Biped robot dance balance control method and device and biped robot
A biped robot, balance control technology, applied in the direction of program control manipulators, manipulators, manufacturing tools, etc., can solve problems such as multi-time, difficult dynamic stability of the robot, and achieve the effect of strong anti-interference ability.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
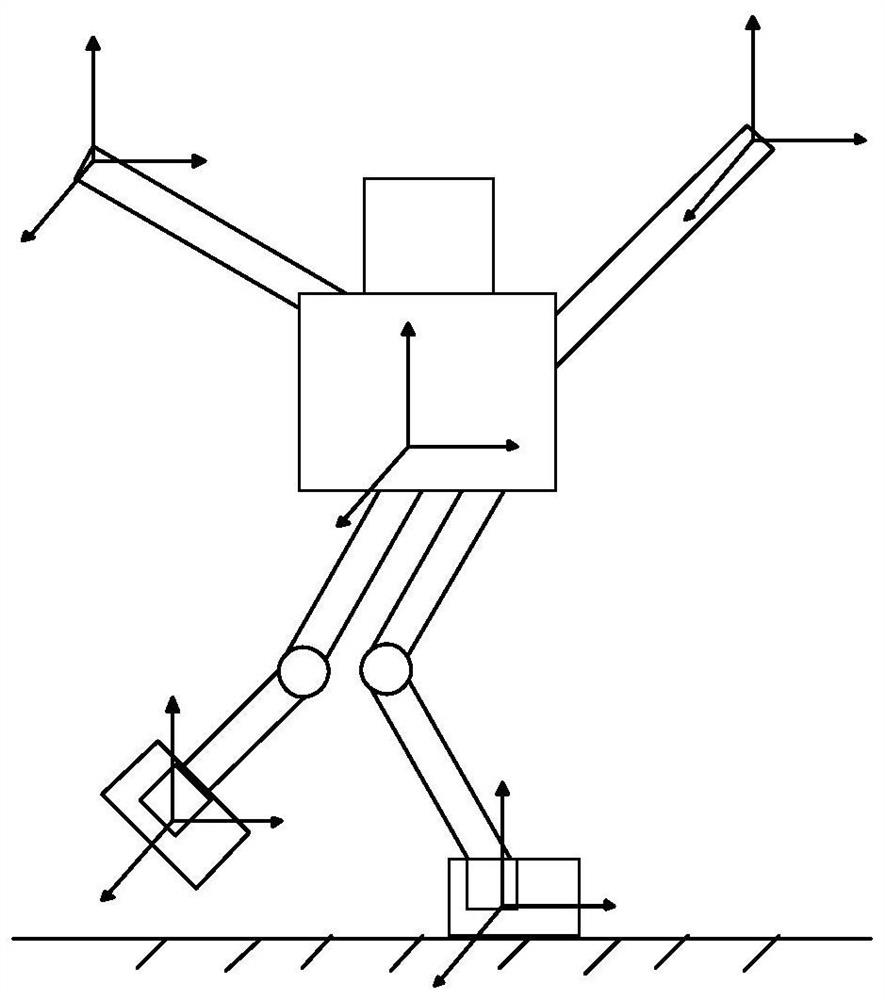
[0053] Please refer to figure 1 and 2 , this embodiment proposes a biped robot dance balance control method, which can be applied to such as figure 1 The robot dancing scene shown. This method is based on ZMP and momentum for balance control, which can realize the stability of the biped robot under the tracking of dance movements.
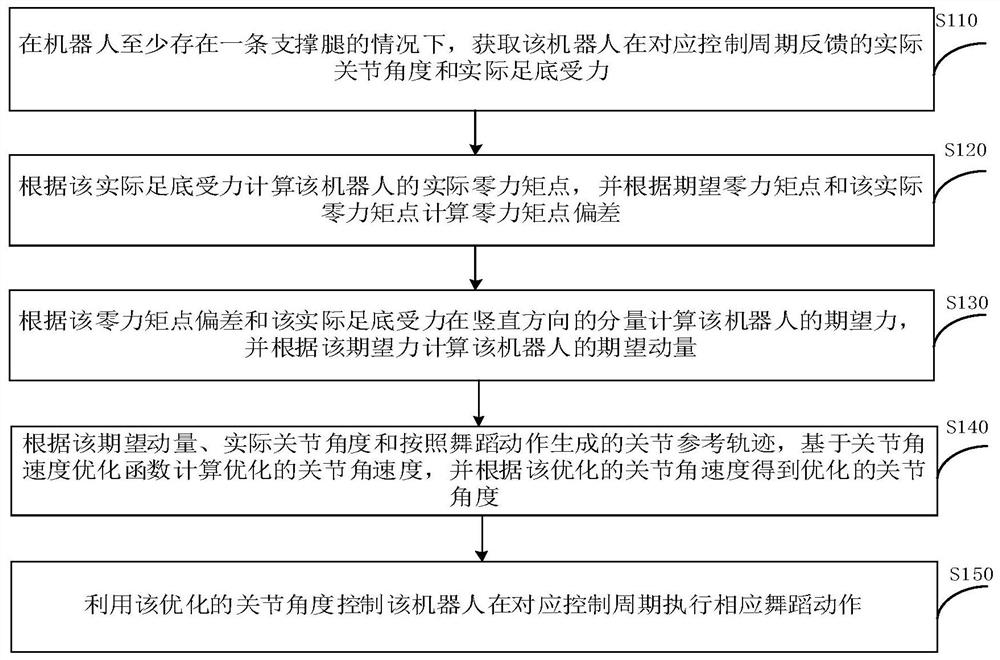
[0054] Exemplarily, as figure 2 Shown, this biped robot dance balance control method comprises:
[0055] Step S110, if the robot has at least one supporting leg, obtain the actual joint angle and the actual plantar force fed back by the robot in the corresponding control cycle.
[0056] In this embodiment, when the whole body of the biped robot performs dance movements, it will always be ensured that at least one leg is in a supporting state (called the supporting leg), and the supporting leg will be in the original position, that is, no position shift will occur. It can be understood that at some moment, the supporting leg of the robot can b...
Embodiment 2
[0119] Please refer to Figure 5 , based on the method of the above-mentioned embodiment 1, this embodiment proposes a biped robot dance balance control device 100. Exemplarily, the biped robot dance balance control device 100 includes:
[0120] The obtaining module 110 is configured to obtain the actual joint angle and the actual plantar force fed back by the robot in a corresponding control cycle when there is at least one supporting leg of the robot.
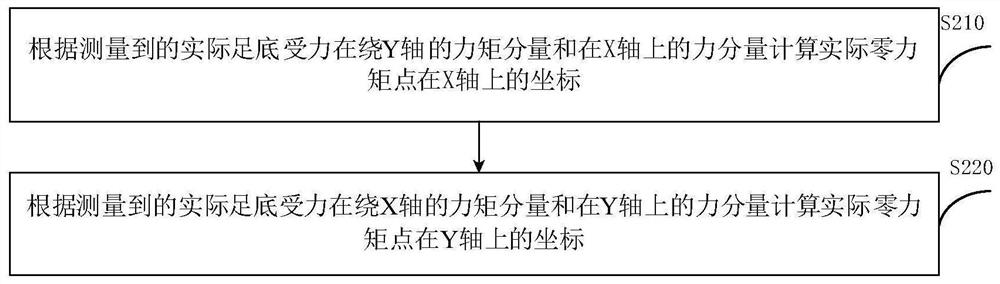
[0121] The deviation calculation module 120 is used to calculate the actual zero-moment point of the robot according to the actual plantar force, and calculate the deviation of the zero-moment point according to the expected zero-moment point and the actual zero-moment point.
[0122] The momentum calculation module 130 is used to calculate the expected force of the robot's ankle according to the deviation of the zero moment point and the vertical component of the actual plantar force, and calculate the expected momentum of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com