Patient follow-up analysis
A follow-up, patient technology, applied in the field of patient follow-up analysis, which can solve problems such as restricted access rights and huge data storage capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
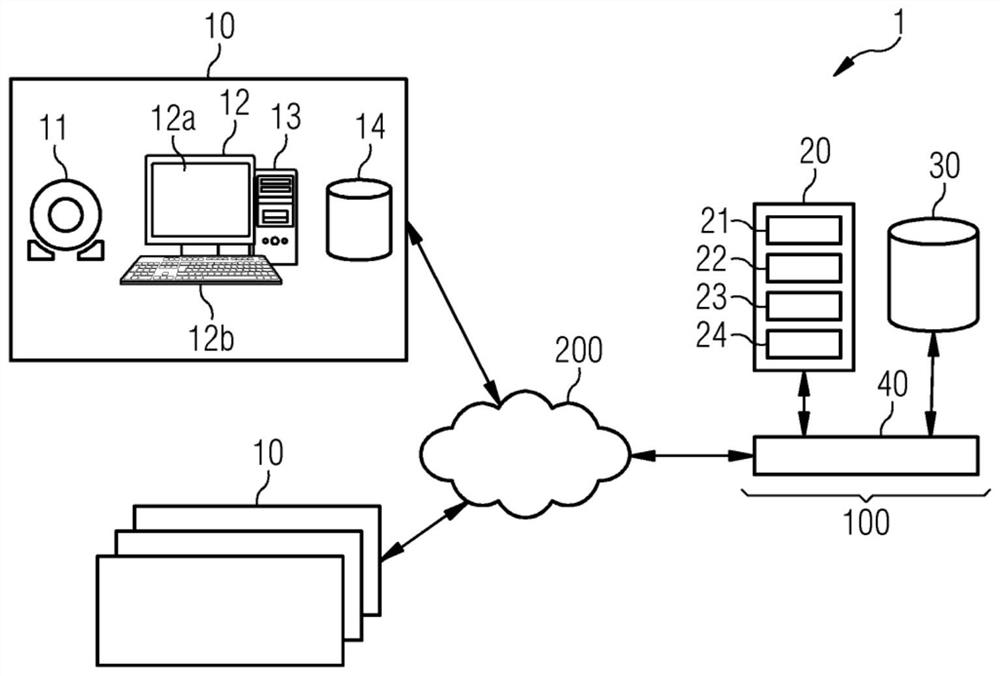
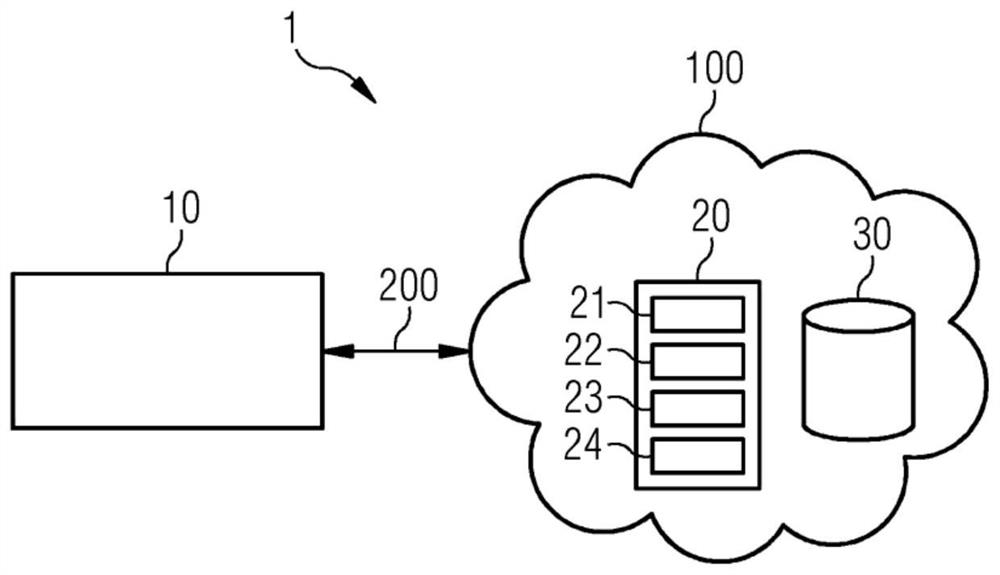
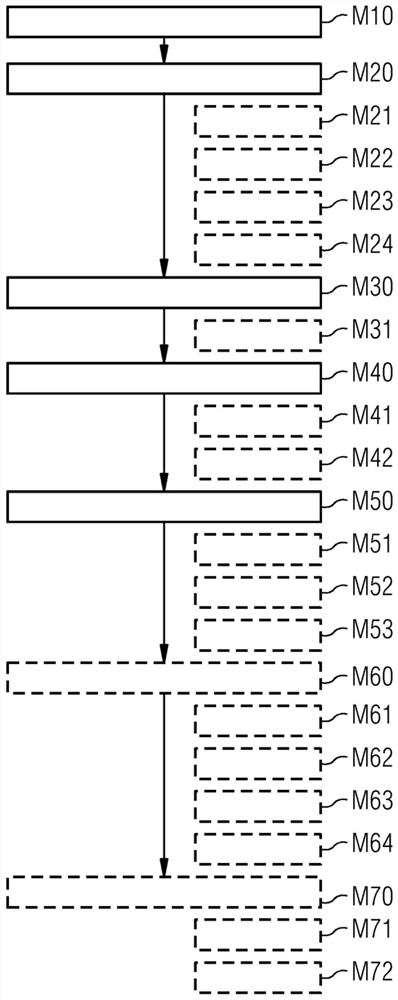
[0089] figure 1 A distributed environment 1 for identifying and quantifying changes in subsequent medical examinations according to an embodiment of the invention is depicted. Environment 1 is suitable for carrying out the method according to one or more embodiments, for example as referenced image 3 and Figure 4 method described further.
[0090] System 1 includes one or more clients 10 and a central processing system 100 . The client 10 and the central processing system 100 are connected via a network 200 . The central processing system 100 is generally configured to control and perform comparisons of data derived from subsequent medical image data in a distributed environment 1 . Client 10 may reside on one or more different local sites. A local site may, for example, relate to a clinical or medical environment such as a hospital or hospital group, laboratory, medical imaging center, clinic or institution. In this example, four clients 10 are shown for illustration....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com