Method for determining equivalent resilience modulus of roadbed top surface by considering viscoelastic property and wet-force coupling of roadbed soil
A technology of elastic modulus and determination method, applied in special data processing applications, geometric CAD, design optimization/simulation, etc., can solve problems such as shortening service life, wetting deformation of subgrade structures, and untimely taking preventive measures. Improve forecast accuracy, high accuracy, and achieve the effect of simple process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
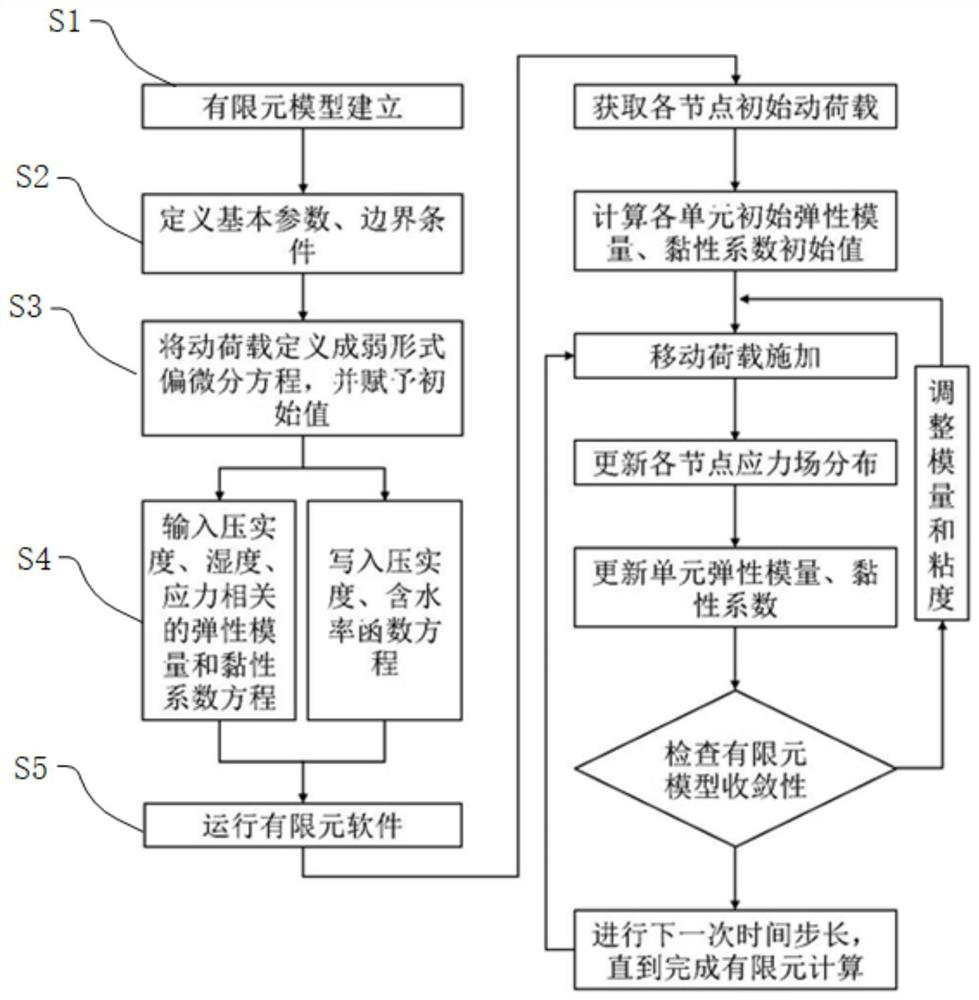
[0047] A method for determining the equivalent elastic modulus of the top surface of the subgrade considering the viscoelastic properties of subgrade soil and wet-force coupling, specifically according to the following steps:
[0048] Step S1: Establish a two-dimensional finite element model of the pavement structure through the COMSOL Multiphysics numerical software; the surface layer is made of 0.20m asphalt concrete, the base layer is made of 0.40m cement stabilized gravel, the subbase is made of 0.20m cement stabilized gravel, and the subgrade is made of 7.0m roadbed soil, the foundation is 2.0m, and the pavement structure parameters are shown in Table 1.
[0049] Table 1 Pavement structure parameters
[0050] layers Structural layer material type Thickness (m) Modulus of resilience (MPa) Density (g / cm 3 )
Poisson's ratio Surface layer Asphalt concrete 0.20 11000 2.35 0.3 grassroots cement stabilized gravel 0.40 9000 2.10 0.25 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com