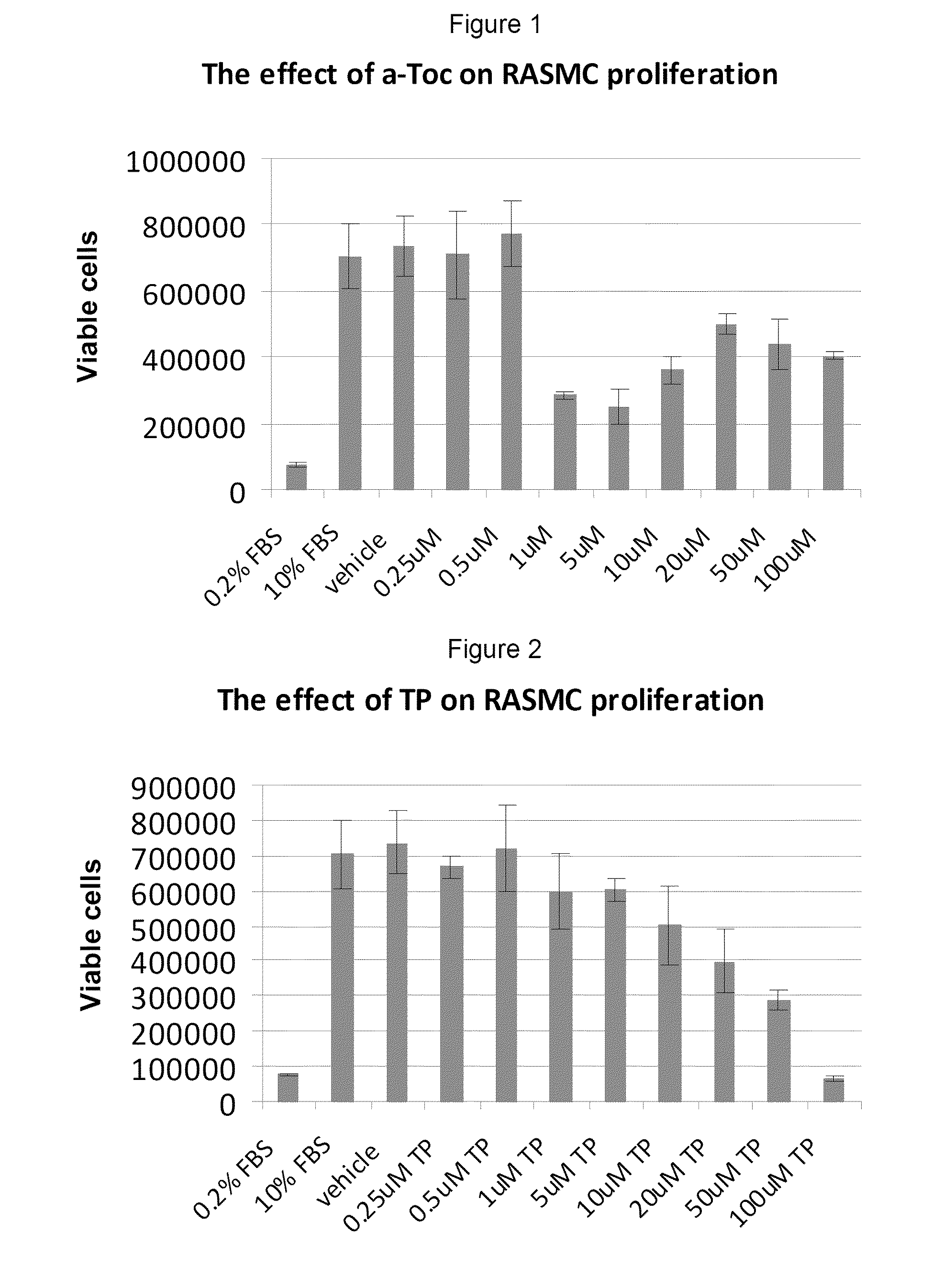
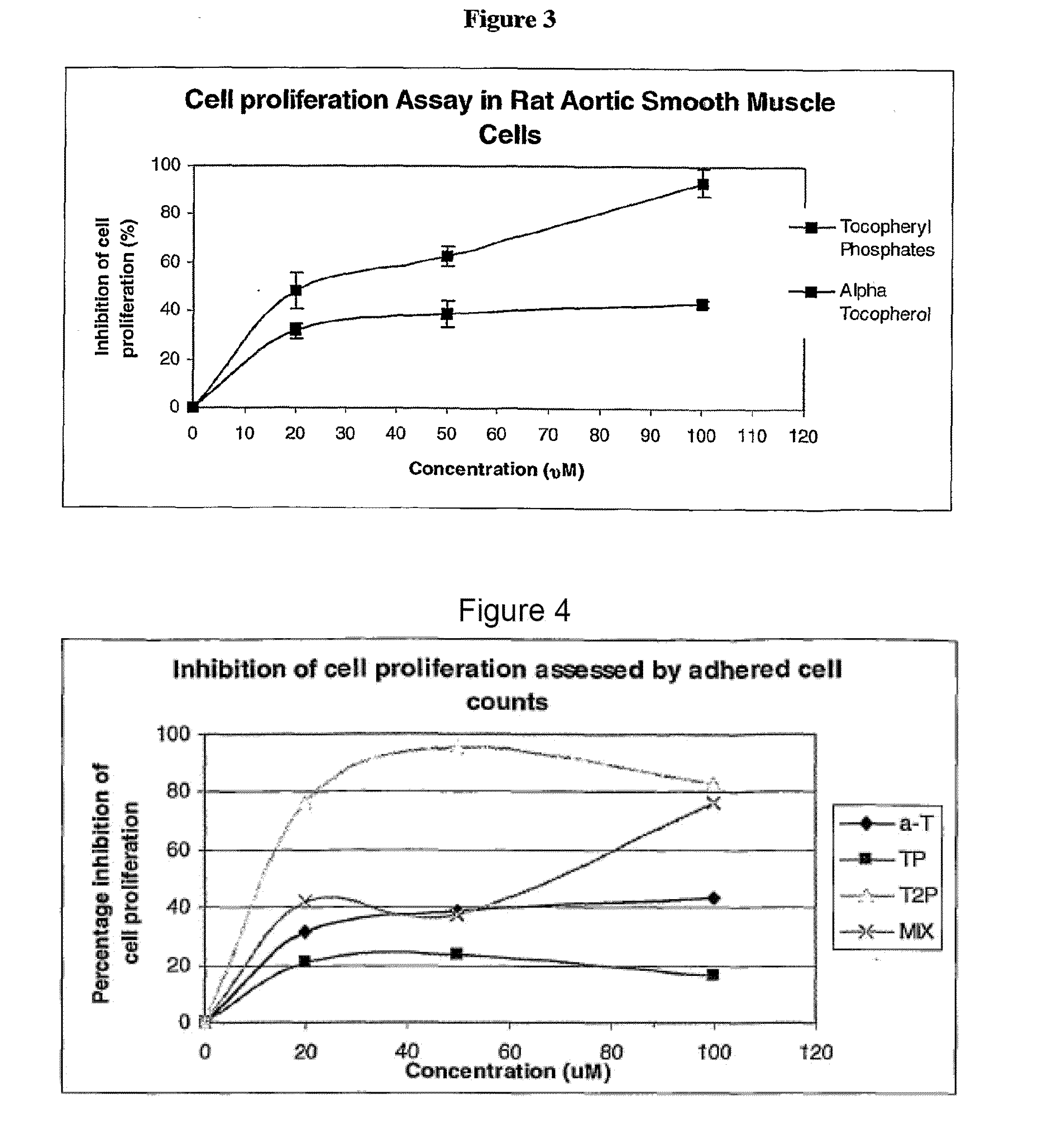
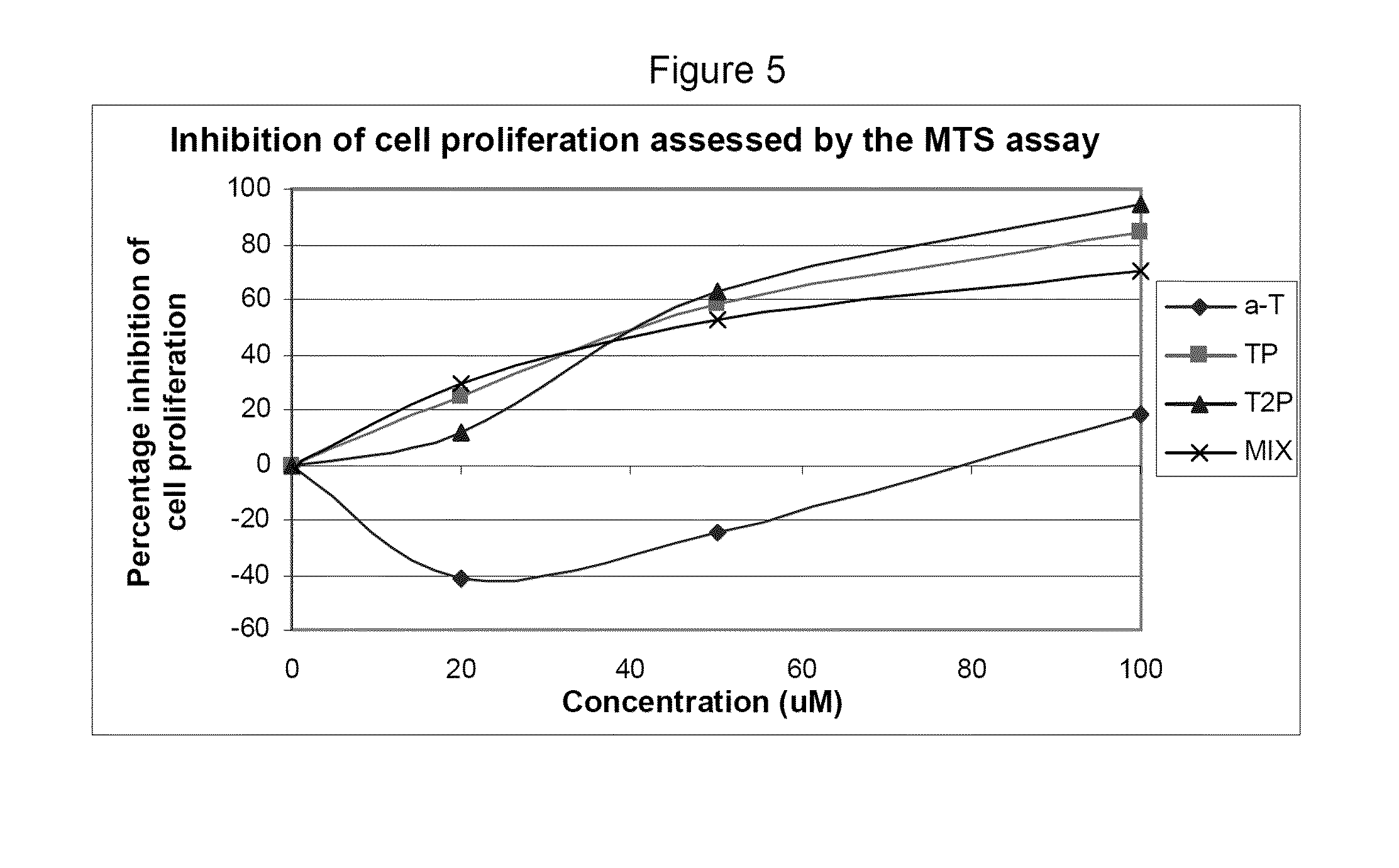
Compounds having Anti-proliferative properties
InactiveUS20110003774A1Scavenger cell expression or oxidised LDL uptake may be reduced or restrainedBiocideOrganic active ingredientsSmooth muscleMonocyte
Owner:VITAL HEALTH SCIENCES PTY LTD
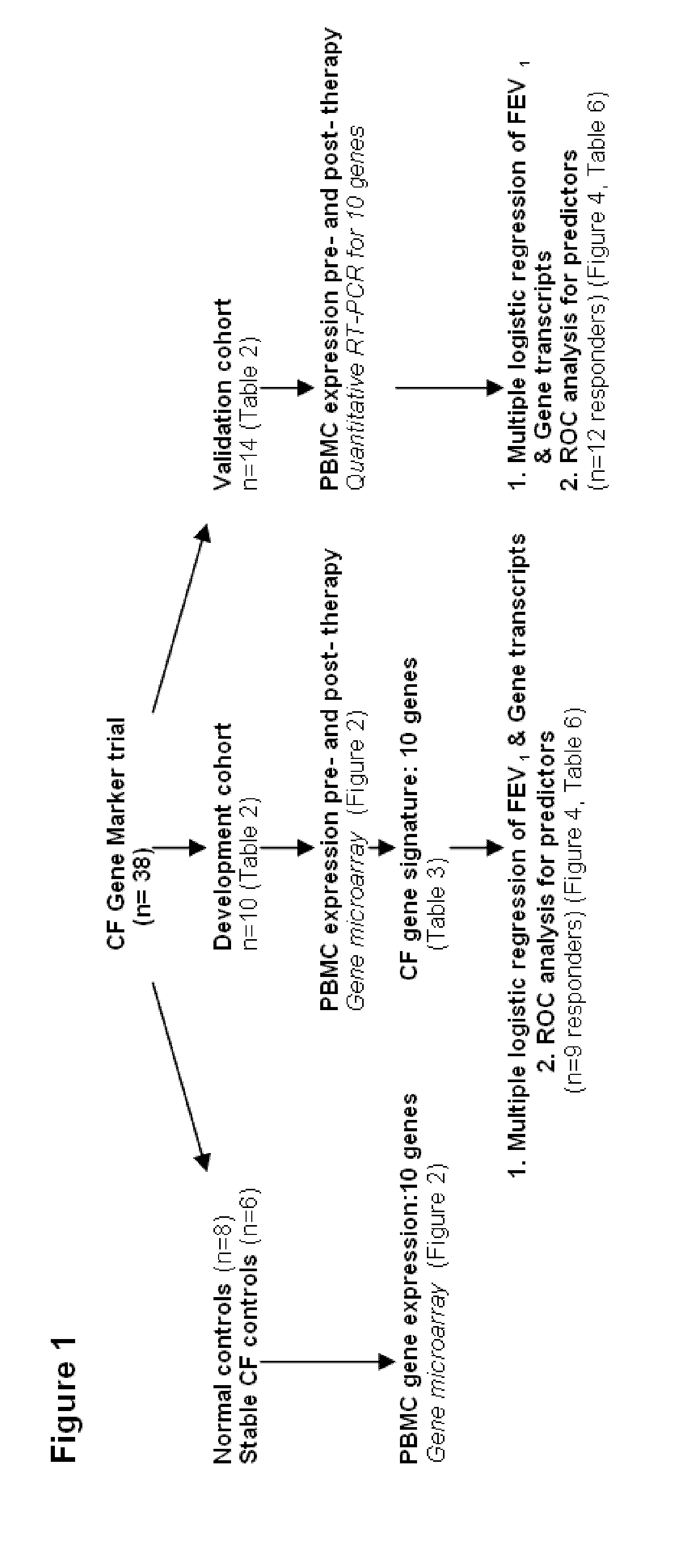
Markers for diagnosis of pulmonary inflammation and methods related thereto
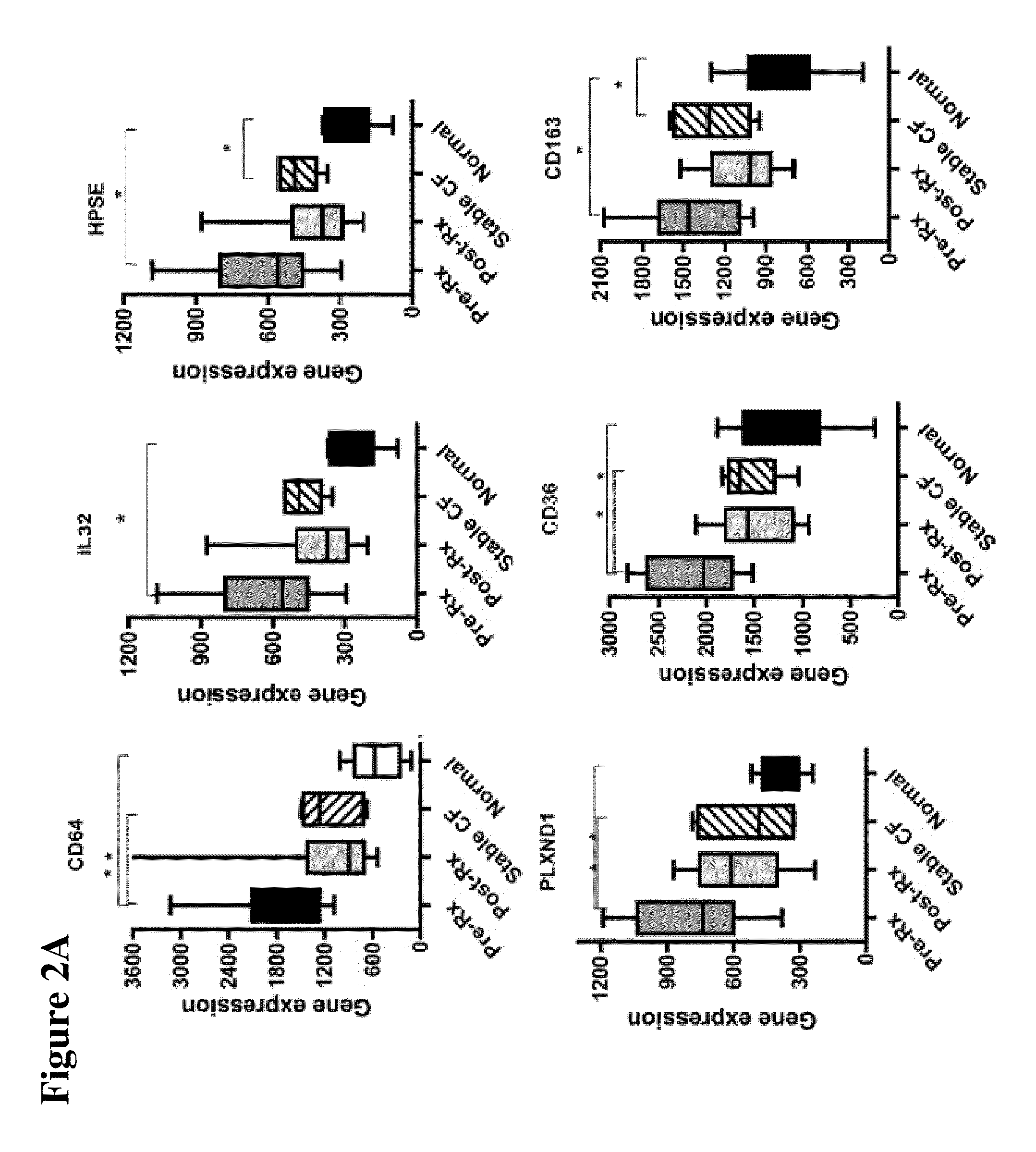
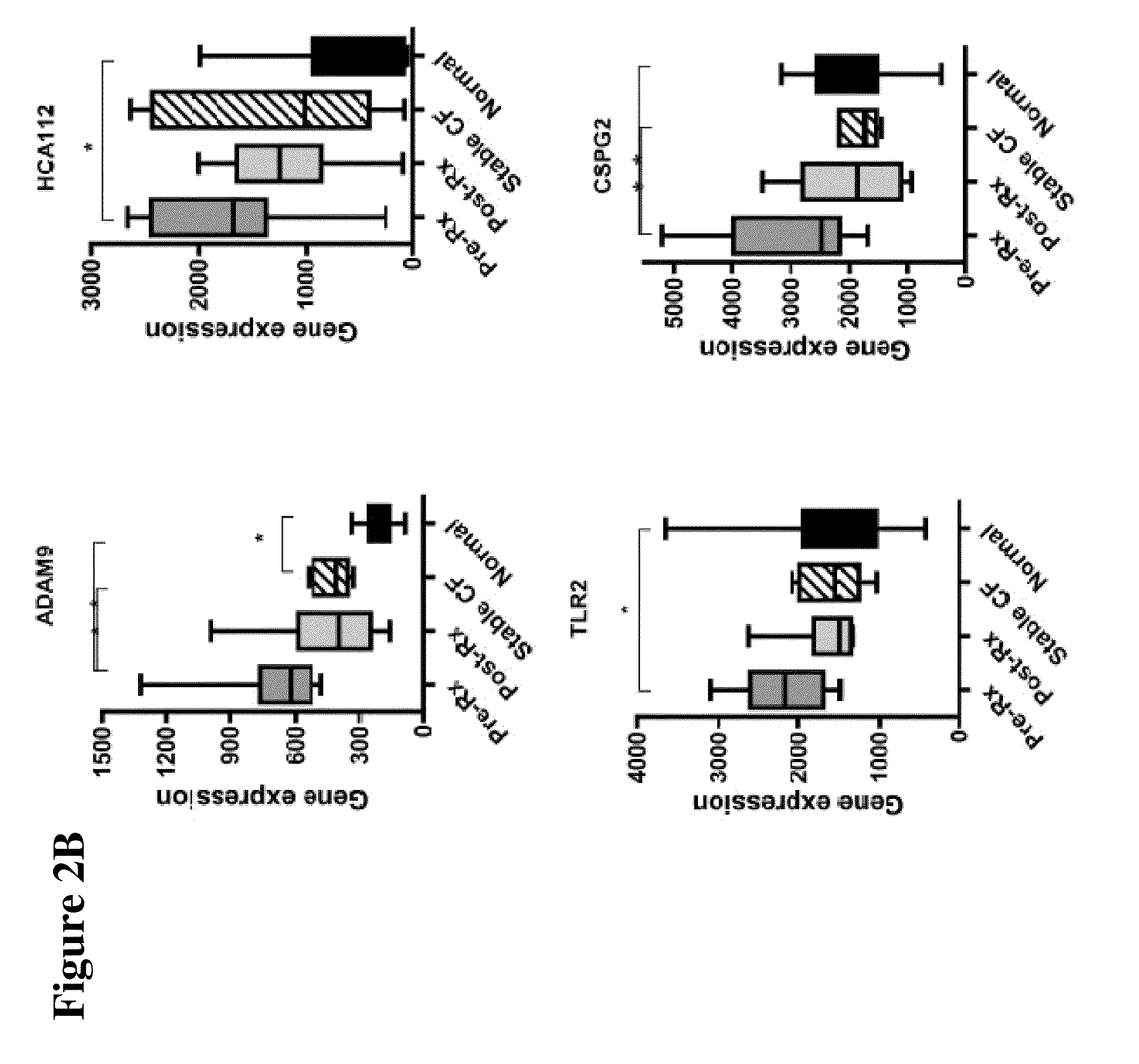
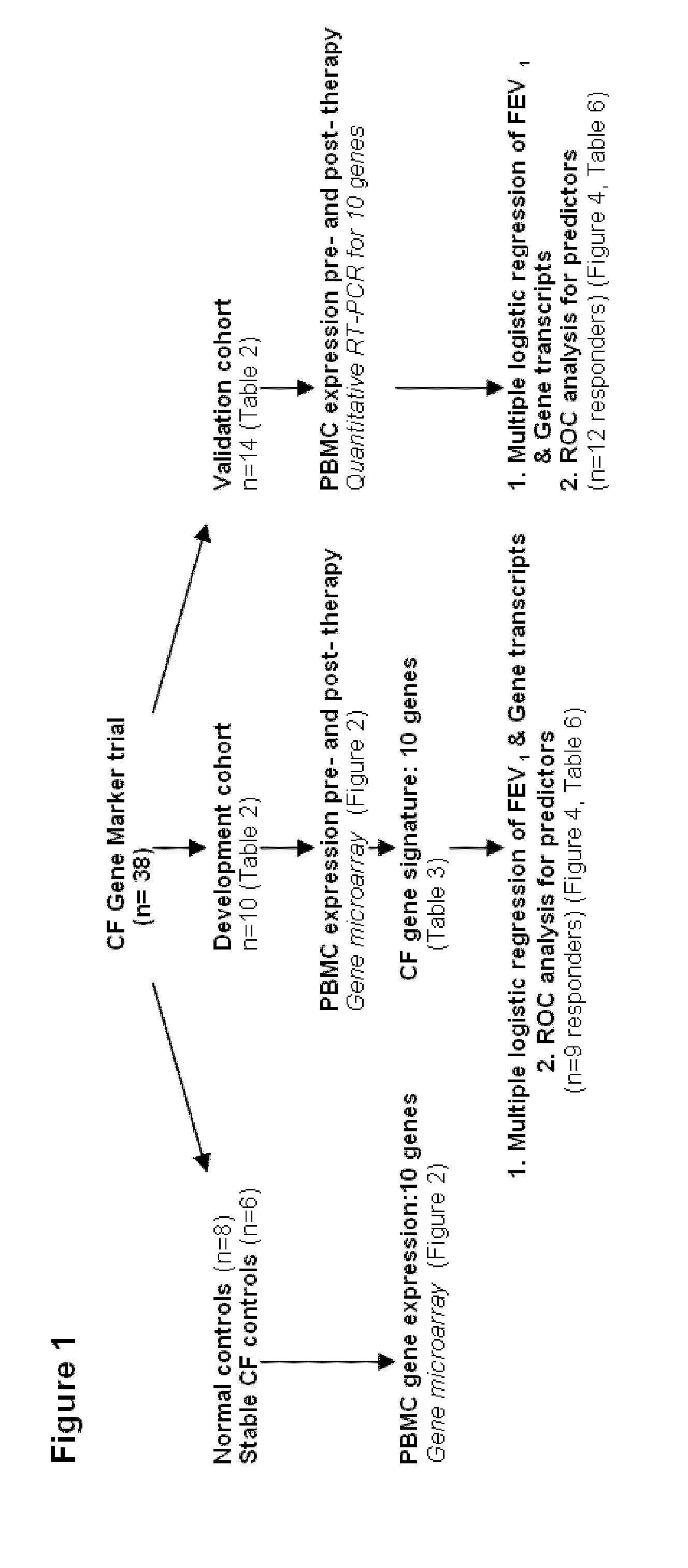
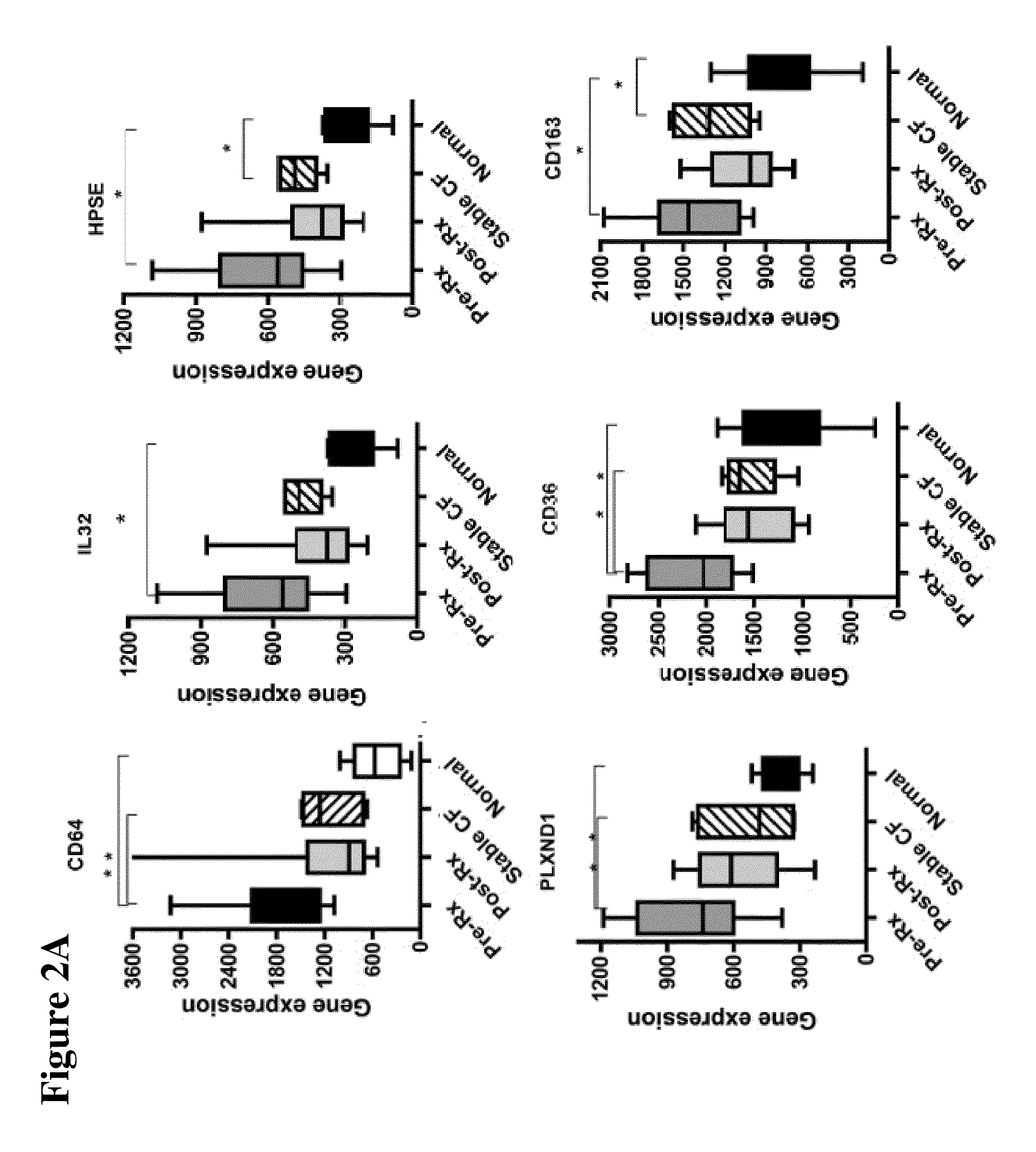
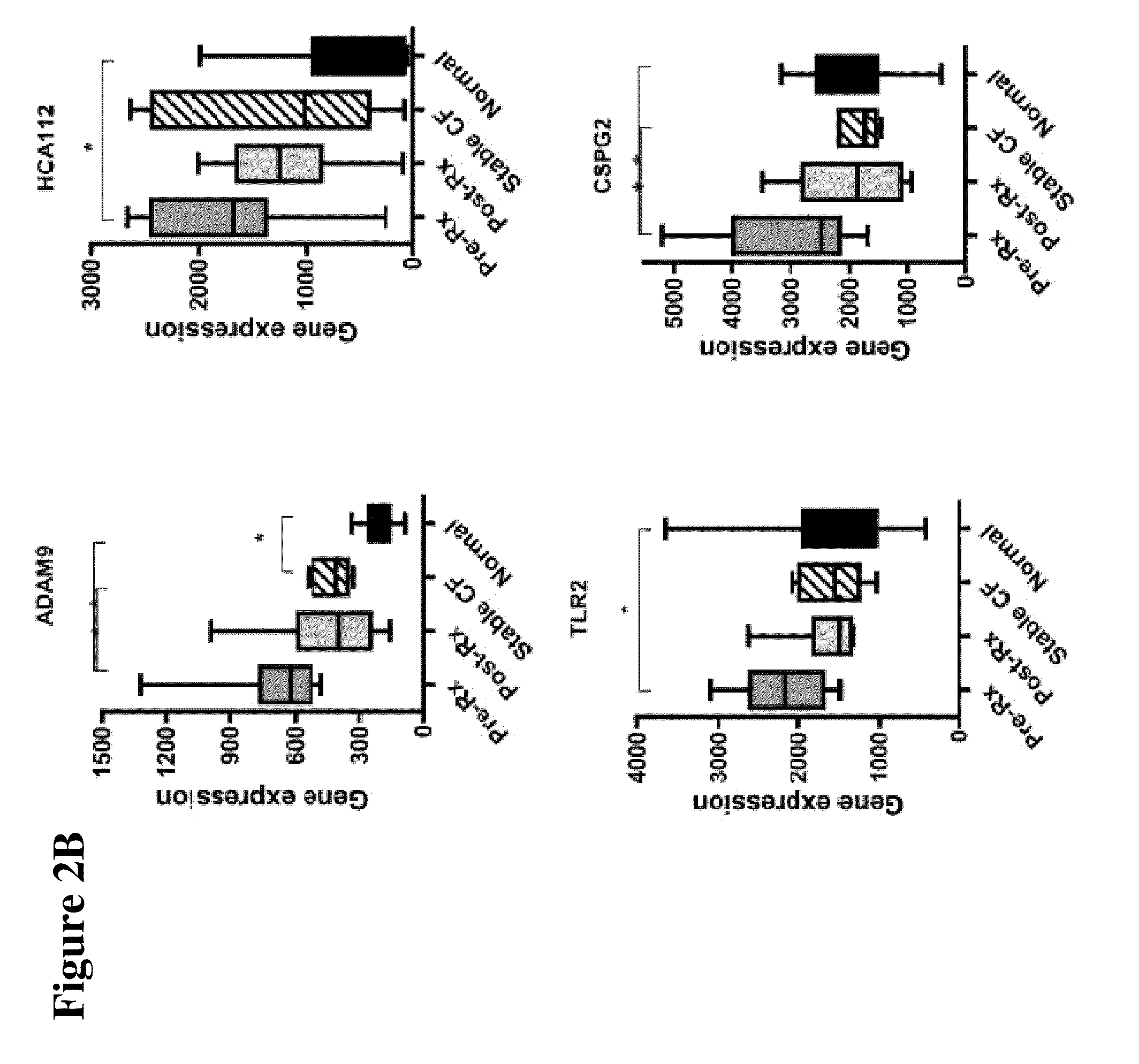
The present invention is related to the novel discovery of a number of genes that were identified as systemic markers of pulmonary inflammation. This discovery allows for development of a novel tool for reliable, rapid and efficient assessment of therapeutic responses and enables design of novel therapies targeted against diseases associated with pulmonary inflammation. In one embodiment, the present invention allows quantification of therapeutic response in patients who have a disease associated with pulmonary inflammation. In preferred embodiments, the genes are CD64, ADAM9, CD36, IL32, HPSE, PLXND1, HCA112, CSPG2, TLR2, and CD163.
Owner:NAT JEWISH HEALTH
Markers for Diagnosis of Pulmonary Inflammation and Methods Related Thereto
The present invention is related to the novel discovery of a number of genes that were identified as systemic markers of pulmonary inflammation. This discovery allows for development of a novel tool for reliable, rapid and efficient assessment of therapeutic responses and enables design of novel therapies targeted against diseases associated with pulmonary inflammation. In one embodiment, the present invention allows quantification of therapeutic response in patients who have a disease associated with pulmonary inflammation. In preferred embodiments, the genes are CD64, ADAM9, CD36, IL32, HPSE, PLXND1, HCA112, CSPG2, TLR2, and CD163.
Owner:NAT JEWISH HEALTH
System for screening fatty acid transport inhibitors, methods of use and modulators identified thereby
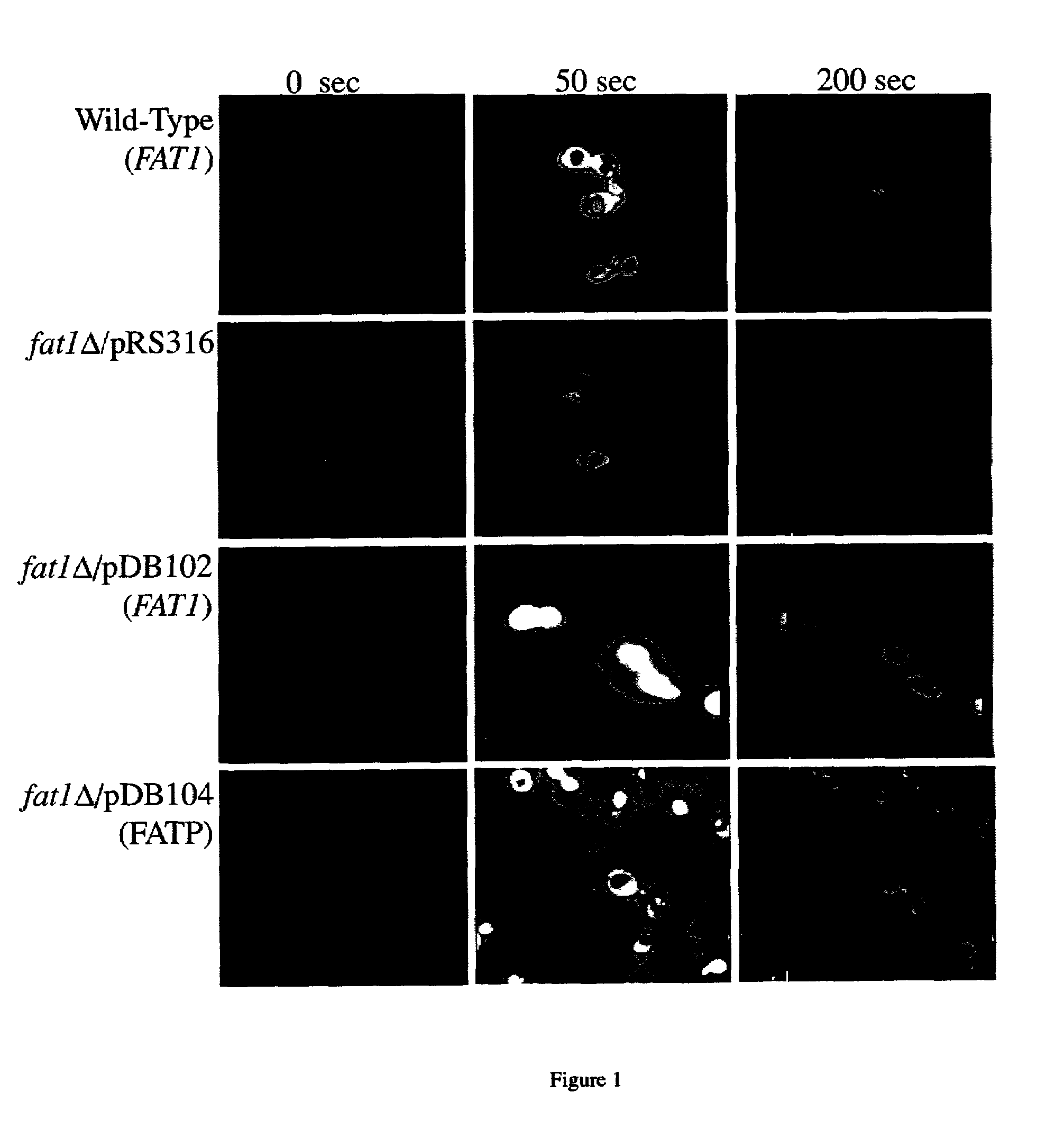
Methods for identifying modulators of fatty acid transport and / or uptake, comprising contacting, under conditions favorable for fatty acid uptake, a putative modulator, e.g., an inhibitor with a system comprising genetic material encoding a fatty acid transport mediator (“TTM”), particularly FAA1, FAA2, FAA3, FAA4, FAT1, fadL, fadD, FATP, CD36 and FABP, or orthologs, homologs, isoforms, variants, analogs, derivatives or fragments thereof, and combinations thereof, or fatty acid transport mediator proteins (“TTMps”), e.g., Faa1p, Faa2p, Faa3p, Faa4p, Fat1p, FadL, fatty acyl CoA synthetase, FATP, CD36 and FABP, or orthologs, homologs, isoforms, variants, analogs, derivatives or fragments thereof, and combinations thereof, and determining the effect of the putative modulator. The test system may be a cell such as Saccharomyces cerevisiae, E. coli, H. sapiens, etc. or an in vitro system.
Owner:ALBANY MEDICAL COLLEGE
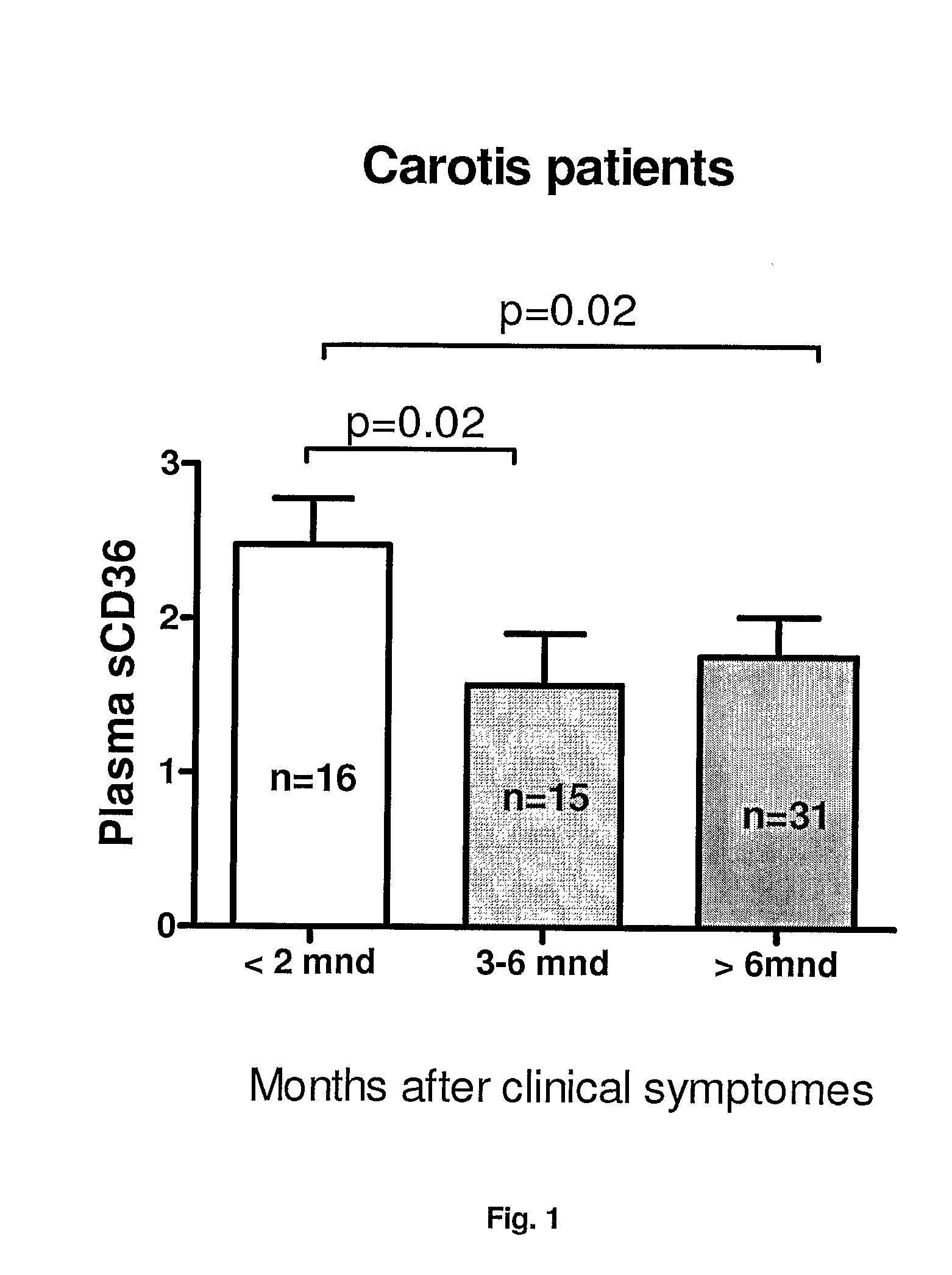
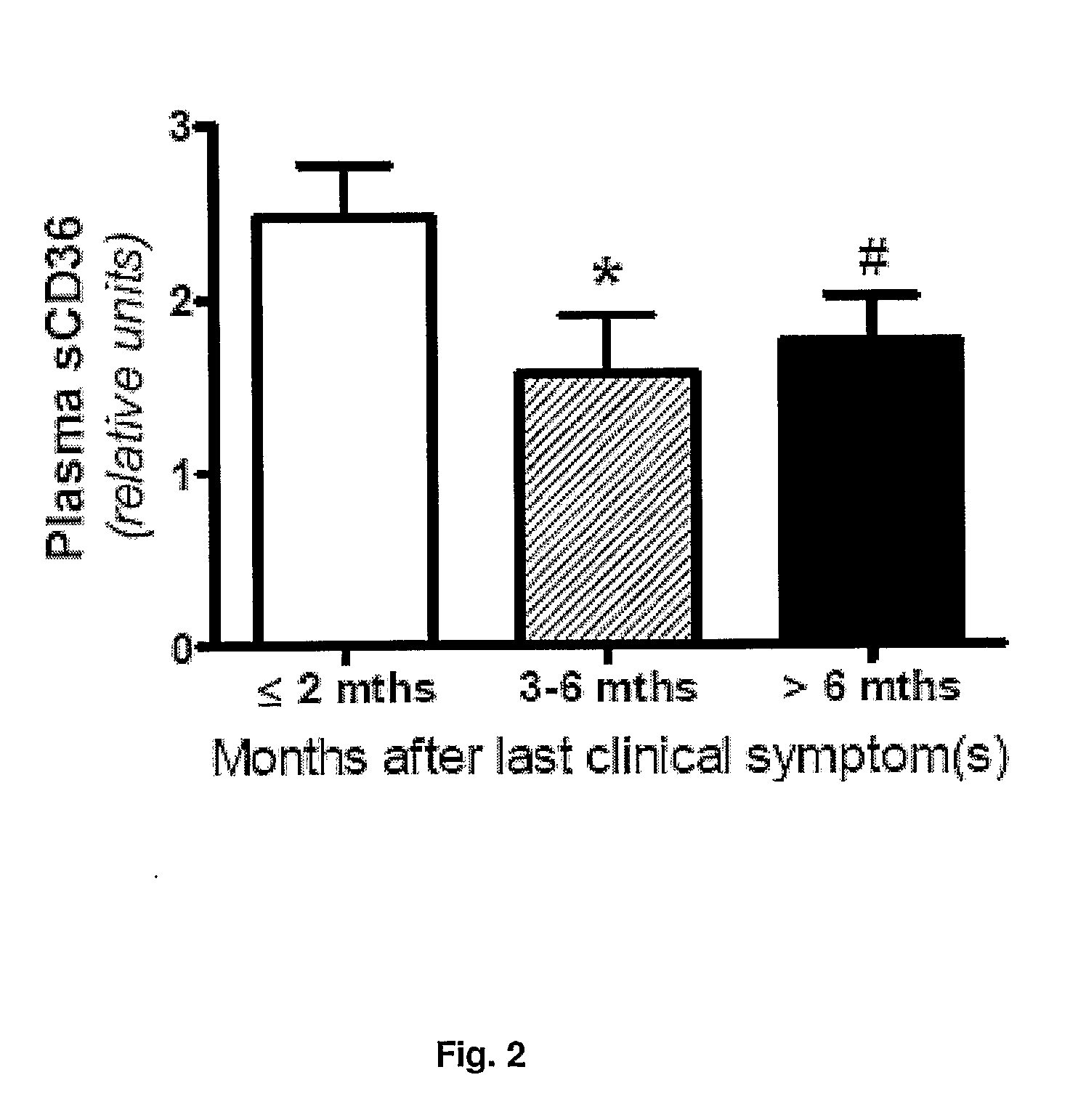
Method for diagnosing atherosclerotic plaques by measurement of cd36
InactiveUS20100105088A1High riskSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementBody fluidTubular stenosis
The present invention relates to diagnosis, classification and monitoring of atherosclerotic plaques in an individual using measurement of the concentration of CD36 in a body fluid and / or the plaque as such. The present invention also relates to diagnosing the burden of atherosclerotic plaques in an individual. Furthermore, the invention relates to a method for diagnosing stenosis caused by atherosclerotic plaques. Within the scope of the present invention are also methods for determining the treatment regime of an individual. Kits and oligonucleotides for use in the methods are claimed.
Owner:HANDBERG AASE
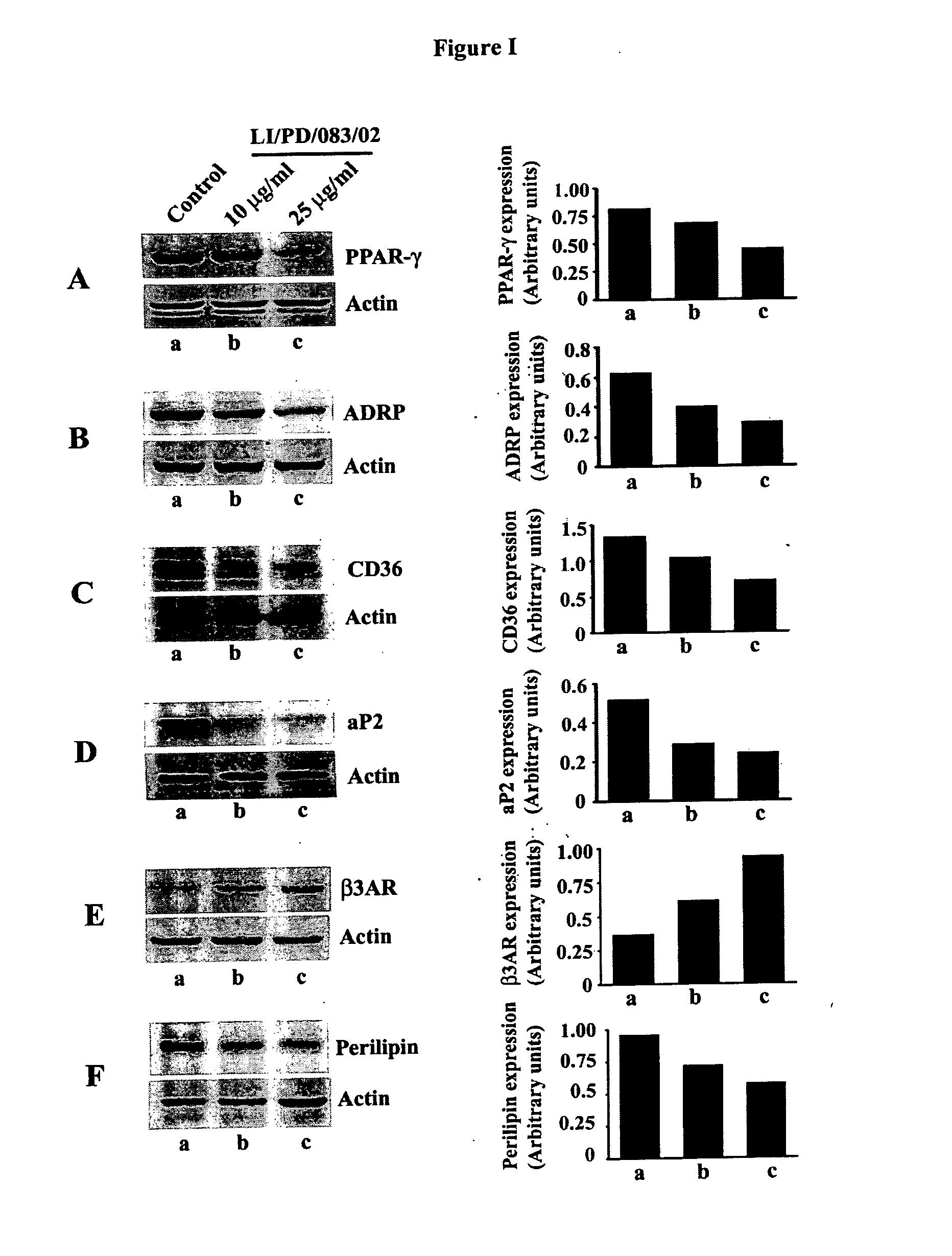
Agents derived from holoptelea integrifolia and their compositions for the control of metabolic syndrome and associated diseases
ActiveUS20120231095A1BiocideHydroxy compound active ingredientsDiseaseAdipose Differentiation-Related Protein
The invention discloses phytochemical agents derived from Holoptelea integrifolia and novel composition(s) comprising at least one component selected from the extract(s), fraction(s) and active compound(s) for the protection and alleviation of Metabolic Syndrome, insulin resistance, endothelial dysfunction, chronic kidney disease, atherosclerosis, diabetes and other disease conditions associated with metabolic syndrome. The invention also discloses the amelioration of certain biomarker molecules such as Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR-γ), Adipose Differentiation Related Protein (ADRP), CD36, Adipocyte Fatty-acid-Binding Protein (aP2 / FABP-4 / A-FABP), beta-3 Adrenergic Receptor (β3AR), Leptin, Perilipin and Adiponectin by using the phytochemical components derived from Holoptelea integrifolia.
Owner:LAILA NUTRACEUTICALS
siRNA drug carrier polymer, preparation method thereof and application in targeted siRNA delivery
ActiveCN106890336AIncreased chance of targetingImprove targetingOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsInflammatory factorsSingle-Chain Antibodies
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Targeting metastasis stem cells through a fatty acid receptor (CD36)
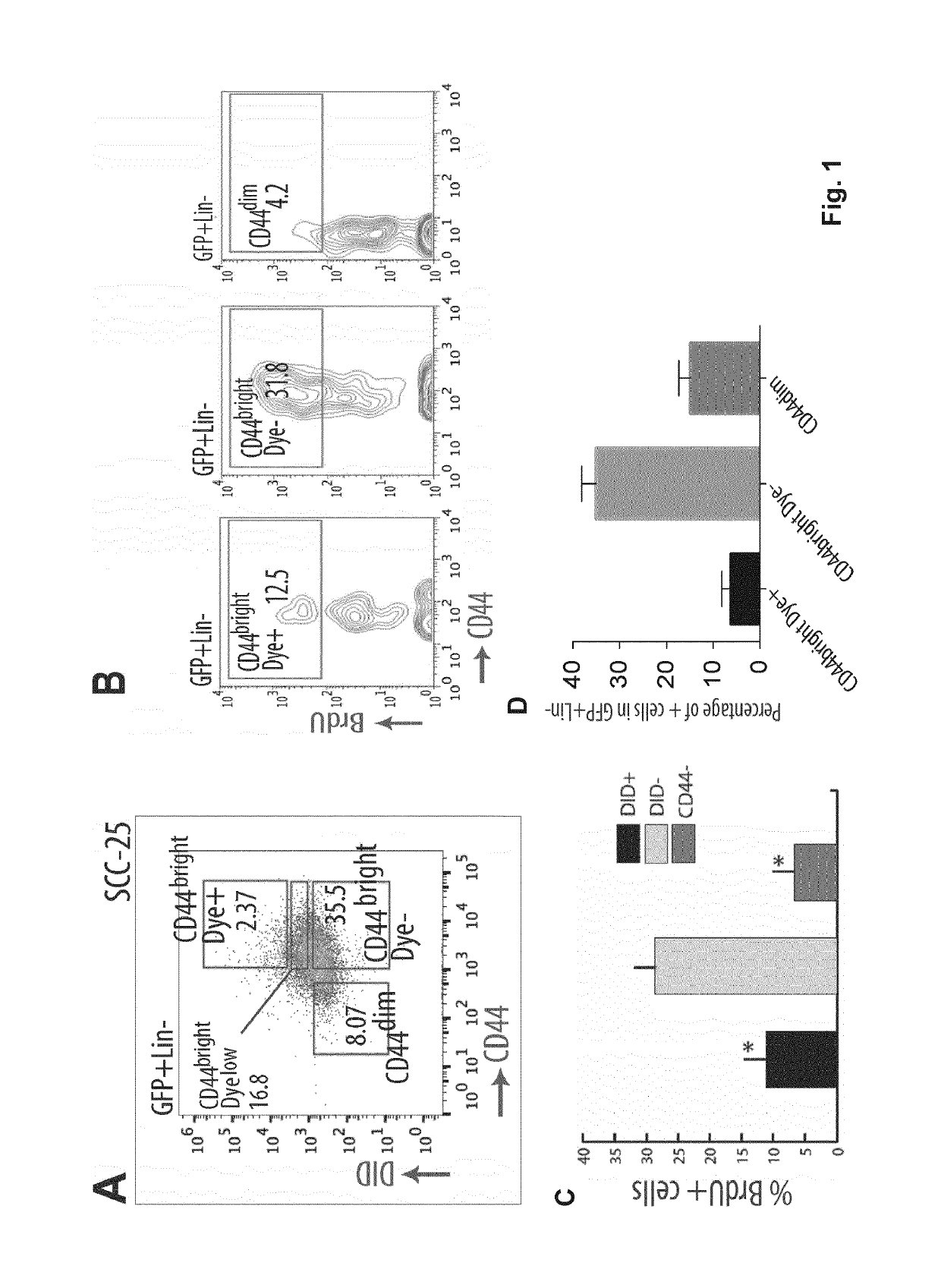
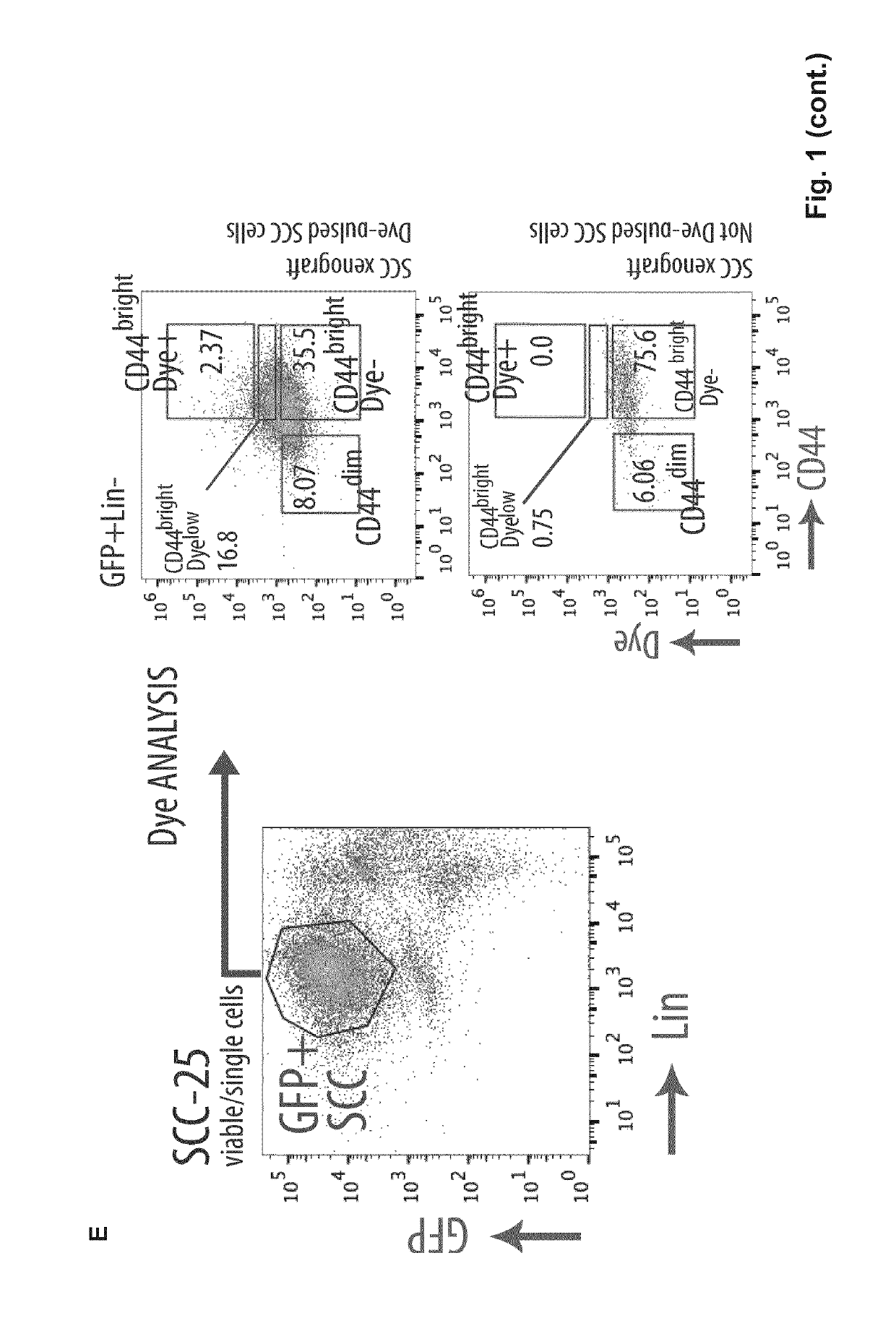
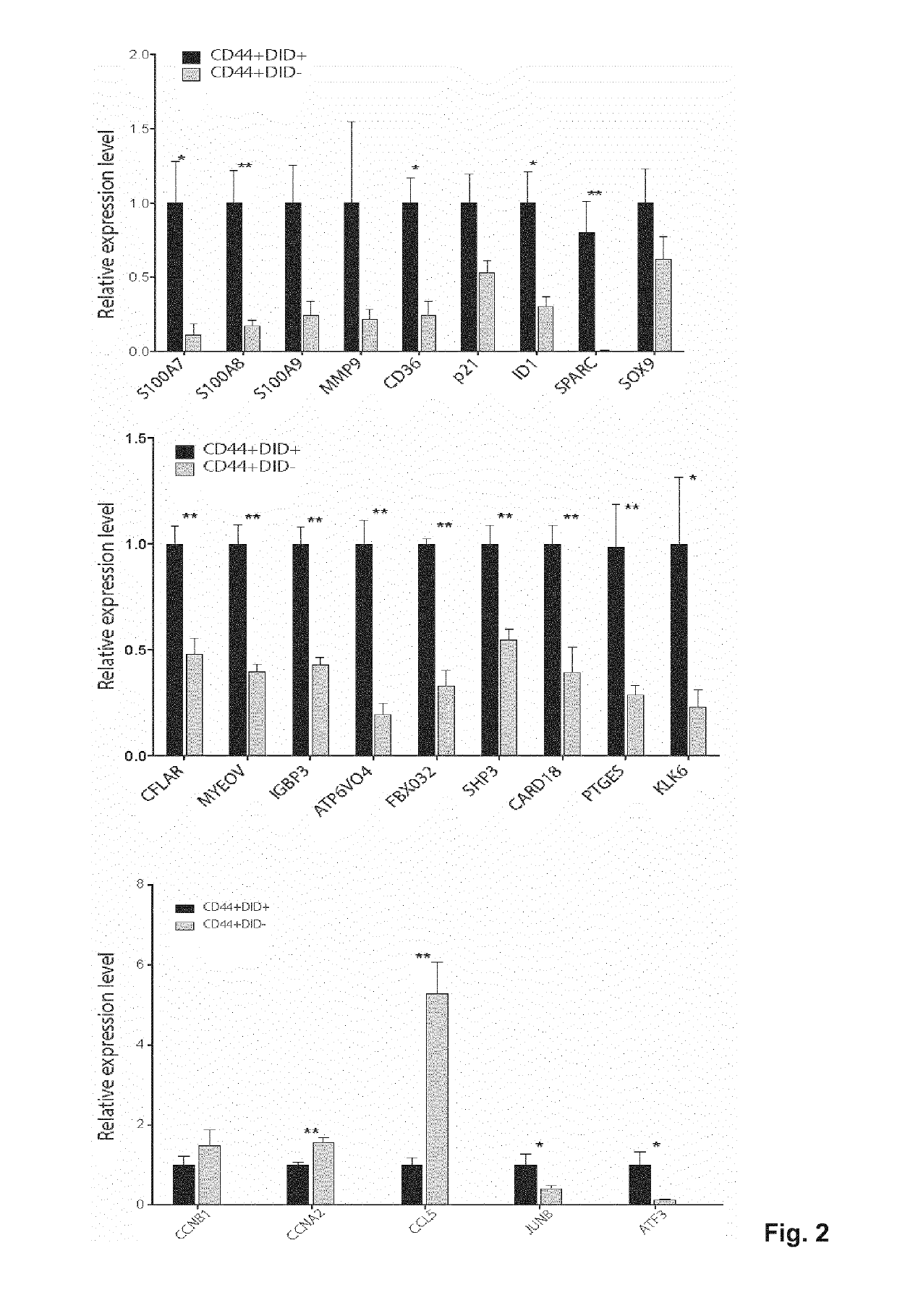
ActiveUS20190106503A1Diminish of metastasis growthPromote growthCompound screeningApoptosis detectionLipid formationLymphatic Spread
Metastasis stem cells are targeted through a fatty acid receptor. Blockers or inhibitors of CD36 activity or expression are for the treatment of oral squamous cell cancer (OSCC), particularly for the treatment of generated metastases and for diminishing generation from primary tumors. Apart from shRNAs, anti-CD36 antibodies are provided as blockers or inhibitors, especially those that block the binding of CD36 to oxidized LDL and fatty acids and their incorporation into cells, because the promotion of their transport is indicated as the mechanism by which CD36 promote metastases dissemination and growth. A method identifies candidates to anticancer agents, particularly for OSCC metastasis, among those that promote in CD36+ cells, in vivo or in vitro, effects associated to CD36 depletion or blocking such as decrease of growth accumulation of lipid droplets and decrease of size in the case of metastases.
Owner:FUNDACIO INST DE RECERCA BIOMEDICA (IRB BARCELONA) +1
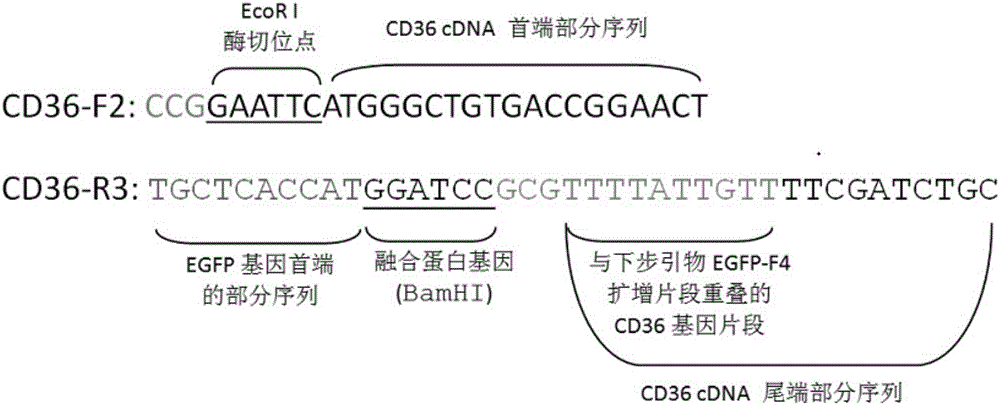
Establishing method of CD36 mutant gene stable eukaryotic expression cell line causing CD36 deletion
InactiveCN106434564AHigh-quality work platformEnsure safetyImmunoglobulin superfamilyMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliDisease
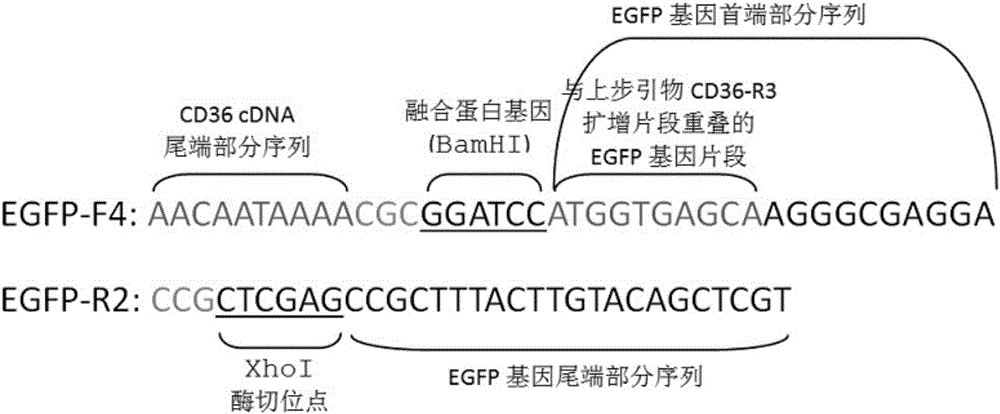
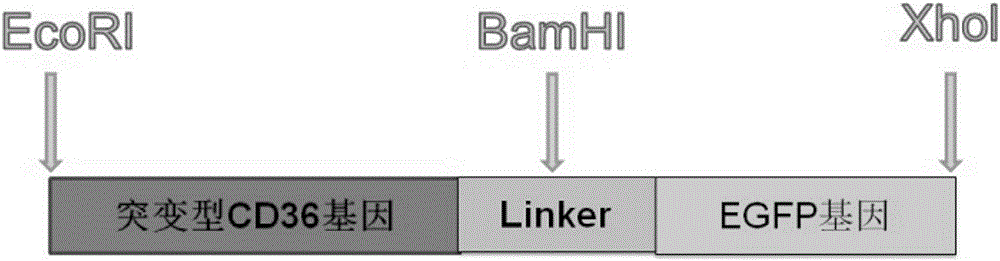
The invention provides an establishing method of a CD36 mutant gene stable eukaryotic expression cell line causing CD36 deletion. The method comprises a while process of extracting total RNA from a CD36 deletion individual and conducting reverse transcription so as to obtain CD36 cDNA of whole segment of a CD36 mutant gene open reading frame; establishing a recombinant cloning vector containing the CD36 mutant gene cDNA and an EGFP fluorescent reporter gene, transforming the recombinant cloning vector into escherichia coli, and conducting plasmid amplification and identification; and transfecting the recombinant cloning vector into CHO-K1 cells, and conducting screening and identification so as to obtain the CD36 mutant gene stable eukaryotic expression cell line. The CD36 is distributed in a plurality of cells and tissues, and CD36 encoding gene mutation can cause the CD36 deletion in the individual. The CD36 takes an important effect in various physiological and pathological processes, involving such diseases as platelet homologous immunization, hypercholesteremia, diabetes, malaria and the like. With the application, the CD36 mutant gene stable eukaryotic expression cell line, which is established by virtue of the technology, can provide a resource and a working platform for researching the structure and the functions of the CD36, explaining physiological and pathological mechanisms which the CD36 participate in and discussing a role in clinical treatment and drug research and development.
Owner:NAN NING INST OF TRANSFUSION MEDICINE +1
Coronary disease testing method and reagent kit
The invention discloses a method for detecting atherosclerosis and / or coronary heart disease susceptibility, which includes detecting whether variation exists in individual CD36, transcript and / or albumen in comparison with normal. The existence of variation shows that the possibility that an individual contracts atherosclerosis and / or coronary heart disease is higher than that of a normal person. The invention also discloses a corresponding detection kit.
Owner:CHINESE NAT HUMAN GENOME CENT AT SHANGHAI
CD36 mutant gene and methods for diagnosing diseases caused by abnormal lipid metabolism and diagnostic kits therefor
InactiveUS6306603B1Improve accuracyEfficient developmentCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesFhit geneBiology
The present invention provides CD36 mutant gene and methods and kits for diagnosing diseases caused by a lipid metabolism abnormality.
Owner:WAKUNAGA PHARMA CO LTD
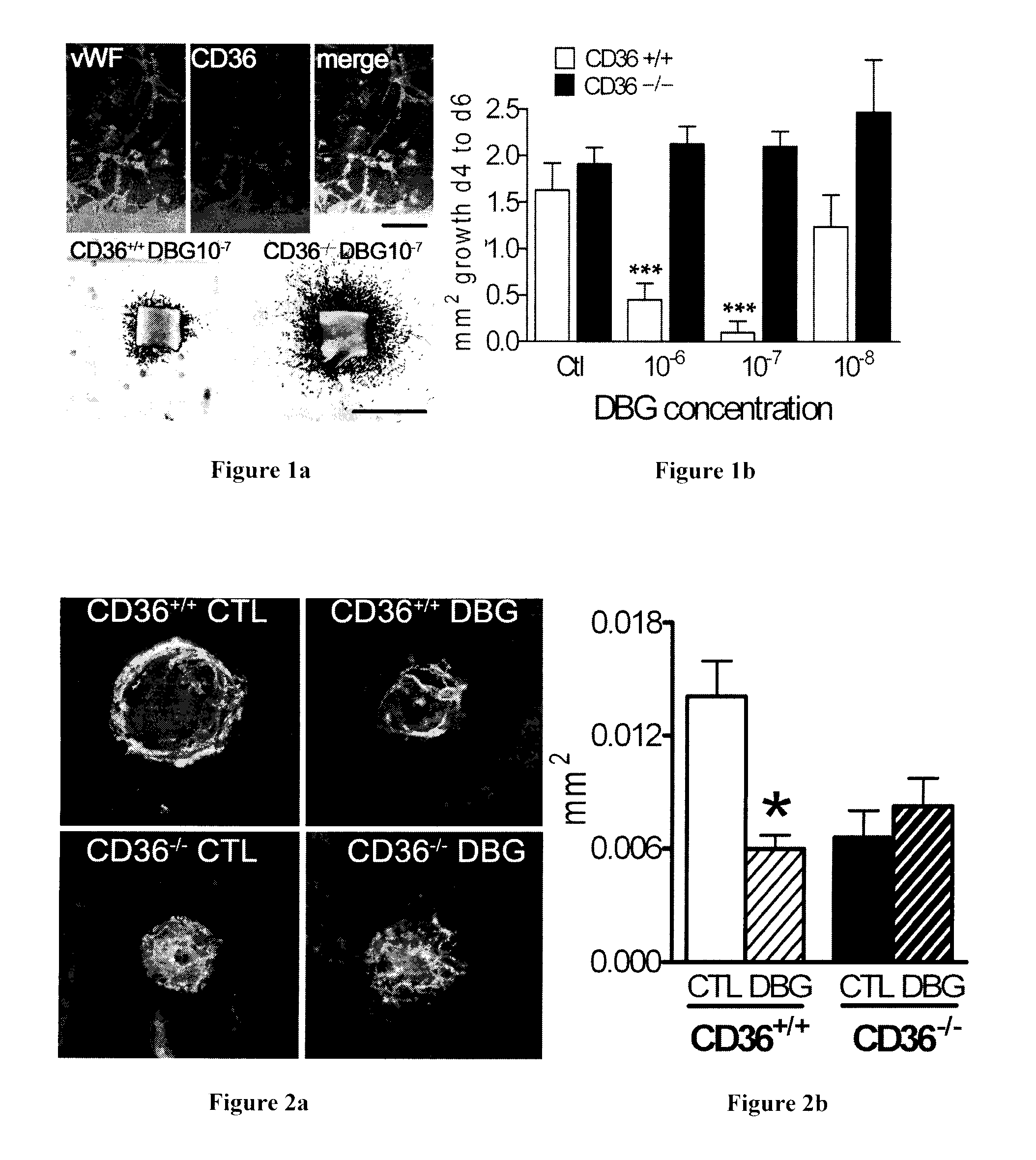
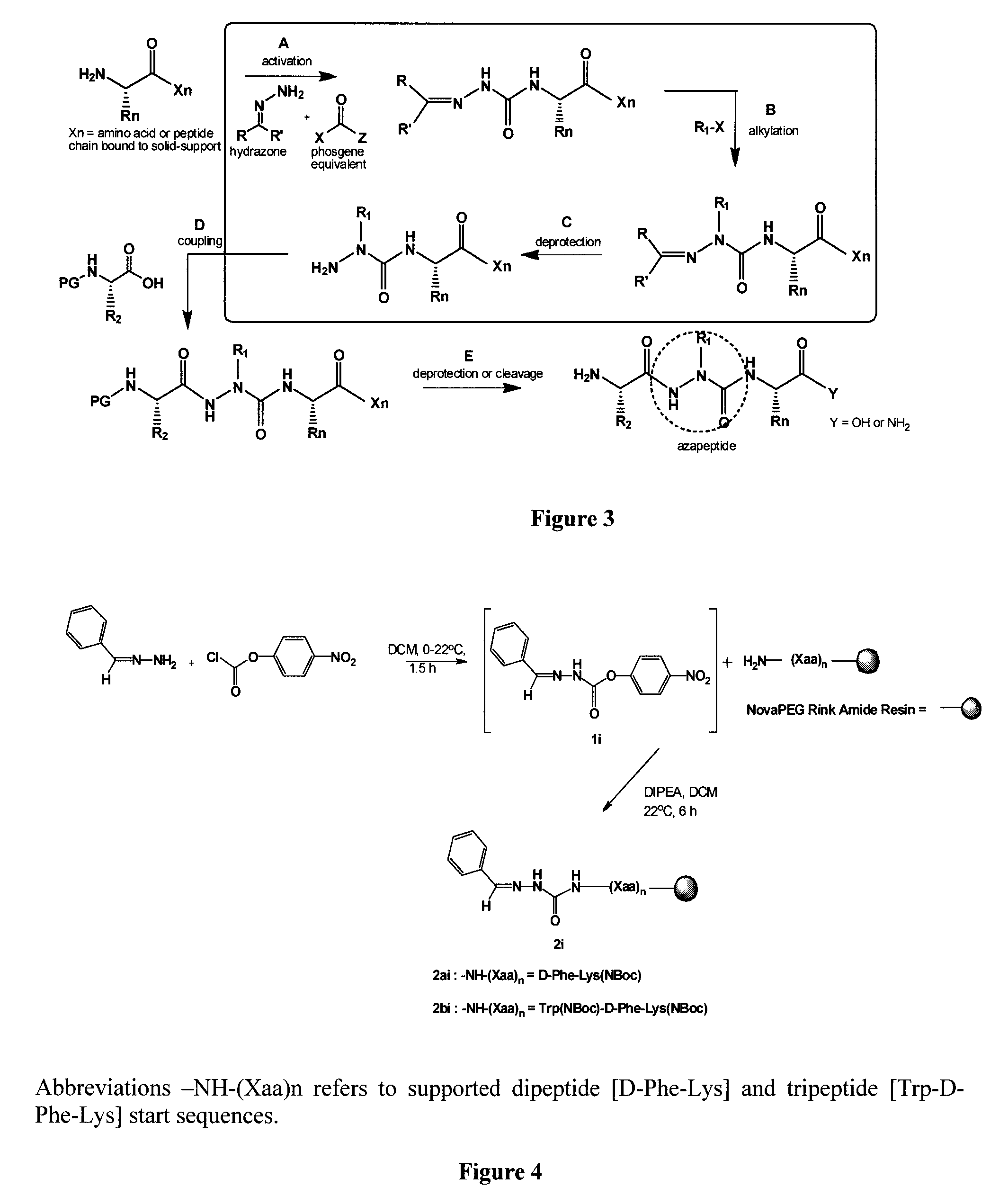
Azapeptides as cd36 binding compounds
ActiveUS20100210566A1Avoid developmentSenses disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsNitrogenGrowth hormone-releasing peptide
An azapeptide derivative of growth hormone releasing peptide (GHRP) of Formula I: A-(Xaa)a-N(RA)—N(RB)—C(O)-(Xaa′)b-B which binds to CD 36.
Owner:VALORISATION RECH LLP +1
Detection kit for auxiliary diagnosis on diabetes and application method of detection kit
InactiveCN104073556AAvoid pollutionSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementDiabetes mellitusNucleotide
The invention discloses a detection kit for auxiliary diagnosis on diabetes. The detection kit comprises primers for detecting single nucleotide polymorphisms of a NFKBIE gene, a CD36 gene and an ADIPOQ gene, wherein the single nucleotide polymorphisms are respectively rs2233424, rs1194182 and rs266729. According to the invention, polymerase chain reaction (PCR) amplification is performed on sample DNA by using the primers of the detection kit, a melting curve of a PCR amplification product is analyzed by using a fluorogenic quantitative PCR instrument, the melting curve is further compared with a standard melting curve, the Tm value of the PCR amplification product is in comparison, and then a corresponding genetic typing result is obtained. The detection kit can be applied to auxiliary detection and prediction on diabetes of a subject and is simple in detection method, high in detection efficiency and high in pertinence, early prevention of diabetes is promoted, and reference is provided for medicine treatment.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
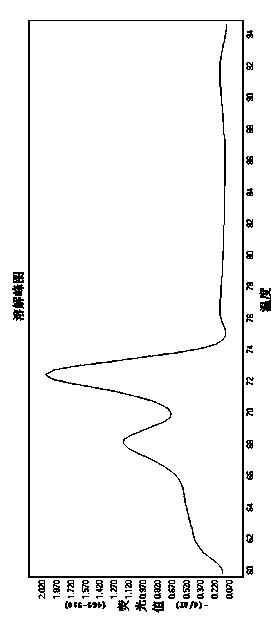
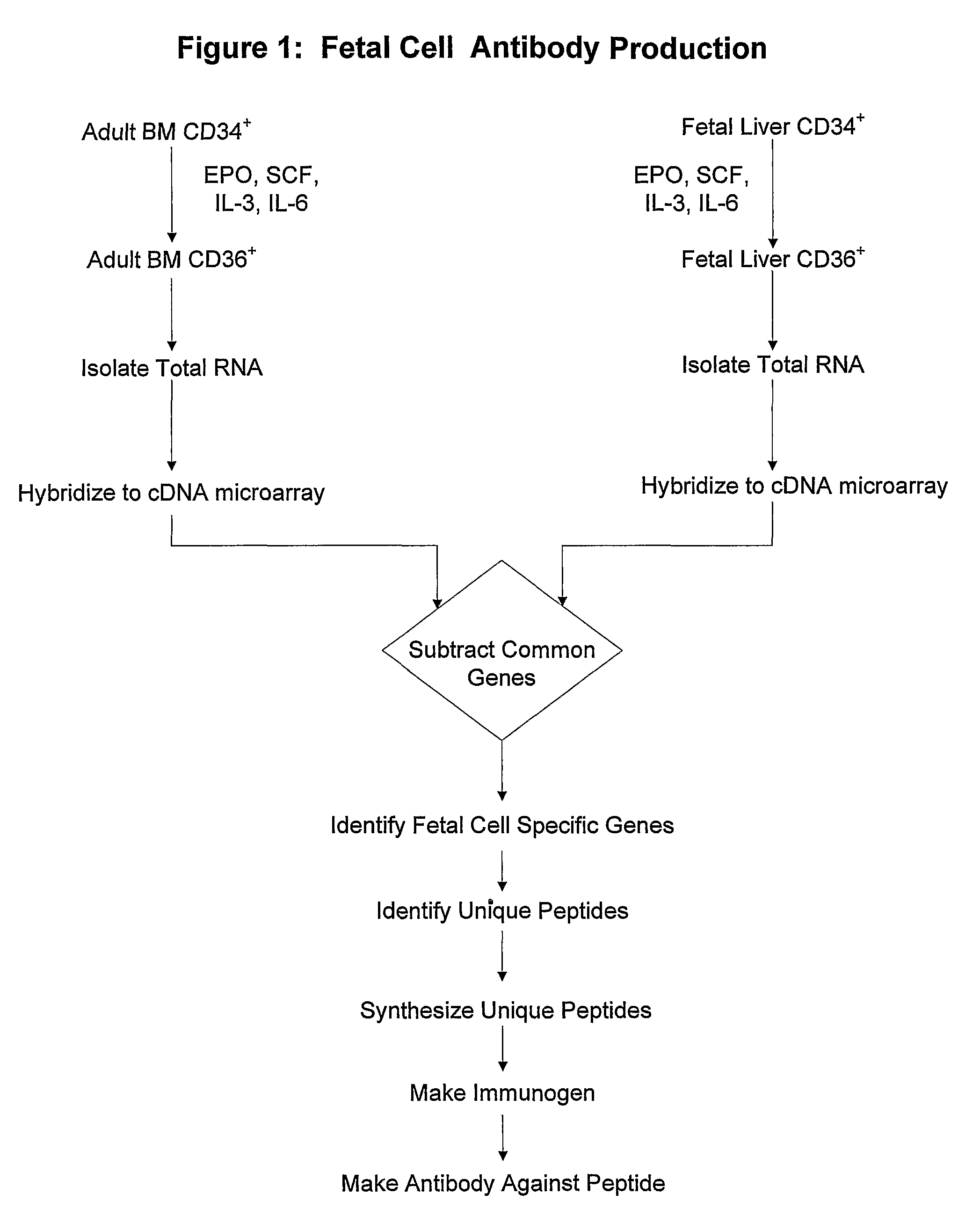
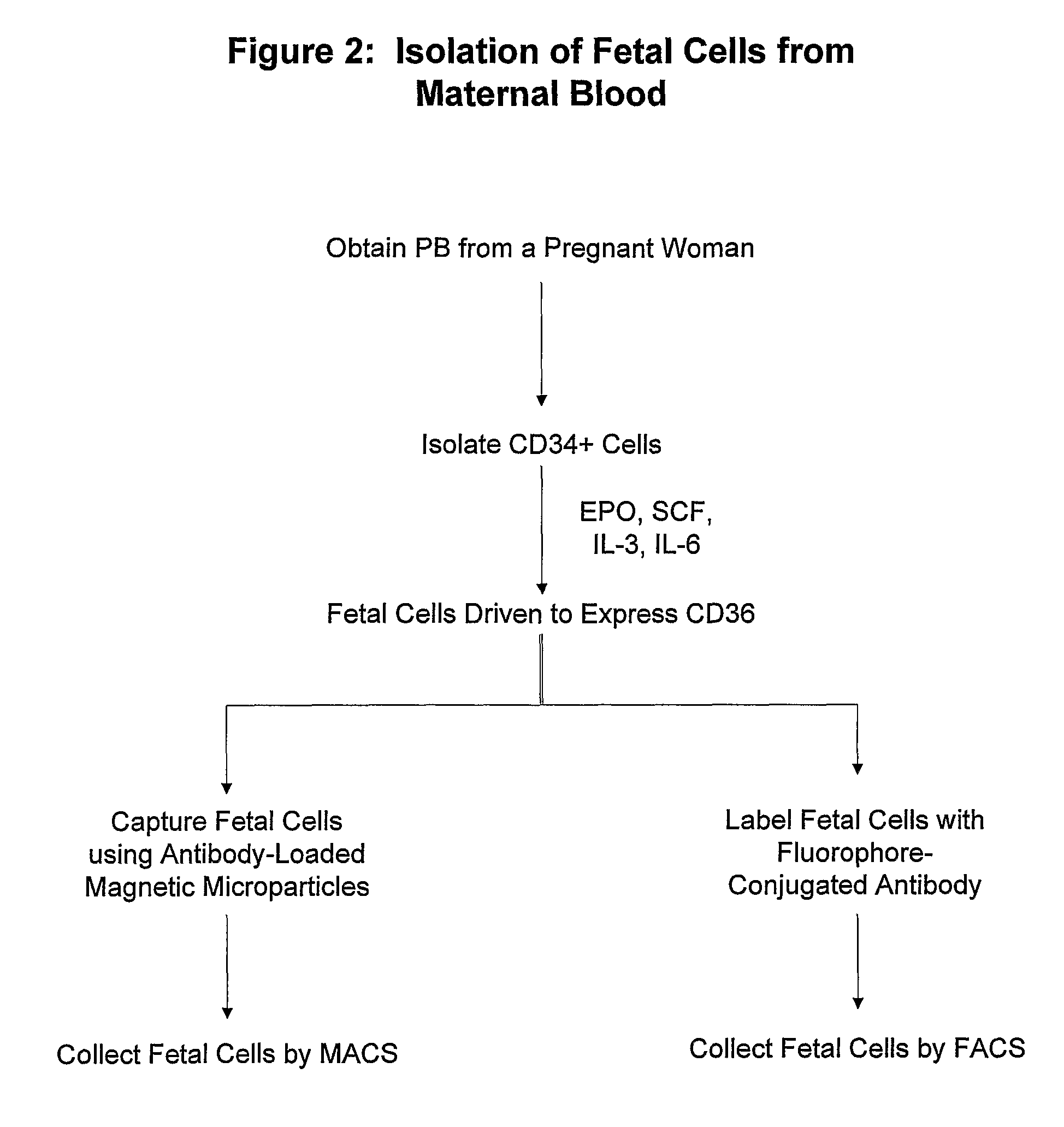
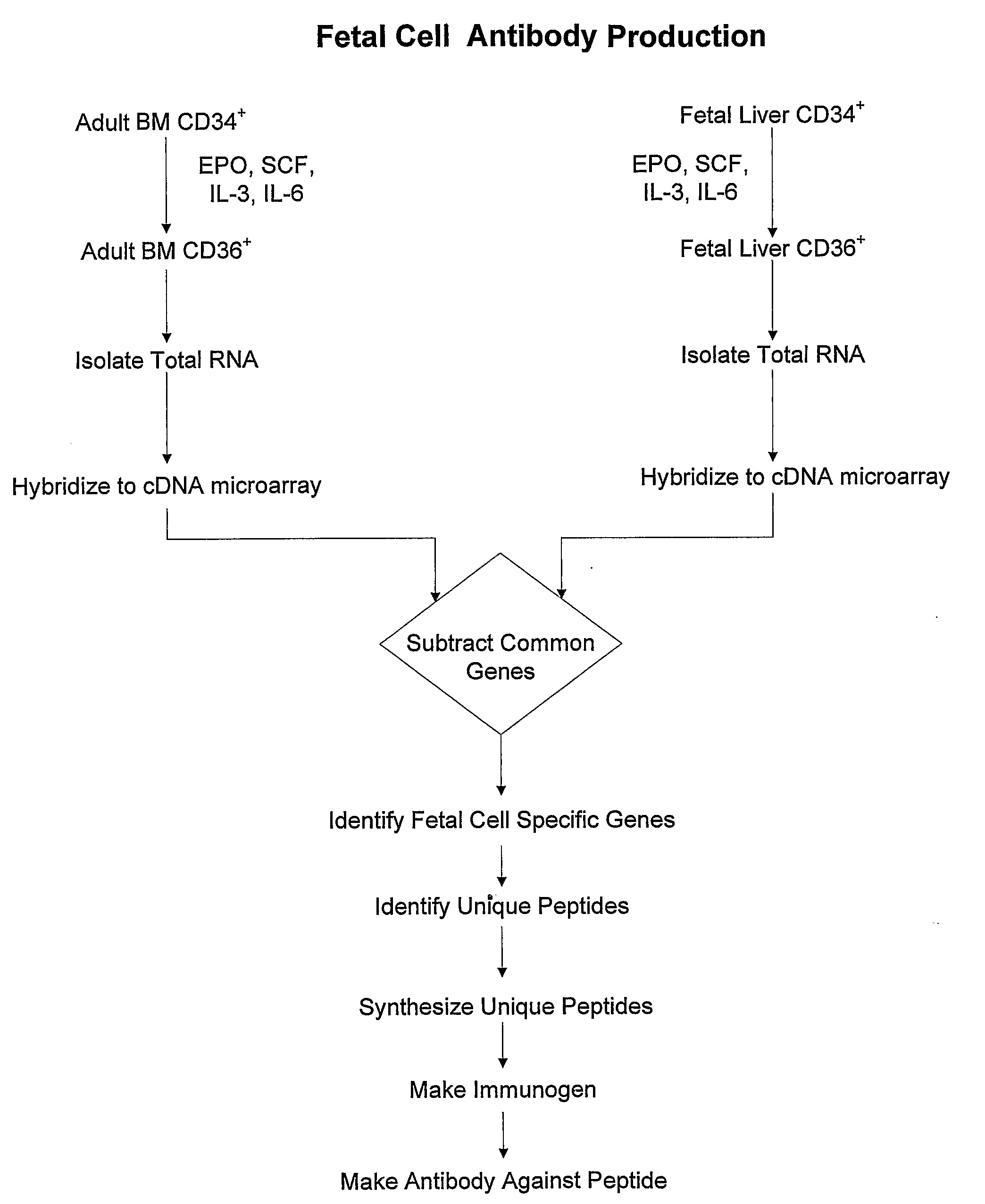
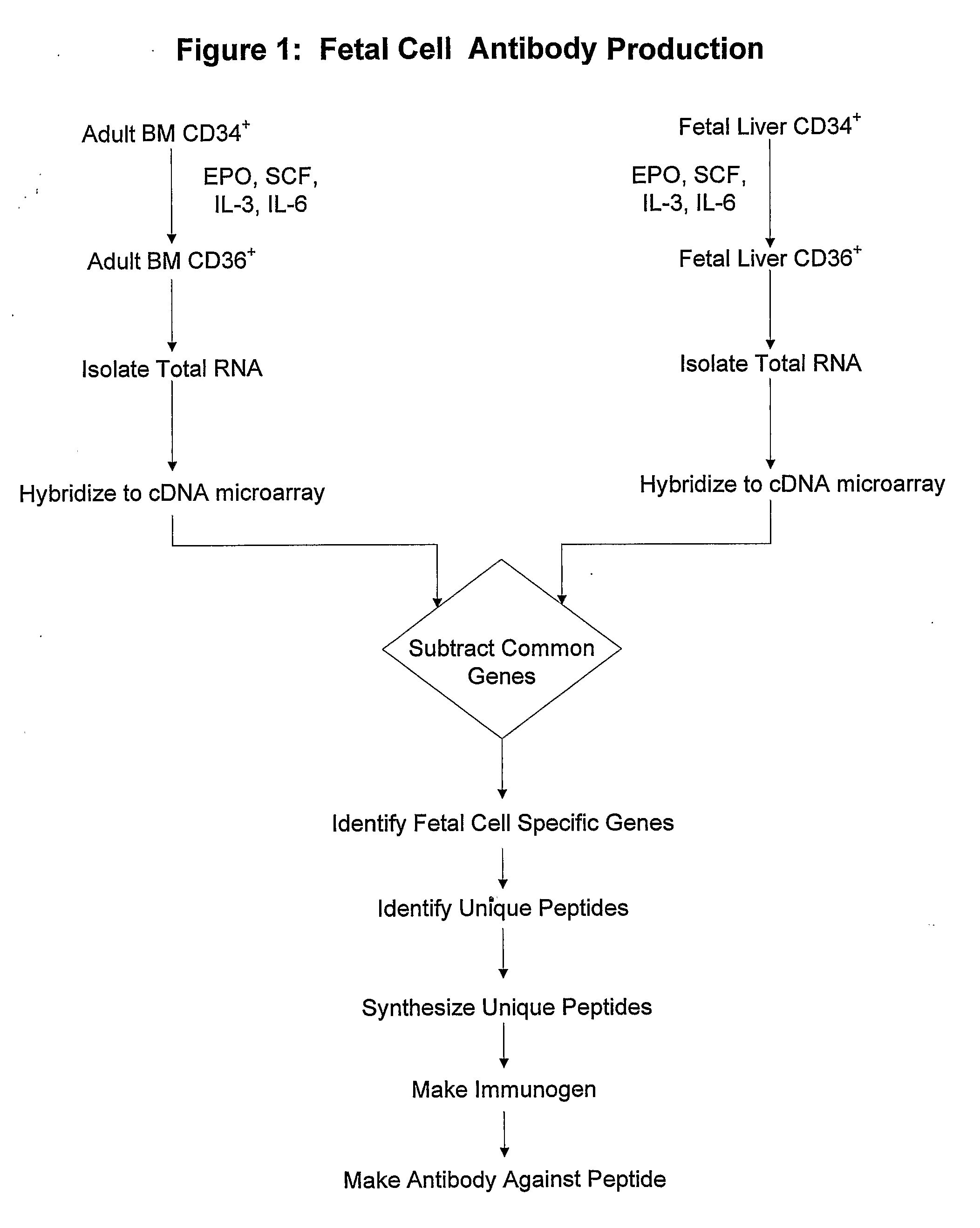
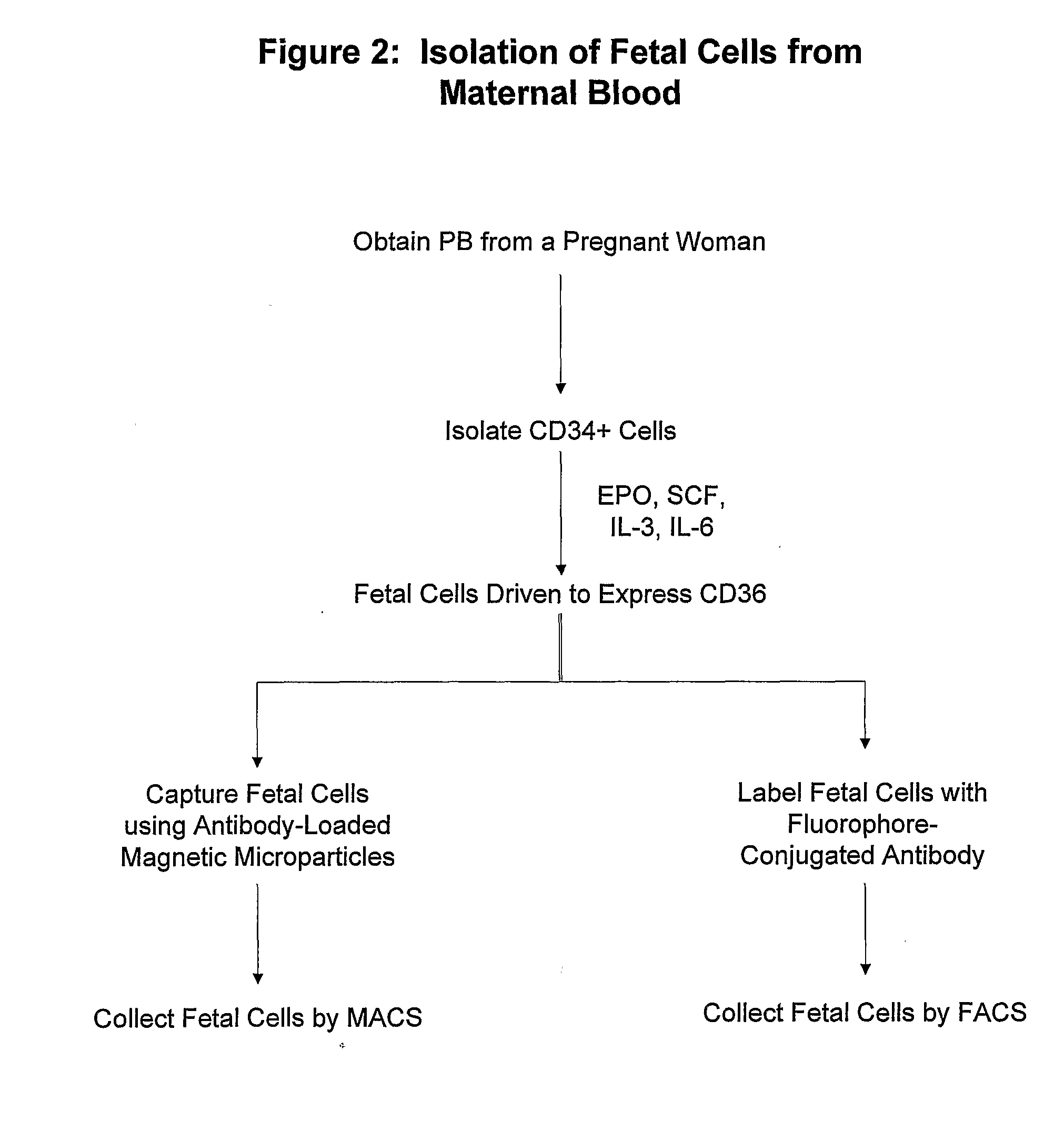
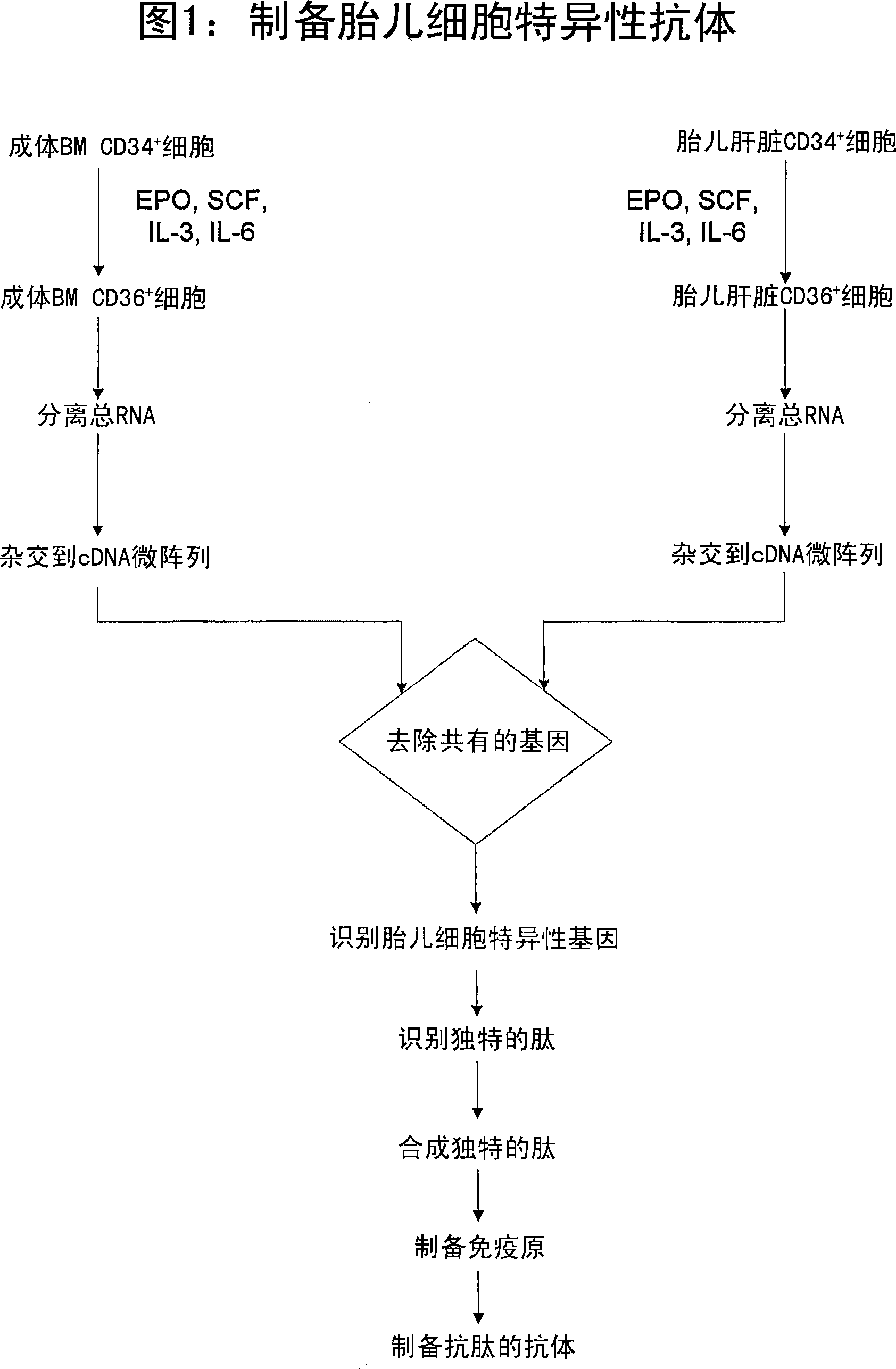
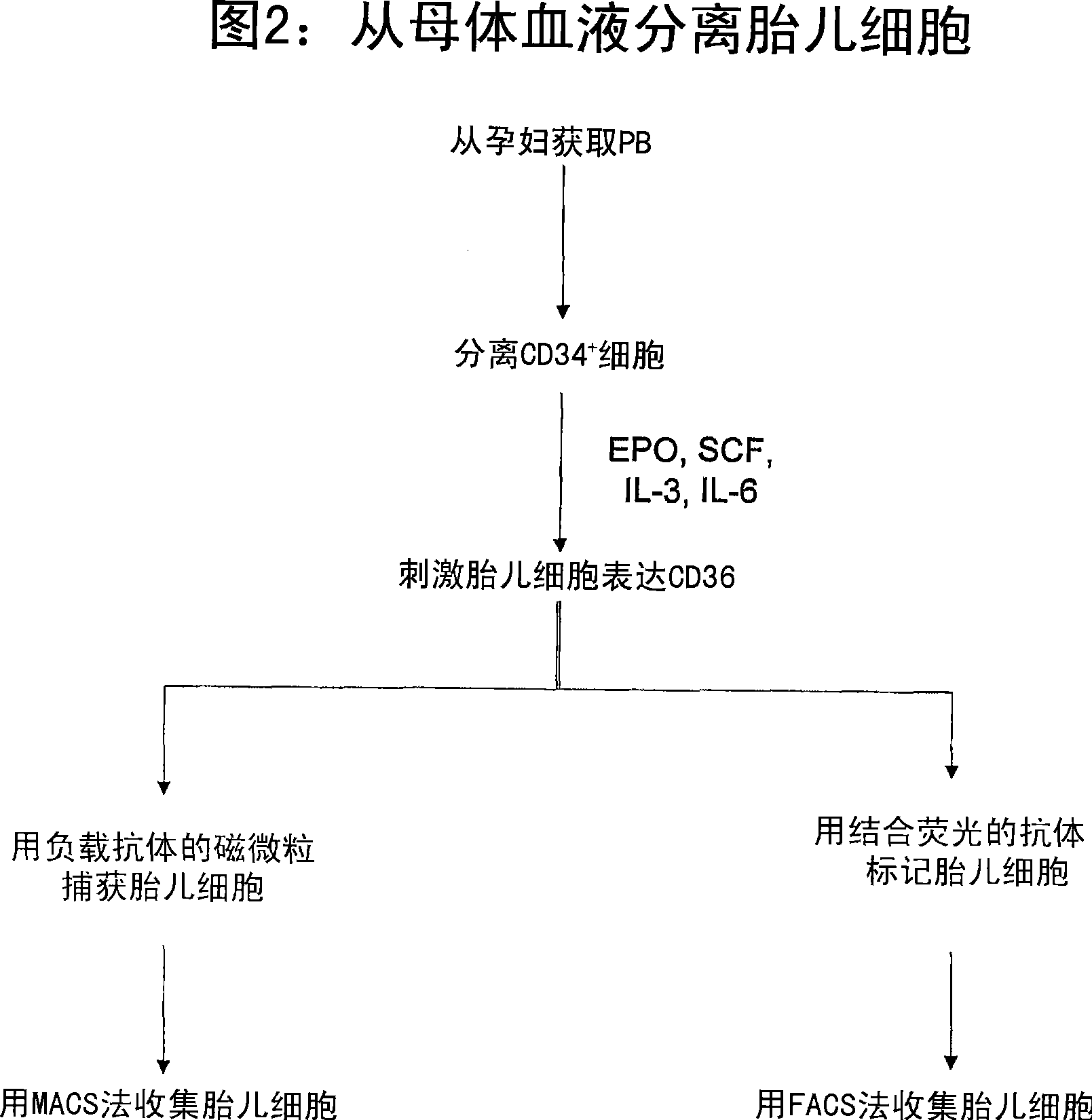
Antibodies against cells of fetal origin
InactiveUS8026054B2Reduce yieldIncrease percentageAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementFetal cellBiological fluids
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Antibodies Against Cells of Fetal Origin
InactiveUS20090011409A1Without posing riskReduce yieldAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementFetal cellOrganism
This invention relates to antibodies that specific bind to fetal CD36+ cells in preference to binding to maternal CD36+ cells and methods for using these antibodies to detect and separate fetal cells from adult biological fluids including maternal peripheral blood.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
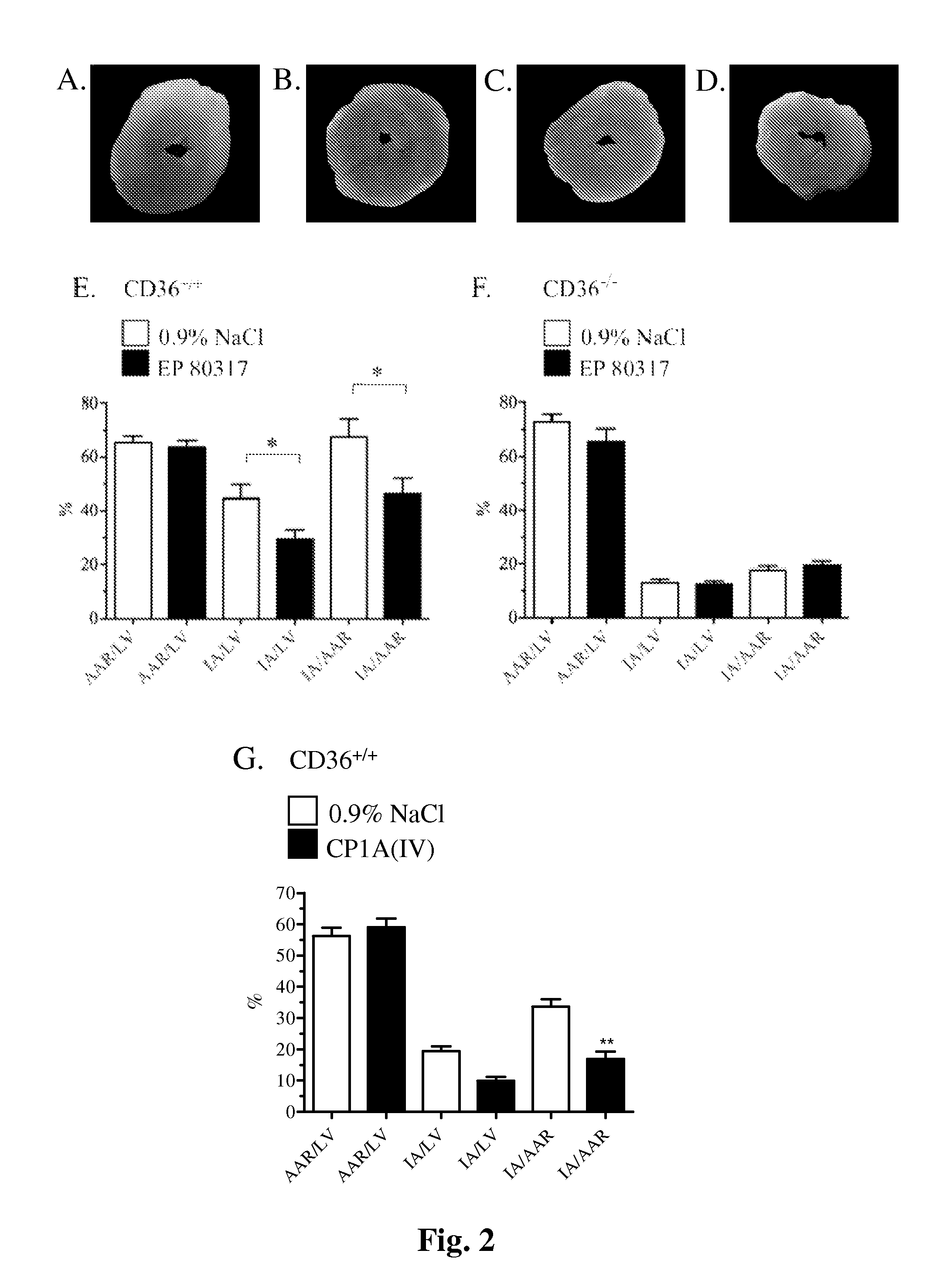
Cd36 modulation and uses thereof
Methods, uses, kits and products are described for the prevention and treatment of ischemia-associated cardiopathies such as myocardial ischemia / reperfusion (I / R) injury, based on the selective modulation of CD36.
Owner:SOCPRA SCI SANTE & HUMAINES S E C +1
Composition comprising eupatorium spp. extract as active ingredient for preventing and treating obesity and metabolic bone disease
InactiveUS20150157675A1Inhibitory activityIncreases activity of ALPBiocidePowder deliveryOsteoblastStem cell line
The present invention relates to a Eupatorium spp. extract having anti-obesity effects as a result of decreasing adipocytes and increasing osteoblasts, as well as the effects of preventing bone disease or fractures by increasing osteoblasts and of preventing osteoporosis by decreasing adipocytes and increasing osteoblasts by the same proportion in mesenchymal stem cells. DCM fraction layers of a Eupatorium spp. stem extract collected on a monthly basis and Eupatorium spp. stem extract collected only in September may inhibit the activity of PPARγ, AP2, CD36, adiponectin C / EBPα, and LPL, which serve as significant factors for adipocyte differentiation in C3H10T1 / 2 cells and primary mesenchymal stem cells, which are pluripotent stem cell lines, and may increase the activity of ALP, osterix, CO1I and RUNX2, which serve as significant factors for osteoblast differentiation. The Eupatorium spp. extract of the present invention exhibits the effects of increasing bone mineral density (BMD) and decreasing adipocytes in bone marrow in an osteoporosis animal model experiment involving an ovariectomy, and therefore may be used as a useful material for preventing and treating osteoporosis.
Owner:SUNG KYUN BIOTECH +1
Anti-atherosclerosis drug efficacy evaluation method based on inflammatory responses
The invention discloses an anti-atherosclerosis drug efficacy evaluation method based on inflammatory responses, wherein the method comprises the following steps: step 1, planting smooth muscle cells on the outer side of a Millicell@insert PE (Poly Ethylene) membrane, and turning after the cells are adhered to the wall for 8 hours; step 2, planting endothelial cells on the inner side of the membrane, and culturing for 6 days totally; step 3, inoculating mononuclear cells THP-1, adding oxLDL, IL-1 and texted drugs, and culturing for 24 hours; step 4, detecting any one of the items of detecting contents of MCP-1 and TNFa in the endothelial cells; detecting the content of CD36 on the surface of the mononuclear cells; detecting the contents of MDA and MMP2 in the smooth muscle cells, observing the change of a smooth muscle cytoskeleton; observing the expression of ICAM-1 of the endothelial cells.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
Preparations of rosa laevigata fruit extracts and uses thereof for regulation of cd36, apoa1, and srb1
InactiveUS20180296624A1Increase gene expressionReducing liver lipid accumulationMetabolism disorderDigestive systemAlcoholBlood lipids
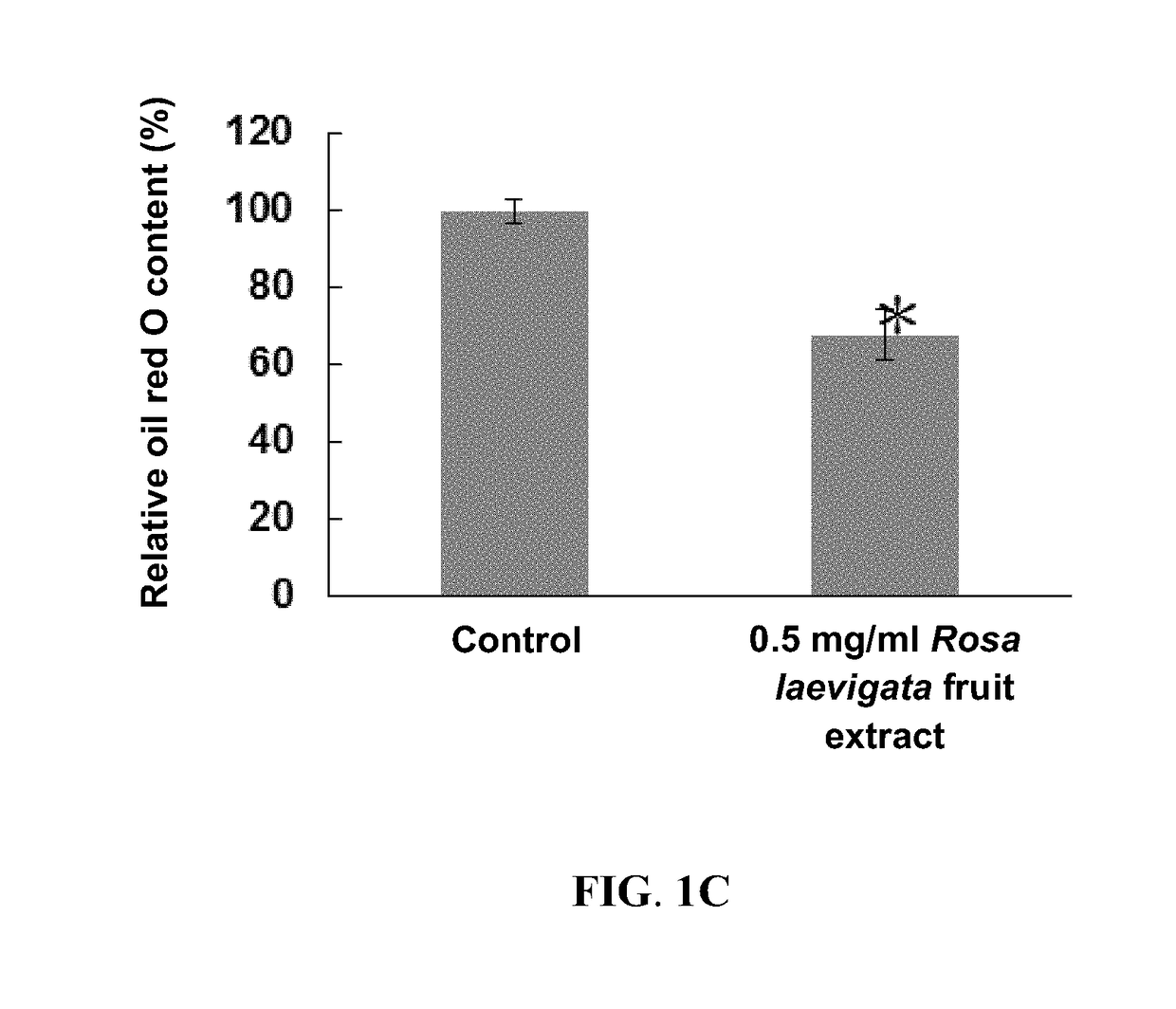
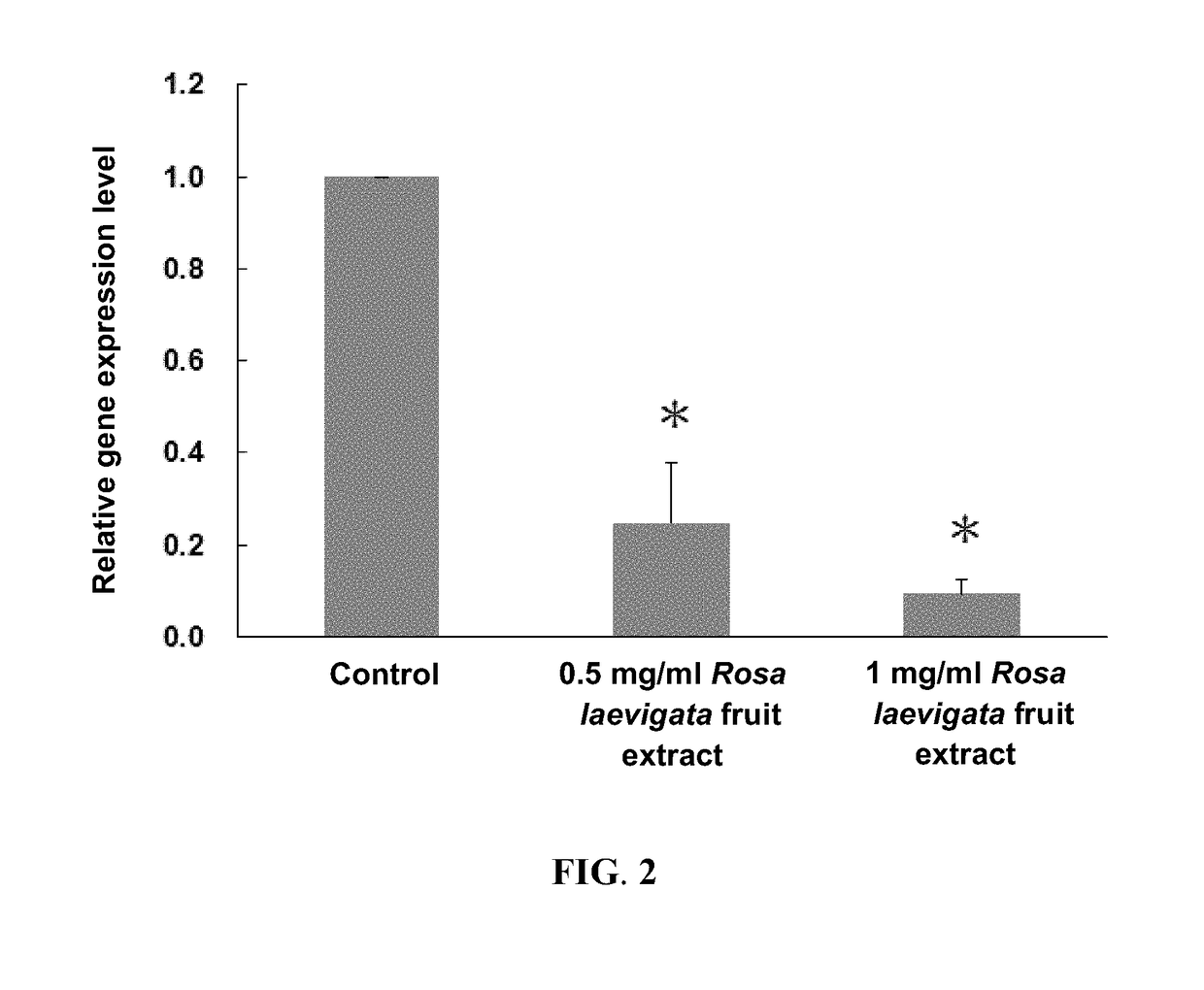
Provided is a method of a method of preparing a Rosa laevigata fruit extract which regulates CD36, ApoA1, and SRB1, including extracting the fruit of Rosa laevigata using water, alcohols, or mixtures of water and alcohols as solvents. Also provided is a method of regulating CD36, ApoA1, and SRB1, including administering to a subject a composition containing an effective amount of the Rosa laevigata fruit extract. By suppressing the gene expression of CD36 and enhancing the gene expression of ApoA1 and SRB1, the Rosa laevigata fruit extract may be used to regulate lipid metabolism and reduce liver lipid accumulation and blood lipid levels.
Owner:TCI CO LTD
Composition and methods for regulating extracellular matrix accumulation
PendingUS20190381133A1Accelerate the accumulation processOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseCell-Extracellular Matrix
There is described herein methods of treating a disease associated with extracellular matrix (ECM) in a patient. In some cases, the methods comprise administering to the patient a therapeutically effective amount of fibroblasts which express CD36.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
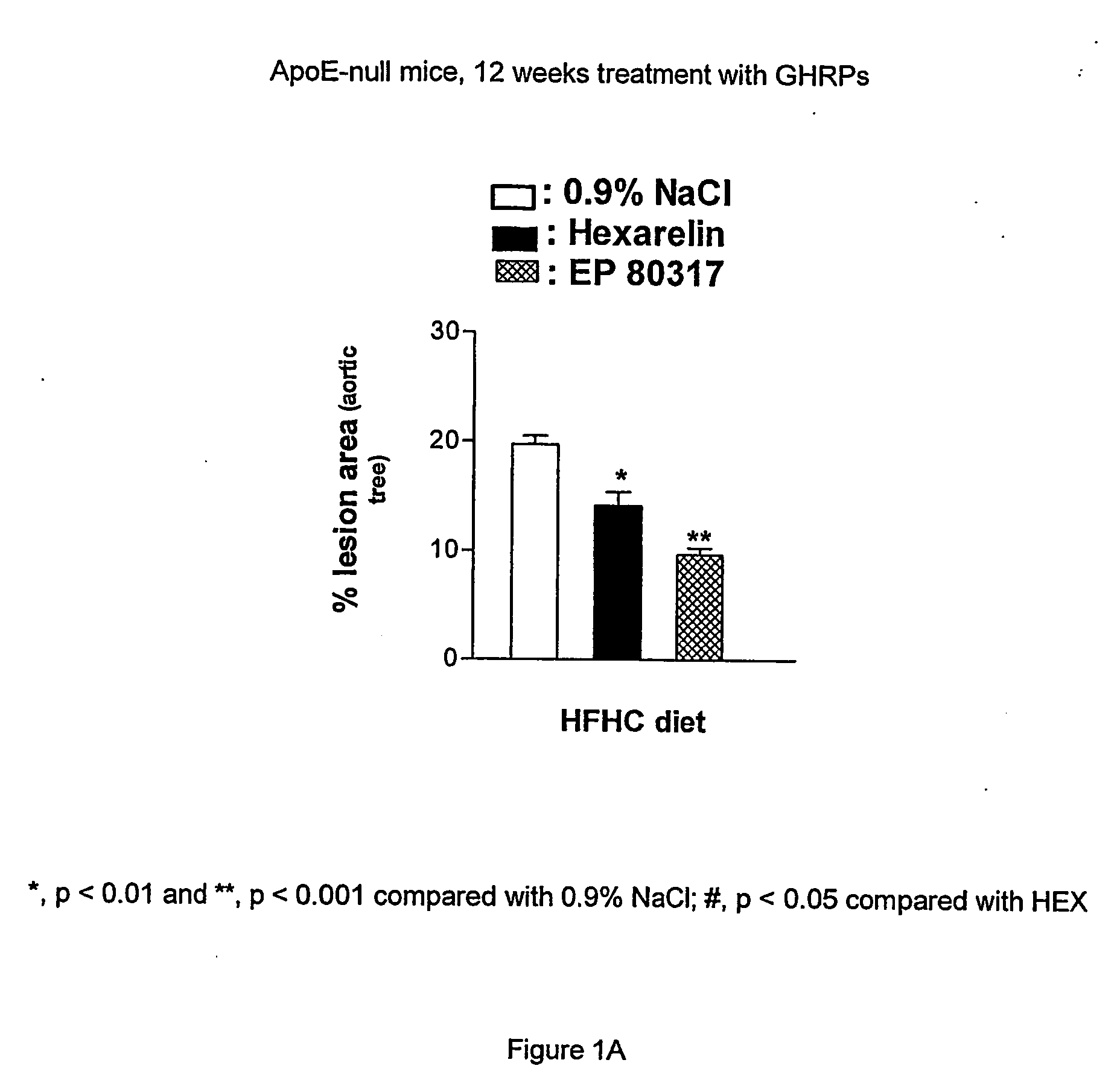
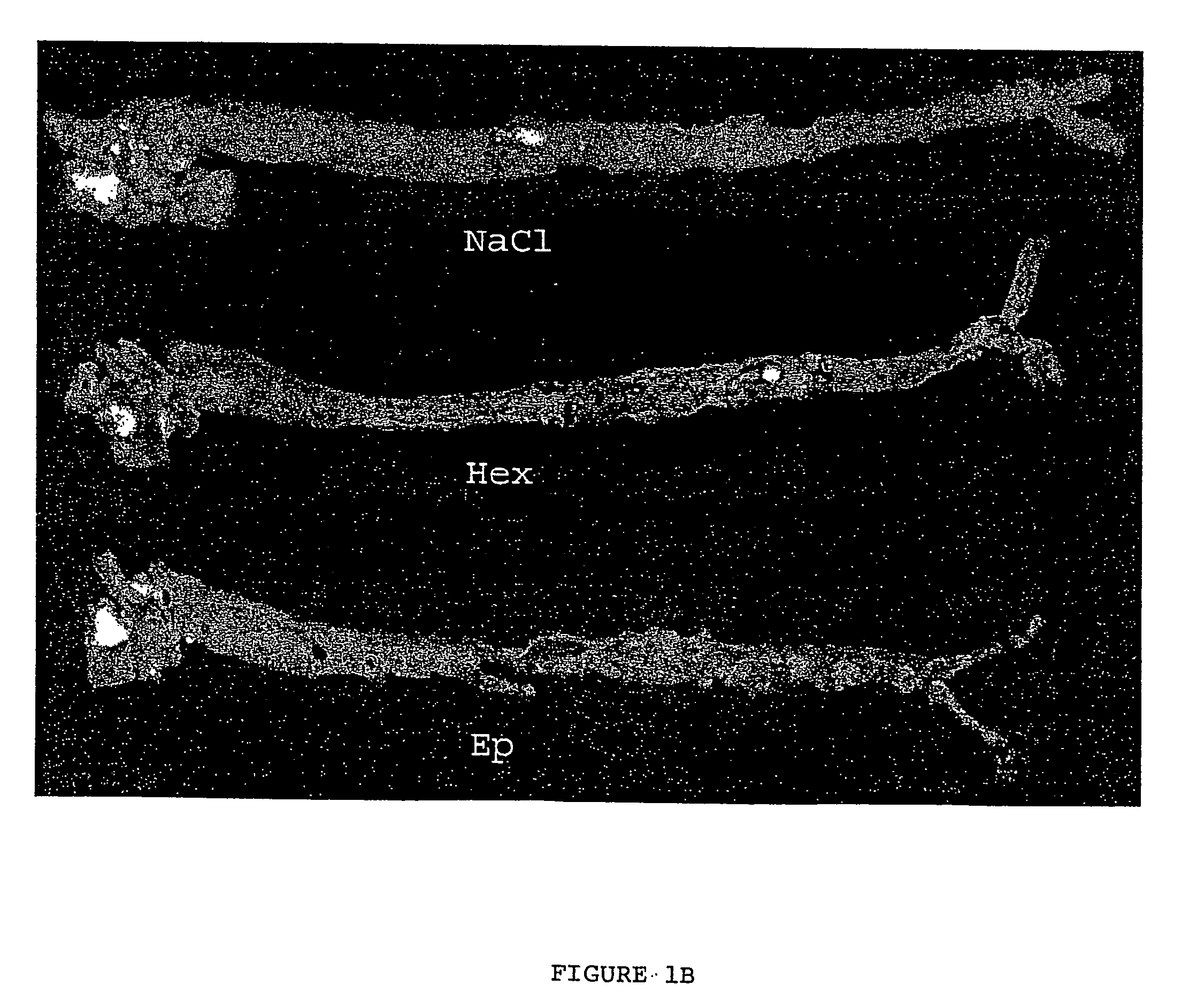
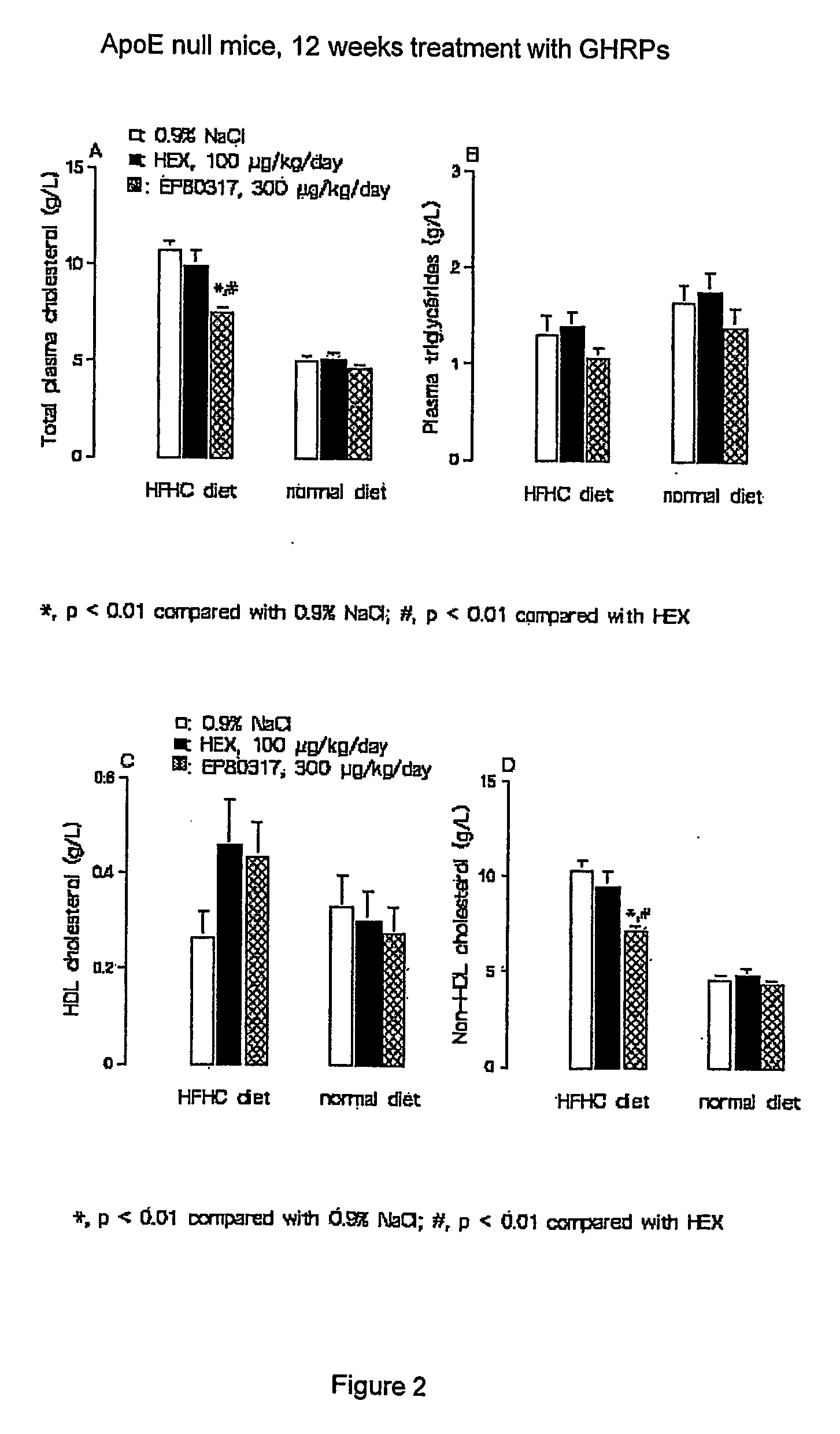
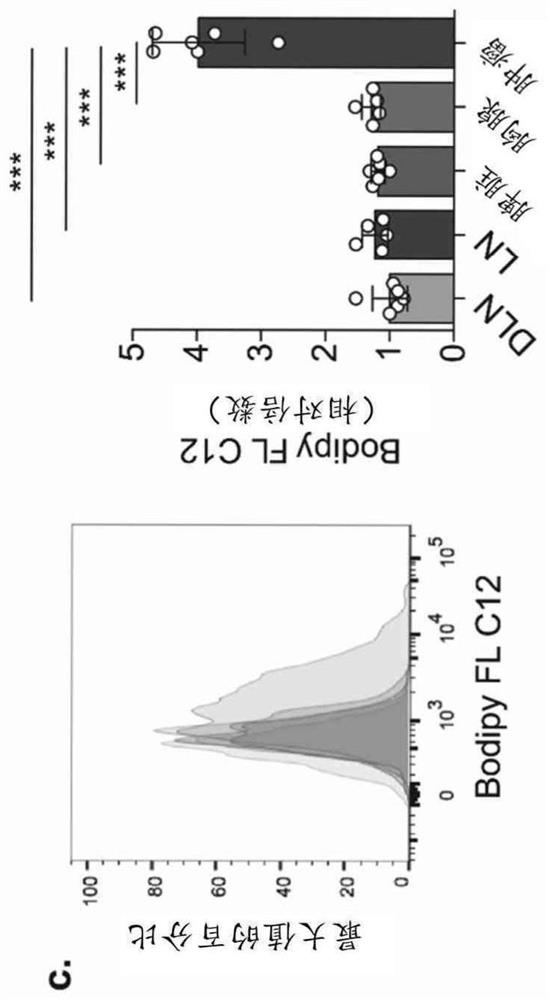
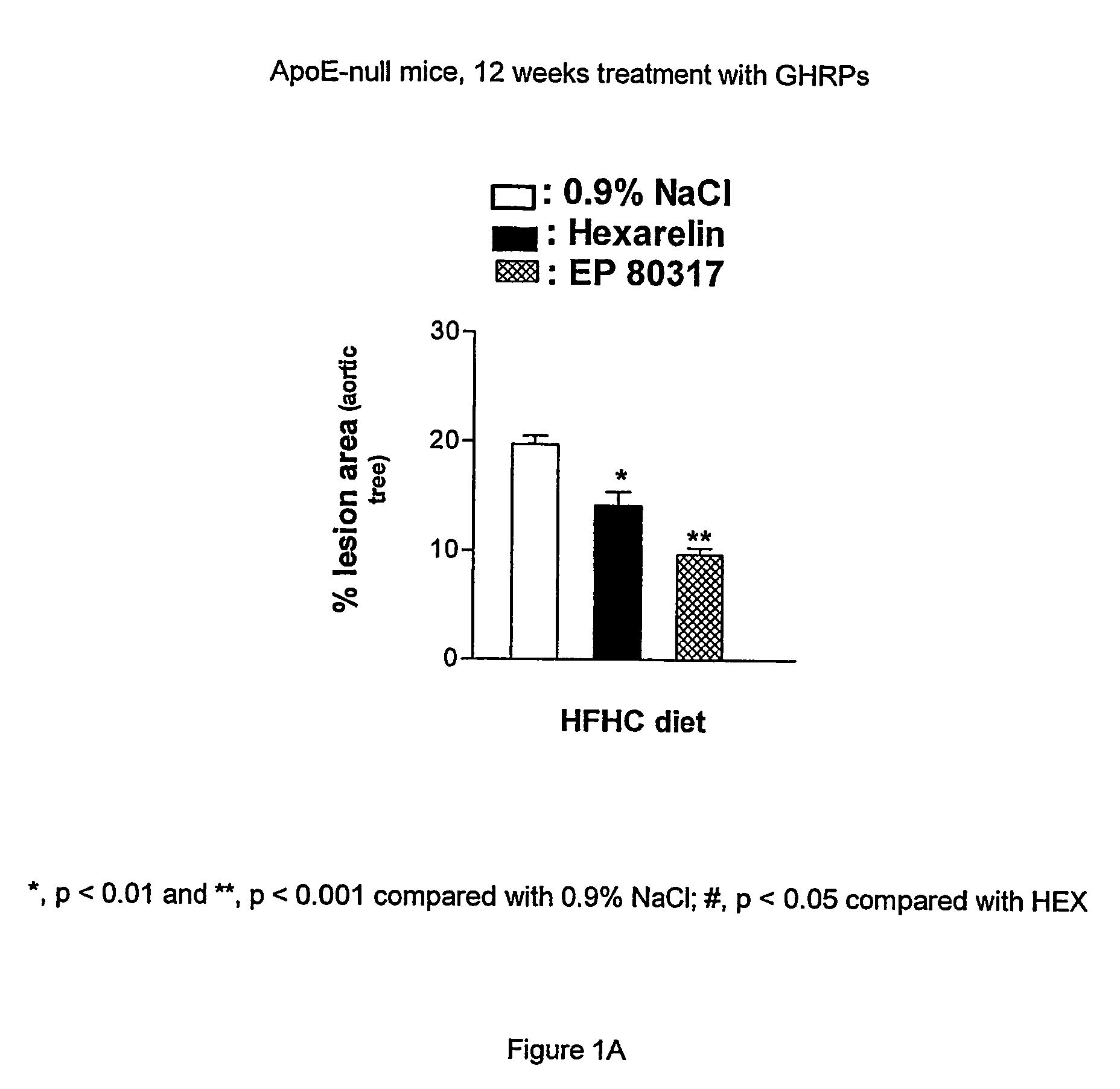
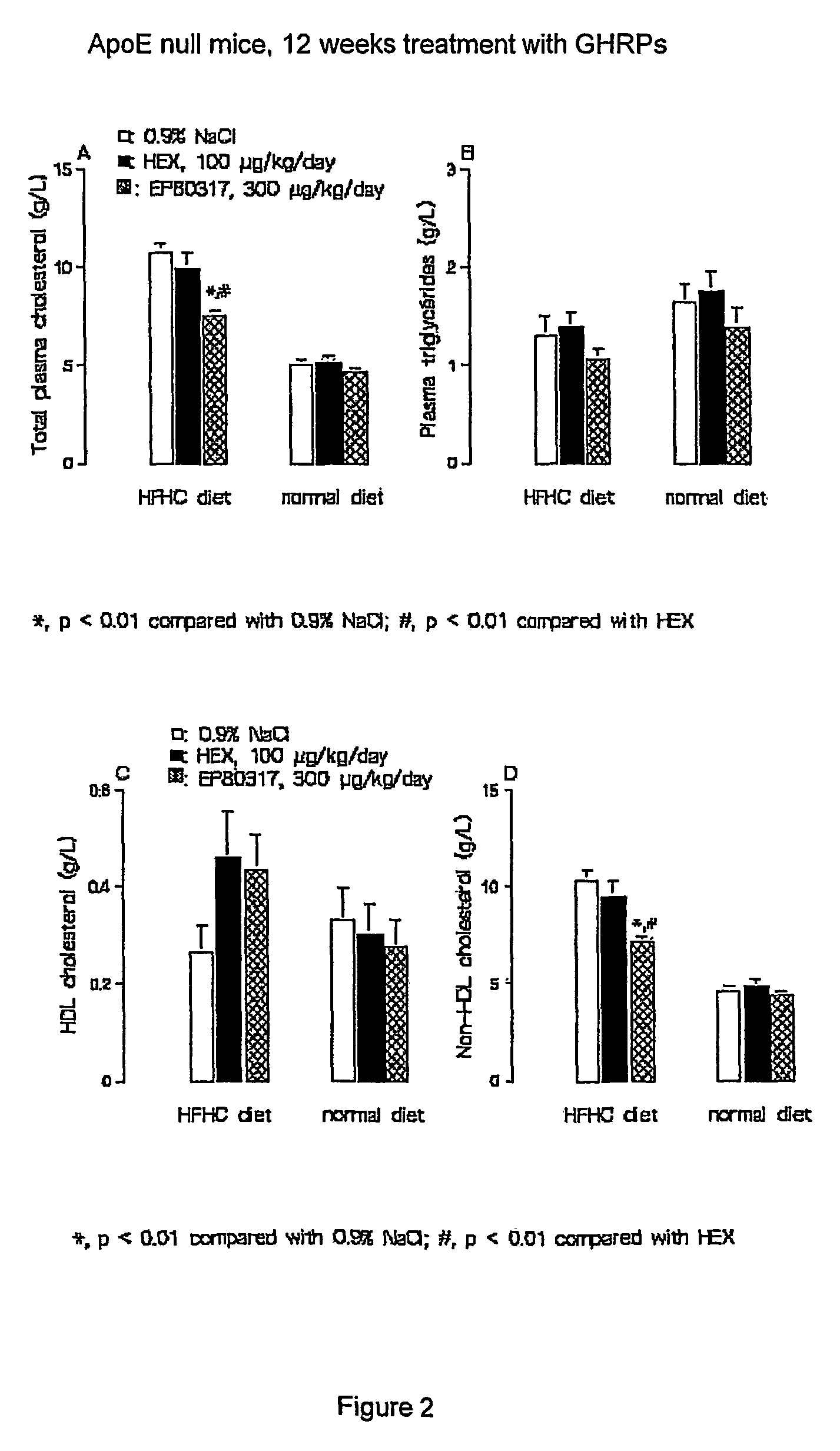
Growth hormone-releasing peptides in the treatment of prevention of atherosclerosis and hypercholesterolemia
InactiveUS20060241054A1Reduce lipid accumulationReduce lesionsPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderScavenger receptorCellular cholesterol
According to the invention there is provided a method of treatment or prophylaxis of atherosclerosis, hypercholesterolemia or a cardiovascular disease associated with atherosclerosis, which method comprises administration of one or more Growth Hormone Releasing Peptides (GHRPs) to a patient in need of such treatment or prophylaxis. There are also provided methods of reducing blood plasma cholesterol levels, as well as methods of modulating the expression of the scavenger receptor CD36 and genes involved in cellular cholesterol efflux.
Owner:VALORISATION HSJ SOC & COMMANDITE CO CHU SAINTE JUSTINE LE CENT HOSPITALIER UNIV MERE ENFANT
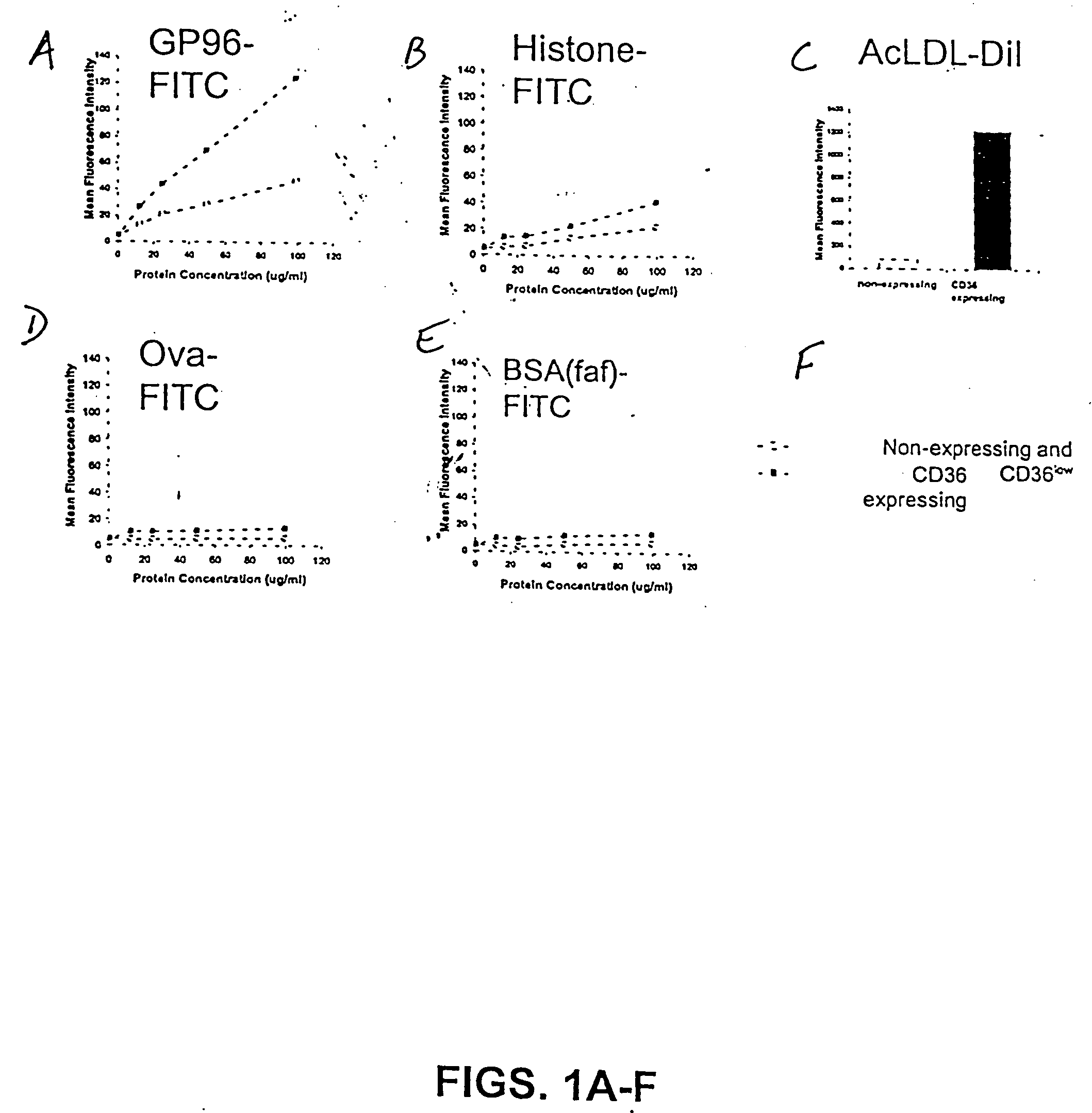
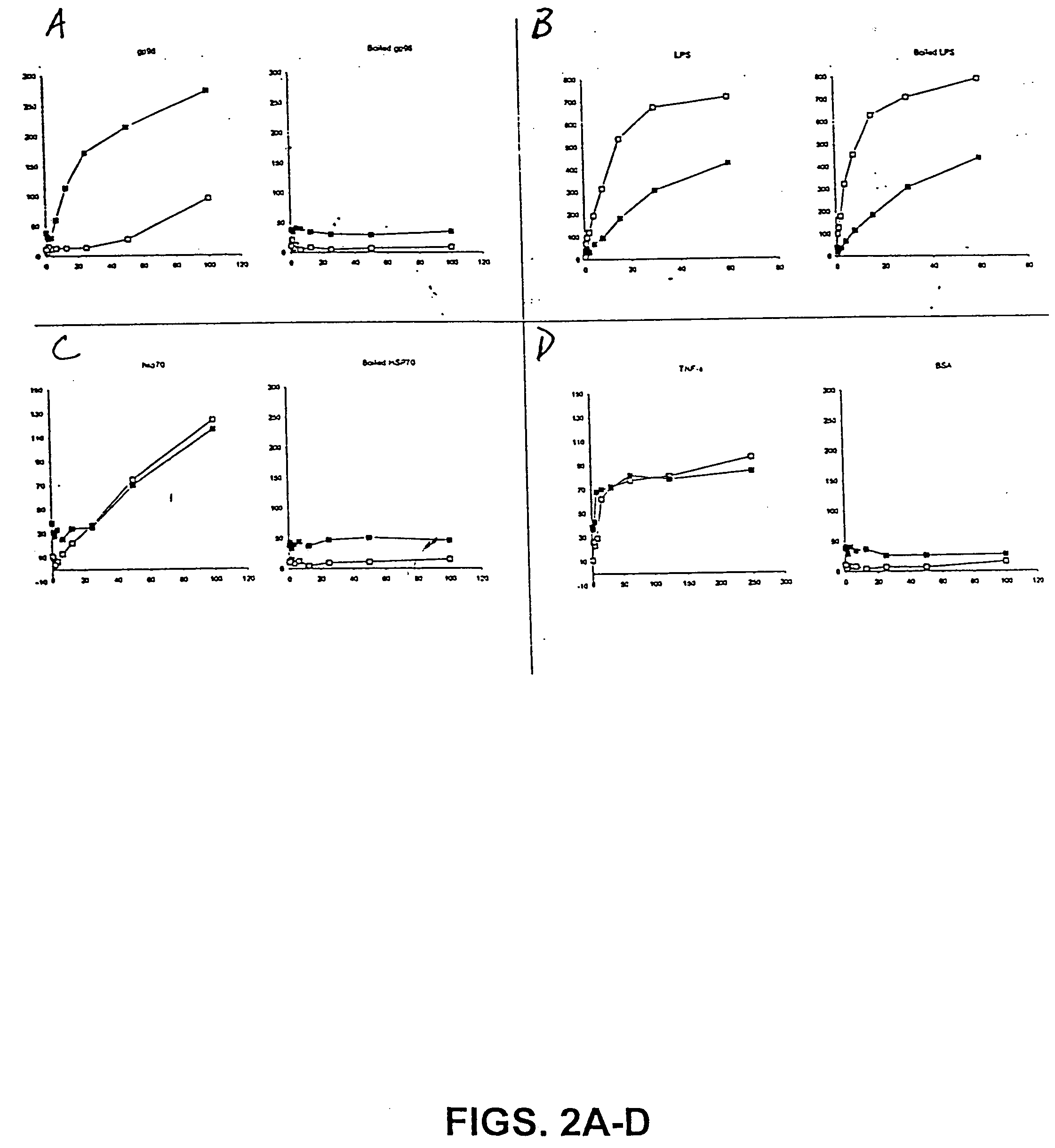
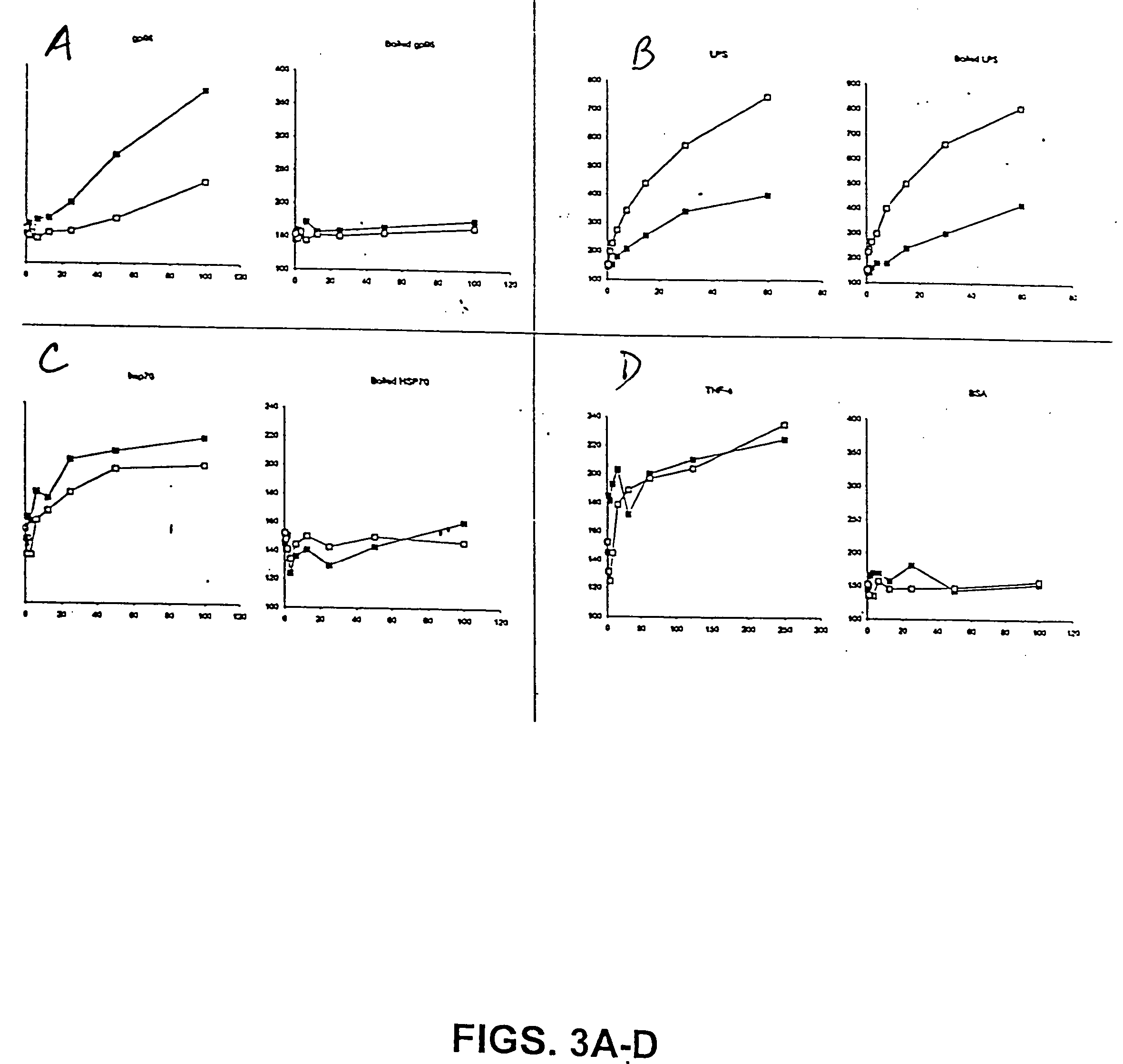
Cd36 as a heat shock protein receptor and uses thereof
InactiveUS20040115737A1Improve immunityEnhance immune responseBiological testingReceptor for activated C kinase 1Antibody
The present invention relates to the use of CD36 ("CD36") receptor as a heat shock protein receptor, cells that express CD36 bound to an HSP, and antibodies and other molecules that bind CD36-HSP complex. The invention also relates to screening assays to identify compounds that interact with CD36, and modulate the interaction of CD36 with its ligand, such as HSPs, and methods for using compositions comprising CD36-receptor sequences for the diagnosis and treatment of immune disorders, proliferative disorders, and infectious diseases.
Owner:ANTIGENICS
Gene functional genetic variation correlated to HDL-C (High-density Lipoproteincholesterol) level and related application thereof
ActiveCN107502666AHelps prevent hyperlipidemiaAids in diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisHigh densityAPOA1 Gene
The invention provides gene functional genetic variation correlated to HDL-C (High-density Lipoproteincholesterol) level and related application thereof. Specifically, the invention provides application of reagent materials and / or instrument equipment for detecting the following protein amino acid sites and / or corresponding gene loci in samples from a to-be-tested individual in preparation of a detection system used for evaluating a blood lipid level and / or abnormal blood lipid onset risk. The protein amino acid sites include CD36 gene rs148910227, APOA1 gene rs12718465 and / or CETP gene rs201790757 heritable variations causing CD36 protein 386th amino acid coding change, APOA1 gene 61st amino acid coding change and / or CETP gene 74th early amino acid termination. The to-be-tested individual with CD36 Arg386Trp and / or CETPTyr74* variation has high high-density lipoproteincholesterol level and / or low abnormal blood lipid onset risk; and the to-be-tested individual with APOA1 Ala61Thr variation has low high-density lipoproteincholesterol level and / or high abnormal blood lipid onset risk.
Owner:FUWAI HOSPITAL CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI & PEKING UNION MEDICAL COLLEGE +3
Application of Tibetan medicine namely epipremnum aureum flower in preparation of medicine for treating atherosclerosis
InactiveCN111870639AIncrease collagen contentImprove stabilityCardiovascular disorderPlant ingredientsCholesterol uptakeBile acid
The invention relates to an application of a Tibetan medicine namely epipremnum aureum flower in preparation of a medicine for treating atherosclerosis, and belongs to the technical field of traditional Chinese medicine. The invention shows that at the animal level, the epipremnum aureum flower alcohol extract can significantly reduce the atherosclerotic plaque area of mice, and the specific mechanism is shown as follows: on one hand, cholesterol absorption is inhibited by reducing the SR-BI expression level, and on the other hand, cholesterol metabolism is promoted to generate bile acid by increasing the CYP7A1 gene expression; and at the cellular level, the epipremnum aureum flower alcohol extract can significantly reduce cholesterol uptake of cells and reduce expression of a macrophagemarker CD36 to reduce cholesterol uptake of macrophages so as to reduce macrophage foaming. The invention provides scientific data and an idea basis for clinical treatment of atherosclerosis through the epipremnum aureum flower, and provides data support for a new method and an action target for clinically preventing and treating cardiovascular diseases.
Owner:JIANGXI UNIVERSITY OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Approach for modulating regulatory t cells and inhibiting tumor growth
PendingCN112703039APeptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against growth factorsRegulatory T cellAutoimmune responses
Provided herein is approach that specifically modulates the activity and / or the number of intratumoral regulatory T (Treg) cells in a subject. Such an approach can be used to reduce the number of intratumoral T regulatory cells in a subject as well as to inhibit tumor growth in a subject having a cancer without eliciting autoimmune responses. The approach relies on the inhibition of CD36 or of PPARbeta.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF LAUSANNE
Growth hormone-releasing peptides in the treatment or prevention of atherosclerosis and hypercholesterolemia
InactiveUS7785567B2Reducing the uptake of oxidised LDLReduce lesionsPeptide/protein ingredientsMetabolism disorderScavenger receptorCellular cholesterol
According to the invention there is provided a method of treatment or prophylaxis of atherosclerosis, hypercholesterolemia or a cardiovascular disease associated with atherosclerosis, which method comprises administration of one or more Growth Hormone Releasing Peptides (GHRPs) to a patient in need of such treatment or prophylaxis. There are also provided methods of reducing blood plasma cholesterol levels, as well as methods of modulating the expression of the scavenger receptor CD36 and genes involved in cellular cholesterol efflux.
Owner:VALORISATION HSJ SOC & COMMANDITE CO CHU SAINTE JUSTINE LE CENT HOSPITALIER UNIV MERE ENFANT
Antibodies binding to CD34+/CD36+ fetal but not to adult cells
InactiveCN101001879AReduce in quantityRaise the ratioMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsFetal cellBiological fluids
This invention relates to antibodies that specific bind to fetal CD36+ cells in preference to binding to maternal CD36+ cells and methods for using these antibodies to detect and separate fetal cells from adult biological fluids including maternal peripheral blood.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
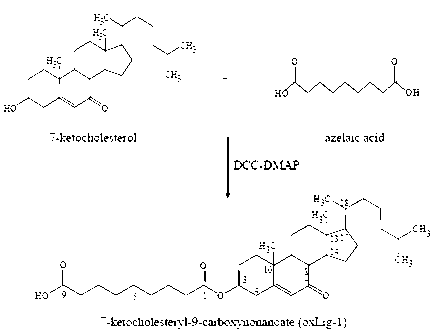
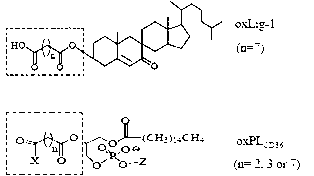
Chemical synthetic method of low affinity ligand of oxidized low density lipoprotein receptor CD36
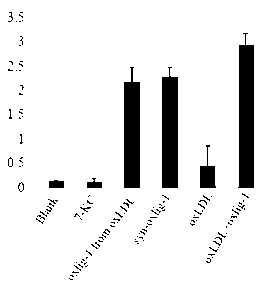
The invention belongs to the field of biochemical engineering, and in particular relates to a chemical synthetic method of a low affinity ligand of an oxidized low density lipoprotein receptor CD36. The method comprises the following steps of: carrying out a chemical reaction on 4-Dimethylaminopyridine, N, N'-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, azelaic acid and 7-ketocholesterol; and obtaining oxLig-1 through extraction, sample mixing, packing, purification and collection. Experiments show that the chemically synthesized oxLig-1 has same physiological activity with that of oxLig-1 separated and purified from oxLDL (oxidized low density lipoprotein), and the oxLig-1 activates cell signaling mediated by CD36. According to the chemical synthetic method disclosed by the invention, oxLig-1 is synthesized by the chemical method, and oxLig-1 has a completely consistent chemical structure with that of the low affinity ligand of CD36 and can activate ERK (Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase) and JNK (Jun N-Terminal Kinase) and up-regulate expression of a cholesterol outflow gene, namely, a triphosadenine binding cassette transporter A1 (ABCA1).
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com