MIMO spatial non-stationary channel estimation method based on image contour extraction
A technology for image contour extraction and channel estimation, which is applied in channel estimation, baseband system, baseband system components, etc., can solve the problems of missing and reconstructed channel performance loss, etc., to achieve guaranteed estimation performance, low computational complexity, and realize estimation with the effect of tracking
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
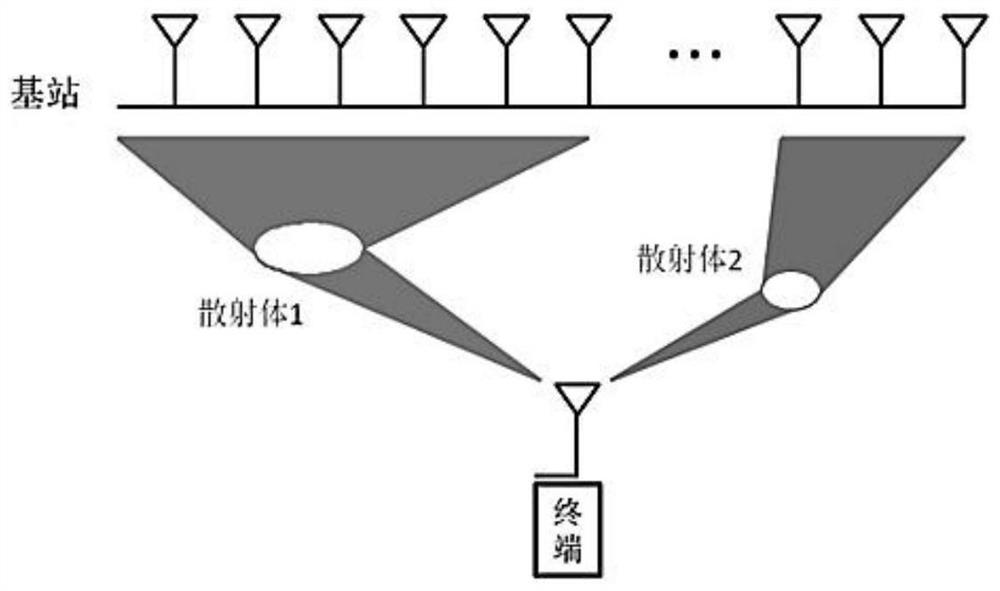
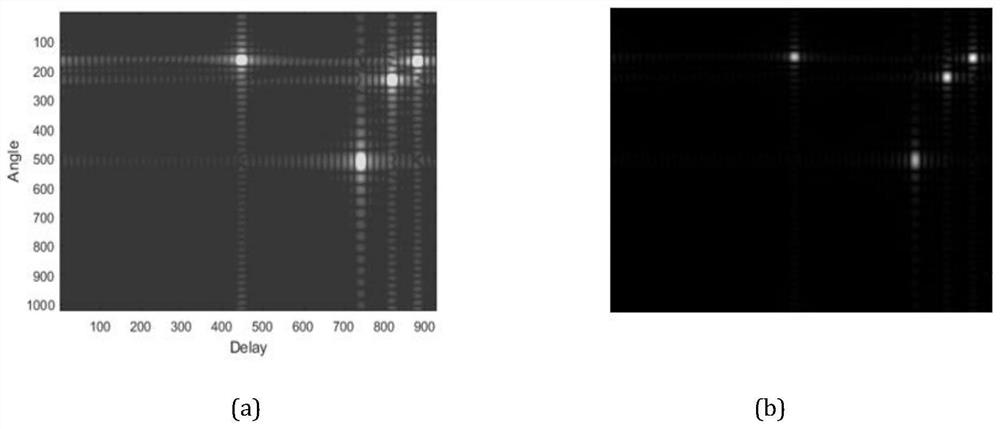
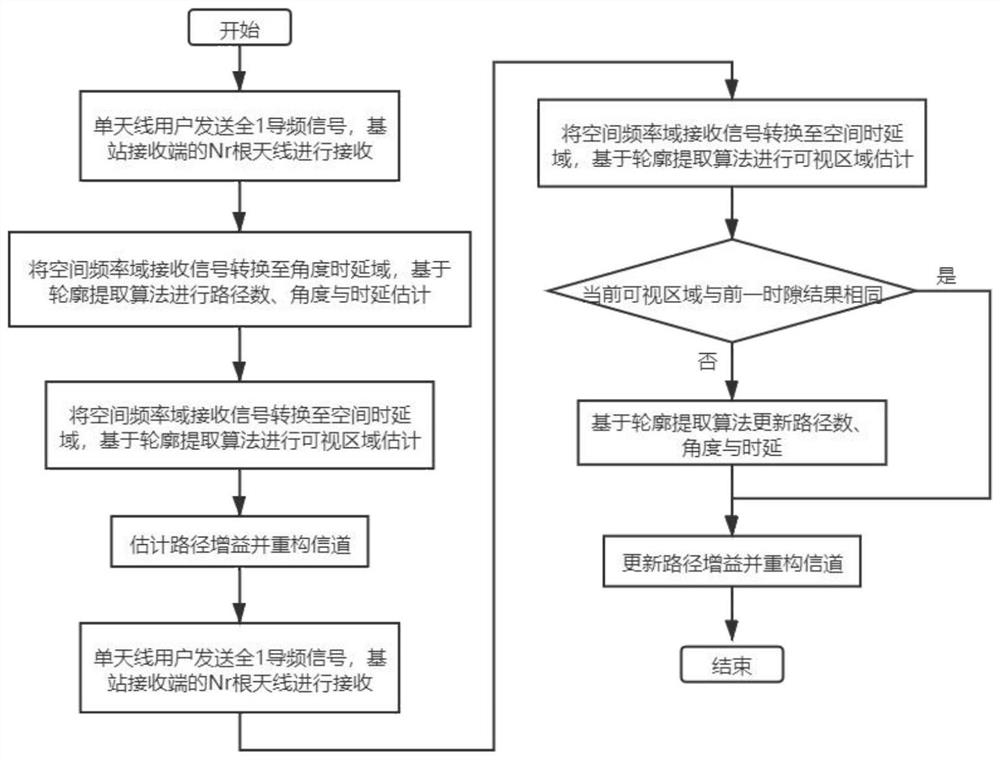
[0021] like Figure 4 As shown, this embodiment is based on a massive MIMO OFDM system with spatially non-stationary characteristics, when the base station receiving end is configured with N r The root transmit antenna forms a uniform linear array, and the antenna spacing is λ is the wavelength of the transmitted signal, and the transmitting end is a single-antenna terminal, then the received signal in the spatial frequency domain after Fourier transform Y=H+N, where: by N r ×N s The complex matrix H composed of elements is the massive MIMO fading correlation coefficient, N s is the number of subcarriers in the frequency domain.
[0022] For the convenience of explanation, what is sent in this embodiment is all 1 pilots, so the transmission signal is omitted here, and N is zero mean and unit variance additive white Gaussian noise, then the wireless channel model of the space non-stationary at both ends of the sending and receiving ends is: Where: L is the number of paths...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com