Application of licochalcone B in preparation of medicine for preventing and treating NLRP3-mediated diseases
A technology of licochalone and drug, which is applied in the fields of biomedicine and drugs, can solve the problems such as the underlying mechanism and the direct target to be elucidated.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
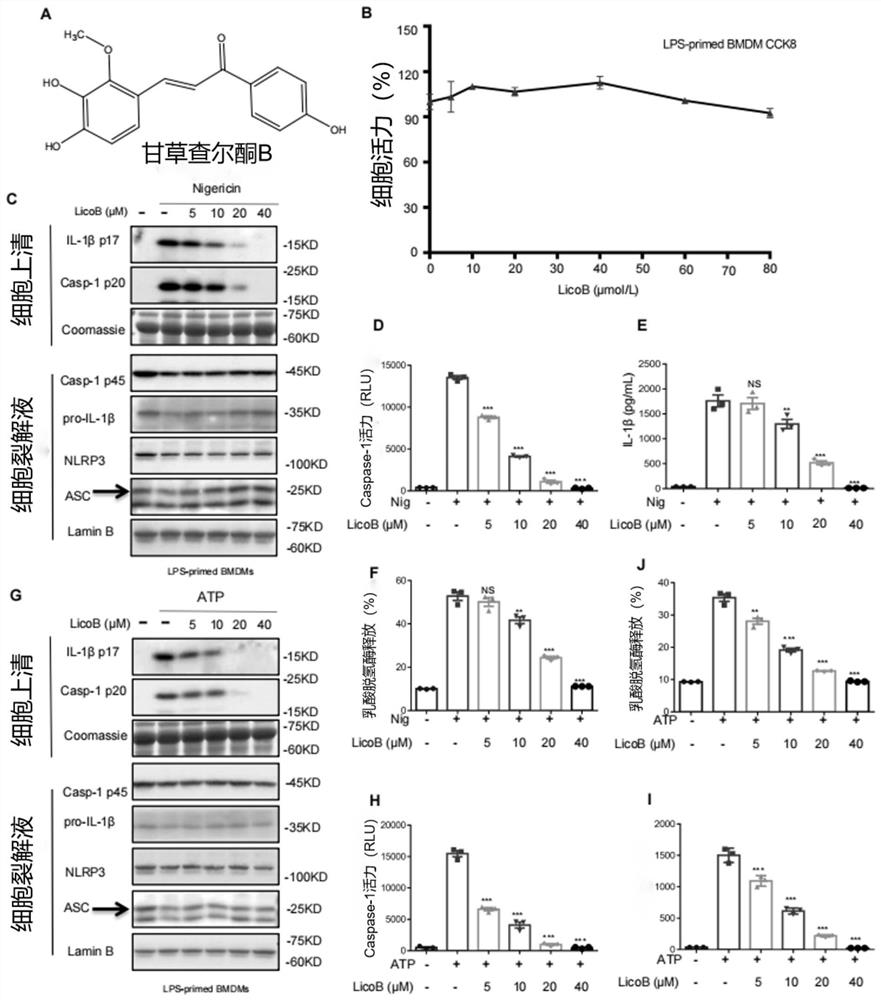
[0088] Example 1, LicoB inhibits classic and non-canonical NLRP3 activation
[0089] To identify potential candidates for the treatment of NLRP3-mediated diseases, we screened for NLRP3 inhibitors and found that LicoB can block NLRP3 inflammasome activation ( Figure 8 A). In order to further study LicoB( figure 1 A) Effect on NLRP3 inflammasome activation, we first tested the cytotoxicity of LicoB in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDM). Cell viability assays showed that LicoB did not exhibit any cytotoxicity at doses below 80 μM in BMDM ( figure 1 B). BMDMs were first primed with LPS, then pretreated with a range of LicoB concentrations, and then stimulated with a 10 μM dose of nigericin or a 5 mM dose of ATP to induce NLRP3 inflammasome activation. The results showed that in LPS-triggered BMDM, LicoB dose-dependently inhibited the production of nigericin ( figure 1 C-E) or ATP ( figure 1 G-I) Triggered caspase-1 activation or IL-1β secretion. Correspondingly,...
Embodiment 2
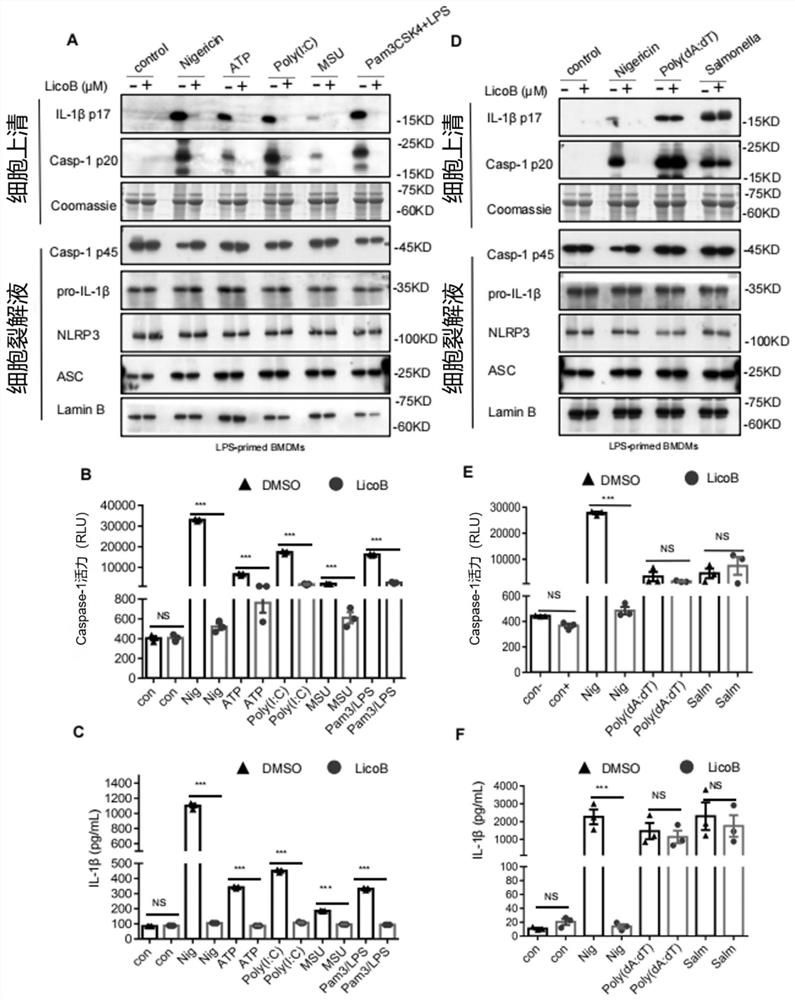
[0092] Example 2, LicoB is a specific inhibitor of NLRP3 inflammasome
[0093] We then investigated whether LicoB specifically inhibits the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome. We performed experiments on the effect of LicoB on the activation of AIM2 and NLRC4 inflammasomes, which can also mediate cleavage of caspase-1 and secretion of IL-1β. LPS-primed BMDMs were transfected with the dsDNA analog poly(dA:dT) to activate the AIM2 inflammasome, or stimulated with Salmonella typhimurium to activate the NLRC4 inflammasome. The results showed that LicoB did not inhibit AIM2- or NLRC4-mediated caspase-1 activation and IL-1β secretion ( figure 2 D-F). The results showed that LicoB specifically inhibited the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome.
Embodiment 3
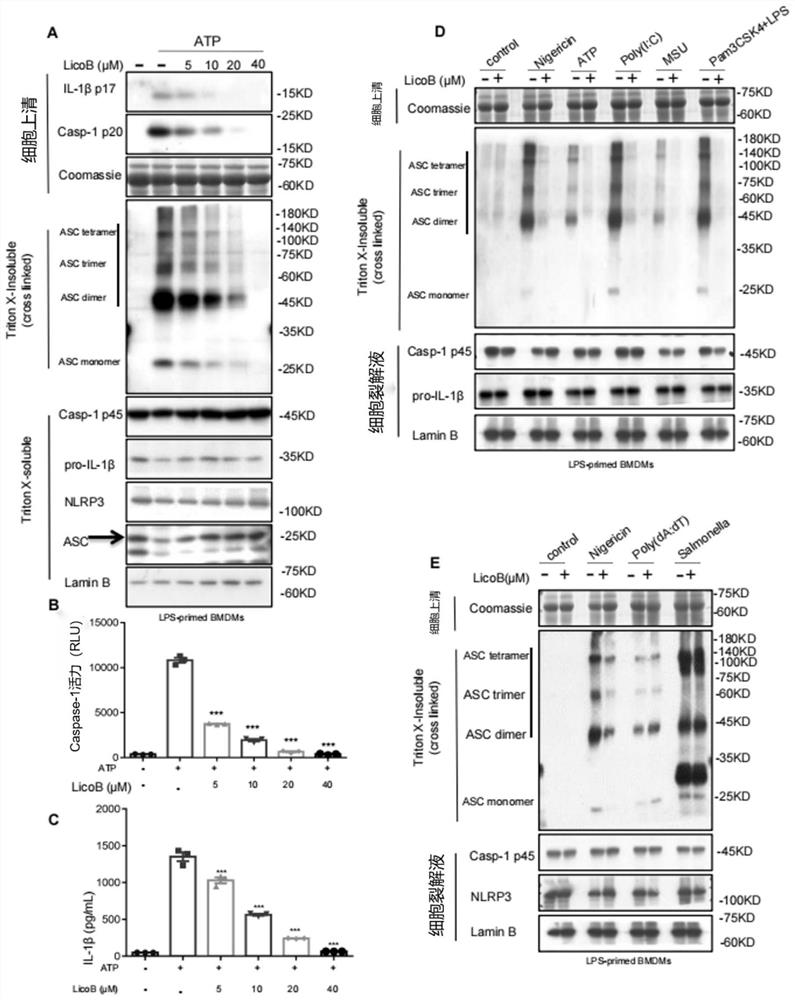
[0094] Example 3, LicoB blocks NLRP3-dependent ASC oligomerization
[0095] After recognizing that LicoB can specifically inhibit the activation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, we further explored the underlying mechanism of this effect. First, an experiment was performed to determine whether LicoB affects ASC oligomerization, a key step in NLRP3 inflammasome activation. LPS-primed BMDMs were stimulated with ATP and higher-order complexes were detected using western blot analysis. The results showed that LicoB attenuated ATP-induced ASC oligomerization in a dose-dependent manner ( image 3 A), which is consistent with the blocking effect of LicoB on caspase-1 cleavage and IL-1β secretion ( image 3 B and C). Further studies showed that LicoB effectively prevented ASC oligomerization induced by other NLRP3 agonists, such as nigericin, poly(I:C), MSU, and cytosolic LPS ( image 3 D). However, LicoB did not affect AIM2 or NLRC4 agonist-induced ASC oligomerization ( image 3 E), ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com