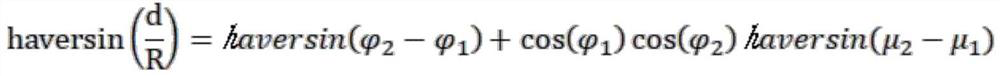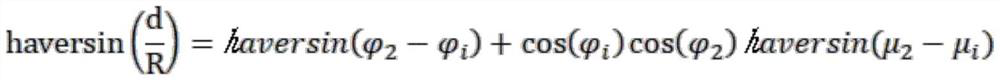A broadband user access method in a satellite network
An access method and satellite network technology, which is applied in the field of broadband user access in satellite networks, can solve problems such as low discrimination, waste of satellite resources, and inability to ensure maximum access benefits, so as to achieve reasonable decision-making, avoid waste, The effect of saving spare beam resources
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
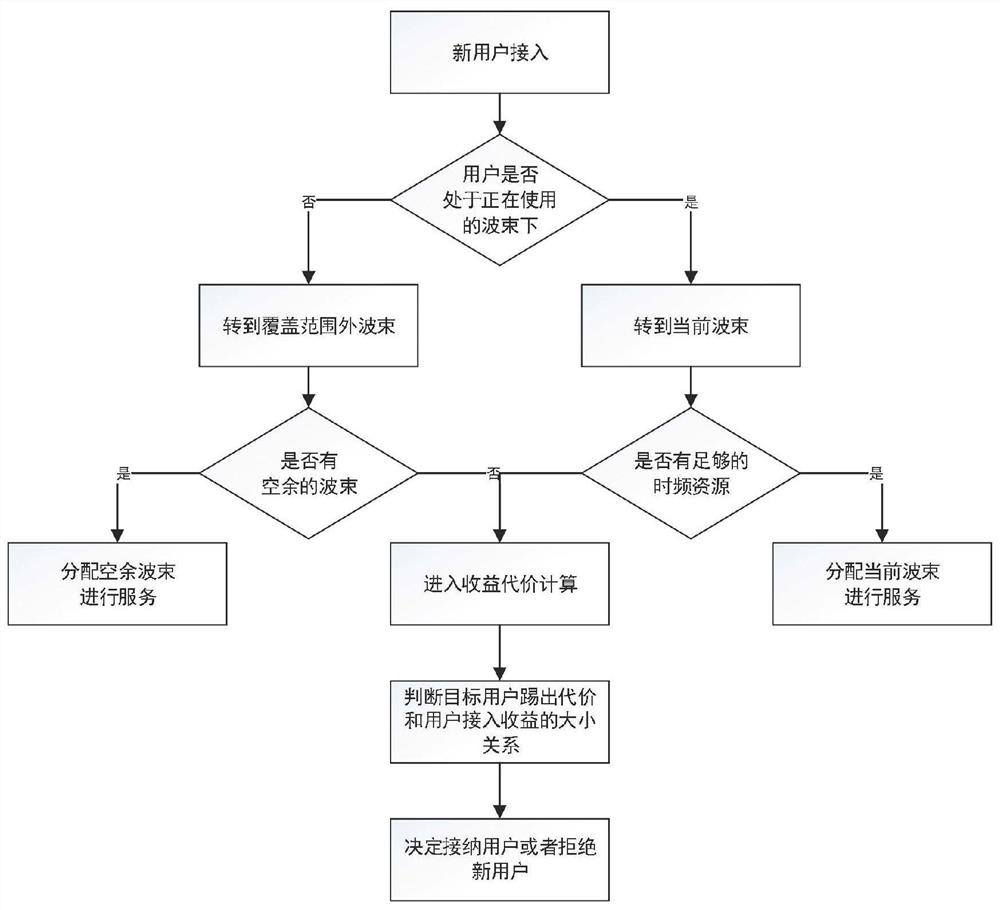
[0033] In this embodiment, the technical solution of the present invention (the main process is as follows: figure 1 shown) are explained in detail.
[0034] In this embodiment, it is assumed that there are a total of 10 available beams in the current satellite system, all beams are in an idle state, and a priority is 1 and the application resource is 1 / 10 of the maximum resource of the beam at any position within the coverage of the satellite beam. of new users.
[0035] (1) After receiving an access request from a new user, the first step is to read the serving beams. In this embodiment, all beams are in an idle state, that is, there are no serving beams. So try to use spare beams.
[0036] (2) Judging whether the spare beam has enough time-frequency resources for the user to use, in this embodiment, the time-frequency resource required by the user is 1 / 10 of the maximum resource of the beam, and there are enough time-frequency resources for the user to use. The beam reso...
Embodiment 2
[0038] In this embodiment, it is assumed that the current satellite system includes 10 beams, and users in all beams are receiving services, and new users within the coverage of beam j being served initiate access requests. The user's priority is 1, and the user's location is The applied resources are 120% of the remaining resources of the current beam. The position of the center of beam j is The beam covers the Earth's surface with a radius R e . Among them, the position coordinates are expressed in latitude and longitude, that is, μ 1 , μ 2 is longitude, is the latitude; suppose α=β=2, the profit coefficient m=1, and the cost coefficient n=2.
[0039] (1) After receiving the access request of a new user, first enter the first step, read the beams that are in service, all beams are in service, then judge the user's location, first obtain the user's location, and each beam The position of the center point of the beam coverage, and the distance between the user posi...
Embodiment 3
[0046] In this embodiment, it is assumed that the current satellite system includes 10 beams, all beams are in use, and the position of the new user is Outside the coverage of the beam being used, the priority of the user is 7, and the application resource is 50% of the maximum time-frequency resource of the beam. The projected radius of the beam on the earth's surface is R e , α=β=2, profit coefficient m=1, cost coefficient n=2, there are 3 users under the beam with the lowest total cost among the 10 beams, and the user priorities are 2, 3, and 4 respectively.
[0047] (1) After receiving the access request of a new user, first enter the first step, read the beams that are in service, all beams are in service, then judge the user's location, and first obtain the user's location and the latitude and longitude of each beam coverage center point Calculate the distance between the user position and the center point of each beam in order, and use the haversine formula (Havers...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com