A secure multi-party computing method for consortium chains
A secure multi-party computing and alliance technology, applied in the field of information security, can solve problems such as low computing efficiency, achieve the effect of improving efficiency, improving efficiency and stability, and reducing the number of encryption and decryption times
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
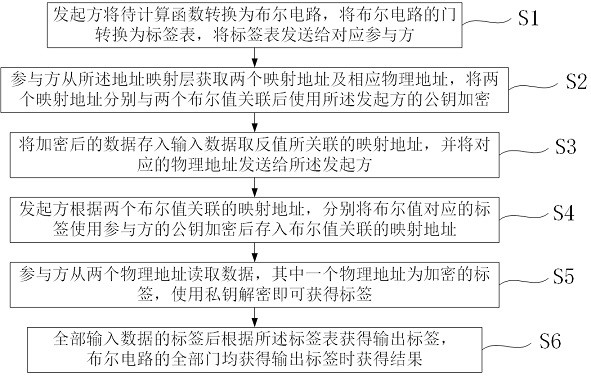
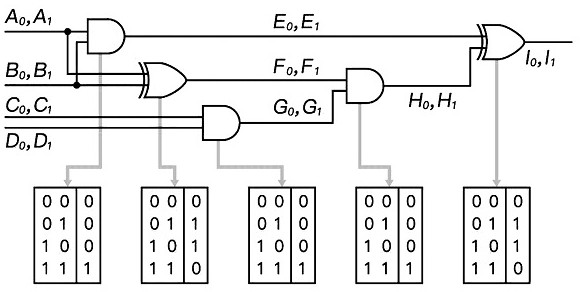
[0022] A secure multi-party computing method for a consortium chain, including an initiator P, several participants R, and an address mapping layer. The address mapping layer pre-establishes the mapping between mapped addresses and physical addresses. Please refer to the attached figure 1 , this method includes the following steps: S1) The initiator P converts the function to be calculated into a Boolean circuit, the initiator P converts the gate of the Boolean circuit into a label table, and sends the label table to the corresponding participant R, and the label table records the input label combination The mapping relationship with the output label. The initiator P of the secure multi-party computation converts the function to be calculated into a Boolean circuit, converts the input and output of each gate of the Boolean circuit into a label table, and realizes the encryption of the Boolean circuit, and then the participant R and the initiator P pass The mapped address laye...
Embodiment 2
[0044] A secure multi-party computing method for consortium chains. This embodiment further improves the mapping address. Please refer to the attached Figure 4 And Table 5, including: S31) In the mapping between the mapping address and the physical address established by the address mapping layer, each mapping address corresponds to several non-adjacent physical addresses, and the storage space pointed to by several physical addresses is a preset value; S32) When using the mapping address to store data, split the data into sub-data, and each sub-data is associated with the identifier of the first physical address; S33) Store each sub-data in a storage space corresponding to a physical address in order, for The physical address for reading data is the first physical address corresponding to the mapped address.
[0045] mapped address real address sidu8ejhu (12,3,42)、(12,3,44)、(12,3,48)、(12,3,52) w89iej31d (12,3,43)、(12,3,45)、(12,3,47)、(12,3,49) … …...
Embodiment 3
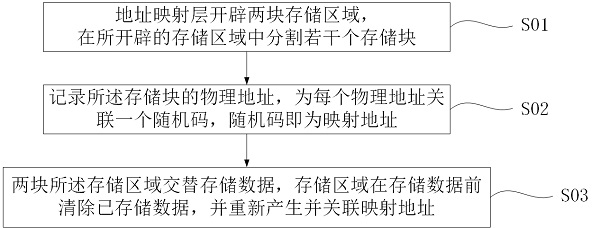
[0051] A secure multi-party computing method for a consortium chain. This embodiment provides a method for establishing a distributed address mapping layer. Please refer to the attached Figure 6 , each consortium chain node runs the address mapping protocol through an external consensus protocol. The address mapping protocol includes a mapping address generation protocol, a data writing protocol, and a data reading protocol. Specifically include: W01) The mapping address generation protocol periodically opens up the storage area, divides the storage area into several storage blocks of preset length, and records the physical address of each storage block; W02) generates several mapping addresses, and the mapping address is random Code, associate a preset number of physical addresses for each mapped address, and the associated physical addresses are non-adjacent physical addresses; W03) store the mapped address and its associated physical address as a mapped address entry; W04) ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com