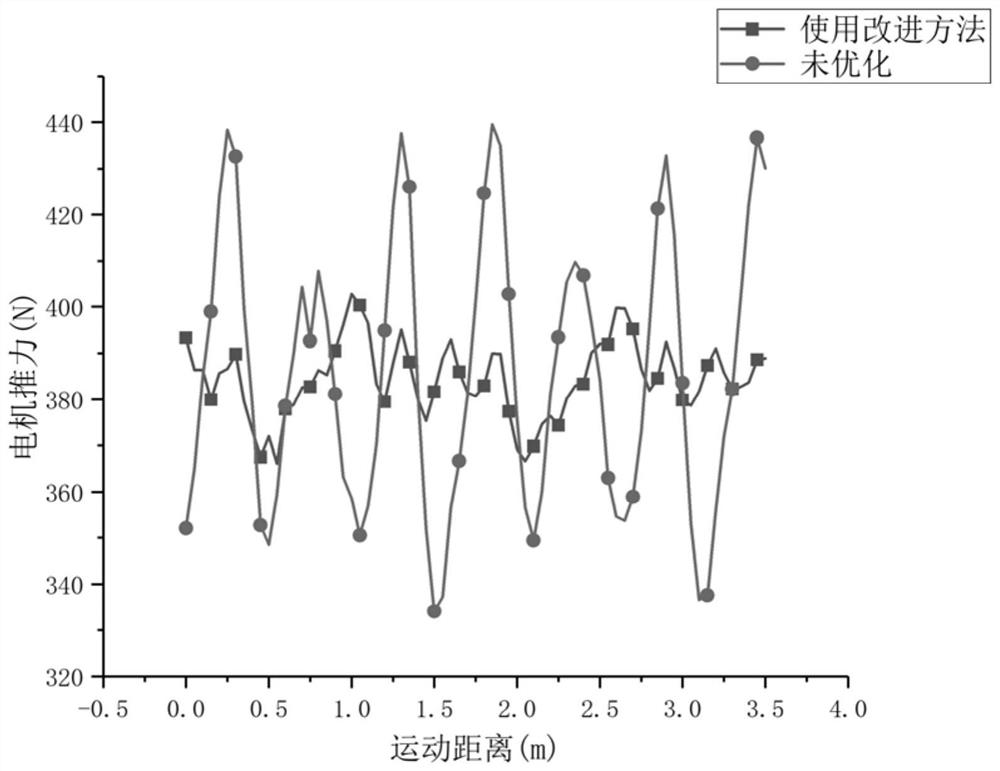
Optimal Design Method for Thrust Fluctuation of Moving Magnet Primary Discontinuous Segmented Linear Motor
A segmented straight line, optimized design technology, applied in the direction of magnetic circuit shape/style/structure, electromechanical devices, electrical components, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the accuracy and reliability of the control system, and achieve improved dynamic performance, accuracy and reliability Sex, the effect of weakening the thrust fluctuation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
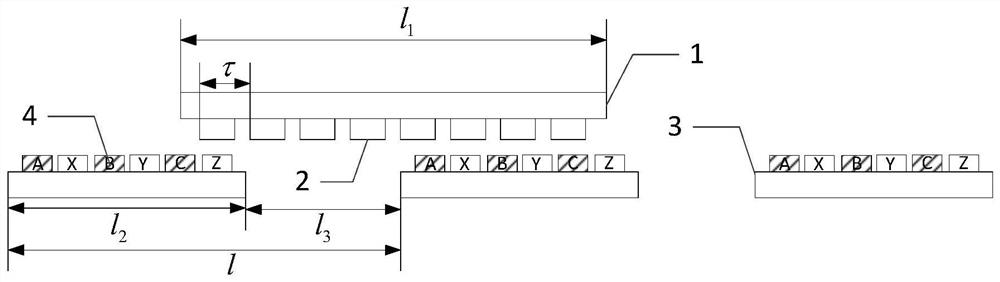
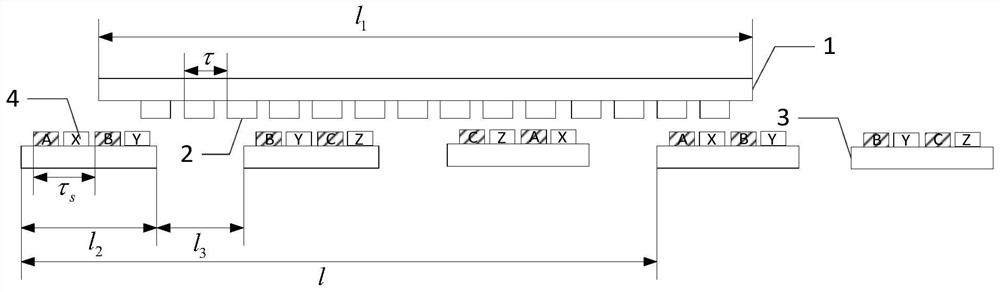
[0018] Embodiment 1: Combining Figure 1 to Figure 3 This embodiment will be described. The thrust fluctuation optimization design method of the moving magnet primary discontinuous segmented linear motor described in this embodiment is optimized for the topology structure of the moving magnet primary discontinuous segmented linear motor. ;
[0019] The topological structure of the moving magnet primary discontinuous segmented linear motor includes a plurality of stators and movers; the plurality of stators are arranged at equal intervals, and the movers are vertically arranged directly above the plurality of stators and extend along the Movement in the direction of the arrangement of multiple stators;
[0020] The structures of the plurality of stators are the same, and the stator includes a primary iron yoke 3 and a plurality of primary windings 4; the plurality of primary windings 4 constitute a primary winding unit and are arranged just above the primary iron yoke 3;
[0...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0029] Specific embodiment 2: This embodiment further defines the thrust fluctuation optimization design method of the moving magnet primary discontinuous segmented linear motor described in the specific embodiment 1. In this embodiment, the effective length of the secondary iron yoke 1 is further limited. The specific method of optimization is:
[0030] Control the secondary iron yoke 1 to satisfy:
[0031] l 1 =ml 2
[0032] where, l 1 is the effective length of the secondary iron yoke 1, m is an integer greater than 1, l 2 is the effective length of the primary iron yoke 3 .
[0033] In this embodiment, the effective length of the secondary iron yoke 1 is controlled to be an integer multiple of the effective length of the primary iron yoke 3; the effective length of the secondary iron yoke 1 is far greater than the effective length of the primary iron yoke 3 to ensure the consistency of the phase sequence .
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0034] Embodiment 3: This embodiment further defines the thrust fluctuation optimization design method of the moving magnet primary discontinuous segmented linear motor described in Embodiment 2. In this embodiment, the installation interval of the primary iron yoke 3 is optimized. The specific method is:
[0035] Control the spacing between the two primary winding units to satisfy:
[0036] l=l 1
[0037] Among them, l is the distance between two primary winding units;
[0038] The distance l between the two primary winding units satisfies:
[0039] l=k(l 2 +l 3 )
[0040] where, l 3 is the installation interval of the primary iron yoke 3, and k is an integer greater than 1.
[0041] In this embodiment, the distance between the two primary winding units is controlled to be equal to the effective length of the secondary iron yoke 1, and the distance l between the two primary winding units is equal to the effective length l of the primary iron yoke 3 2 Installation int...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com