Biped robot path planning method and device and biped robot
A biped robot and path planning technology, applied in the field of robot navigation, can solve problems that are not suitable for biped robots
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
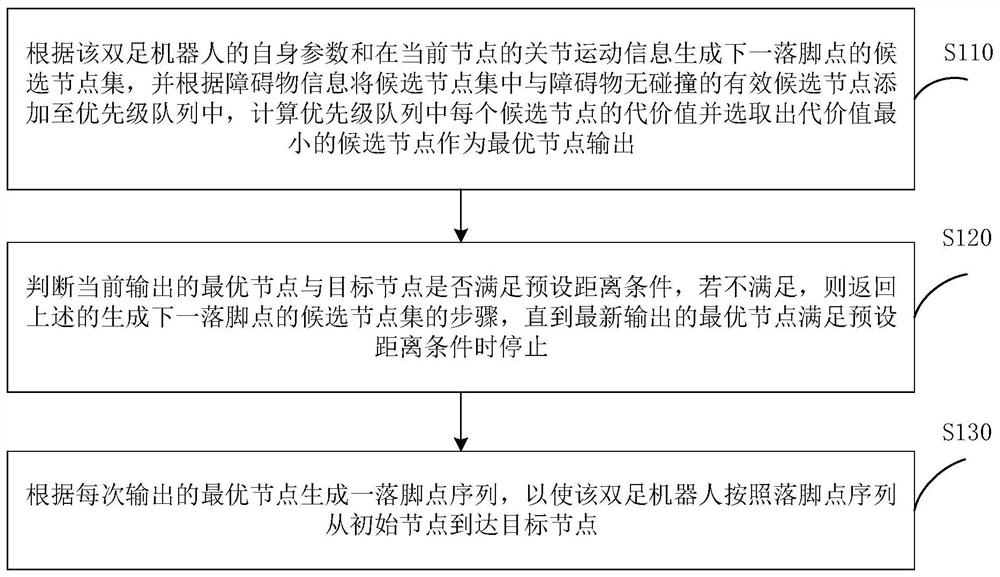
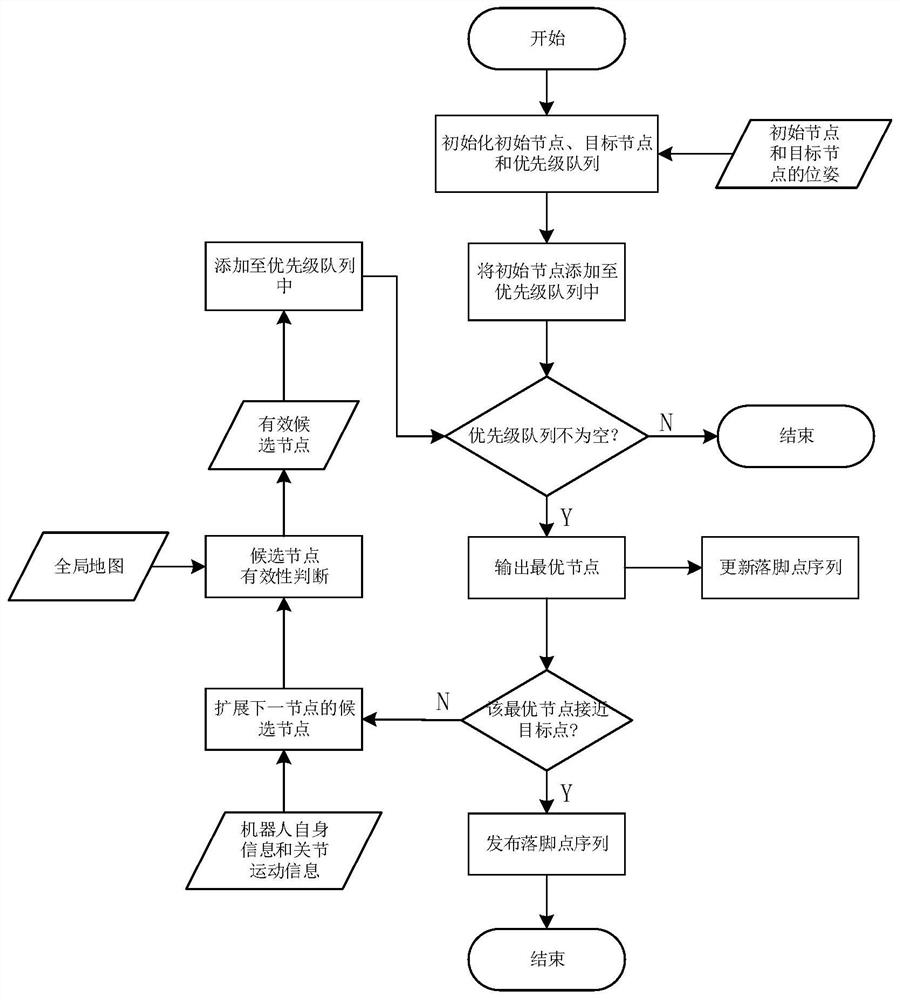
[0053] figure 1 A schematic flow chart of the first method for path planning of a biped robot according to an embodiment of the present application is shown. The method of this embodiment uses the footprint set of the biped robot to sequentially search for sub-nodes on the nodes on the path, not only can realize the path planning of the biped robot from the starting point to the end point, but also combines the information based on the biped robot itself and the two The footprint set generated by the joint movement information of the legs is used to expand the sub-nodes, which can greatly reduce the amount of node searches.
[0054] In this embodiment, before performing the following step S110, the method further includes:
[0055] Receive navigation information, the navigation information includes a global map of the biped robot walking, the global map includes obstacle information, designated initial nodes and target nodes.
[0056] Generally, when the biped robot receives...
Embodiment 2
[0076] Please refer to Figure 4 The difference between the biped robot path planning method proposed in this embodiment and the method in the above-mentioned embodiment 1 is that this embodiment also optimizes the above-mentioned path node search process through the global path, thereby speeding up the path search speed and improving the path planning efficiency. Wait.
[0077] Exemplarily, the method further includes: generating a global path from the initial node to the target node based on a preset path planning algorithm according to the received navigation information and the preset expansion radius of the biped robot. Wherein, the global path can be used to optimize the above-mentioned cost evaluation function and / or reduce the number of candidate nodes in the above-mentioned candidate node set.
[0078] Exemplarily, when generating the global path, the biped robot can be regarded as a center of mass but has a larger expansion radius, and at this time, it can be quickl...
Embodiment 3
[0099] Please refer to Figure 9 , based on the method of Embodiment 1 above, this embodiment proposes a path planning device 100 for a biped robot. Exemplarily, the biped robot path planning device 100 includes:
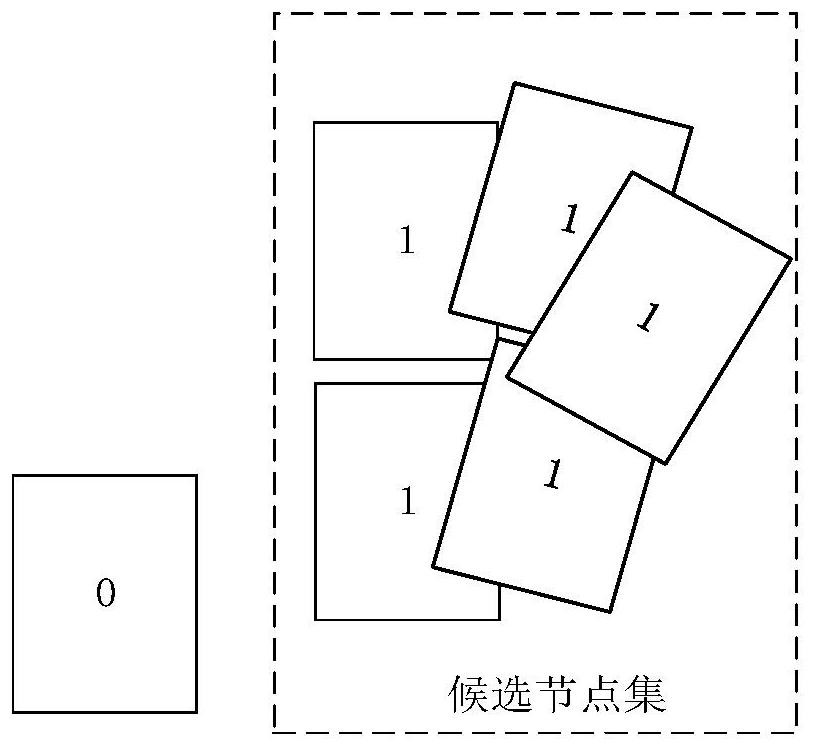
[0100] The selection module 110 is used to generate a set of candidate nodes for the next foothold according to the parameters of the biped robot itself and the joint motion information of the current node, and gather the candidate nodes that have no collision with the obstacle according to the obstacle information. The candidate nodes are added to the priority queue, and are also used to calculate the cost value of each candidate node in the priority queue and select the candidate node with the smallest cost value as the optimal node output. Wherein, the priority queue is a data structure in which the cost values of the candidate nodes in the priority queue are calculated by using the constructed cost evaluation function and sorted according to the cost values ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com