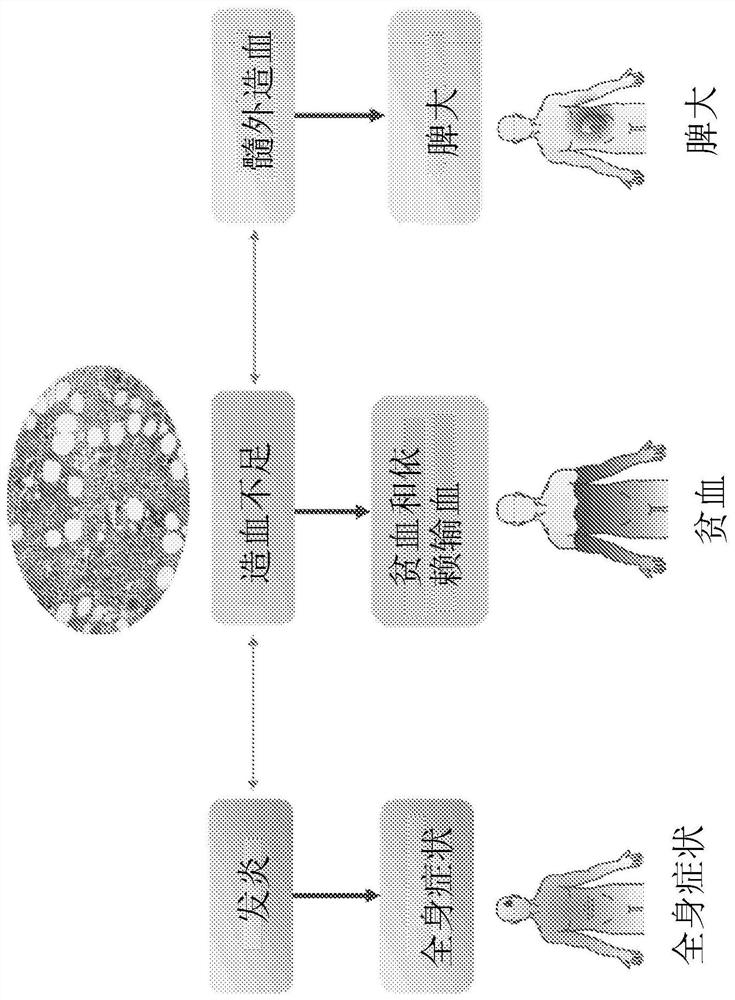
Platelet count-agnostic methods of treating myelofibrosis
A technology for bone marrow fibrosis and platelet count, which can be used in pharmaceutical formulations, medical preparations containing active ingredients, antitumor drugs, etc., and can solve problems such as dose reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0185] Example 1: SIMPLIFY-1 and SIMPLIFY-2
[0186] Mometinib (MMB) is a potent, selective, orally bioavailable small molecule inhibitor of JAK1, JAK2, and ACVR1 developed for the treatment of myelofibrosis (MF). However, in two phase III clinical trials (SIMPLIFY-1 and -2) in first-line and second-line treatment of MF, MMB was unable to meet both the predefined secondary endpoint of TSS response in SIMPLIFY-1 and the primary of SRR in SIMPLIFY-2 end.
[0187] In the SIMPLIFY-1 trial (NCT01969838), the effect of MMB and ruxolitinib (RUX) on JAK inhibitor-naïve patients with a platelet count ≥50x 10 9 / L in patients with myelofibrosis. Patients (N=432) with high-risk or intermediate-2 risk or symptomatic intermediate-1 risk myelofibrosis received 24 weeks of 200 mg MMB once daily or RUX 20 mg twice daily (or per label), All patients thereafter could receive open-label mometinib. Efficacy was measured with the aim of demonstrating the non-inferiority of MMB to RUX by sple...
Embodiment 2
[0193] Example 2: SIMPLIFY-1 and SIMPLIFY-2 Reanalysis
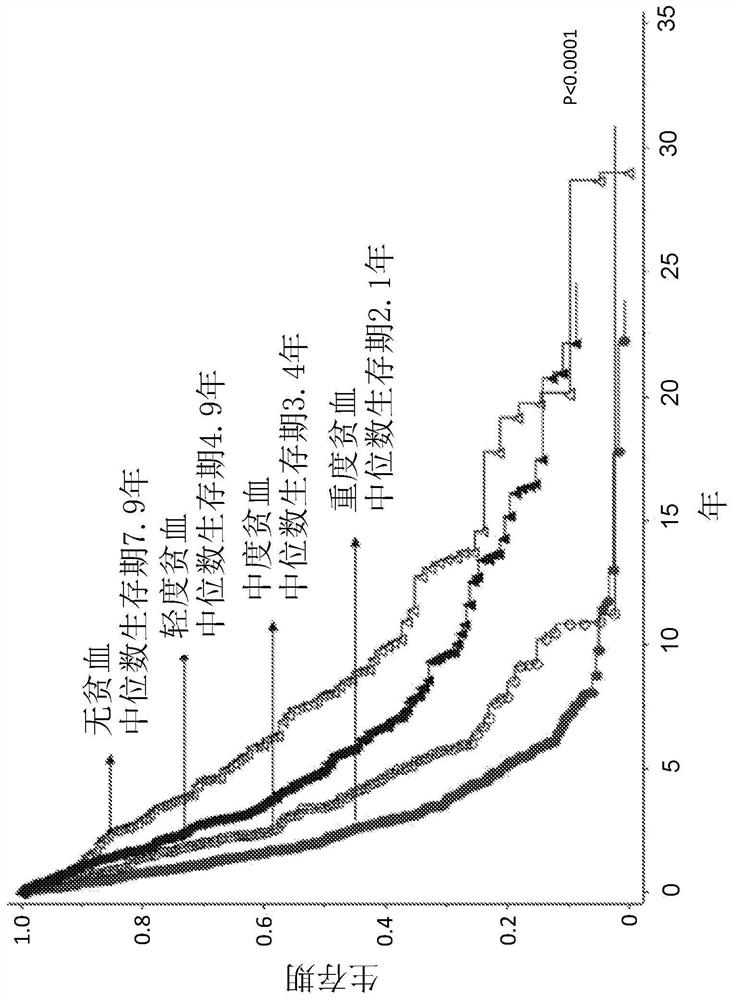
[0194] We reanalyzed data from the SIMPLIFY-1 and SIMPLIFY-2 trials and found mometinib was effective at platelet counts of 150x10 9 Effective in reducing spleen size (SSR), improving Total Symptom Score (TSS), and improving infusion-independence rates in patients with / L or less, without mometinib administration causing thrombocytopenia and thus requiring no intervention for thrombocytopenia Reduce or interrupt dose. Our reanalysis showed that MMB was effective in JAKi-naïve patients and as second-line therapy for RUX, providing reduced risk of thrombocytopenia in patients with or at risk of thrombocytopenia from underlying disease and current standard of care. Benefits of splenomegaly, improvement of symptoms associated with myelofibrosis, and increased rates of infusion independence.
[0195] Platelet levels during MMB or RUX treatment
[0196] Figure 31 Shown is a graph of mean (± standard error) platelet co...
Embodiment 3
[0261] Kinetic and time-to-event analyzes demonstrated that for mometinib-treated patients who did not receive Janus kinase inhibitors of patients with myelofibrosis, significantly reduced blood transfusion requirements compared with ruxolitinib head-to-head
[0262] Mometinib (MMB) is a potent, selective, orally bioavailable small molecule inhibitor of JAK1, JAK2, and ACVR1 developed for the treatment of intermediate- and high-risk myelofibrosis (MF). Systemic inflammation, integral to the pathogenesis of MF, results in increased ACVR1 activity, which in turn increases hepcidin secretion, leading to disturbances in iron homeostasis and iron-limiting anemia (Ganz T. "Systemic Iron Homeostasis:, Physiol Rev. 2013; 93:1721–41; and Langdon JM, Yates SC, Femnou LK et al. “Hepcidin-dependent and hepcidin-independent regulation of erythropoiesis in a mouse model of anemia of chronic inflammation”, Am J Hematol. 2014;89:470–9). Inhibition of ACVR1 by MMB is unique within the JAK ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Dilution degree | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com