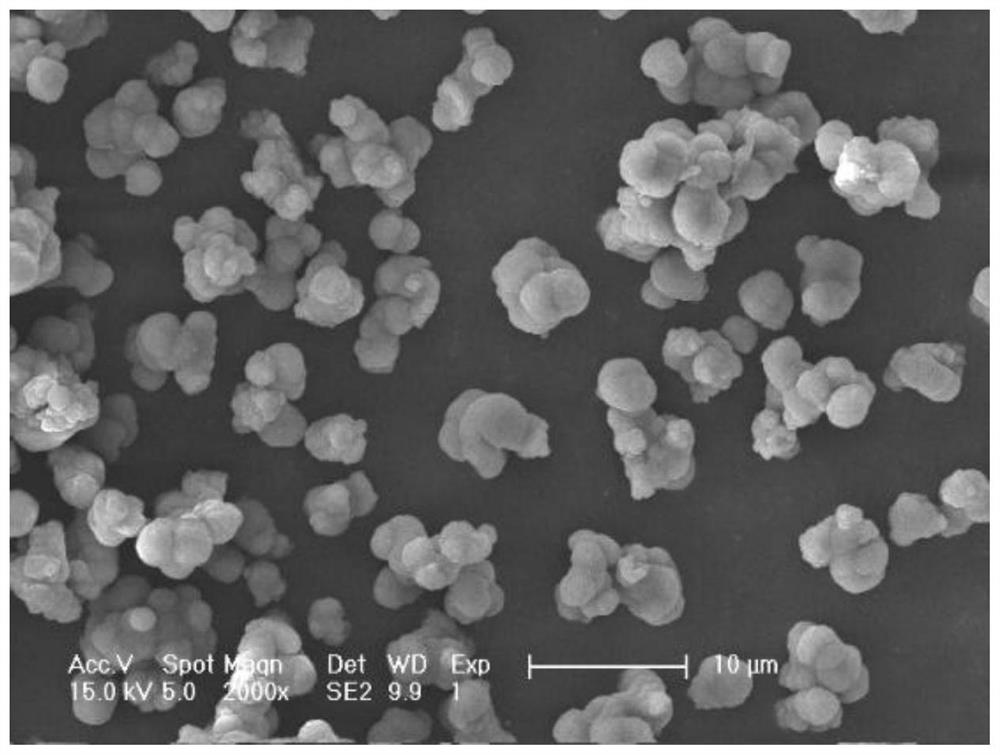
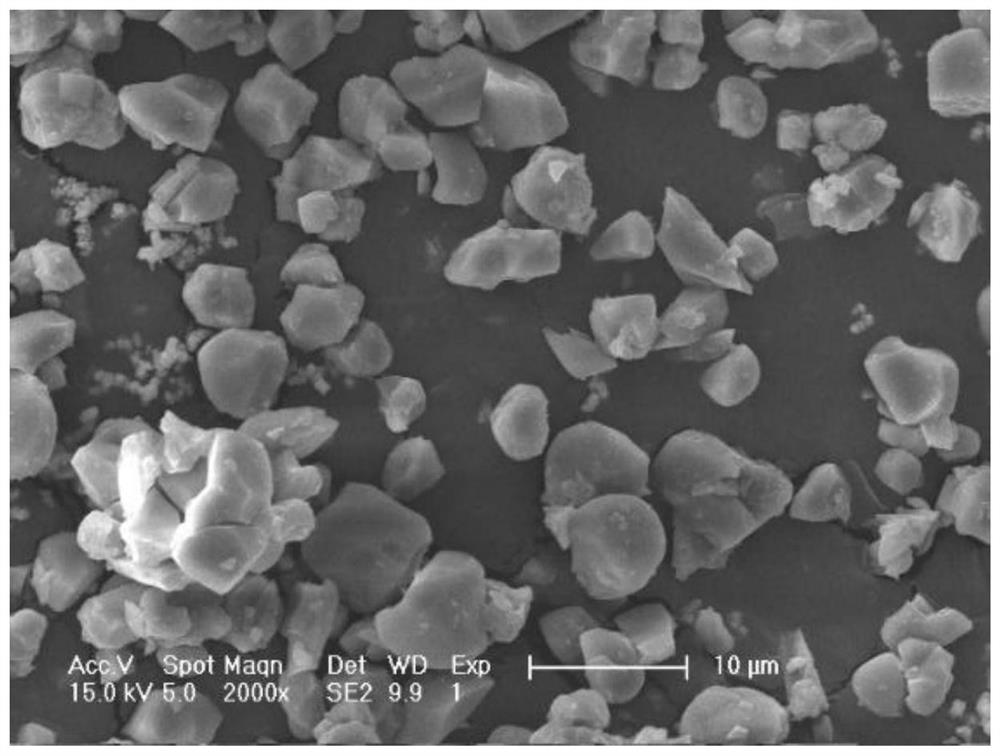
A method for saving energy and recycling hazardous waste containing iron and aluminum
A hazardous waste and energy-consumption technology, applied in the direction of protective devices against harmful chemicals, etc., can solve the problems of resin/extractant pollution, failure to separate iron, aluminum and heavy metals, high impurity content, etc., and achieve obvious solid-liquid separation , save usage, reduce the effect of reaction temperature
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0151] Example 1 Removal of iron and aluminum impurities in zinc-containing electroplating waste sludge
[0152] (1) Dissolve 20 g of zinc-containing electroplating waste sludge in 100 mL of a solution containing 2M nitric acid and 2M hydrochloric acid, heat at 80°C, and stir at 80rpm.
[0153](2) Add citric acid to the mixed acid solution in step (1), and the amount of citric acid added is 1 mL of citric acid every 30 times, until the gelatinous substance disappears completely, and the stirring system rotates evenly. After stirring for 2h, pass through a 1mm sieve, and collect the slurry under the sieve.
[0154] (3) Add 100 mL of a solution containing 2M nitric acid and 2M hydrochloric acid to the slurry obtained in step (2), continue to stir for 12h, then pass through a 0.45-micron filter cloth, collect the filtrate, and use NaOH to adjust the pH of the filtrate to 0.18, at this time The concentrations of iron, aluminum and zinc in the filtrate were 10.1, 3.2 and 3.2 g / L, ...
Embodiment 2
[0160] Embodiment 2 Removal of iron and aluminum impurities in strontium-containing waste residue
[0161] (1) Dissolve 20g of strontium-containing waste residue in 100mL of 4M hydrochloric acid solution, heat at 80°C, stir at 80rpm, and stir for 2h, no suspension is formed;
[0162] (2) Pass the mixture of step (1) through a 1mm sieve, and collect the slurry under the sieve. Add 100mL of 4M hydrochloric acid solution to the slurry, continue stirring for 12h, then pass through a 0.45-micron filter cloth to collect the filtrate, and use NaOH to adjust the pH of the filtrate to 0.18. At this time, the concentrations of iron, aluminum and strontium in the filtrate are 5.4 and 8.2, respectively. and 1.7g / L.
[0163] (3) Take 20 mL of the filtrate in step (2), heat it to 60° C. in a water bath, and add sodium dihydrogen phosphate. When the amount added is 1.0 g, the hydrodynamic radius is 0.62 microns by sampling and measuring. To the remaining solution, 9.0 g of sodium dihydroge...
experiment example 1
[0206] Experimental Example 1 Concentration determination of iron and aluminum impurities in zinc-containing electroplating waste sludge
[0207] The determination of iron, aluminum and zinc concentrations in the supernatant was carried out for Example 1 and Comparative Examples 1 to 5 respectively, and the test results were shown in Table 1.
[0208] It can be seen from Table 1 that the content of iron and aluminum in Comparative Example 1 and Comparative Example 2 is much higher than that in Example 1, indicating that the method of directly adjusting the pH of the solution with alkali and trying to remove impurities through the difference in pH of metal precipitation is effective. not good.
[0209] Further, according to Comparative Example 1 and Comparative Example 2, it can be seen that with the increase of pH, the metal is gradually precipitated, and the content of iron and aluminum in the supernatant is significantly reduced.
[0210] It can be seen from Example 1 and C...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com