Battery sensor for temperature-independent current measurement using shunt
A battery sensor and shunt technology, which is applied in the direction of measuring electricity, measuring electrical variables, and components of electrical measuring instruments, etc., can solve problems such as direct placement of contacts for measuring shunt voltage.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
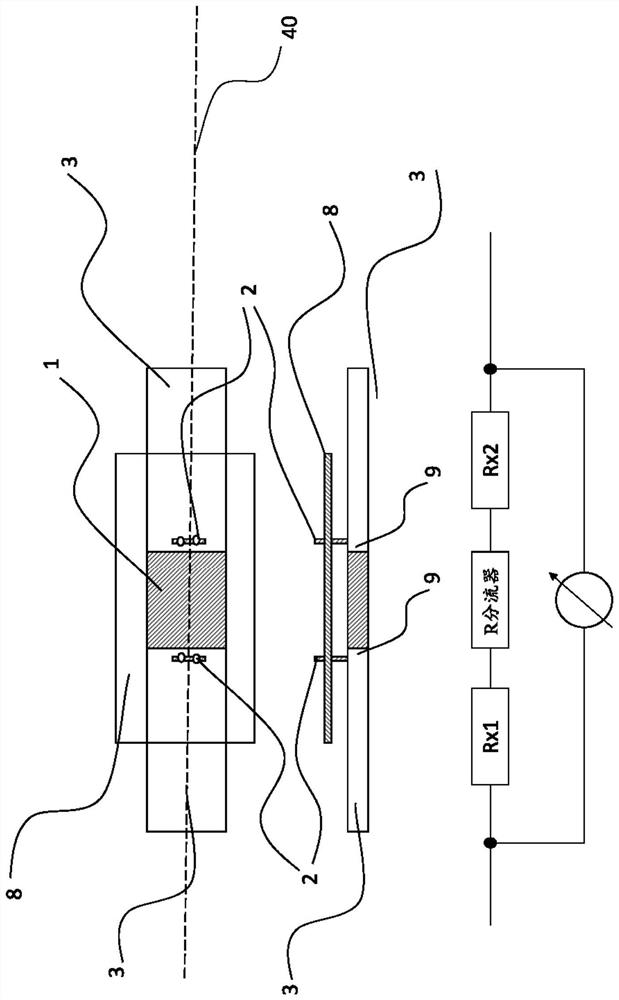
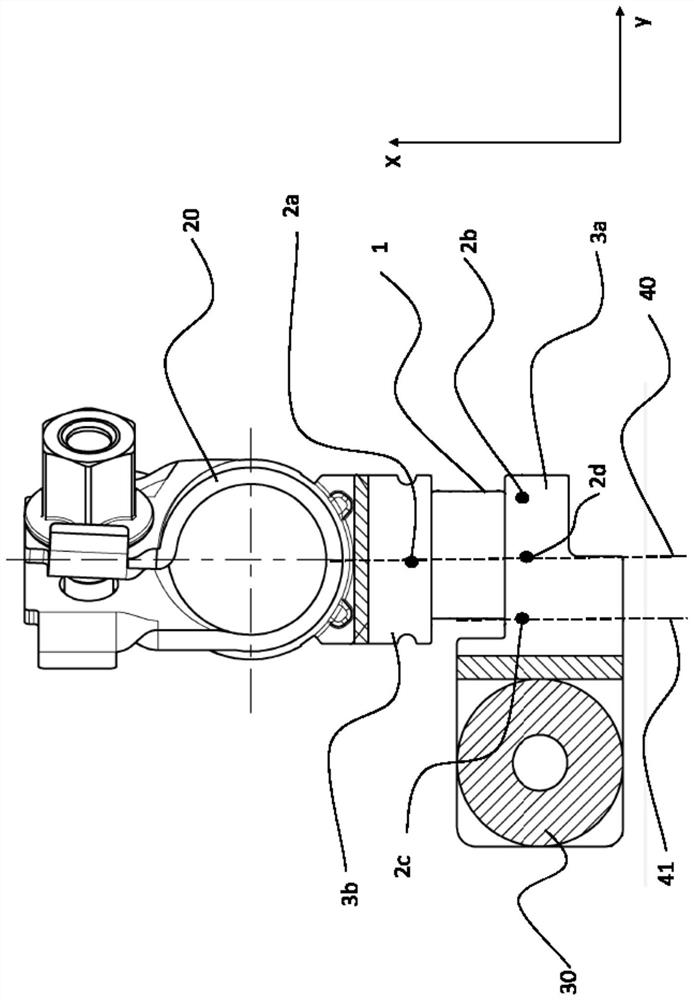
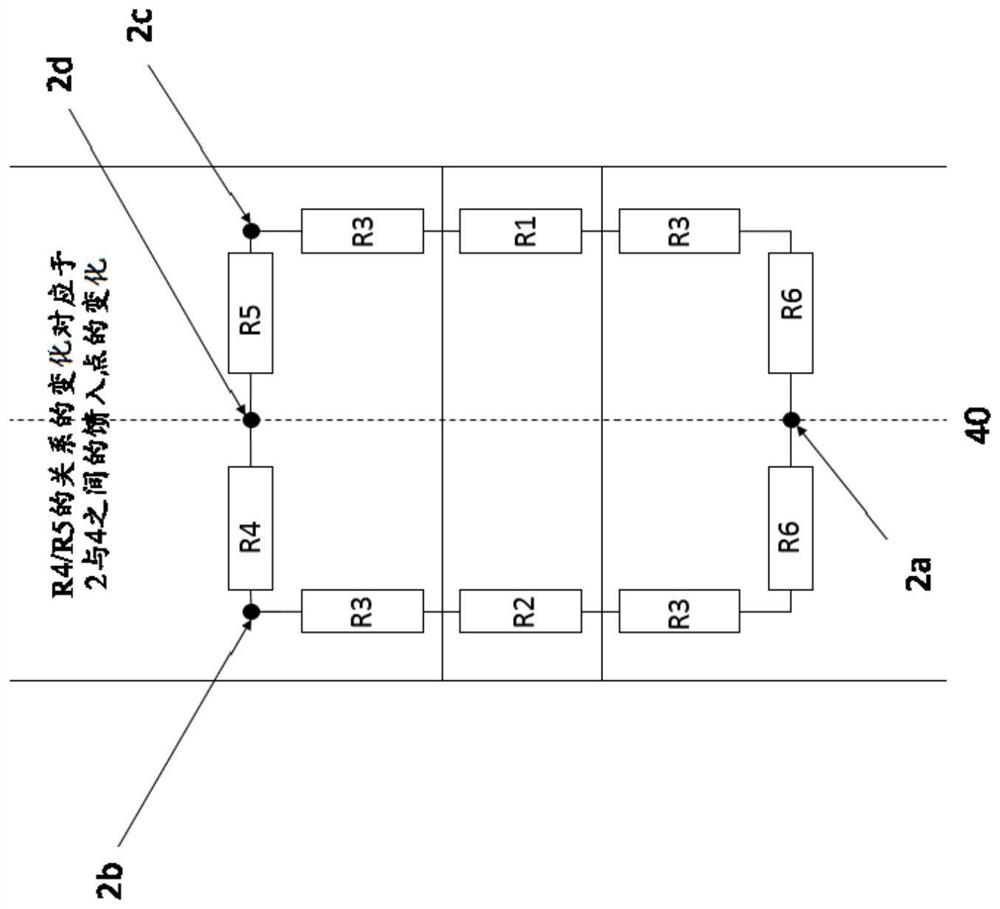
[0033] exist figure 1A common battery sensor is schematically shown in . The battery current is measured according to the shunt principle, wherein the voltage drop at the shunt resistor caused by the current to be measured is measured according to Ohm's law and with the aid of calibration parameters which ultimately represent the resistance value of the shunt at the respective operating point ) to convert the measured voltage drop into a current value. The heart of a shunt is the measurement path defined by the tap point (2) for the shunt voltage to be measured and usually contains a dedicated resistive alloy (1). The resistance alloy (1) is fixedly connected (for example welded) to the connecting element (3) on opposite sides viewed in the direction of current flow. The connection part is used to connect the shunt to the circuit to be measured. A connecting part is thus designed, for example, as an adapter ( 30 ) for connecting (screwing, clamping, soldering) current cable...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com