Path planning method based on improved A* algorithm
A path planning and local path planning technology, applied in two-dimensional position/channel control, vehicle position/route/altitude control, non-electric variable control, etc. question
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
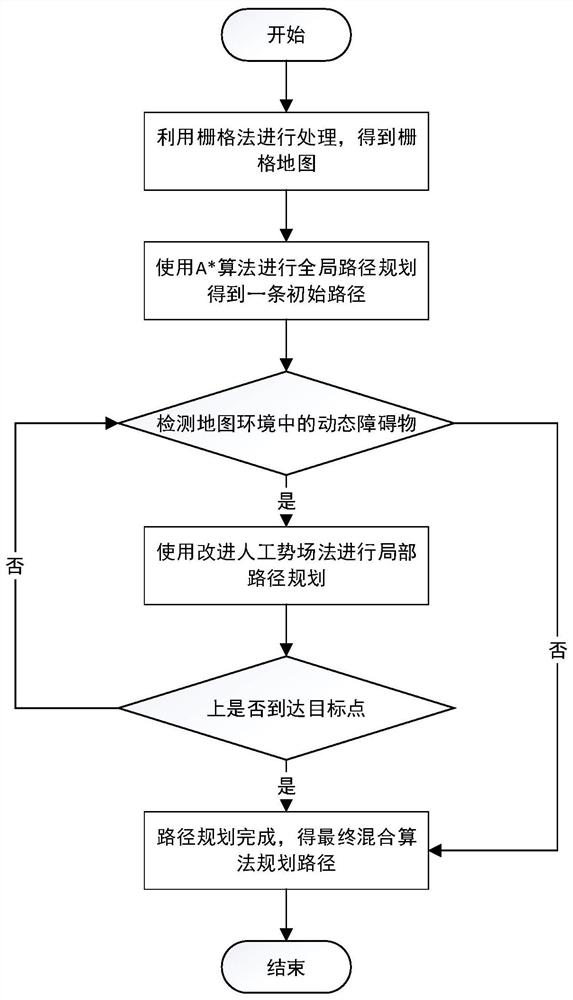
[0053] A kind of path planning method based on the improved A* algorithm of this embodiment, such as figure 1 As shown, the method is realized through the following steps: the method refers to processing the road condition map collected by a grid method to obtain a grid map; after that, using the ant colony algorithm to optimize and improve the A* algorithm; after that, The artificial potential field method is used for local path planning, and the artificial potential field method is improved and optimized for the shortcomings of local minima and unreachable targets; after that, a hybrid path planning algorithm is designed by combining the improved A* algorithm with the artificial potential field method , to provide a suitable control algorithm for the subsequent vehicle path planning; after that, by adopting a suitable path planning algorithm, the system automatically plans a feasible path, and the vehicle avoids obstacles according to the path, so as to reach the target posit...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0055] The difference from Embodiment 1 is that a path planning method based on the improved A* algorithm in this embodiment, the hybrid path planning algorithm designed by combining the improved A* algorithm with the artificial potential field method specifically includes:
[0056] Step 1, using the improved A* algorithm for global path planning to obtain an initial path;
[0057] Step 2. Detect whether there are dynamic obstacles in the map environment;
[0058] If so, use the improved artificial potential field method for local path planning, and improve and optimize it for the shortcomings of local minima and unreachable targets;
[0059] If not, it is considered that the path planning is completed, and the final hybrid algorithm planning path is obtained.
[0060] Step 3. After using the improved artificial potential field method for local path planning, judge whether to reach the destination point;
[0061] If not, return to step 2;
[0062] If so, it is considered th...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0067] The difference from the specific embodiment 1 or 2 is that, in the path planning method based on the improved A* algorithm in this embodiment, in the step of using the improved artificial potential field method for local path planning, since the artificial potential field method performs local In path planning, there are two defects of local minimum and target unreachable.
[0068] local minima problem
[0069] When using the artificial potential field method for local path planning, in the force field, the vehicle is subjected to the repulsion of obstacles and the attraction of the target point to make it travel along the path with a lower potential field in the environment, thereby avoiding obstacles reach the target location. However, sometimes, the repulsive force and the gravitational force received by the guided vehicle are 0 after synthesis, and the guided vehicle no longer moves. At this time, the position of the guided vehicle is not the minimum point of the g...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com