PM2.5 comprehensive domain space-time calculation inference method based on multi-source city big data
A big data and urban technology, applied in the direction of reasoning methods, complex mathematical operations, etc., can solve problems such as sampling deviation, lack of matching of time and space in training data, and achieve the effect of reducing pollution emissions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
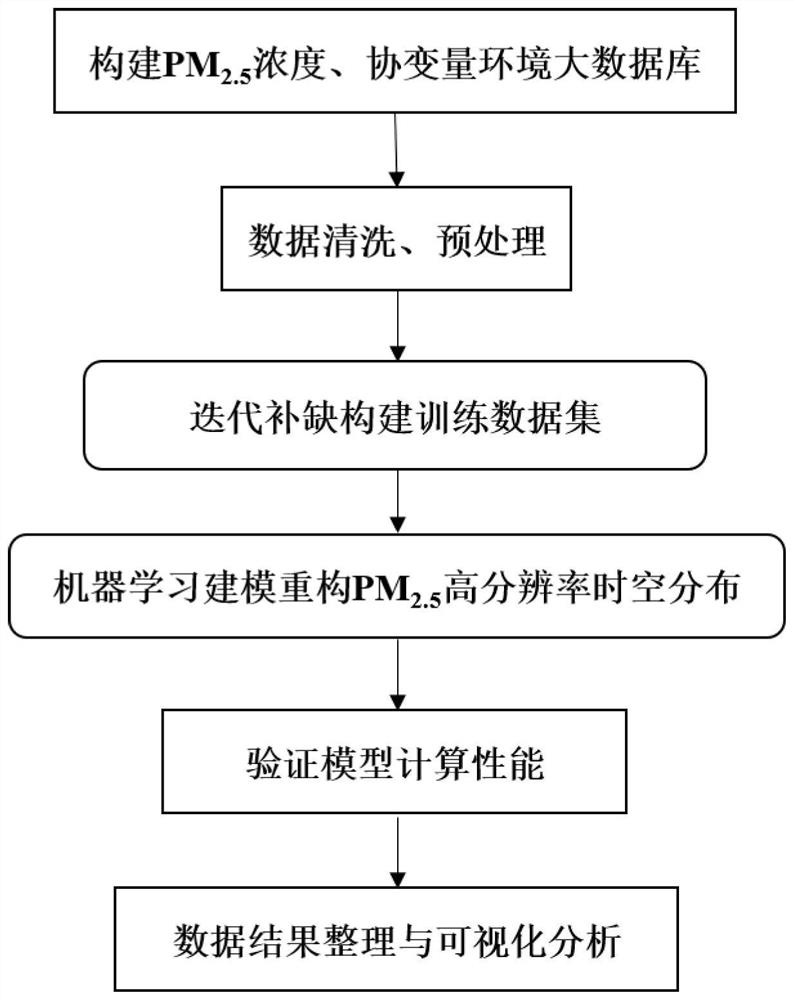
[0113] A certain city is an important industrial city in the Central Plains. Due to heavy industrial structure, energy structure partial to coal, unreasonable industrial layout, and slow environmental infrastructure construction, etc., it is facing unprecedented pressure to improve environmental quality in the early stage of the battle against environmental pollution. The primary pollutants are mainly particulate matter. PM for urban scale 2.5 The reconstruction of high-resolution spatio-temporal distribution is an important basis for fine-grained air quality control. Real-time discovery and location of high-potential pollution sources will help the city's air pollution prevention and control work.
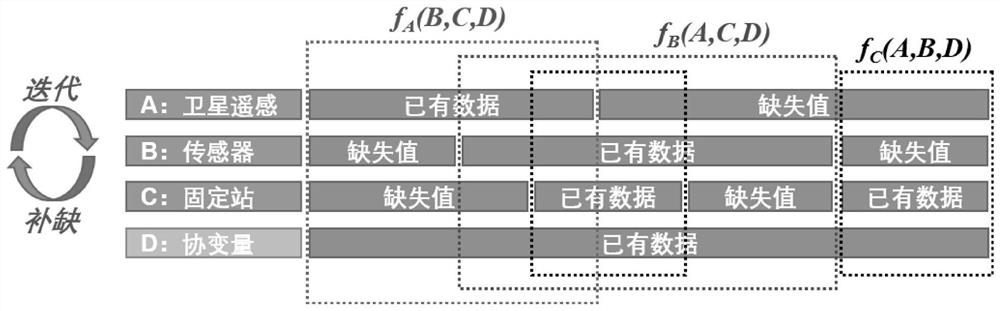
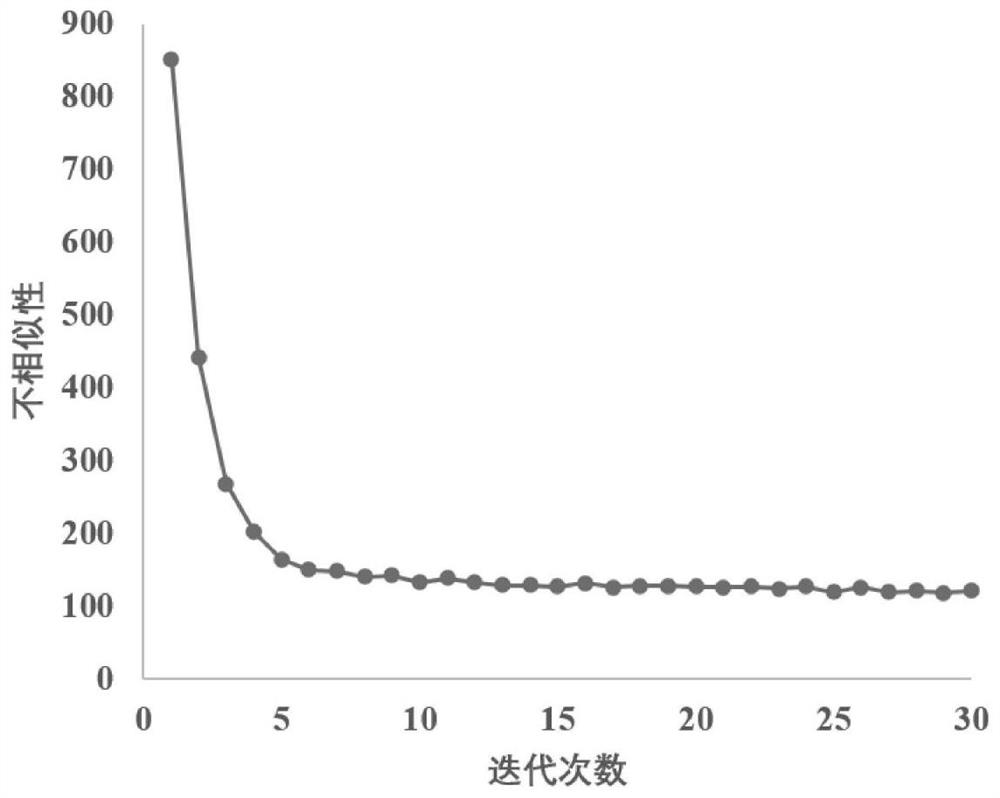
[0114] This embodiment utilizes iterative filling-gradient booster algorithm (II-GBM), based on the XGBoost machine learning calculation module, for the ground PM monitored by fixed stations and sensors 2.5 Concentration, as well as the multi-angle atmospheric correction algorith...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com