Method for in-situ synthesis aluminum-based composite material with vacuum degassing function
An aluminum-based composite material, in-situ self-generated technology, applied in the field of aluminum-based composite materials, can solve problems such as low temperature oxidation resistance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
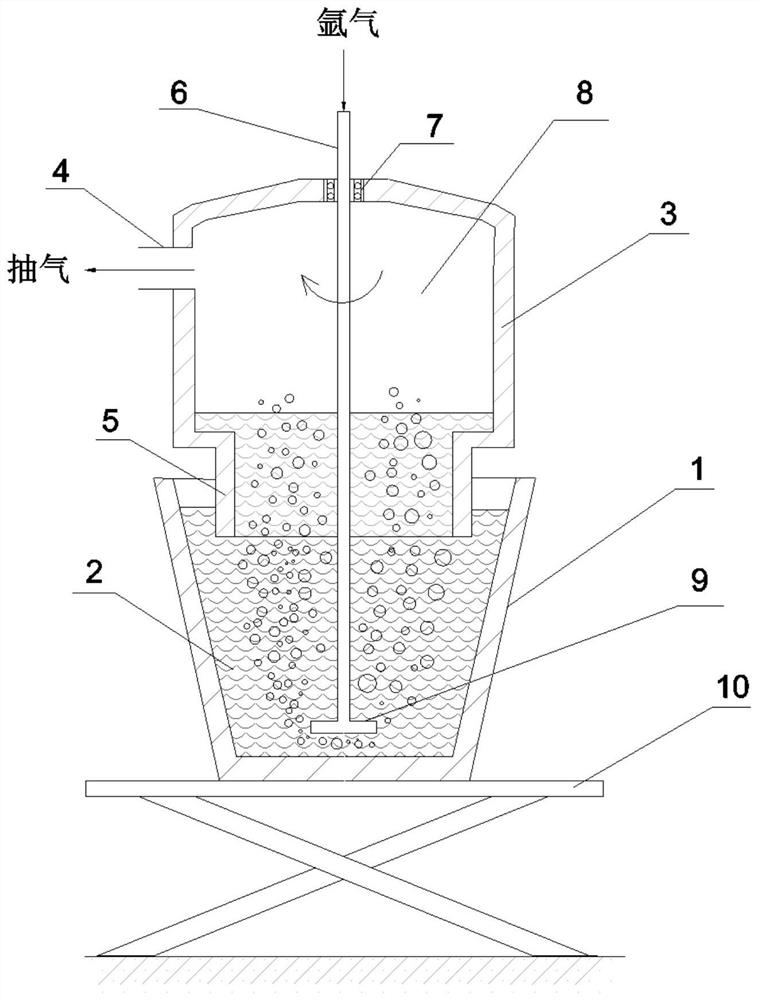
[0035] Such as figure 1 As shown, the pure aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate is melted at 700-760° C., the aluminum melting furnace 1 containing the aluminum melt 2 is placed on the hydraulic lifting table 10, and reaction salts and reaction aids are added for reaction. The hydraulic lifting table 10 is raised so that the dip tube 5 of the vacuum bag 3 arranged above the aluminum melting furnace 1 is immersed into the aluminum melt 2 . The vacuum chamber 8 of the vacuum bag 3 is evacuated through the pumping port 4, so that the aluminum melt 2 enters the vacuum bag 3 under atmospheric pressure.
[0036] At the same time, the aluminum melt is sprayed with argon rotation: the graphite rotor is lowered, and the rotating rod 6 of the graphite rotor passes through the sealed bearing 7 arranged on the top of the vacuum bag 3, passes through the vacuum chamber 8, and inserts the nozzle 9 into the bottom of the aluminum melt 2. At the bottom, argon gas is blown in through the midd...
Embodiment 2
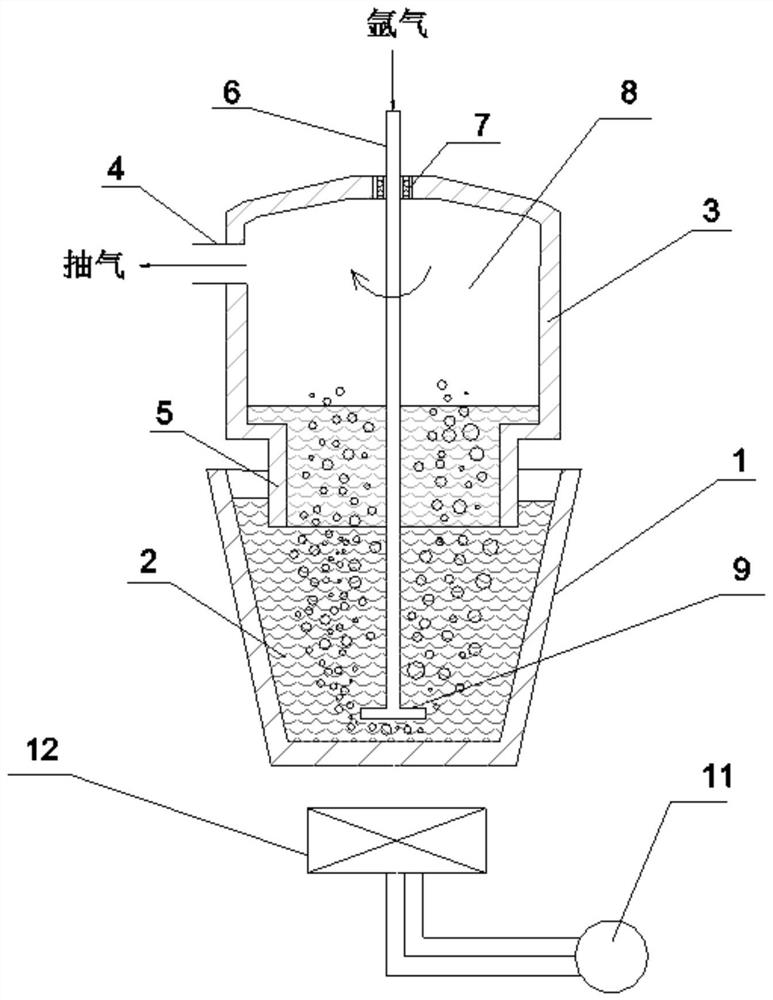
[0045] Such as figure 2 As shown, the pure aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate is melted at 700-760°C, the aluminum melt 2 is placed in the aluminum melting furnace 1, and reaction salts and reaction aids are added for reaction. The immersion tube 5 of the vacuum bag 3 arranged above the aluminum melting furnace 1 is immersed into the aluminum melt 2 . The vacuum chamber 8 of the vacuum bag 3 is evacuated through the pumping port 4, so that the aluminum melt 2 enters the vacuum bag 3 under atmospheric pressure.
[0046] At the same time, the aluminum melt is sprayed with argon rotation: the graphite rotor is lowered, and the rotating rod 6 of the graphite rotor passes through the sealed bearing 7 arranged on the top of the vacuum bag 3, passes through the vacuum chamber 8, and inserts the nozzle 9 into the bottom of the aluminum melt 2. At the bottom, argon gas is blown in through the middle hole of the rotating rod 6 and ejected from the rotating nozzle 9. The formed bubbl...
Embodiment 3
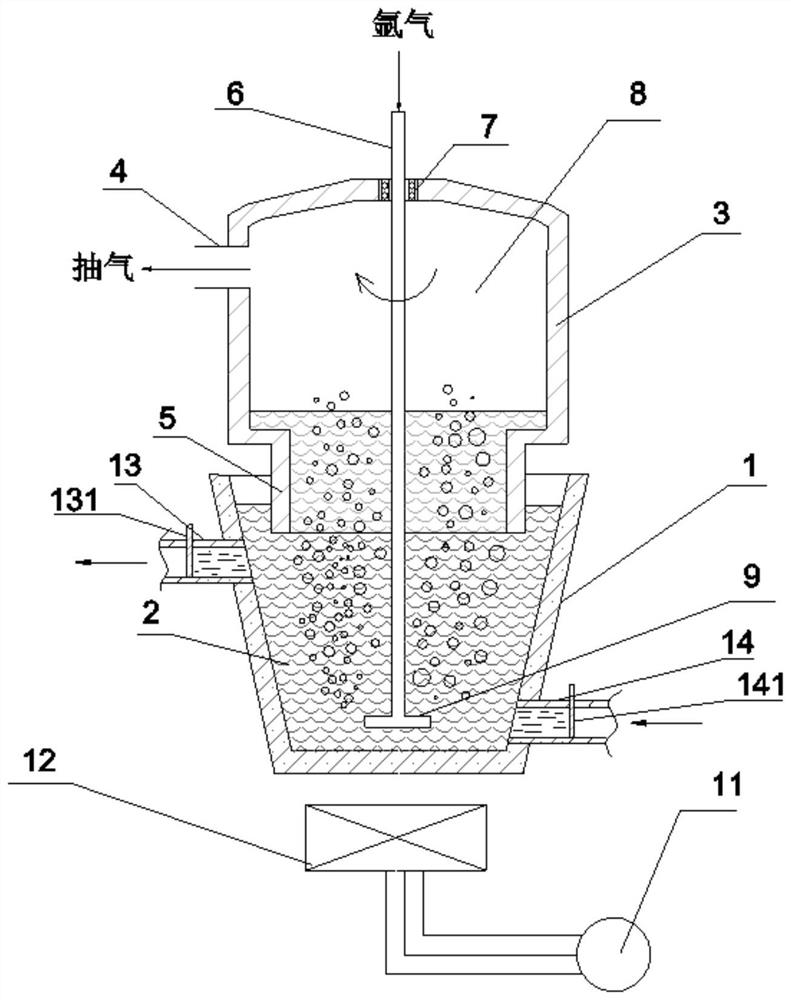
[0056] Such as image 3 As shown, the pure aluminum or aluminum alloy substrate is melted at 700-760°C, the aluminum melt 2 is placed in the aluminum melting furnace 1, and reaction salts and reaction aids are added for reaction. The immersion tube 5 of the vacuum bag 3 arranged above the aluminum melting furnace 1 is immersed into the aluminum melt 2 . The vacuum chamber 8 of the vacuum bag 3 is evacuated through the pumping port 4, so that the aluminum melt 2 enters the vacuum bag 3 under atmospheric pressure.
[0057] At the same time, the aluminum melt is sprayed with argon rotation: the graphite rotor is lowered, and the rotating rod 6 of the graphite rotor passes through the sealed bearing 7 arranged on the top of the vacuum bag 3, passes through the vacuum chamber 8, and inserts the nozzle 9 into the bottom of the aluminum melt 2. At the bottom, argon gas is blown in through the middle hole of the rotating rod 6 and ejected from the rotating nozzle 9. The formed bubble...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com