Path planning method and industrial robot
An industrial robot and path planning technology, applied in manipulators, manufacturing tools, program-controlled manipulators, etc., can solve problems such as low efficiency, inability to automatically identify obstacles, and low accuracy, avoiding redundant calculations, and improving obstacle avoidance and path planning. The effect of efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
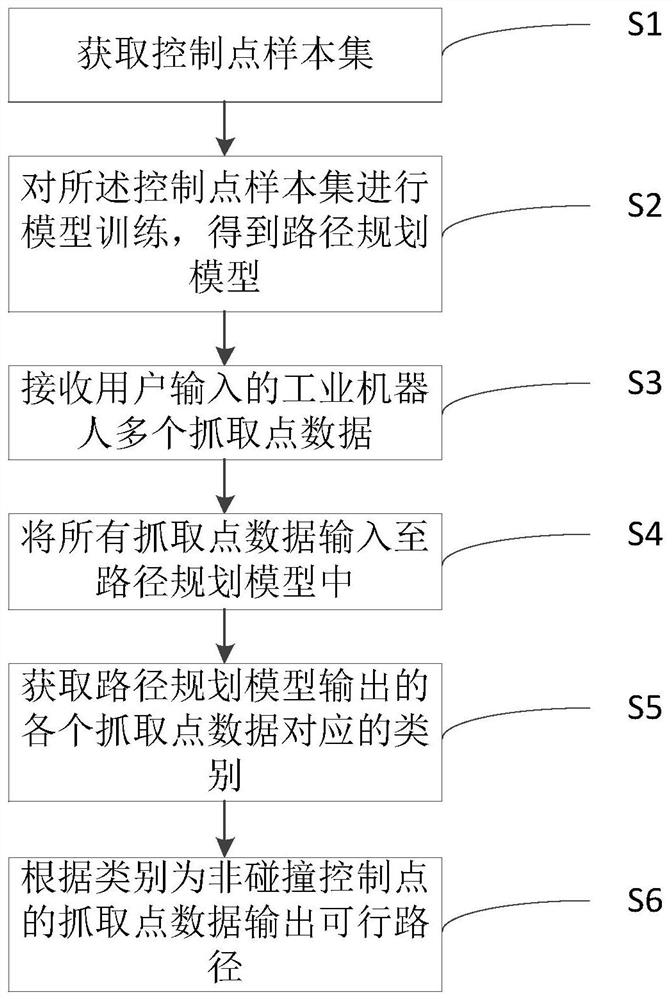
[0055] A path planning method, see figure 1 , including the following steps:
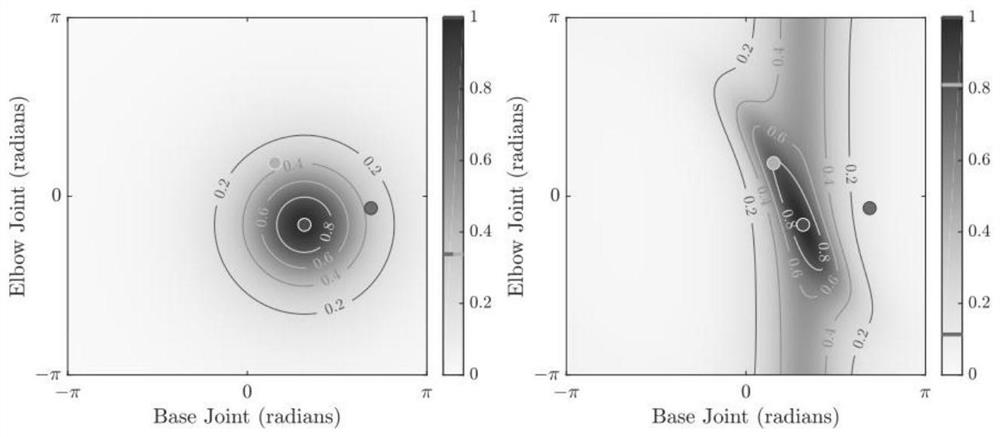
[0056] S1: Obtain a control point sample set; the samples in the control point sample set include historical grab point data and their categories of industrial robots; the categories are collision control points or non-collision control points, such as figure 2 shown;
[0057] Specifically, the historical grab point data is the position x of the end axis of the industrial robot n , where x n ∈R D , D is the dimension of the vector space R in the real number field, n takes a value from 1 to N, and N is the number of end axes of the industrial robot. The position x of the end axis of the industrial robot n Visual recognition technology can be used to obtain the pose of the flange at the end of the robot and the pose of the workpiece through image data and point cloud data.
[0058] The category is y n , where y n ∈{1,-1}; when y n = 1, the category is a non-collision control point, that is, ...
Embodiment 2
[0090] An industrial robot includes a processor and a memory, the processor and the memory are connected to each other, wherein the memory is used to store a computer program, the computer program includes program instructions, and the processor is configured to call the The program instruction executes the path planning method described in the first embodiment.
[0091] It should be understood that in the embodiment of the present invention, the so-called processor may be a central processing unit (Central Processing Unit, CPU), and the processor may also be other general-purpose processors, digital signal processors (Digital Signal Processor, DSP), dedicated integrated Circuit (Application Specific Integrated Circuit, ASIC), off-the-shelf programmable gate array (Field-Programmable Gate Array, FPGA) or other programmable logic devices, discrete gate or transistor logic devices, discrete hardware components, etc. A general-purpose processor may be a microprocessor, or the pro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com