A parallel computing method for multicast beamforming based on user subset selection
A beamforming and subset selection technology, applied in diversity/multi-antenna systems, channel estimation, space transmit diversity and other directions, can solve the problems of unclear physical meaning of the algorithm, the number of users should not be too large, and the problem lack of analysis, etc. Clear meaning, low problem dimension, and the effect of increasing computational complexity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0088] The following describes several preferred embodiments of the present invention with reference to the accompanying drawings, so as to make the technical content clearer and easier to understand. The present invention can be embodied in many different forms of embodiments, and the protection scope of the present invention is not limited to the embodiments mentioned herein.
[0089] In the drawings, components with the same structure are denoted by the same numerals, and components with similar structures or functions are denoted by similar numerals. The size and thickness of each component shown in the drawings are shown arbitrarily, and the present invention does not limit the size and thickness of each component. In order to make the illustration clearer, the thickness of parts is appropriately exaggerated in some places in the drawings.
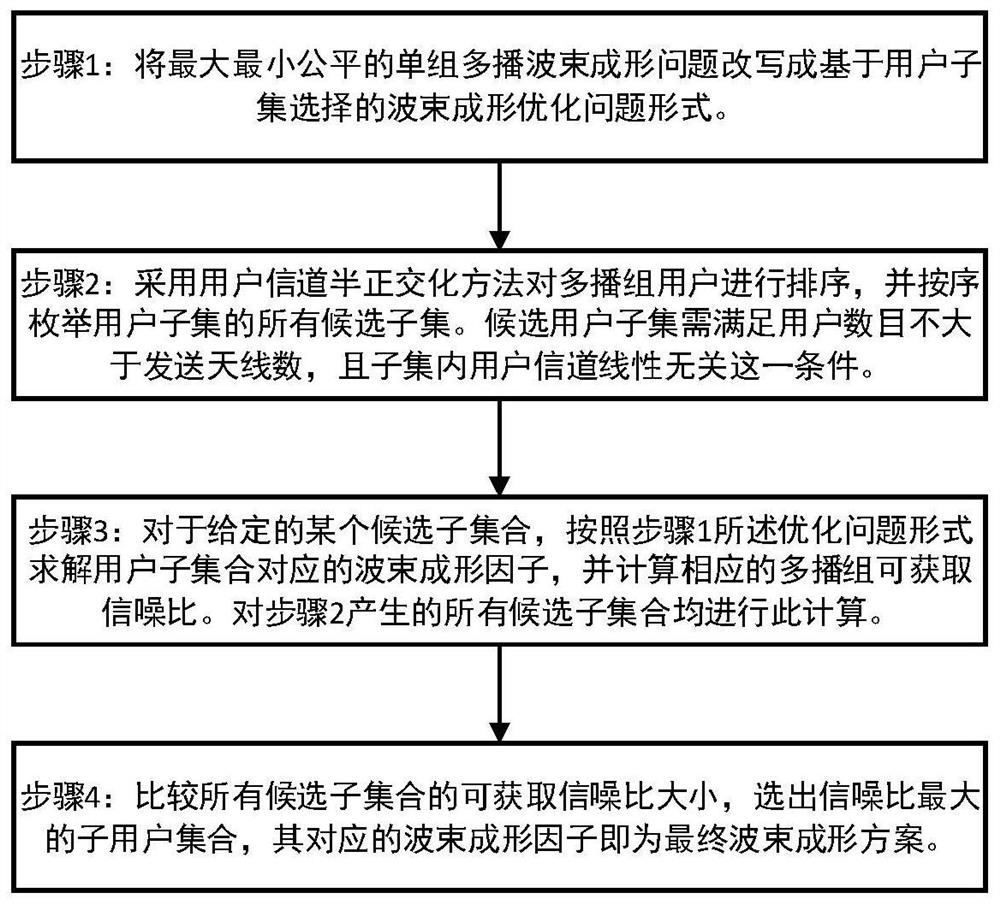
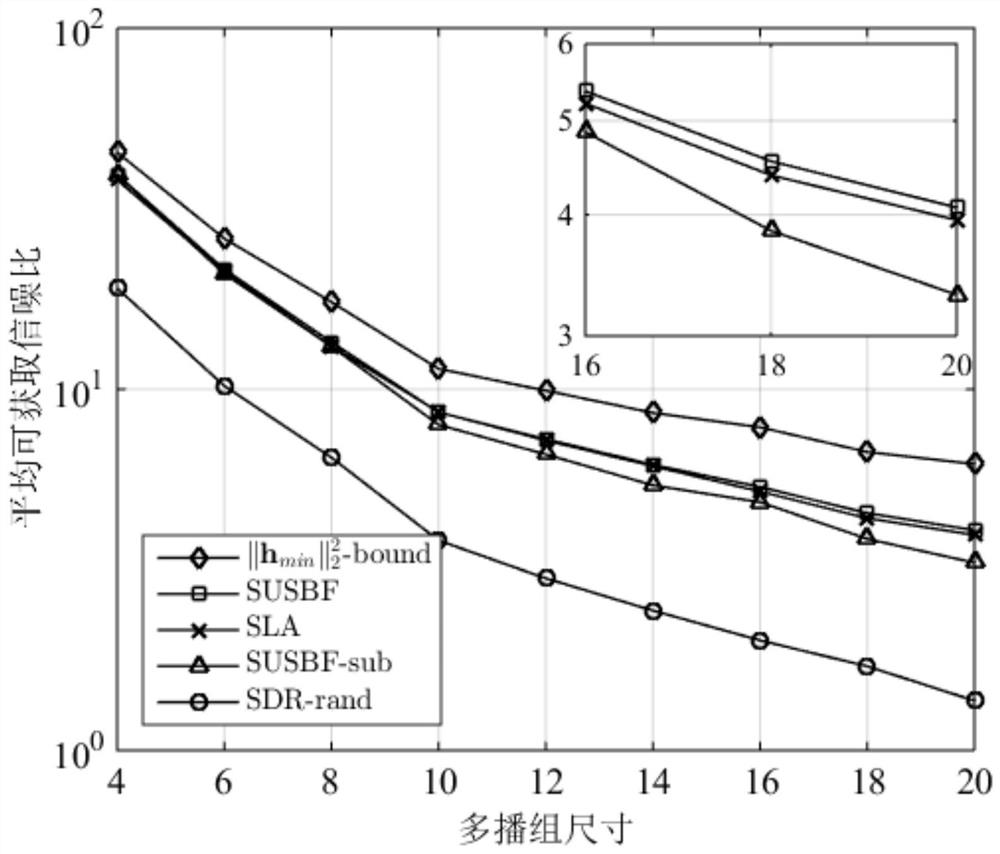
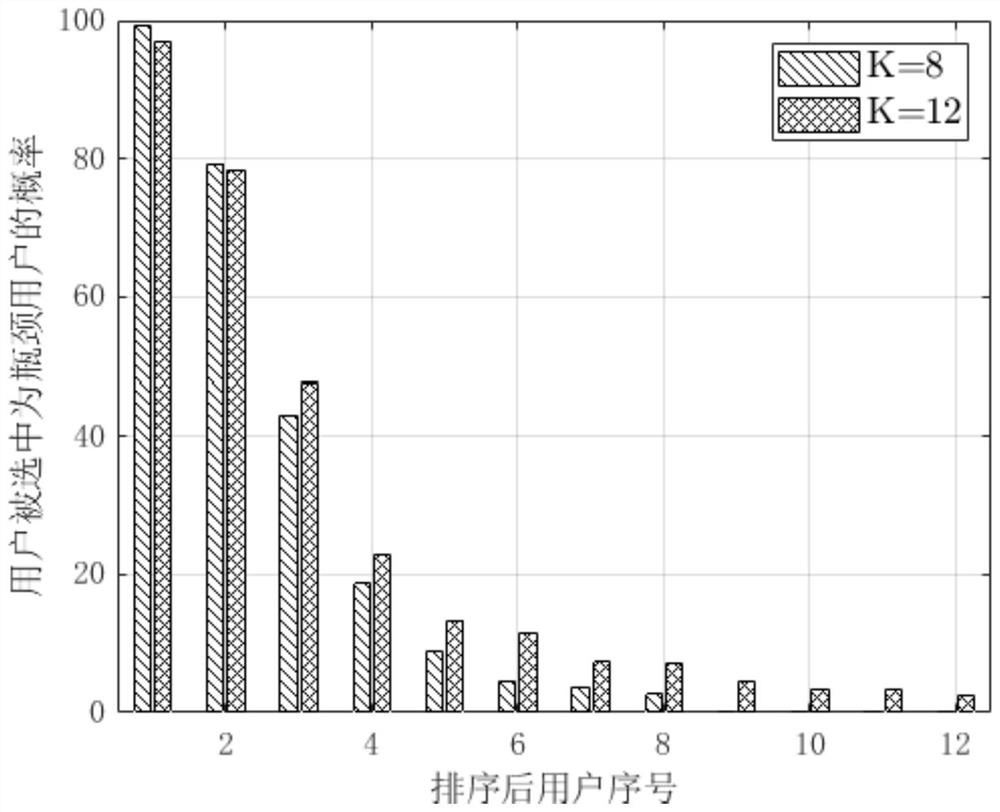
[0090] The multicast beamforming algorithm based on user subset selection proposed by the present invention comprises the following...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com