Bacterial identification and typing analysis genomic database and identification and typing analysis methods
A bacterial identification and genome technology, applied in the field of bacterial genome identification and typing, can solve the problems of deviation of identification results, identification threats, difficulty in distinguishing the integrity of genome drafts and contamination, etc., to achieve the effect of improving speed and easy operation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
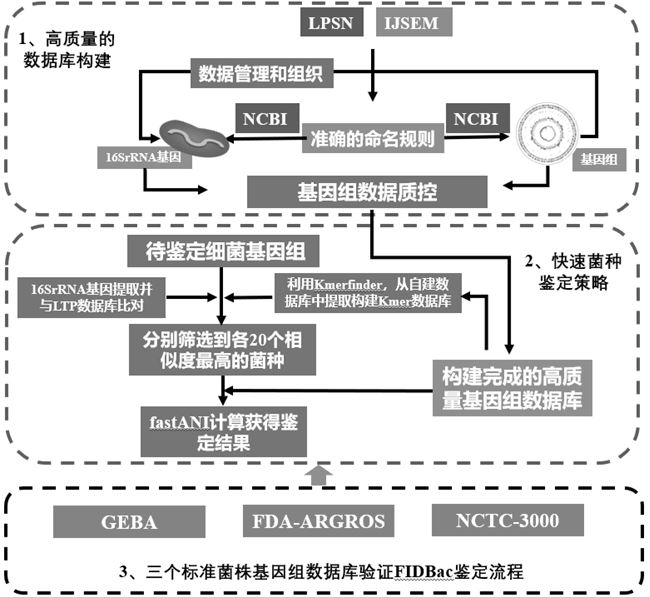
[0035] As shown in Figure 1, the construction process of the bacterial identification and typing analysis genome database MDBACDB of the present invention is as follows:
[0036] 1) Collect bacterial genome information from NCBI, and collect meta-information including "strain", "culture collection", "clone" and "annotation", establish a corresponding table of genome information and meta-information, and clarify the source of each genome.
[0037]2) Obtain a list of validly published bacterial name and type strains from the LPSN and consult Bergey's Handbook of Archaeal and Bacterial Systems and IJSEM's articles. After screening, the bacterial genomes of qualified strains are obtained and entered into the database for management.
[0038] 3) After screening the bacterial genome sequences in the library, the construction of MDBACDB is completed. Erroneous, low-quality bacterial genomes were filtered by the self-written Python program MDBacQCTools.
[0039] The steps for qualit...
Embodiment 2
[0043] As shown in Figure 1, the bacterial genome data analysis platform FIDBac of the present invention is analyzed as follows:
[0044] 1) Obtain the genome sequence GCF_008121515.1_genomic.fna of the published bacteria;
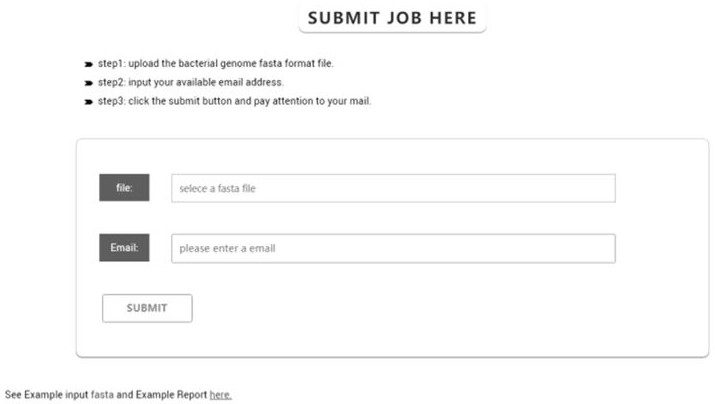
[0045] 2) Submit to the bacterial genome data analysis platform FIDBac ( image 3 ), and the identification analysis was performed by the self-compiled Python program FIDBac.
[0046] The analysis process of FIDBac is as follows: first, extract the 16S rRNA sequence in the genome of the bacteria to be identified (GCF_008121515.1_genomic.fna) and compare it with the LTP database; secondly, use Kmerfinder (v3.1) to extract from GCF_008121515.1_genomic.fna The K-mers of MDBACDB were compared with the K-mer database of MDBACDB; again, the top 20 bacterial ID numbers screened in the first two steps were obtained, and the genome sequences were extracted from the bacterial genome database MDBACDB, using fastANI (v1. 1) Calculate the ANI value of the query genom...
Embodiment 3
[0048] As shown in Figure 1, the bacterial genome data analysis platform FIDBac of the present invention is analyzed as follows:
[0049] 1) Obtain Staphylococcus capitis from NCBI, Bacillus cereus , Bacillus anthracis The genome sequences of GCA_001650475.1, GCA_002564865.1 and GCA_000725325.1;
[0050] 2) Extract the 16S rRNA gene sequence from the genome, use the 16S rRNA gene sequence and the reference database LTP for BLAST alignment and identification, and sort by Score value.
[0051] 3) Submit to the bacterial genome data analysis platform FIDBac ( image 3 ), and the identification analysis was performed by the self-compiled Python program FIDBac. The analysis process of FIDBac is as follows: first, the 16S rRNA sequences in the genomes of the bacteria to be identified (GCA_001650475.1.fna, GCA_002564865.1.fna and GCA_000725325.1.fna) are extracted and compared with the LTP database; secondly, Kmerfinder (v3 .1), the K-mers extracted from GCF_008121515.1_genomic...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com