Patents
Literature
866 results about "Drug candidate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Candidate drug. Candidate drug: a compound (small molecule, antibody, etc.) with strong therapeutic potential and whose activity and specificity have been optimised. The point of departure for fundamental researchers (fundamental and academic research) consists in identifying and validating therapeutic targets likely to be involved in...
Rodent HER2 tumor model
The invention concerns HER<HIL><PDAT>2< / BOLD><PDAT>-transgenic non-human mammals, animal models for screening drug candidates for the treatment of diseases and disorders associated with the overexpression of HER<HIL><PDAT>2< / BOLD><PDAT>. In particular, the invention concerns animal models designed to test drug candidates for the treatment of HER<HIL><PDAT>2< / BOLD><PDAT>-overexpressing cancers, including breast cancer, that are not responding or poorly responding to current treatments.< / PTEXT>
Owner:SAN VALLEY SYST +1
Analysis of metabolic activity in cells using extracellular flux rate measurements
InactiveUS20070087401A1To promote metabolismEliminate needMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysisGeneration rateOxygen
Disclosed are methods for non-destructively measuring in vitro the effect on cellular metabolism of the addition to animal cells in culture of a soluble molecule potentially capable of perturbing the biological state of the cells, such as a drug or drug candidate, a toxin, a ligand known or suspected to bind to a cell surface receptor, a nutrient, a cytokine, a growth factor, a chemokine, a metabolism inhibitor or stimulator. Also disclosed are methods for measuring cell viability, vitality, or quality, e.g., in anticipation of the execution of an experiment on the cells. The measurements are done by observing alteration in the rates of consumption or production of extracellular solutes related to aerobic and anaerobic cellular metabolism, such as oxygen, protons, nutrients, carbon dioxide, lactate, or lactic acid. The methods are particularly useful in drug discovery efforts, such as cancer drug discovery and searches for modulators of cellular metabolism.
Owner:SEAHORSEBIOSCIENCE INC
Dual resonance energy transfer nucleic acid probes
InactiveUS7081336B2Quick checkEasy to useSugar derivativesMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorDiseaseCell specific
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Transgenic animal model for modelling pathological anxiety, a method for identifying compounds for treatment of diseases or disorders caused by pathological anxiety and a method for using wfs1 protein as a target for identifying effective compounds against pathological anxiety
InactiveUS20100146645A1Low environmental changeImprove anxietyCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsBiological testingTolerabilityClinical psychology
The invention discloses the transgenic animal model for pathological anxiety, the method to generate this model, the method to test drugs and drug candidates for the treatment of pathological anxiety and the method to use Wfs1 as target for screening of new anxiolytic drugs to treat pathological anxiety. This animal model is useful to test potential drug candidates for the treatment of diseases caused by pathological anxiety and to screen therapeutic compounds for the psychiatric disorders caused by reduces stress-tolerance and deficiency in adaptation to environmental challenges.
Owner:TARTU ULIKOOL THE UNIV OF TARTU
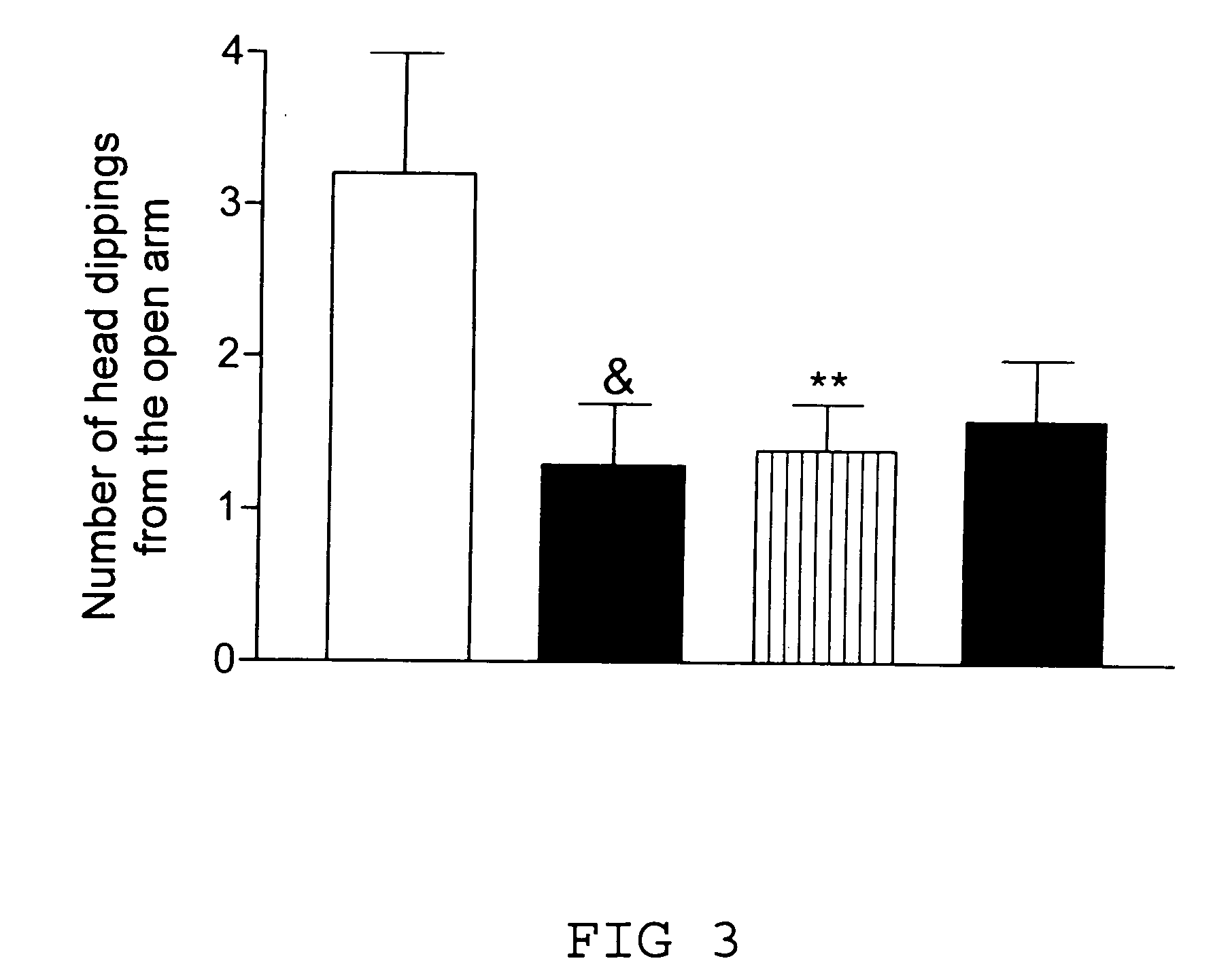
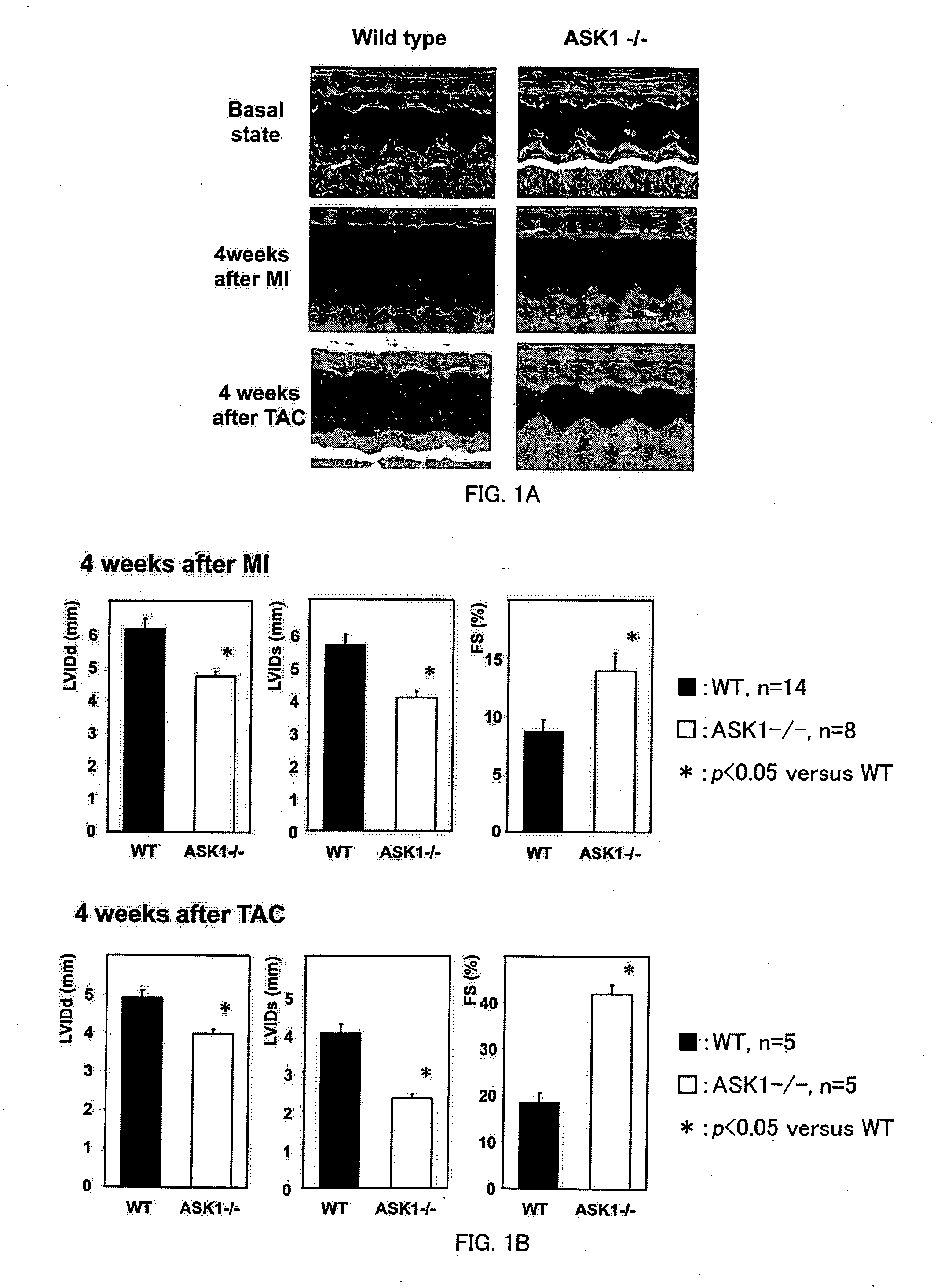
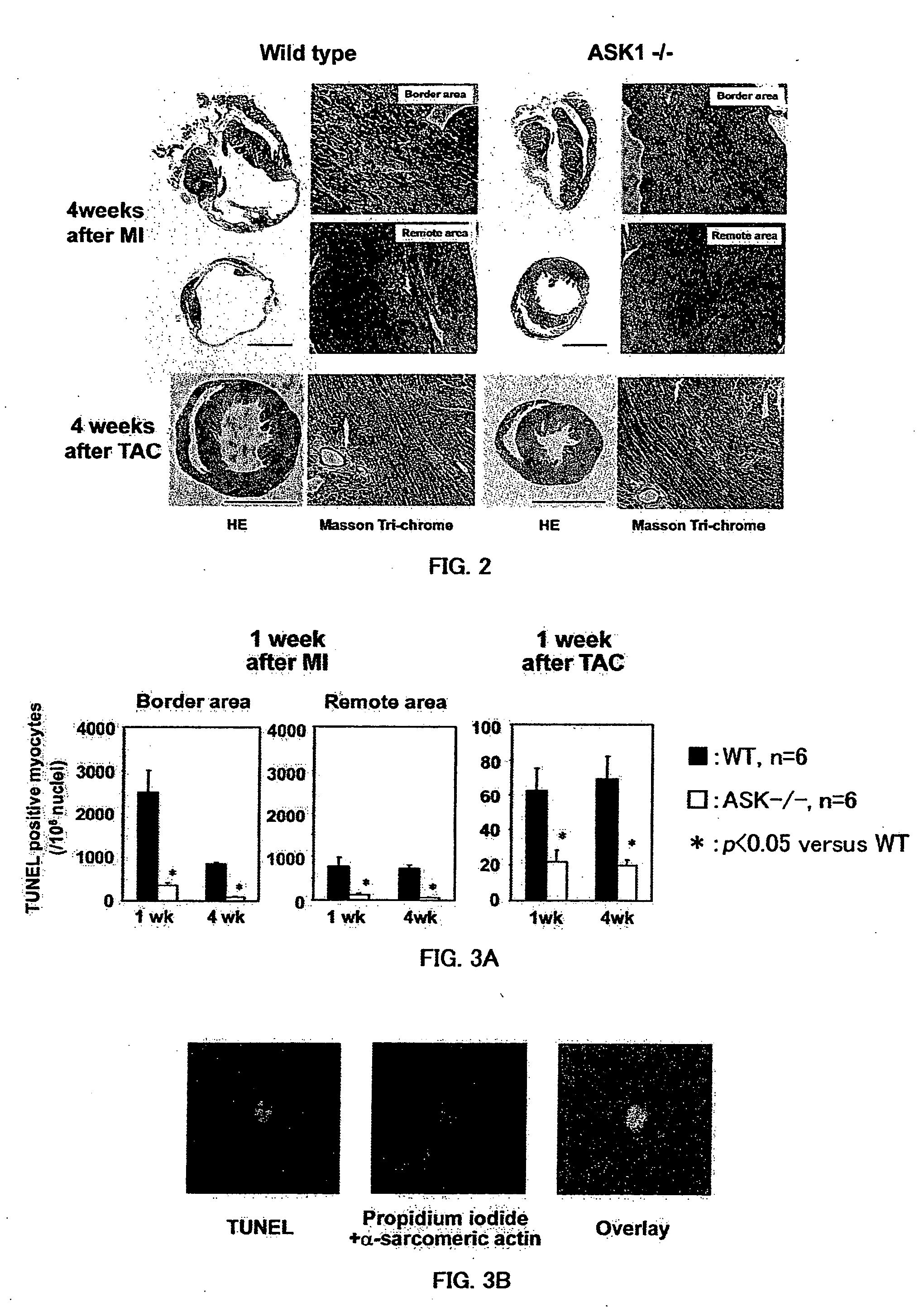
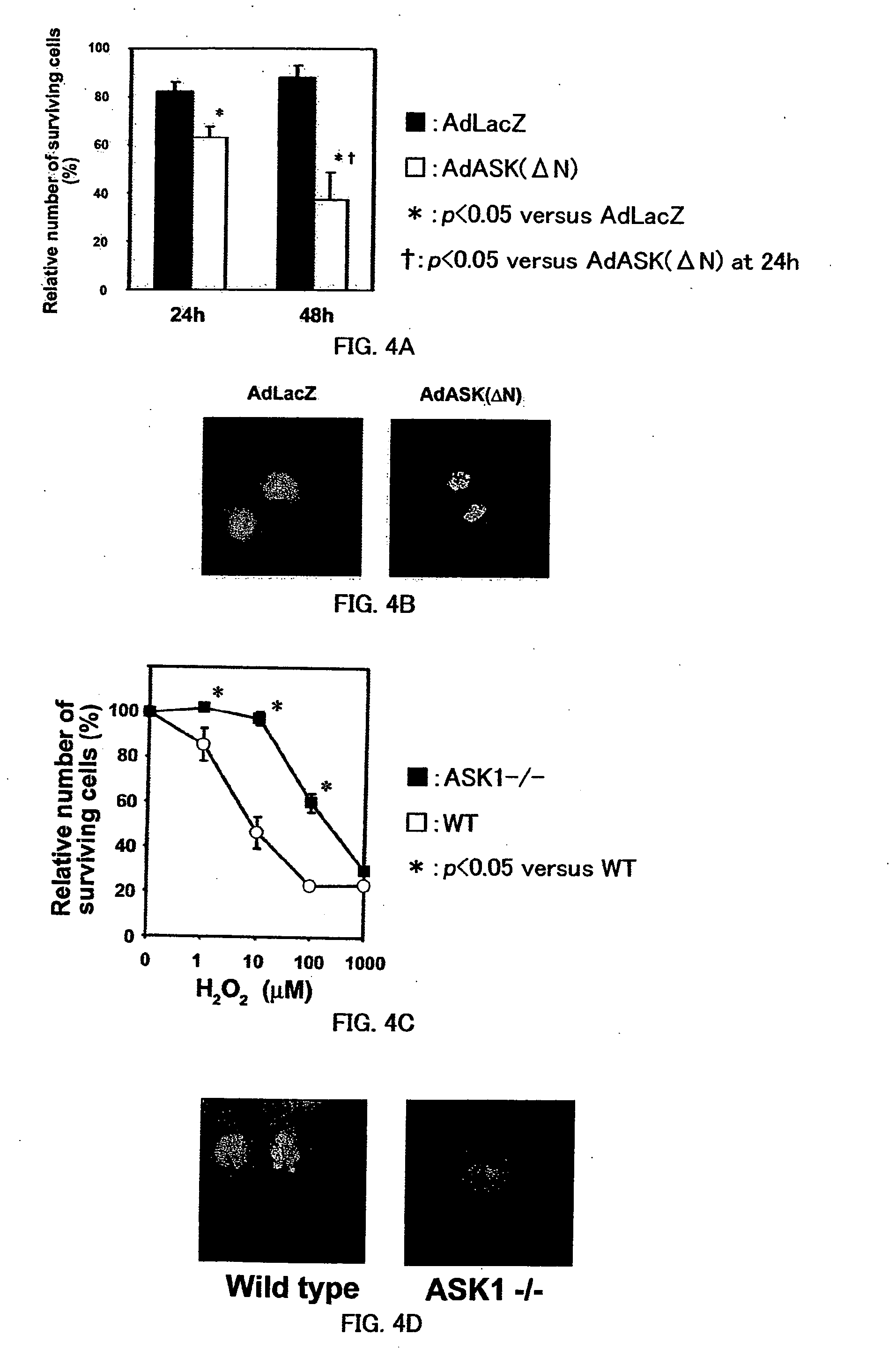
Remedy for cardiac failure containing ask1 inhibitor as active ingredient and method for screening the same
InactiveUS20070167386A1Inhibit functional expressionPreventing cardiac failureOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsManagement of heart failureLeft Ventricle Remodeling
The present invention provides a drug for at least one of prevention and treatment of cardiac failure capable of suppressing cardiac depression and the onset of cardiac failure in ventricular remodeling, and a method for screening the drug. The drug for at least one of prevention and treatment of cardiac failure of the present invention contains a compound that inhibits a functional expression of ASK1 protein in a cardiomyocyte as an active ingredient, and a method for screening a drug for at least one of prevention and treatment of cardiac failure of the present invention includes selecting a medicinal component for at least one of prevention and treatment of cardiac failure from a drug candidate compound by using inhibition of a functional expression of ASK1 protein as an indication. As shown in FIG. 1, if ASK1 protein is removed, for example, the ventricle dilation can be attenuated in ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction, pressure loading, or the like, which makes it possible to prevent and treat cardiac failure.
Owner:OSAKA INDAL PROMOTION ORG
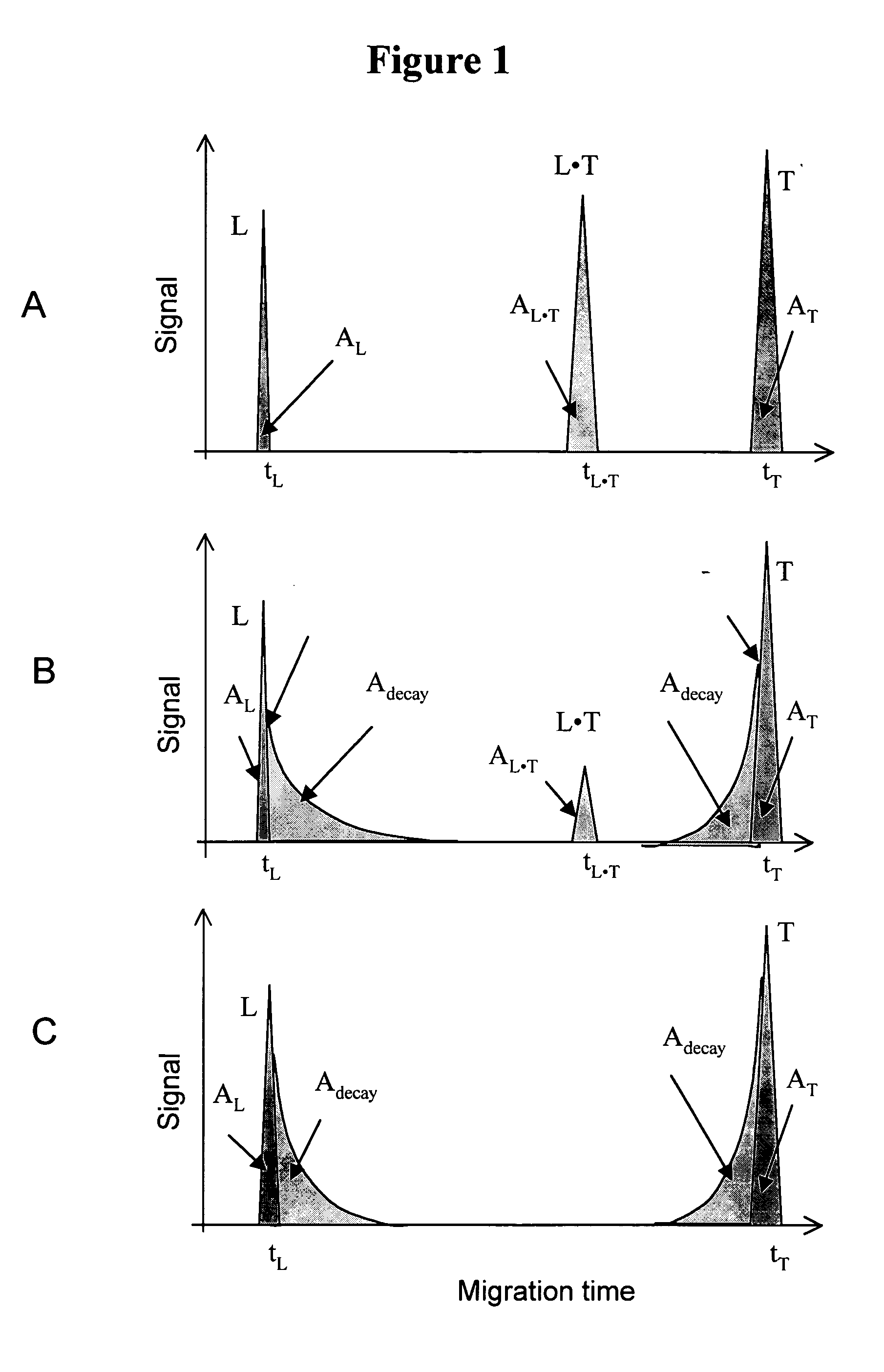
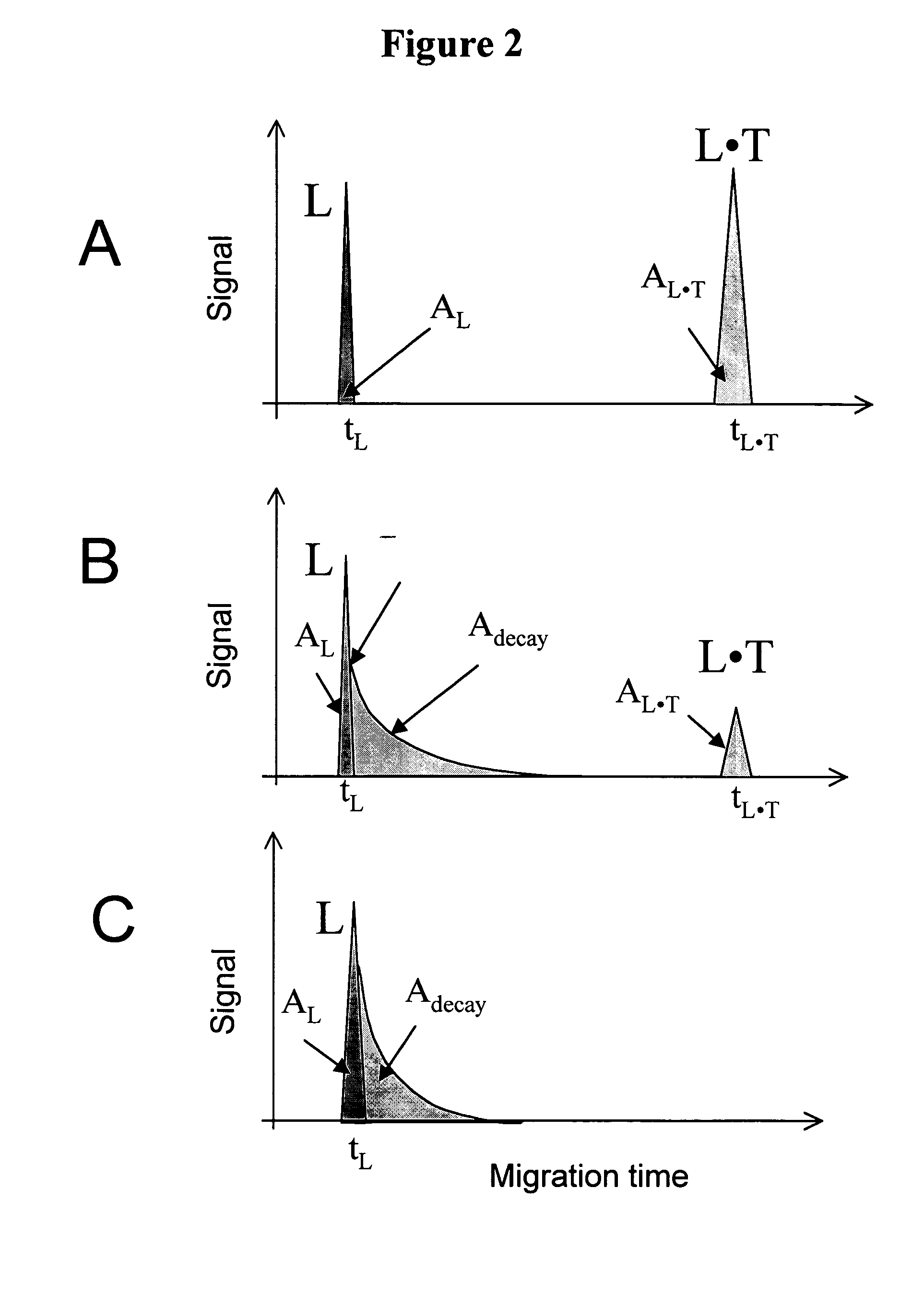
Non-equilibrium capillary electrophoresis of equilibrium mixtures (NECEEM) - based methods for drug and diagnostic development
ActiveUS20050003362A1Enhances electrophoretic separationEasy to separateCompound screeningApoptosis detectionSolid substrateNucleotide Aptamers
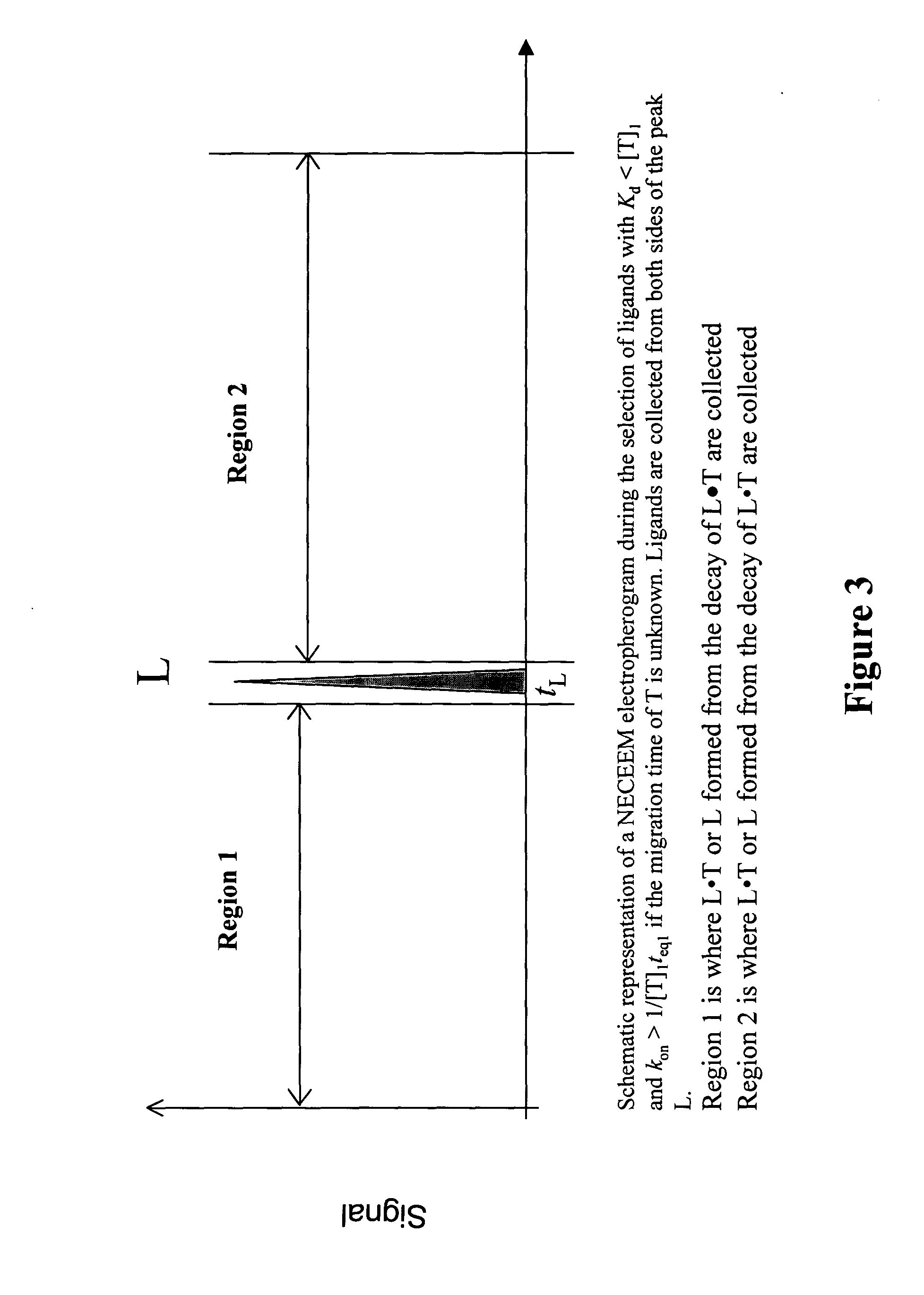
The invention discloses a Non-Equilibrium Capillary Electrophoresis of Equilibrium Mixtures (NECEEM) method and NECEEM-based practical applications. The NECEEM method is a homogeneous technique, which, in contrast to heterogeneous methods, does not require affixing molecules to a solid substrate. The method of the invention facilitates 3 practical applications. In the first application, the method allows the finding of kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of complex formation. It advantageously allows for revealing two parameters, the equilibrium dissociation constant, Kd, and the monomolecular rate constant of complex decay, koff, in a single experiment. In the second practical application, the method of this invention provides an approach for quantitative affinity analysis of target molecules. It advantageously allows for the use of affinity probes with relatively high values of koff. In the third practical application, the method of this invention presents a new and powerful approach to select target-binding molecules (ligands) from complex mixtures. Unique capabilities of the method in its third application include but not limited to: (a) the selection of ligands with pre-determined ranges of kinetic and thermodynamic parameters of target-ligand interactions, (b) the selection of ligands present in minute amounts in complex mixtures of biological or synthetic compounds such as combinatorial libraries of oligonucleotides, and (c) the selection of ligands for targets available in very low amounts. In particular, the method of this invention provides a novel approach for the selection of oligonucleotide aptamers. The NECEEM-based method can be used for discovery and characterization of drug candidates and the development of new diagnostic methods.
Owner:KRYLOV SERGEY
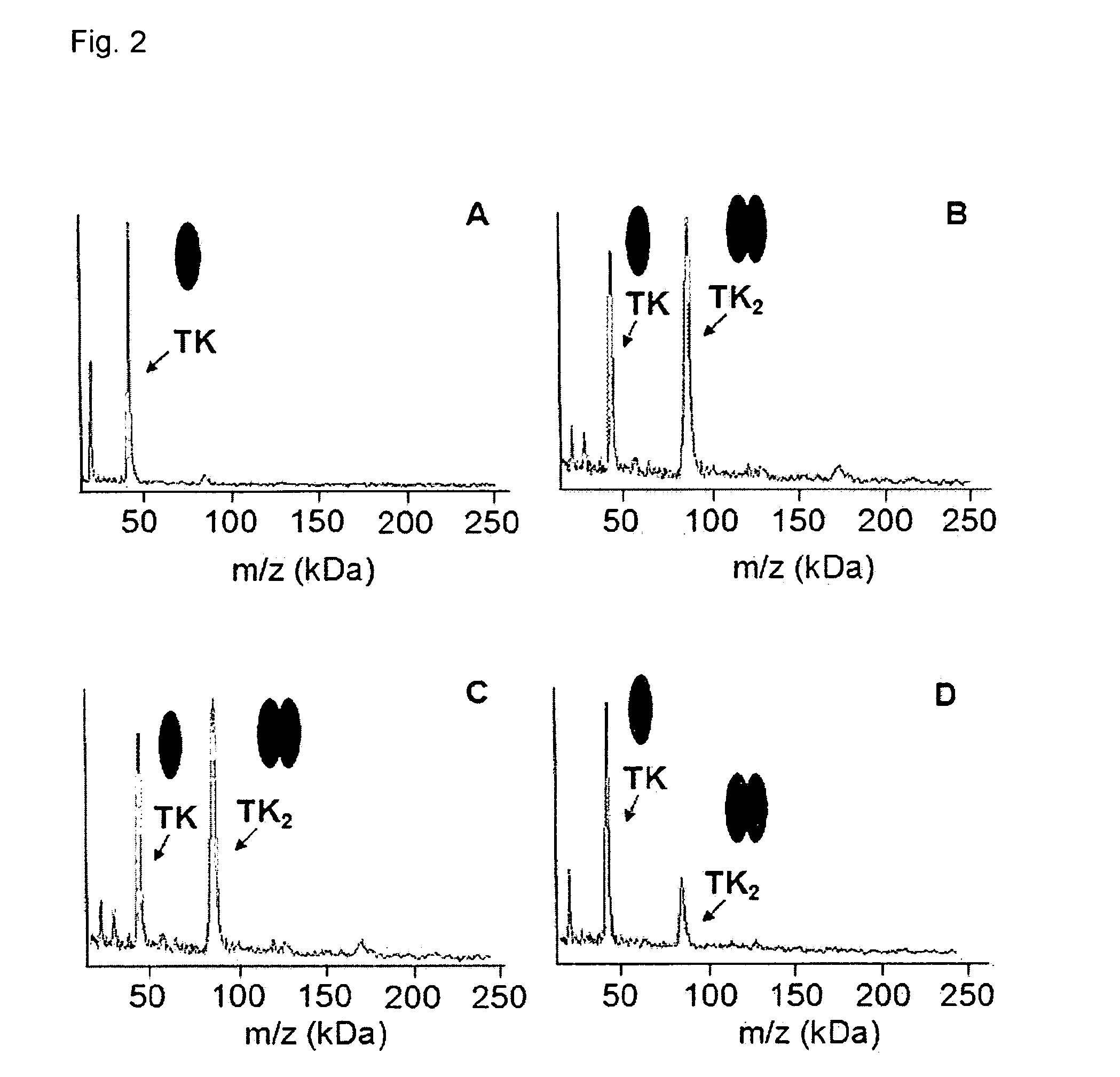
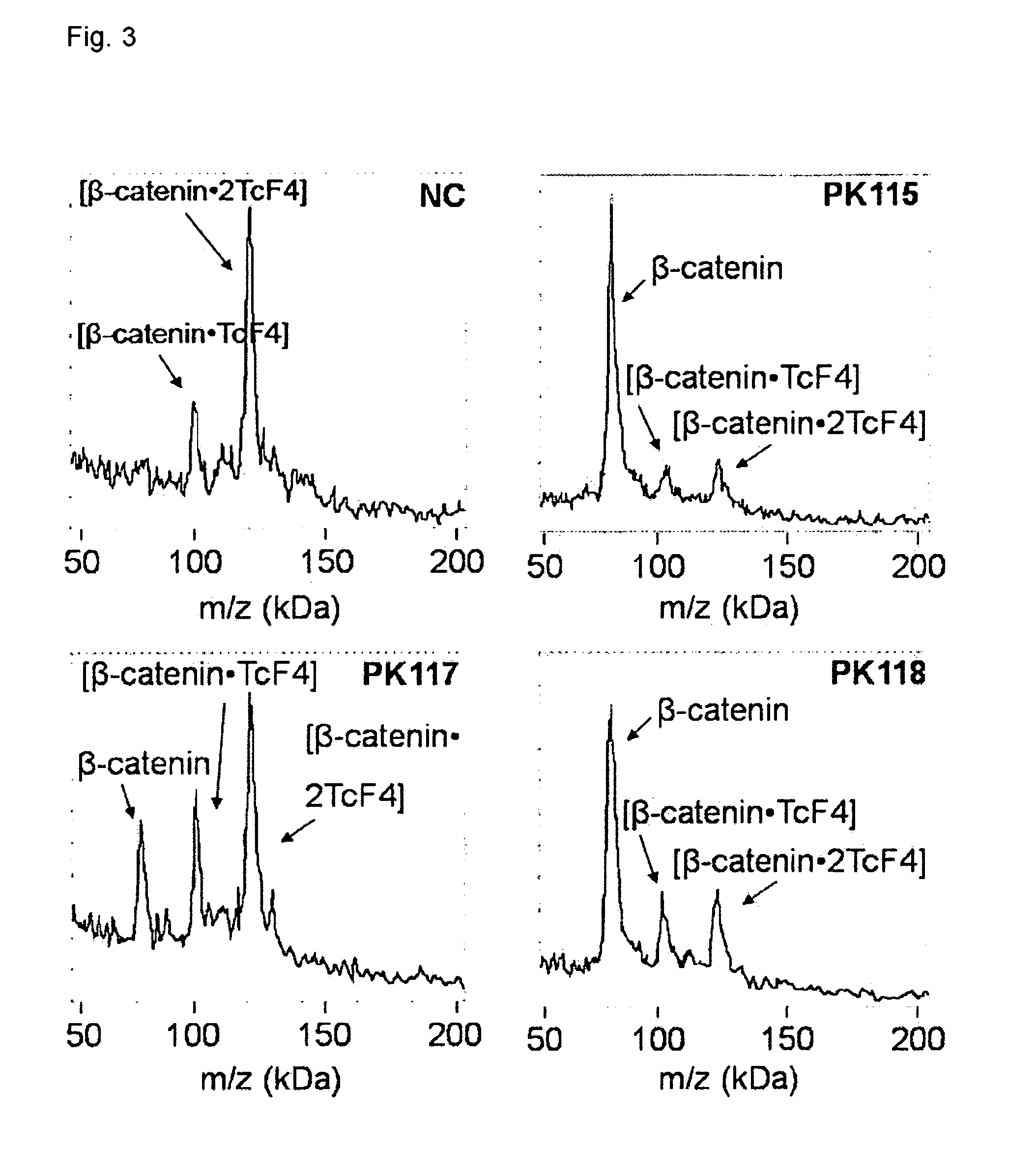
Direct mass spectrometric analysis of drug candidates targeting protein complexes
ActiveUS20100099200A1Improve throughputEasy to detectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein targetProtein-protein complex
The invention relates to a method of using high mass matrix assisted laser desorption-ionization (MALDI) mass spectrometry for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of the effect of drug candidates on protein complexes such as protein-protein interactions in purified samples or complex biological matrices, as well as to the use of this method for lead compound optimization, drug characterization, drug manufacturing processes, and drug quality control processes, including automated high throughput applications.
Owner:COVALX
Lipid mediated screening of drug candidates for identification of active compounds
InactiveUS20030198664A1Reduce solubilityMicroencapsulation basedMicrobiological testing/measurementLipid formationSolubility
The subject invention provides liposome formulations that are capable of specifically targeting cell types. The subject invention also provides for the encapsulation of new chemical entities (NCE) or other drug candidate molecules (DCM) within liposomes that specifically target a particular cell type. The subject invention, advantageously, solubilizes compounds, with low solubility in aqueous environments, and permits screening of these compounds against intact cells for biological activity in the absence of detergents that can damage cell membranes. Also provided are methods of preparing liposome formulations that target a specific cell type and methods of delivering therapeutic agents to target cells.
Owner:BRISTOL MYERS SQUIBB CO +1
Enrichment method for variant proteins with altered binding properties
InactiveUS20060115874A1Valid choiceHigh affinity bindingVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsEnrichment methodsAntibody fragments
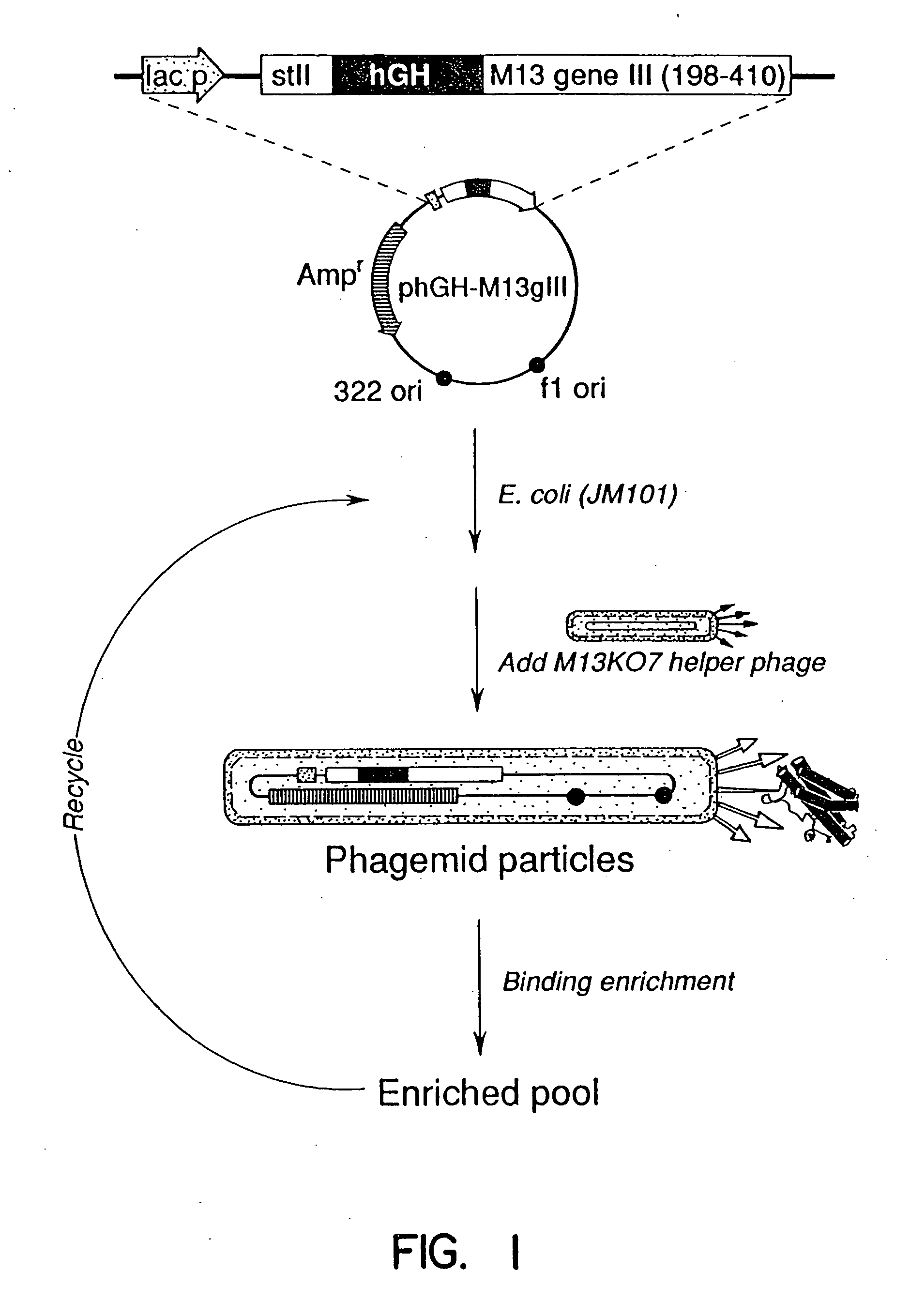
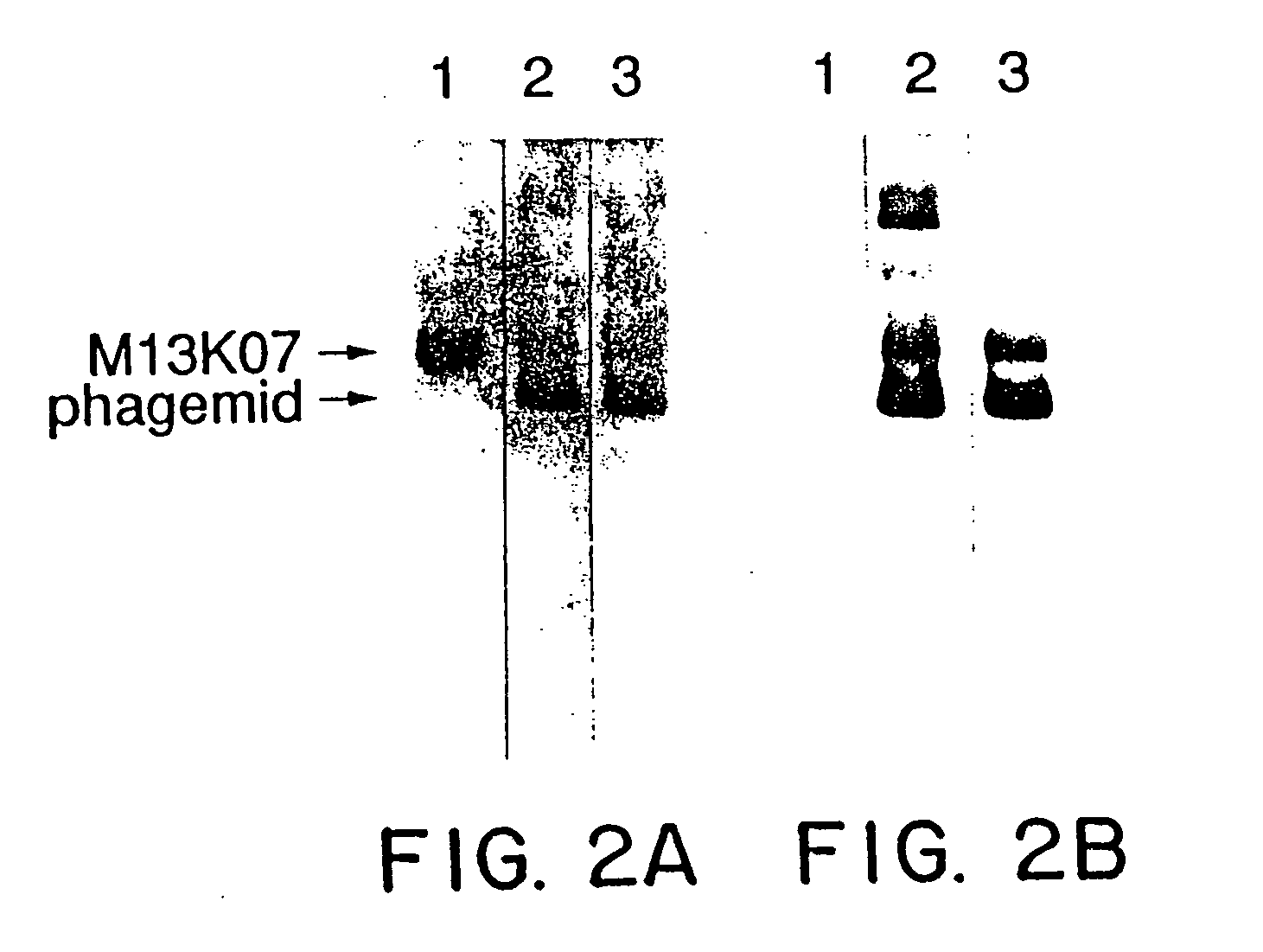
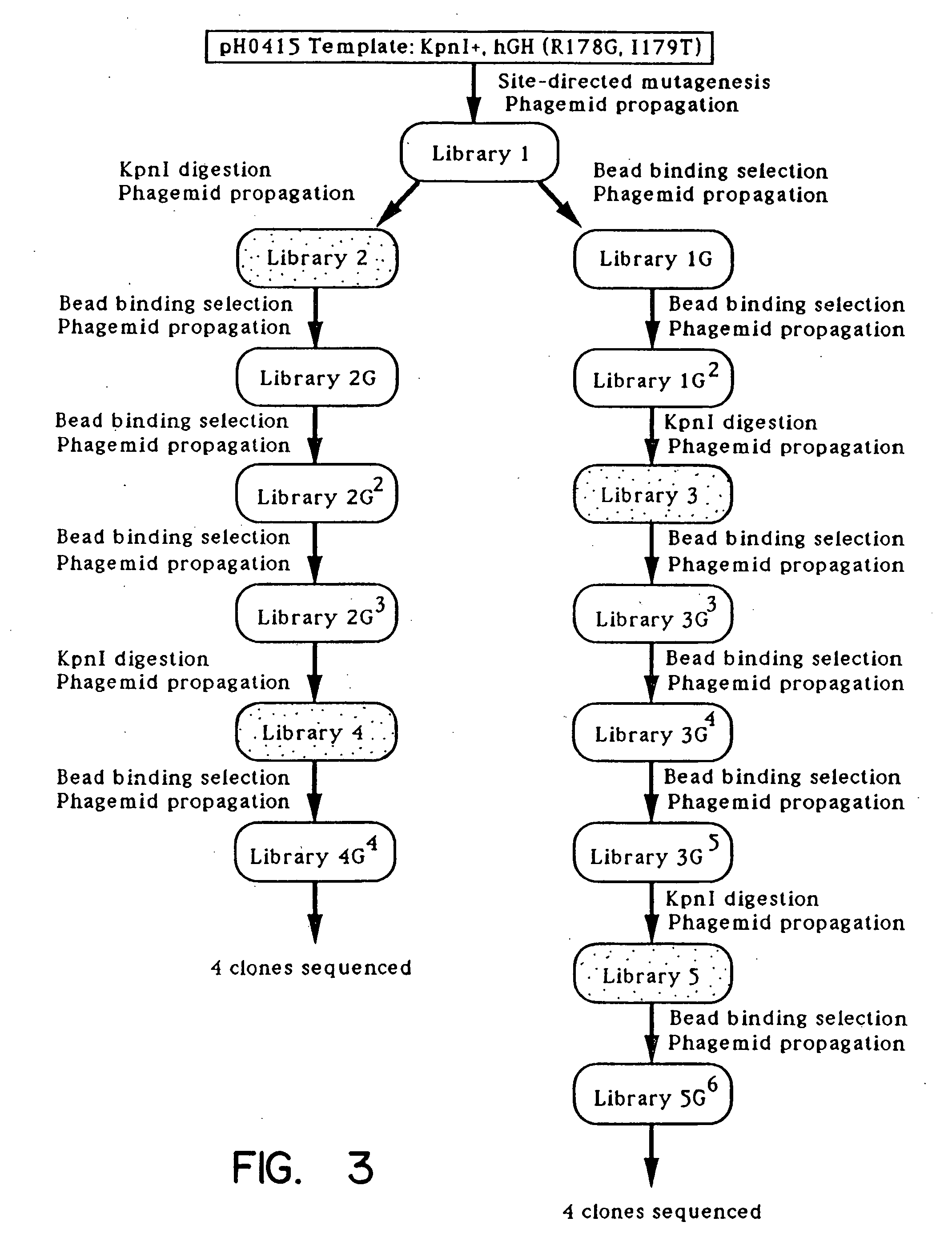
A method for selecting novel proteins such as growth hormone and antibody fragment variants having altered binding properties for their respective receptor molecules is provided. The method comprises fusing a gene encoding a protein of interest to the carboxy terminal domain of the gene III coat protein of the filamentous phage M13. The gene fusion is mutated to form a library of structurally related fusion proteins that are expressed in low quantity on the surface of a phagemid particle. Biological selection and screening are employed to identify novel ligands useful as drug candidates. Disclosed are preferred phagemid expression vectors and selected human growth hormone variants.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
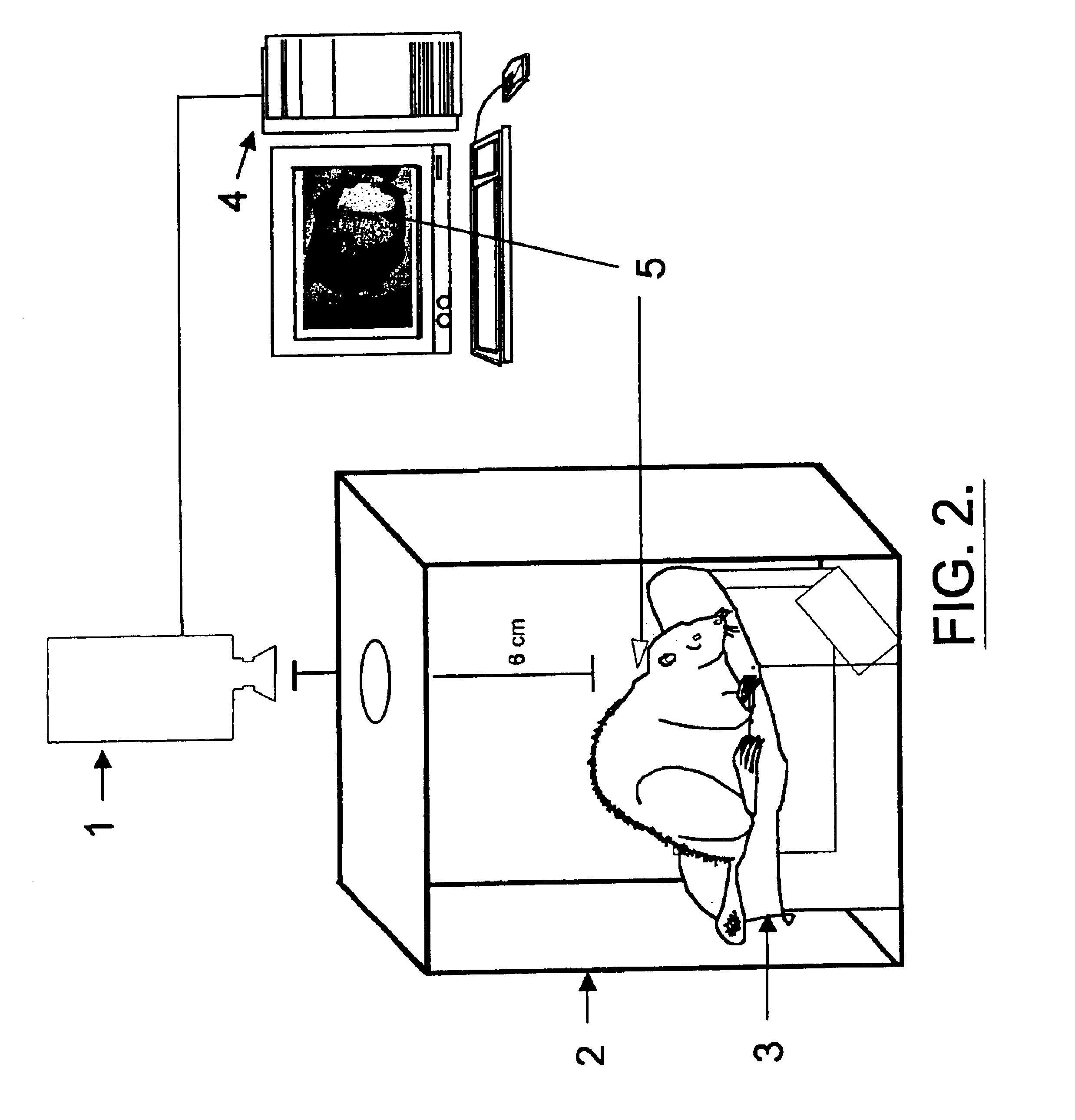
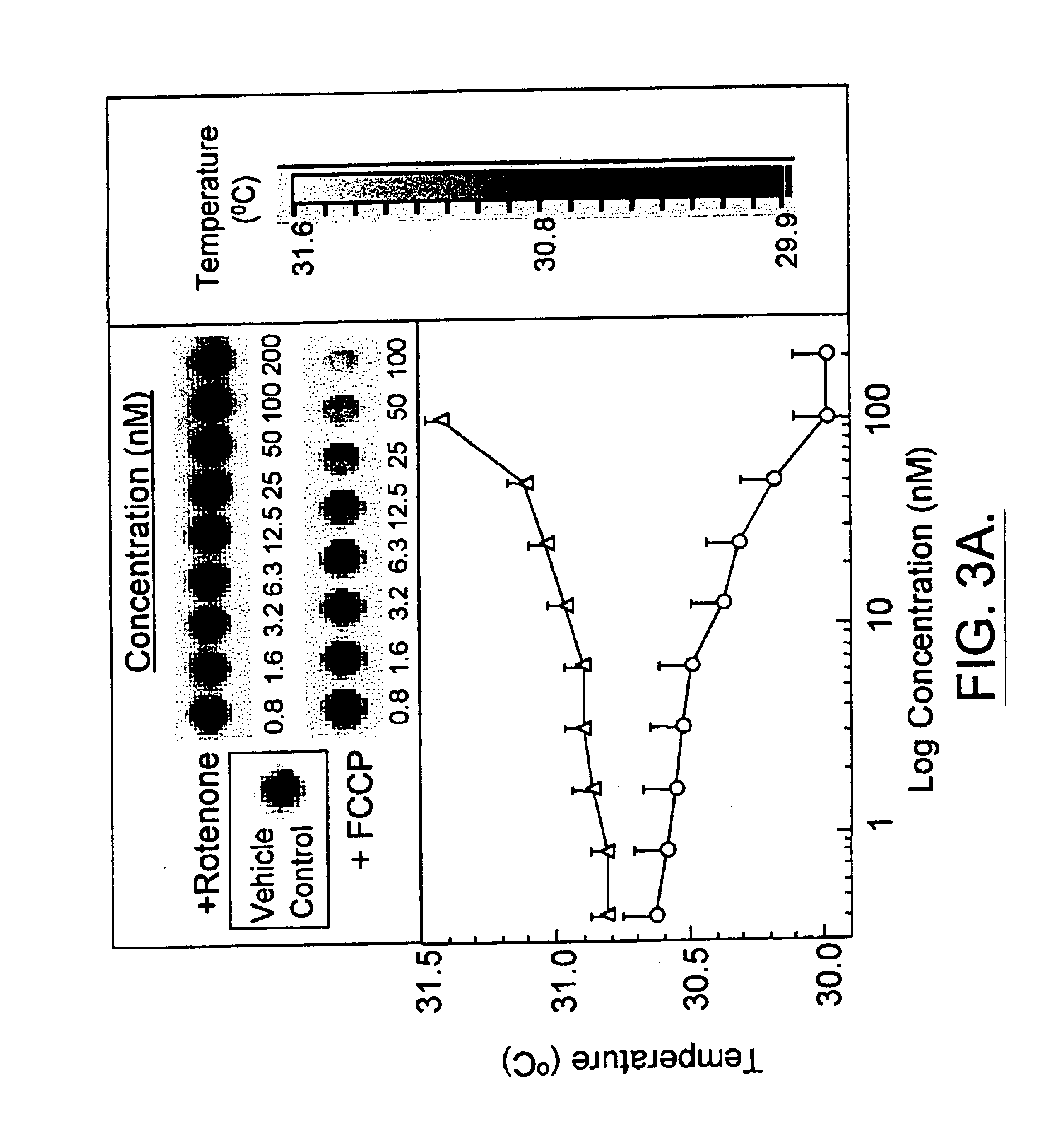
Infrared thermography
InactiveUS6881584B1High expressionAbundantly expressDiagnostics using lightMaterial heat developmentCell freePresent method
The present invention relates, in general, to thermography and, in particular, to a method of using infrared thermography to monitor physiological and molecular events that elicit a thermogenic response in animals (including humans), plants, tissues, cells and cell-free systems. The present method can be used for screening, identifying, and ranking drug candidates for multiple diseases, disorders and conditions.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Therapeutic cell preparation grafts and methods of use thereof
A biological preparation including genetically modified cells together with biocompatible matrices and methods of use thereof are provided. The biological preparation is useful in treating a subject at risk for or suffering from a disease in a controllable dosage and time-dependent manner, and for in vitro and in vivo screening of candidate drug therapies
Owner:KLEIN MATTHEW B +1
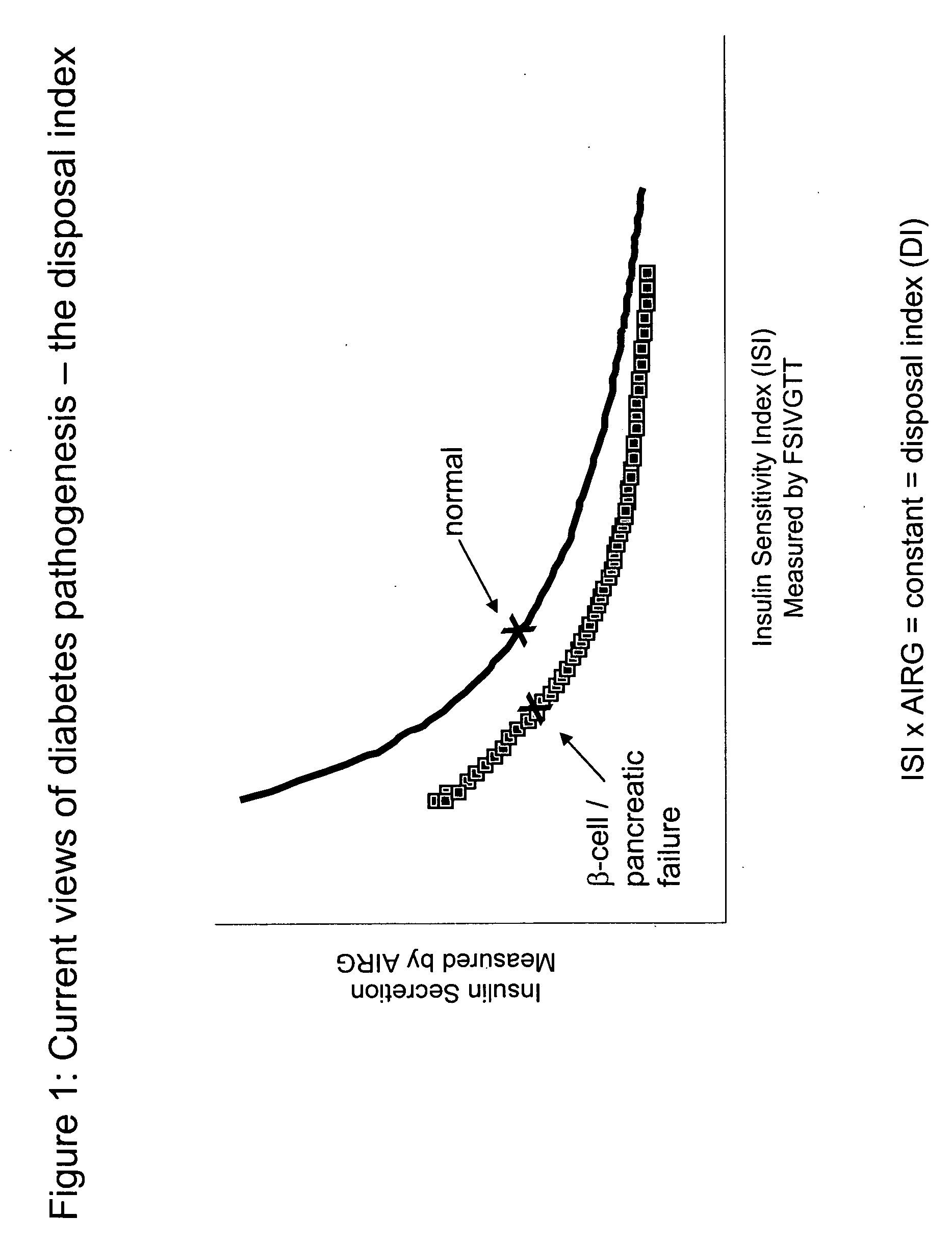
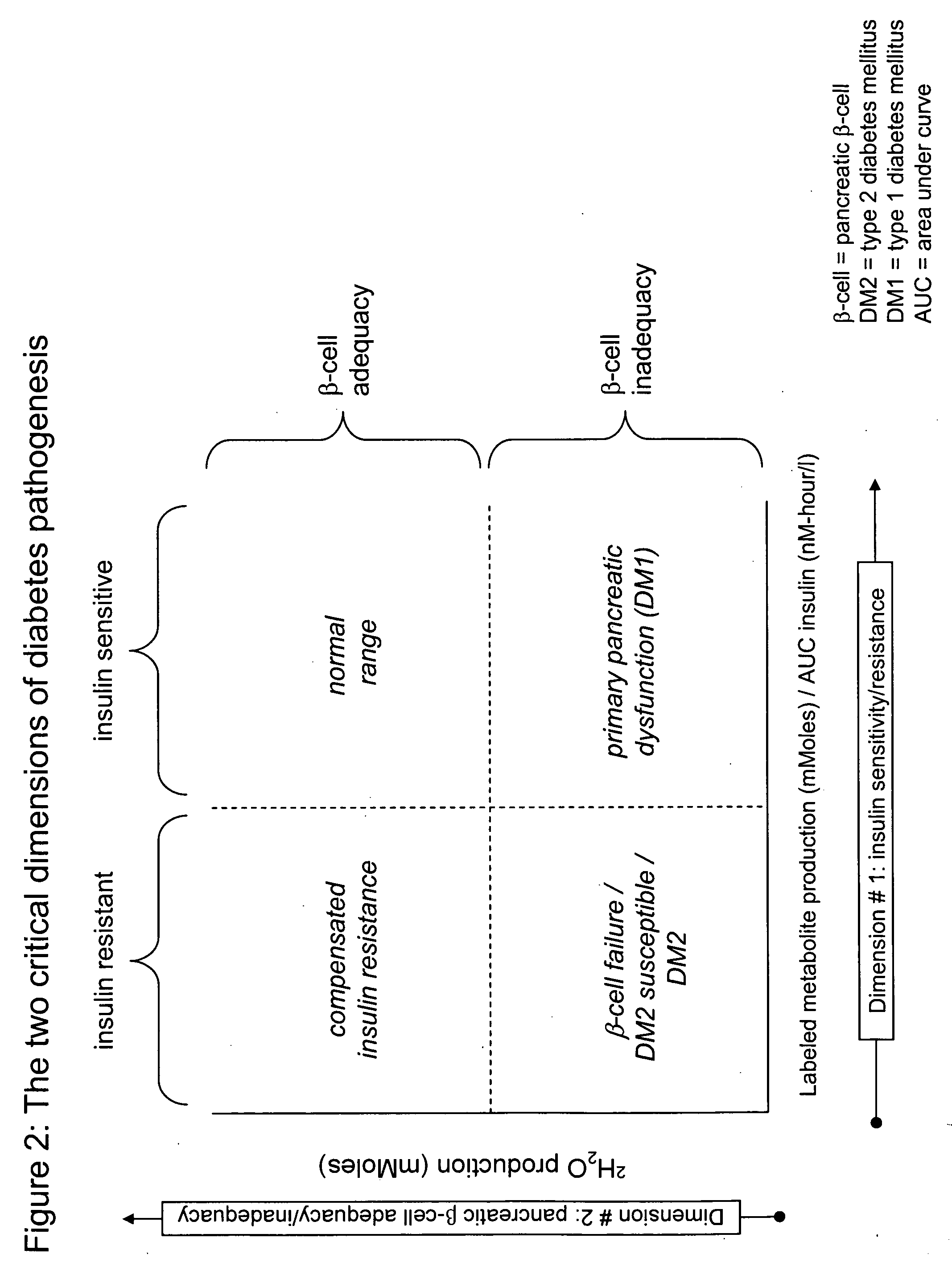
Monitoring two dimensions of diabetes pathogenesis seperately or concurrently (insulin sensitivity and beta-cell sufficiency): uses in diagnosis, prognosis, assessment of disease risk, and drug development
InactiveUS20060280682A1Improve responseReduce sensitivityCompounds screening/testingDisease diagnosisDisease riskDisease progression
Provided are methods for determining concurrently with a simple, minimally invasive test, the adequacy of pancreatic beta-cell compensation and / or the presence of tissue insulin resistance in a subject human or an experimental animal. The methods allow for the determination of a subject's or experimental animal's susceptibility to developing type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM2) or to progression to more advanced forms of DM2. Among other uses, the methods allow for diagnostic classification of subjects for decisions regarding therapeutic interventions, clinical differentiation between type 1 DM and DM2, clinical monitoring of treatments intended to reduce risk of developing DM2 in non-diabetic subjects, clinical monitoring of agents intended to improve existing DM2 and to prevent progression of DM2, clinical development and testing of new compounds, candidate agents, or candidate therapies for preventing progression to DM2 or disease progression in existing DM2, and preclinical screening of candidate agents or candidate therapies in experimental animals to identify and characterize agents having insulin-sensitizing properties, pancreatic stimulatory or regenerative properties or other desirable actions.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
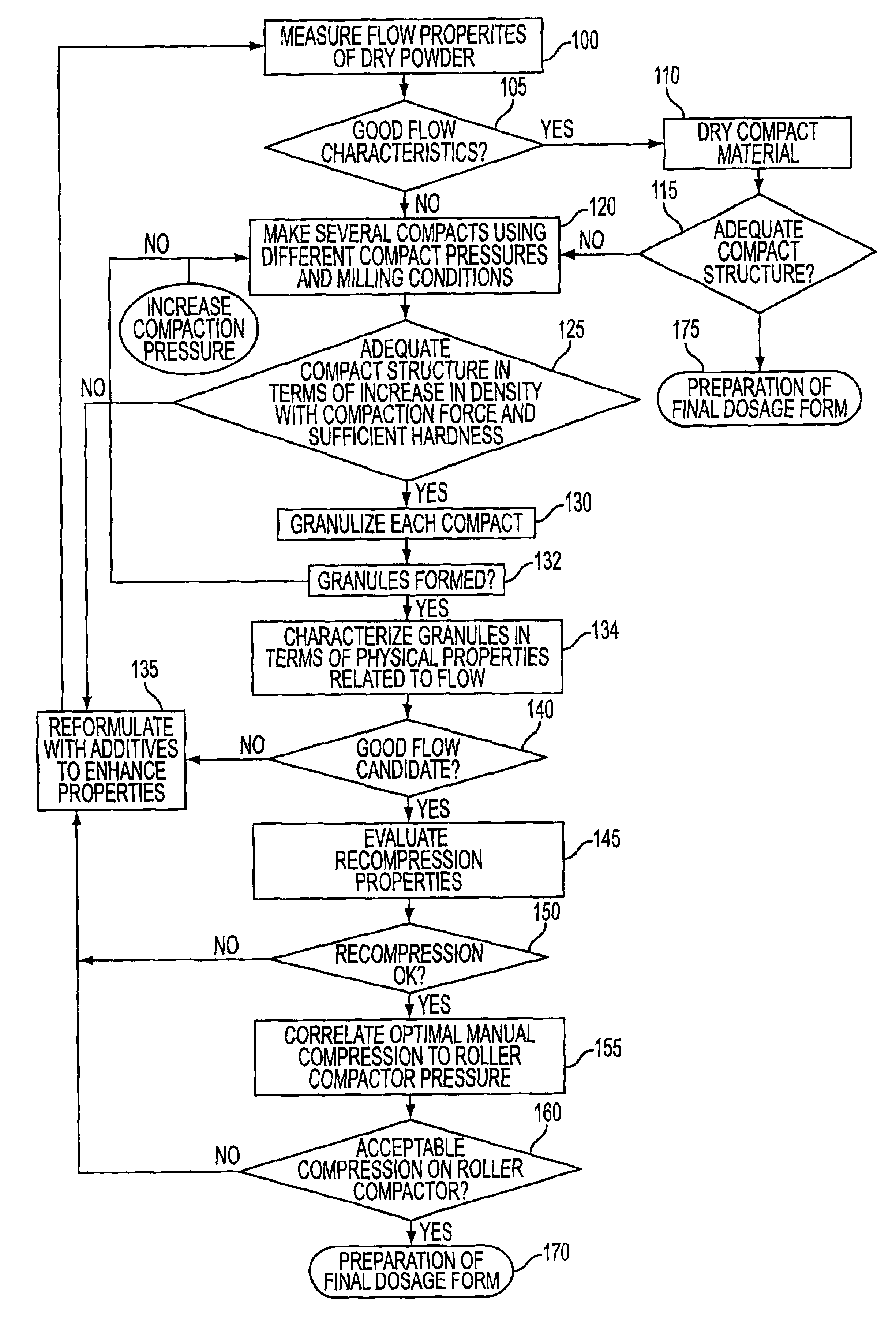
Method for predicting the suitability of a substance for dry granulation by roller compaction using small sample sizes
An apparatus for fabricating small compacts of formulations of a drug candidate, and a method for determining if a drug candidate, alone or in a formula mix, is suitable for dry granulation by a roller compactor based on physical measurements generated in part from such small compact.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARMA INC
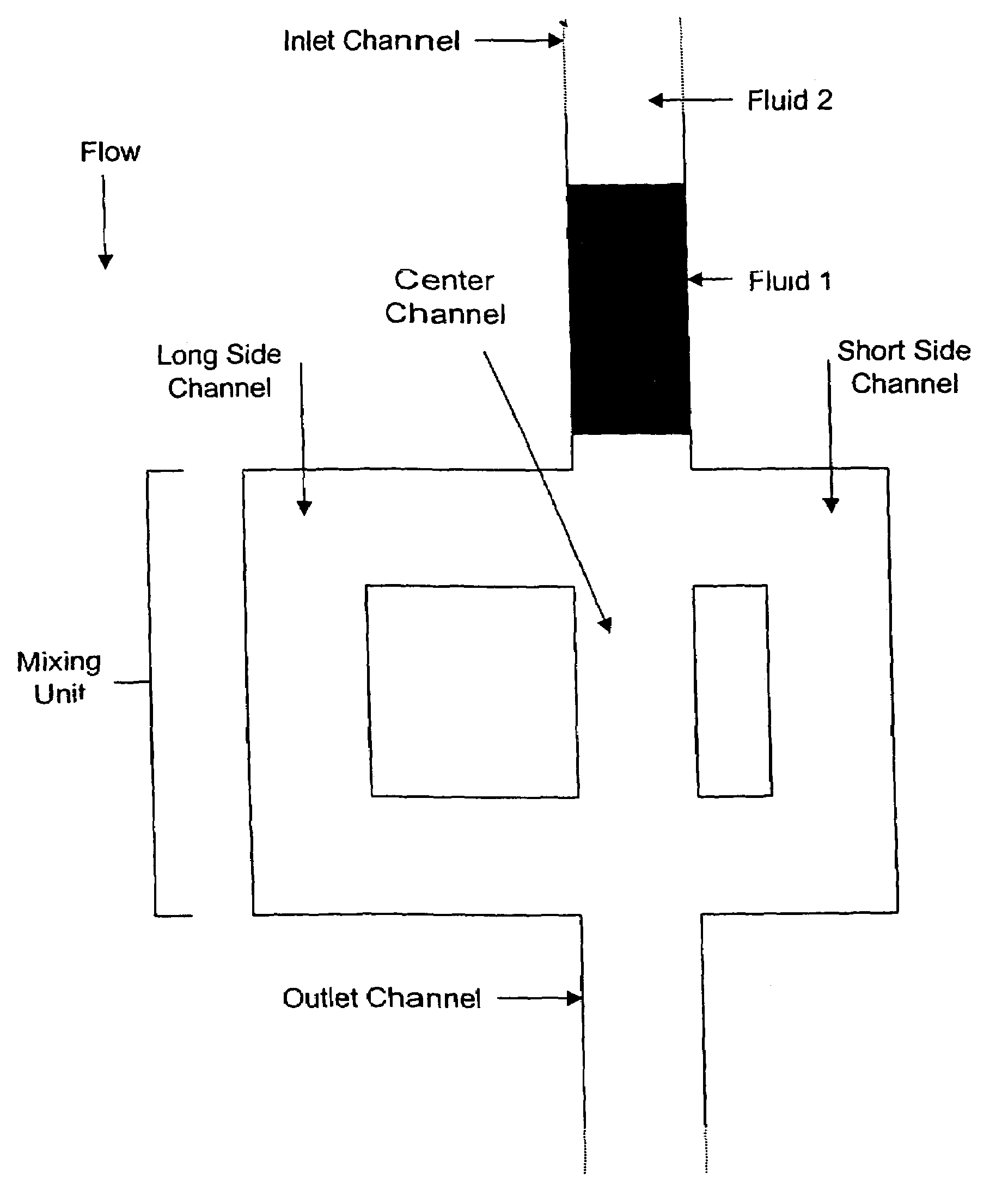
Microfluidics devices and methods for performing based assays
InactiveUS20050136545A1Low cost of reagentsShorten reaction timeSpecific gravity using centrifugal effectsLaboratory glasswaresMedicineCell based assays
This invention provides methods and apparatus for performing microanalytic analyses and procedures, particularly miniaturized cell based assays. These methods are useful for performing a variety of cell-based assays, including drug candidate screening, life sciences research, and clinical and molecular diagnostics.
Owner:TECAN TRADING AG
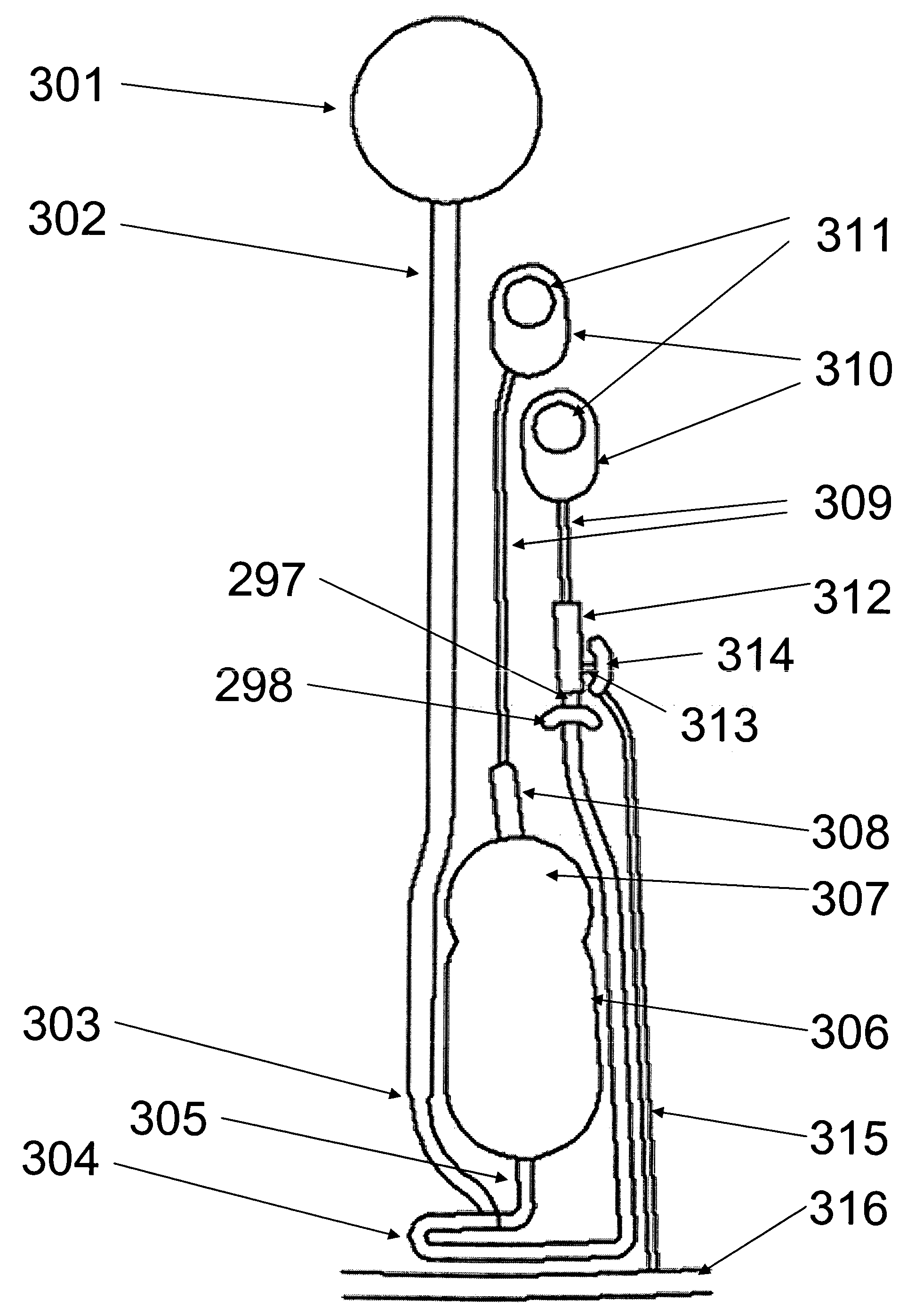
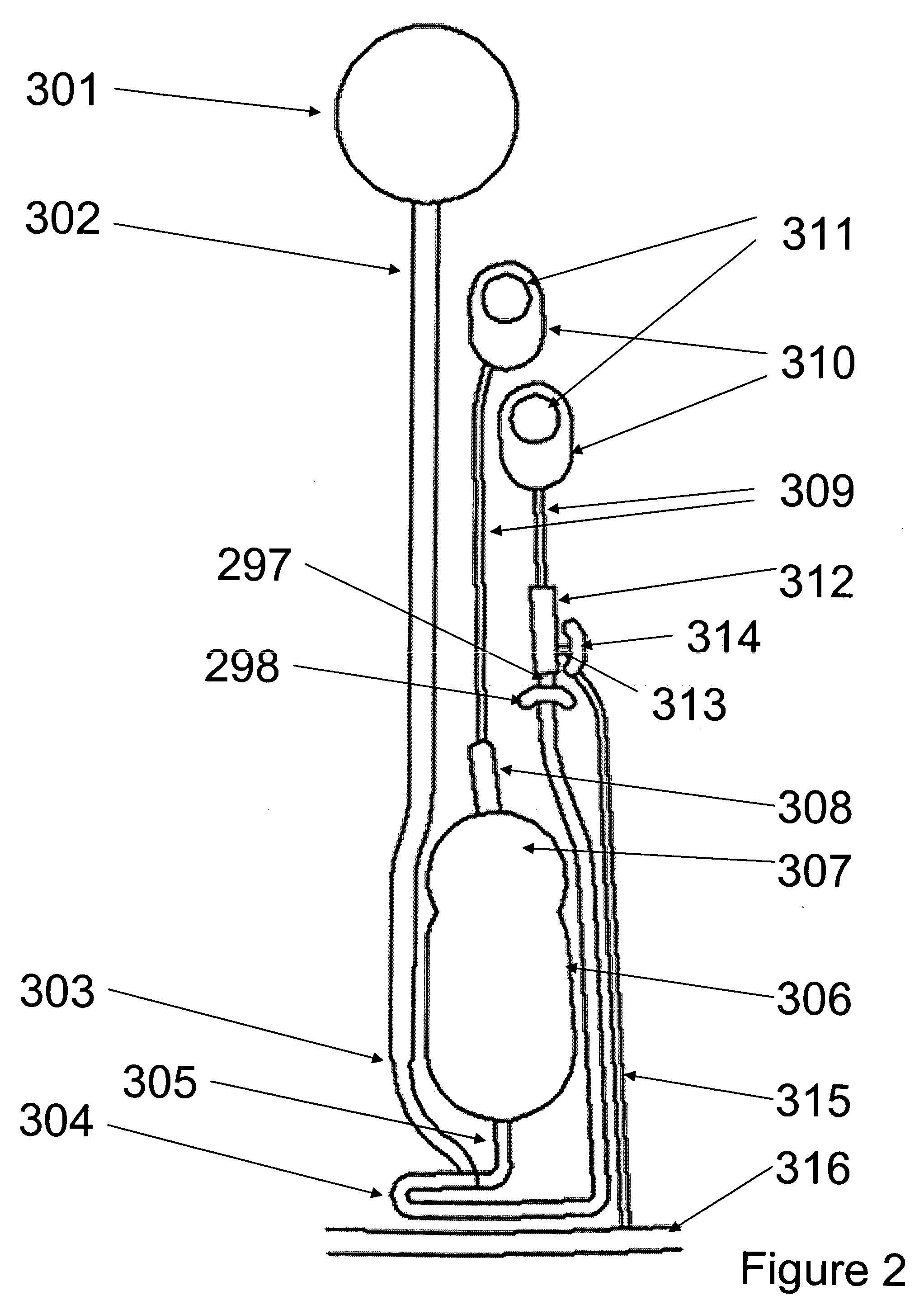
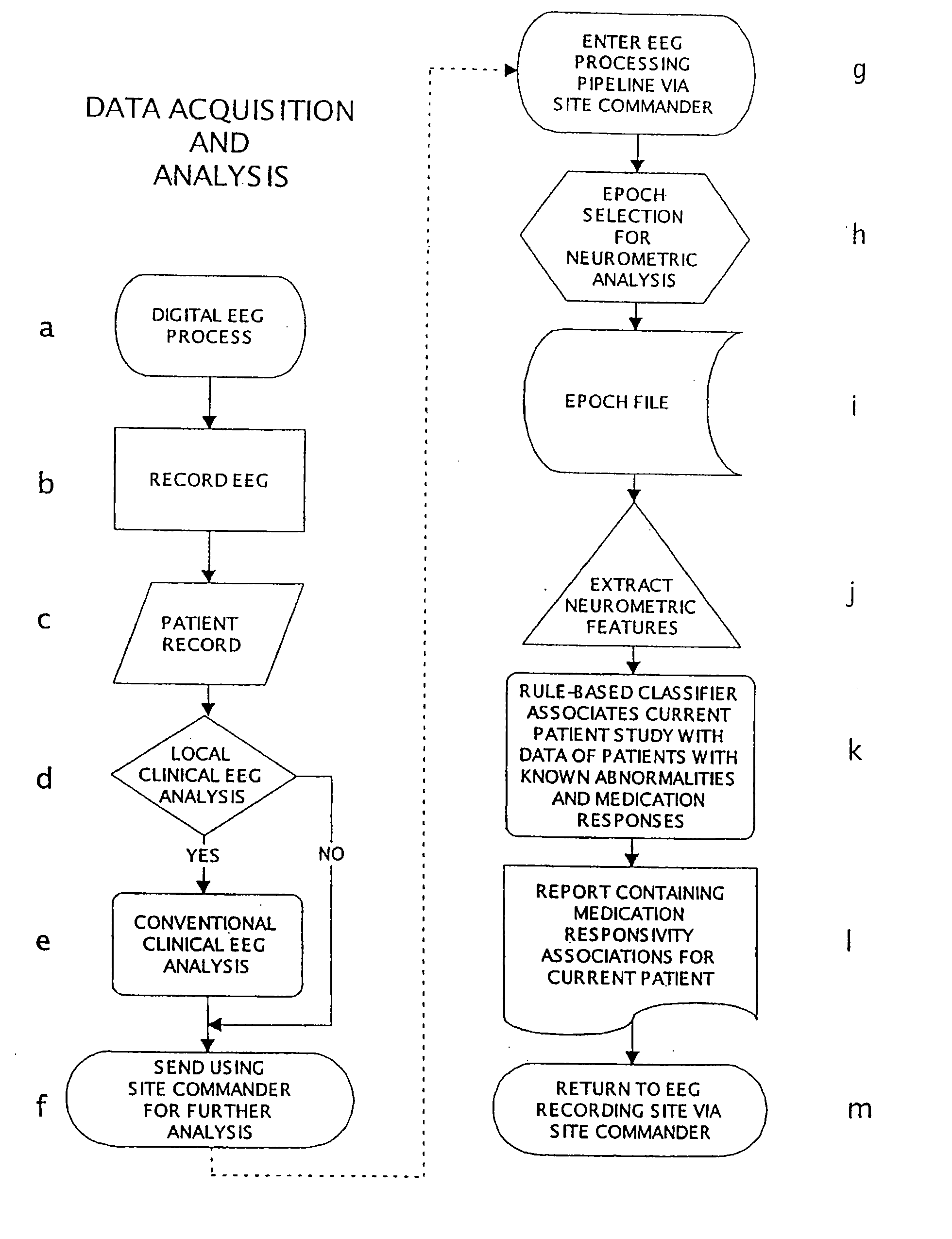
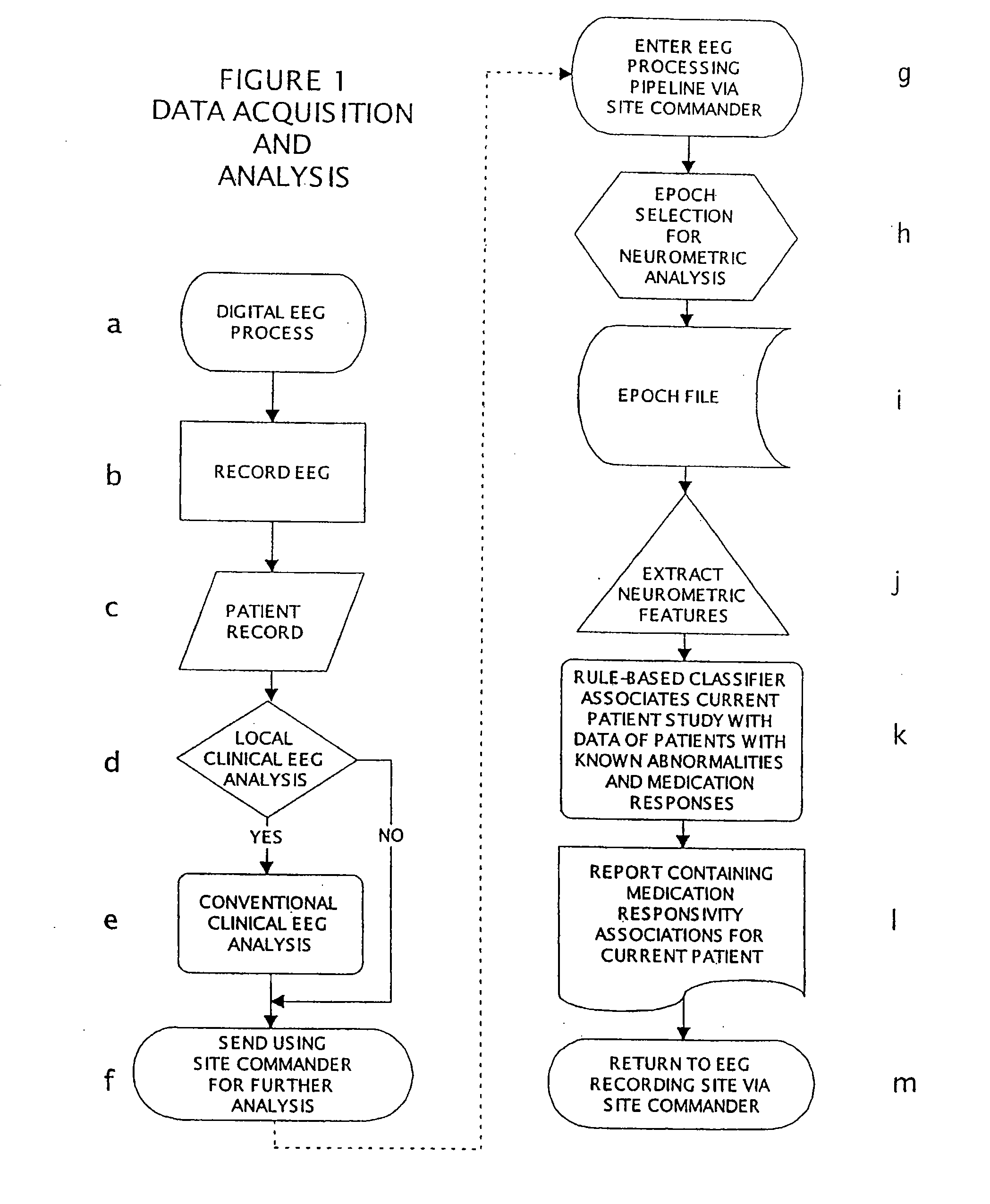
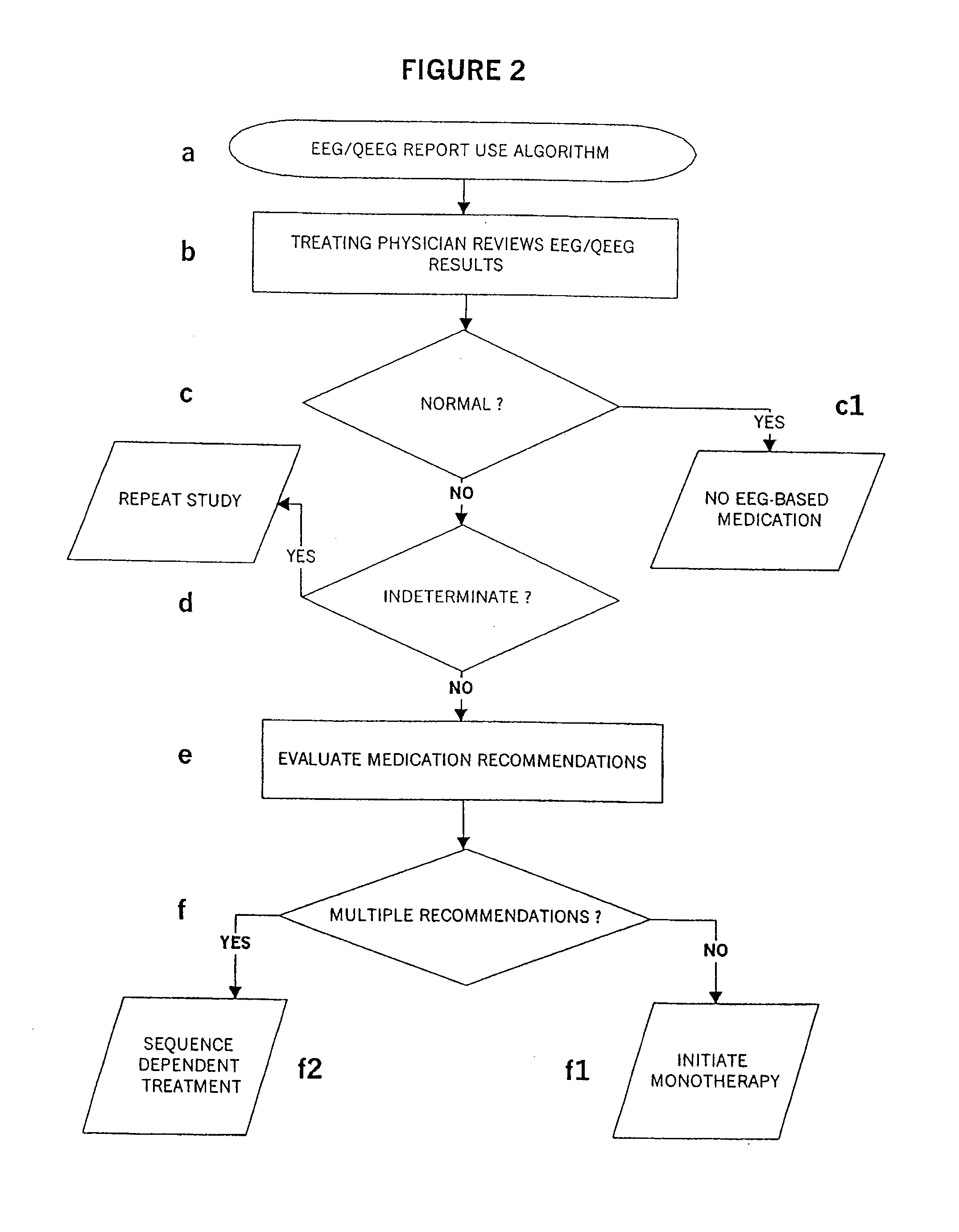
Methods For Classifying And Treating Physiologic Brain Imbalances Using Quantitative EEG
Owner:CNS RESPONSE
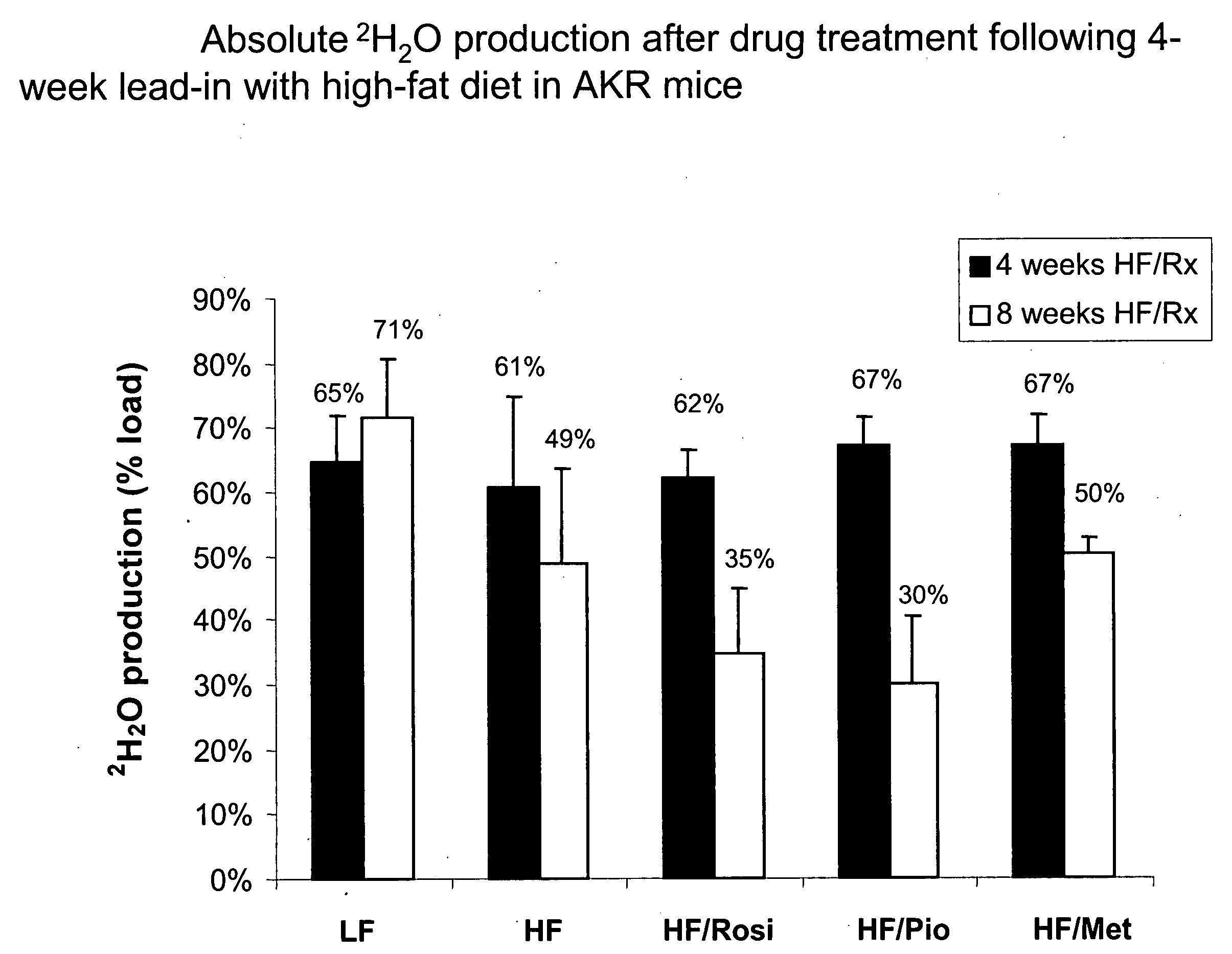
Method of enhancing the efficiency of a pharmaceutical business
InactiveUS20060100903A1Improve abilitiesData processing applicationsDrug and medicationsMetaboliteControl system
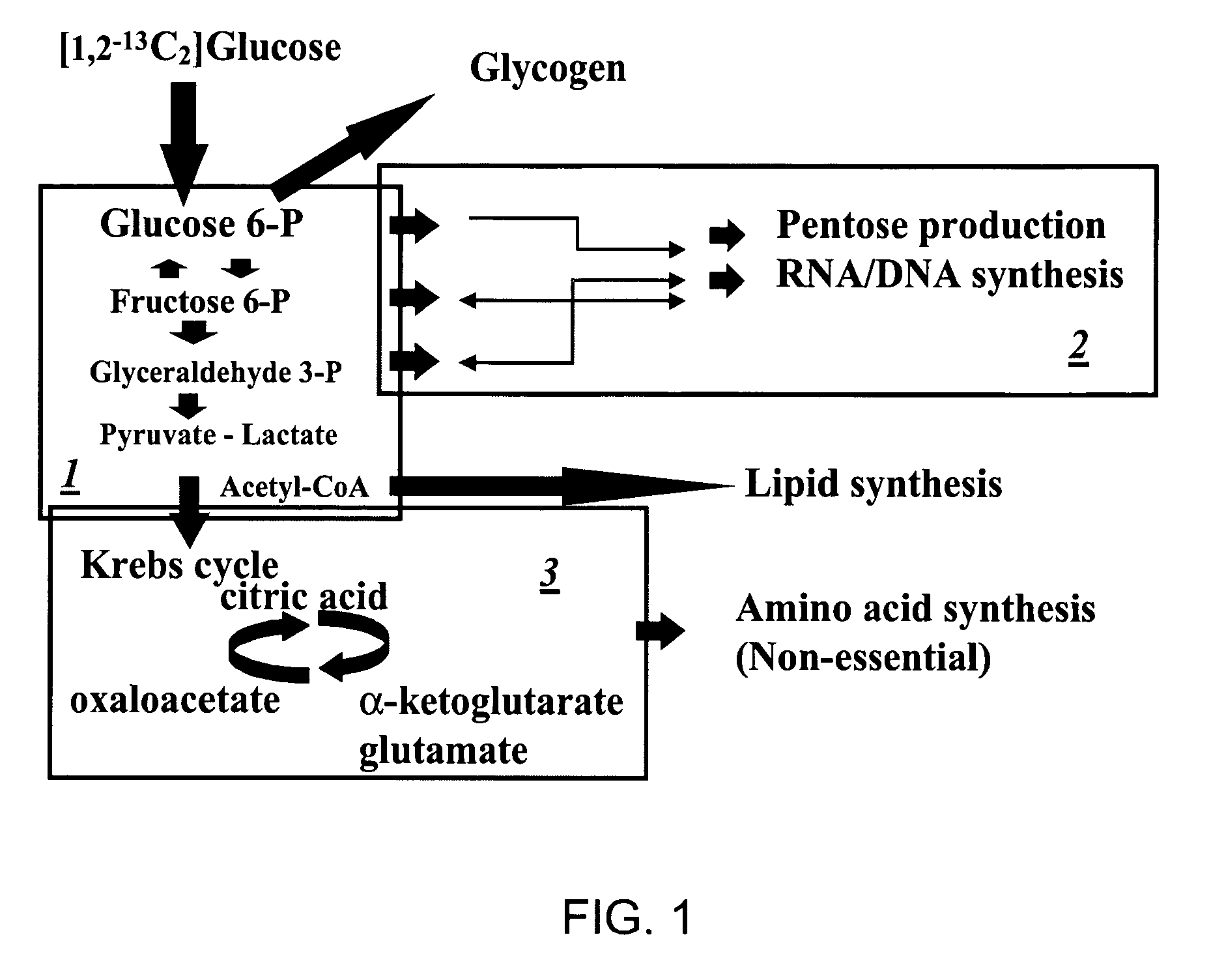
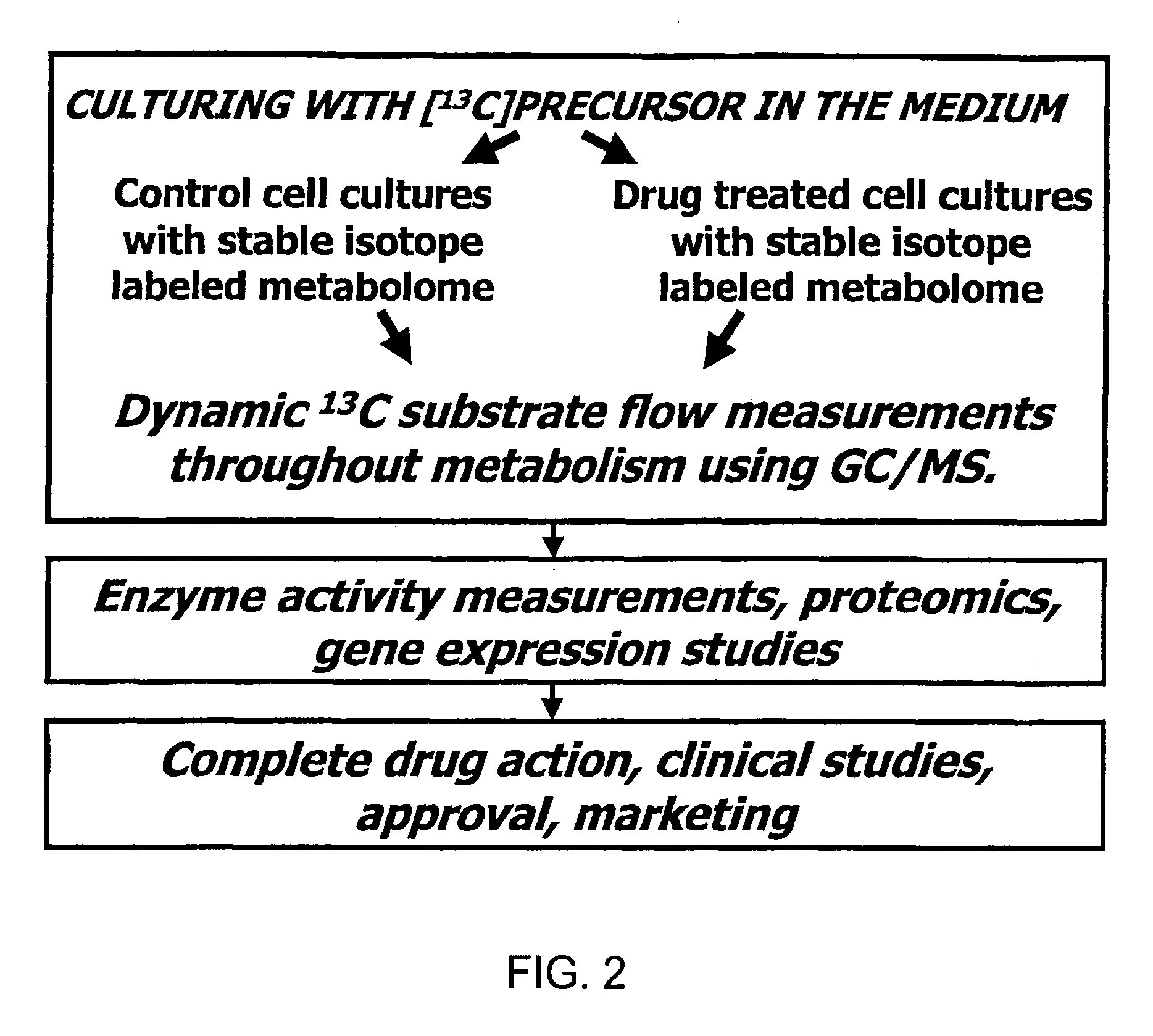
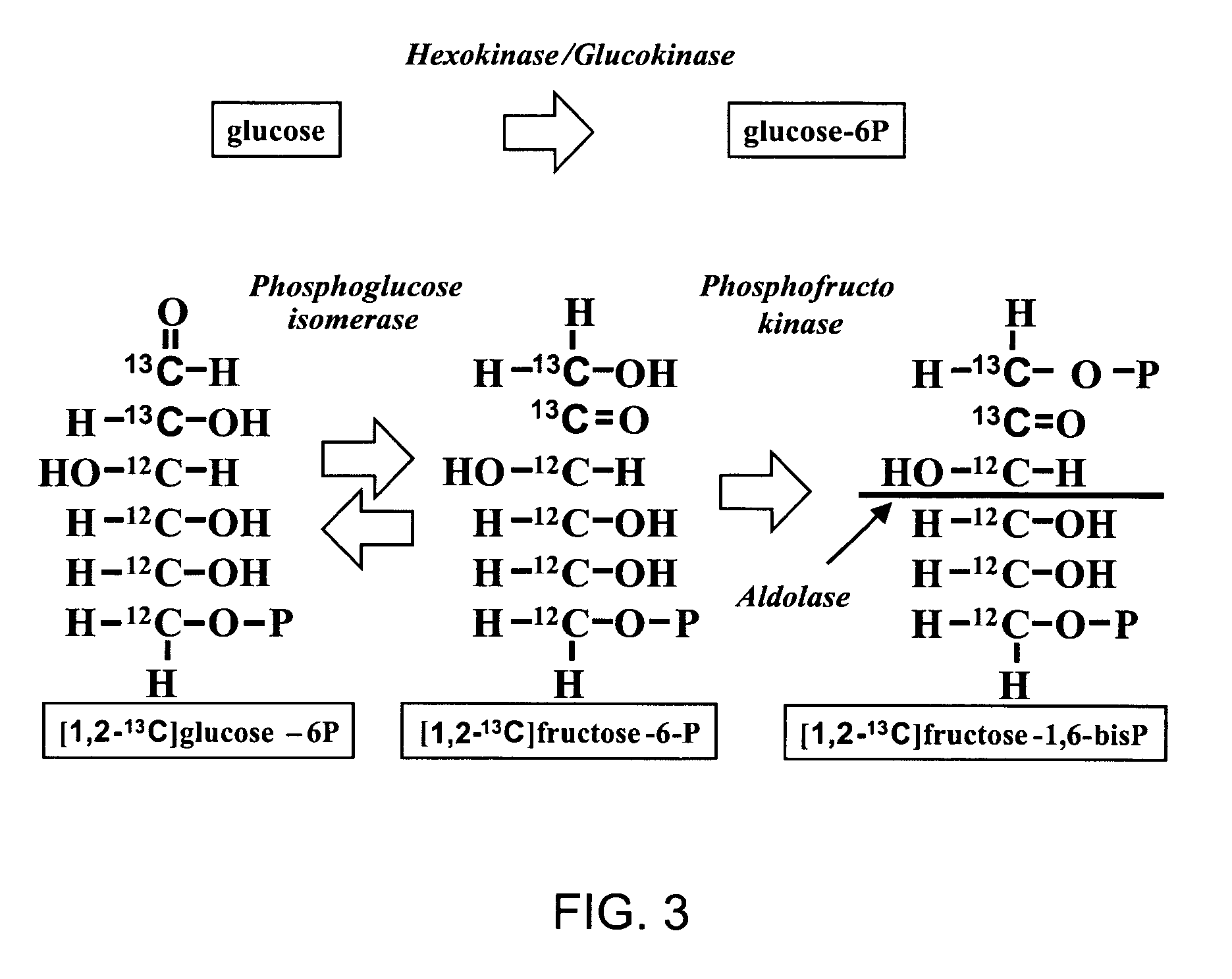
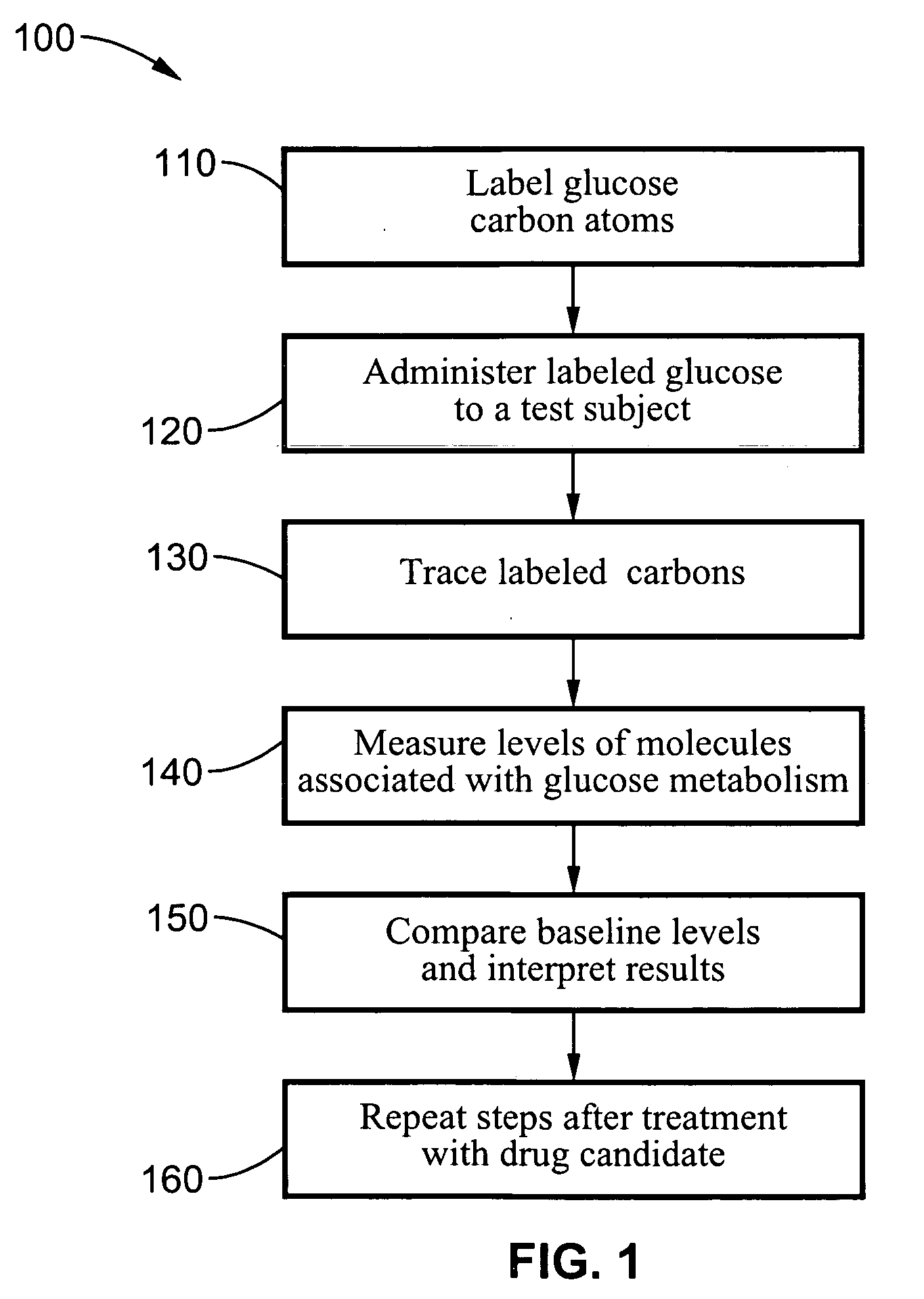
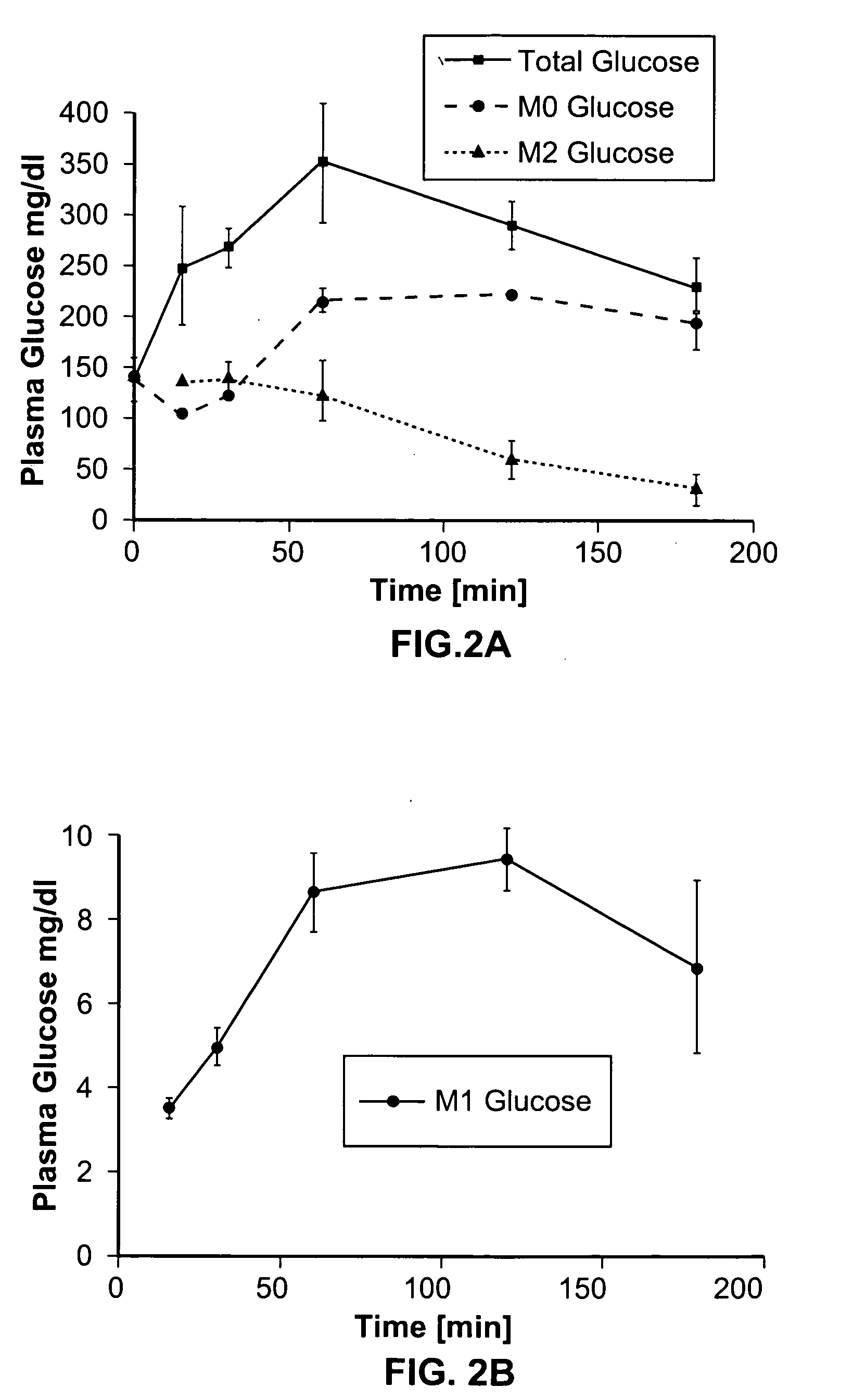
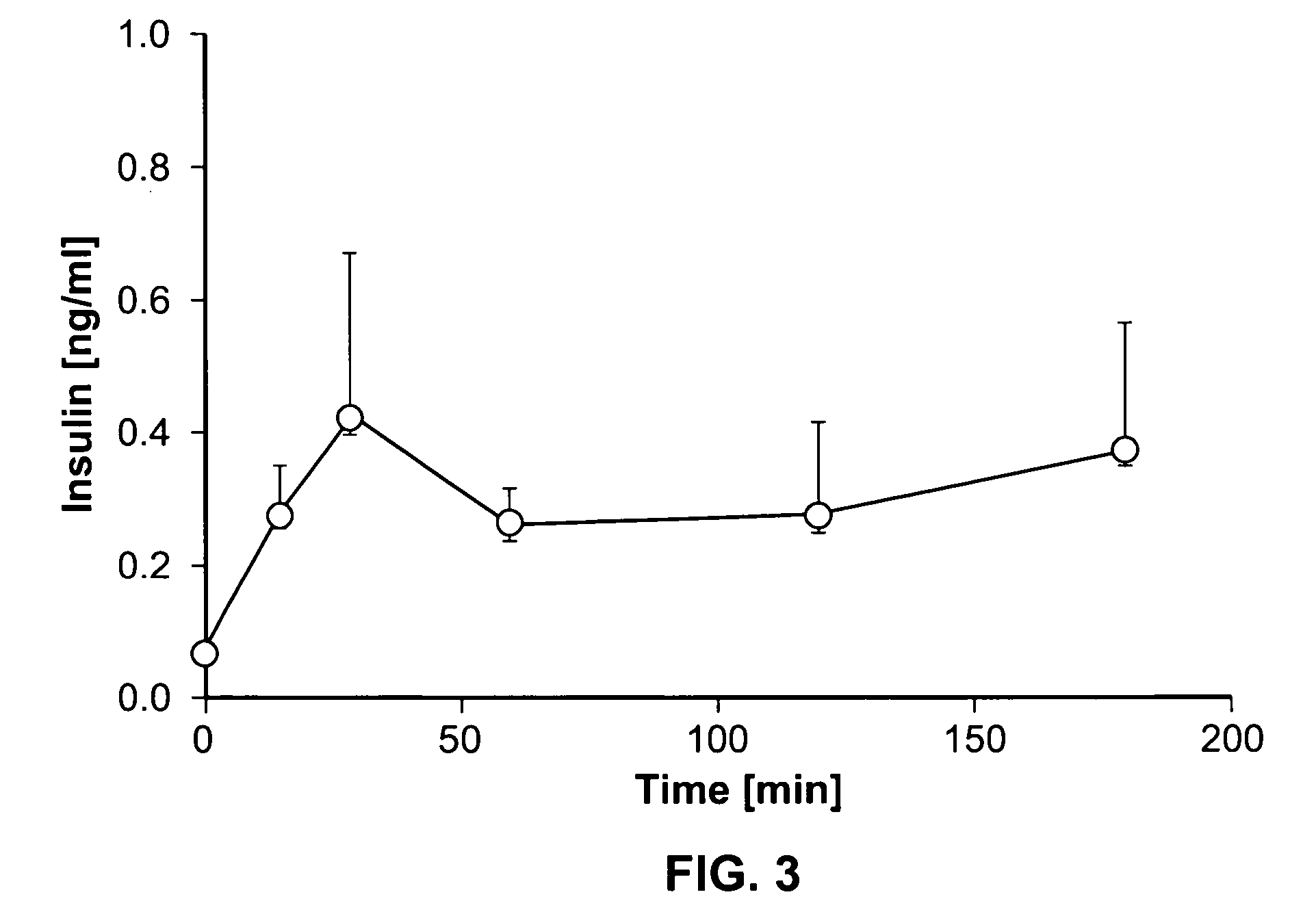
A method of doing business is disclosed whereby the process for selecting drug candidates is improved. The method involves the application of a technology which makes it possible to determine metabolic processes involved in the formation of any glucose-based metabolite. A precursor molecule is labeled with a stable carbon (13C) isotope at specific positions. The label is allowed to distribute and rearrange in the system. Metabolites are recovered and analyzed against a control system or known biochemical reactions and / or cycles to determine information such as metabolic pathway substrate flux caused by a compound acting on the system.
Owner:LOS ANGELES BIOMEDICAL RES INST AT HARBOR UCLA MEDICAL CENT
Drug-carrier complexes and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20060019911A1Biological functionalityWide safety marginSugar derivativesGenetic material ingredientsSolubilityBiological body
Drug-carrier complexes, drug carriers, pharmaceutical formulations, methods of delivery drugs to an organism or tissue culture, methods of increasing the solubility of a substance, targeted carriers, drug delivery systems and implants are described. The compositions and methods of the invention include forming complexes having reversible associations between nucleotides and drugs. The compositions and methods of the invention can be employed to target drugs to cells, organisms or combinations of cells to treat and to study the underlying mechanisms of diseases, and to test drug candidates.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Dynamic hepatic recycling glucose tolerance test
Systems and methods are described providing a hepatic recycling glucose tolerance test for the diagnosis of types and subtypes of diabetes mellitus and other hyperglycemic or hypoglycemic conditions. A method is also provided for screening candidate drugs for treating various types of abnormal glucose metabolism and to monitor whether the course of treatment is effective. The method also allows the correlation of gene activity, hormone and metabolite levels with glucose flux and recycling and an assessment of the degree of hepatic insulin resistance. The method utilizes a preferably non-radioactive stable labeled glucose to asses the relative rates of carbon flow in the liver and provides a hepatic recycling constant that is a measure of the relative rate of glucose recycling. The labeled glucose may be introduced to the patient orally, intravenously or by intraperitoneal administration for the desired effect.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
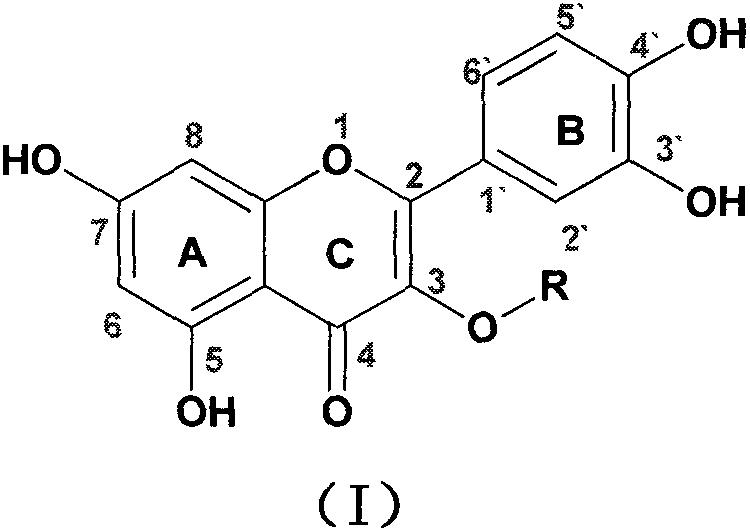
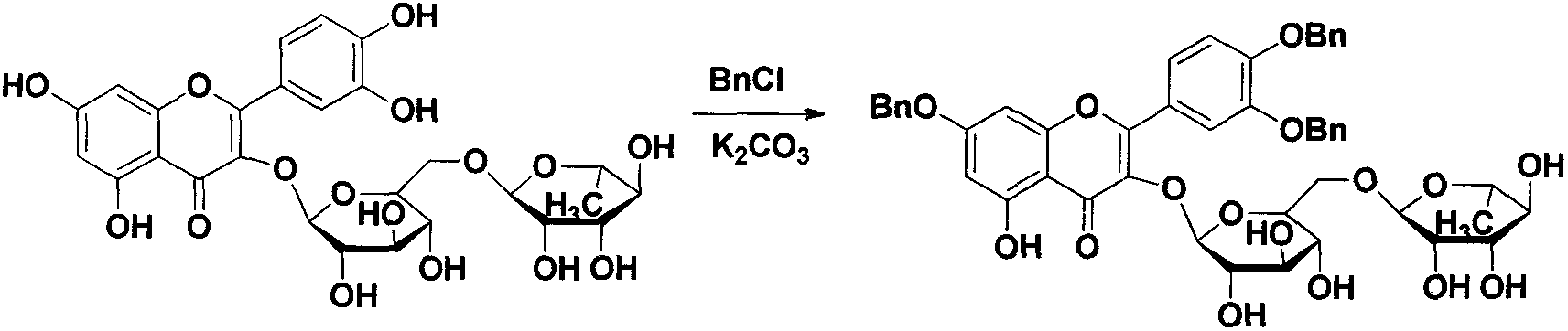
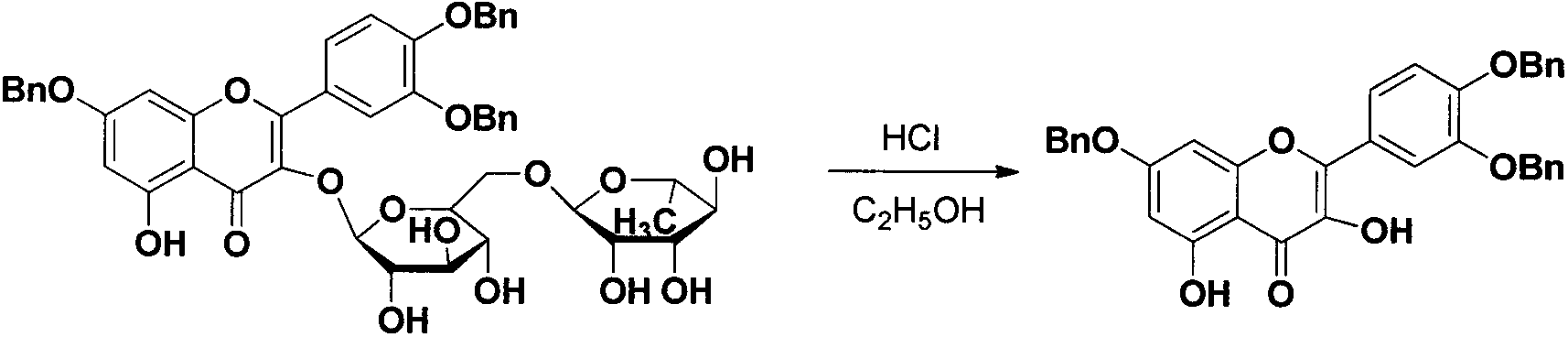
Quercetin-3-O-acyl ester and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102659735AEnhanced inhibitory effectOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryRutinHydrolysis
The invention relates to quercetin-3-O-acyl ester and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of pharmaceutical chemistry. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking cheap rutin as a starting raw material and preparing a quercetin-3-O-acyl ester compound through benzylation, hydrolysis under the acidic conditions, esterification, catalytic hydrogenolysis and other reactions. The method has the characteristics of good selectivity, mild reaction condition, high yield, low cost, simplicity and convenience in operation, easiness in industrial production and the like. In addition, the inhibitory effect of the obtained quercetin-3-O-acyl ester on human esophageal squamous carcinoma cells EC9706, human prostatic cancer cells PC-3 and human gastric cancer cells MGC-803 is remarkably superior to that of quercetin; and the quercetin-3-O-acyl ester can be used in the field of foods and medicines and is possible to develop into a new candidate drug for treating tumor.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIV
Harnessing network biology to improve drug discovery
InactiveUS20060160109A1Enable optimizationMaterial nanotechnologyPeptide librariesToxicantOn pathway
This invention provides principles, methods and compositions for ascertaining the mechanism of action of pharmacologically important compounds in the context of network biology, across the entire scope of the complex pathways of living cells. Importantly, the principles, methods and compositions provided allow a rapid assessment of the on-pathway and off-pathway effects of lead compounds and drug candidates in living cells, and comparisons of lead compounds with well-characterized drugs and toxicants to identify patterns associated with efficacy and toxicity. The invention will be useful in improving the drug discovery process, in particular by identifying drug leads with desired safety and efficacy and in effecting early attrition of compounds with potential adverse effects in man.
Owner:ODYSSEY THERA INC
Infrared thermography
InactiveUS6983753B1Inhibit thermogenesisFacilitates production of heatSurgeryDiagnostic recording/measuringDiseasePresent method
The present invention relates, in general, to thermography and, in particular, to a method of using infrared thermography to monitor physiological and molecular events that elicit a thermogenic response in animals (including humans), plants, tissues, cells and cell-free systems. The present method can be used for screening, identifying, and ranking drug candidates for multiple diseases, disorders and conditions.
Owner:GLAXO WELLCOME INC
Drug testing system with bio-artificial liver
InactiveUS20050130254A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsArtificial liverLiver slice
A drug testing system using a liver-slice culture apparatus. The apparatus has a chamber with plasma and gas valves, animal liver slices being positioned securely in the chamber so as to maximize the surface area of liver slices exposed to the culture medium. Plasma is supplied to the chamber so that it rises to contact the liver slices, and is alternately removed from contacting the liver slices. Gas is supplied to the top of the chamber. The system also includes a reservoir for containing media entering and exiting the chamber. Methods are provided for assessing the toxicity of a drug or drug candidate.
Owner:HEPAHOPE
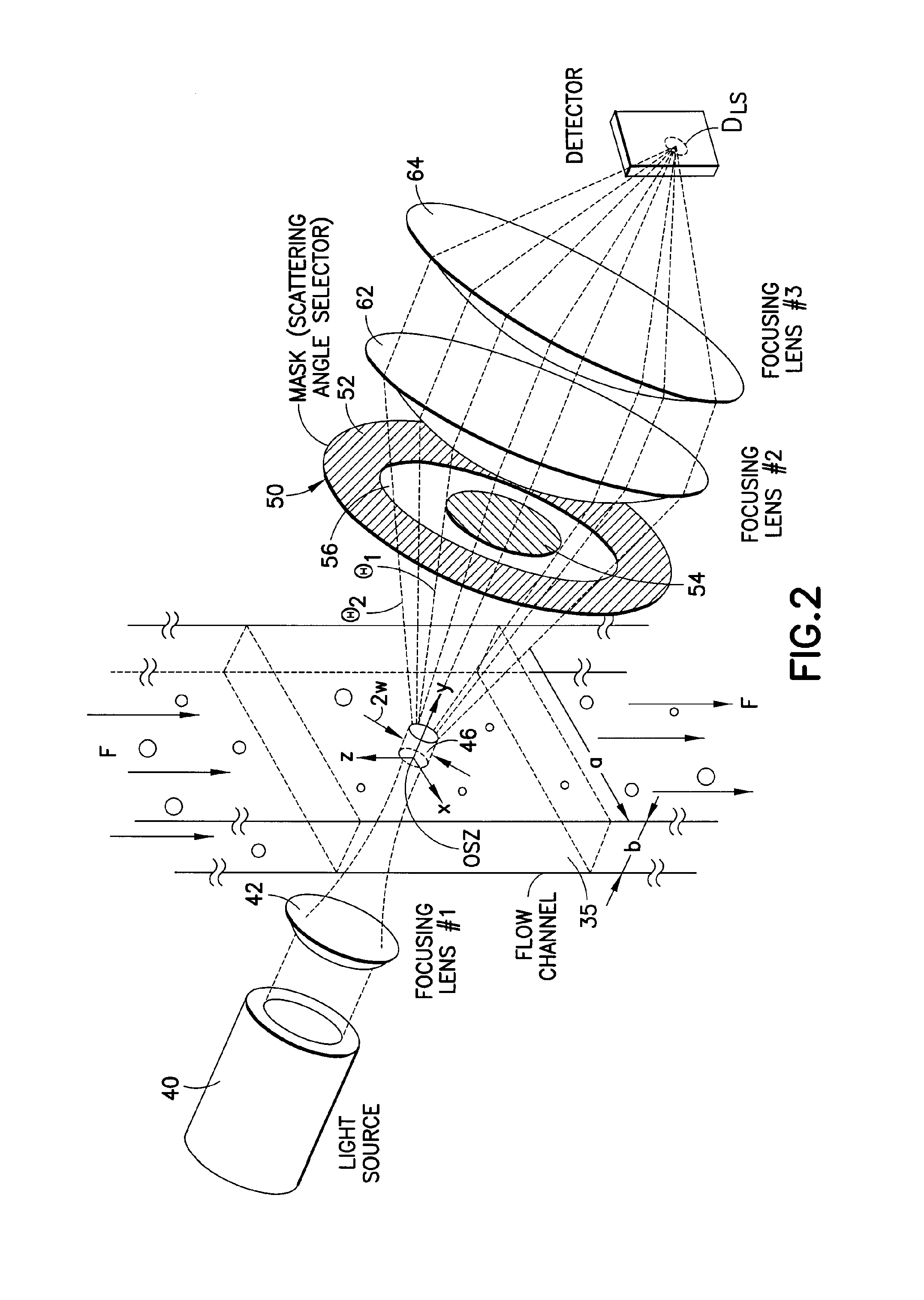
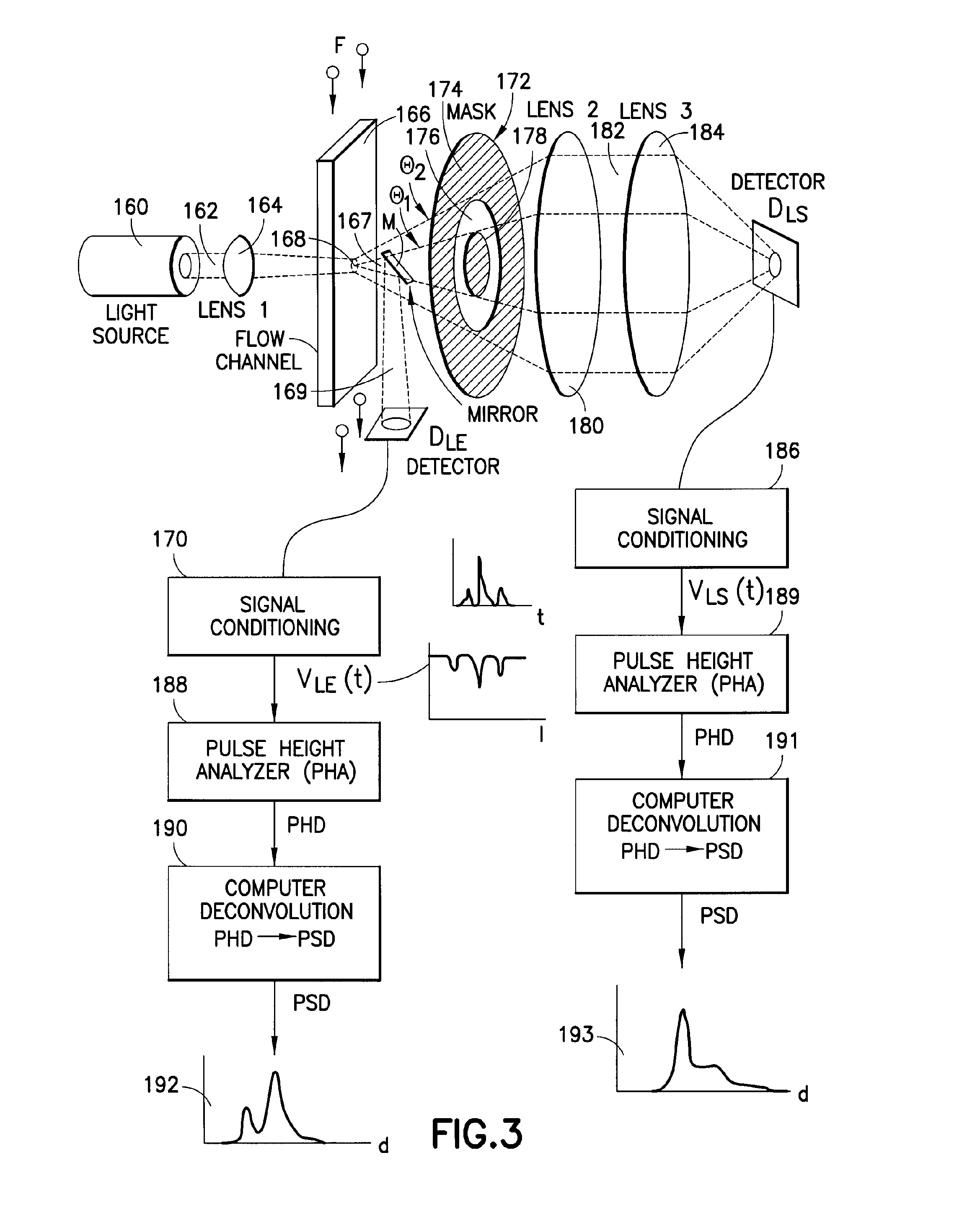
Use of focused light scattering techniques in biological applications
ActiveUS20100035235A1Large particle sizeHigh throughput screeningCompound screeningApoptosis detectionLiquid mediumParticle density
Methods for using focused light scattering techniques for the optical sensing of biological particles suspended in a liquid medium are disclosed. The optical sensing enables one to characterize particles size and / or distribution in a given sample. This, in turn, allows one to identify the biological particles, determine their relative particle density, detect particle shedding, and identify particle aggregation. The methods are also useful in screening and optimizing drug candidates, evaluating the efficacy and dosage levels of such drugs, and in personalized medicine applications.
Owner:INVITROX
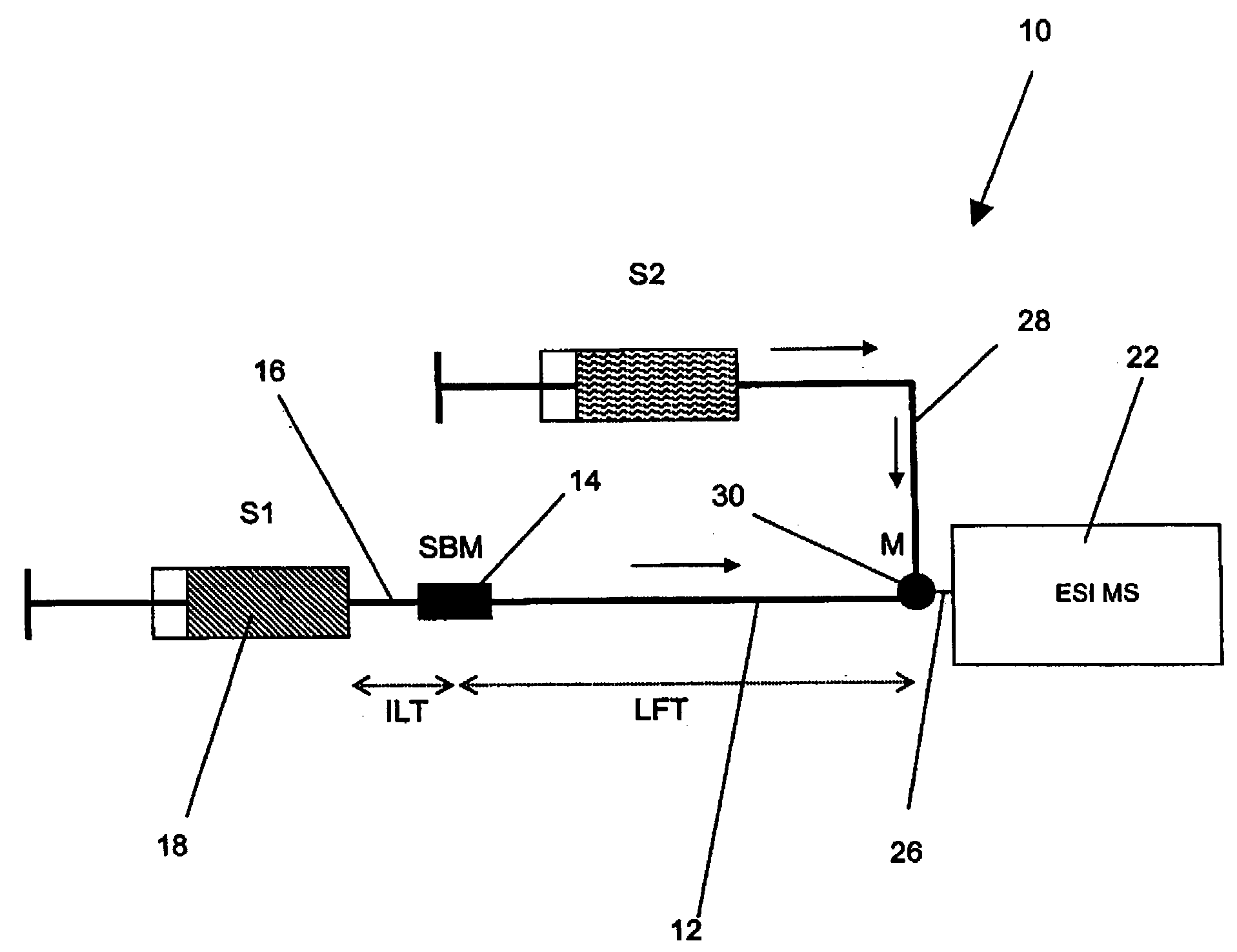
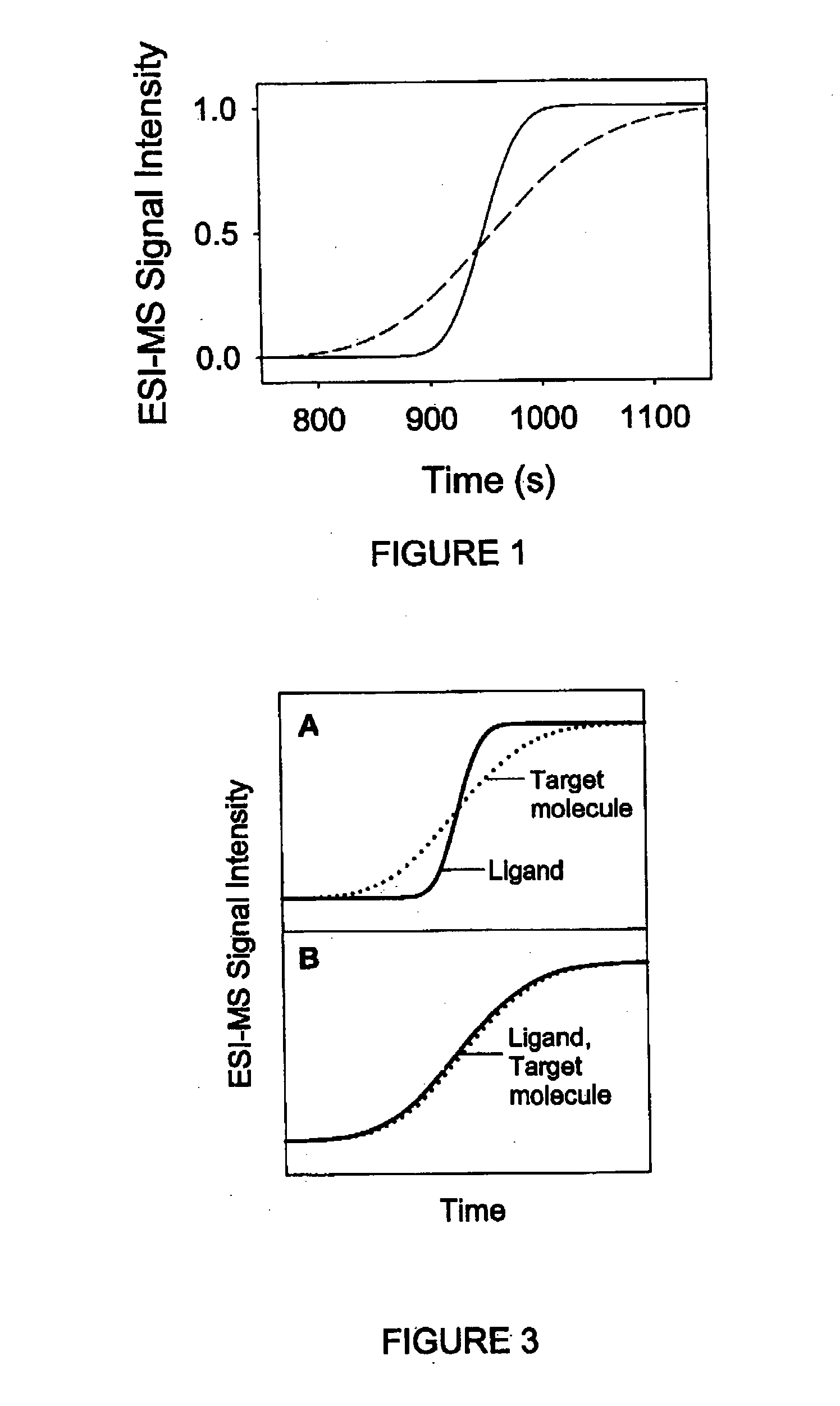
Method and apparatus for the detection of noncovalent interactions by mass spectrometry-based diffusion measurements
InactiveUS20030234356A1Accurate measurementShorten the timeSamples introduction/extractionSurface/boundary effectHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsGas phase
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for detecting the noncovalent binding of a potential ligand (such as a drug candidate) to a target, e.g. a biochemical macromolecule such as a protein. The method is based on the Taylor dispersion of an initially sharp boundary between a carrier solution, and an analyte solution that contains the potential ligand(s) and the target. Dispersion profiles of one or more potential ligands are monitored by mass spectrometry at the exit of the laminar flow tube. Potential ligands will usually be relatively small molecules that have large diffusion coefficients. In the absence of any noncovalent interactions in solution, very steep dispersion profiles are expected for these potential ligands. However, a ligand that binds to a large target in solution, will show an apparent diffusion coefficient that is significantly reduced, thus resulting in a more extended dispersion profile. Noncovalent binding can therefore be detected by monitoring dispersion profiles of potential ligands in the presence and in the absence of the target. In contrast to other mass spectrometry-based methods for detecting noncovalent interactions, this method does not rely on the preservation of specific noncovalent interactions in the gas phase. This method has an excellent sensitivity and selectivity, therefore it can be used for testing multiple potential ligands simultaneously. The method is therefore useful for the high throughput screening of compound libraries.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN ONTARIO
NMR-solve method for rapid identification of bi-ligand drug candidates
Methods for rapidly identifying drug candidates that bind to an enzyme at both a common ligand site and a specificity ligand site, resulting in high affinity binding. The bi-ligand drug candidates are screened from a focused combinatorial library where the specific points of variation on a core structure are optimized. The optimal points of variation are identified by which atoms of a ligand bound to the common ligand site are identified to be proximal to the specificity ligand site. As a result, the atoms proximal to the specificity ligand site can then be used as a point for variation to generate a focused combinatorial library of high affinity drug candidates that bind to both the common ligand site and the specificity ligand site. Different candidates in the library can then have high affinity for many related enzymes sharing a similar common ligand site.
Owner:TRIAD BIOTECH
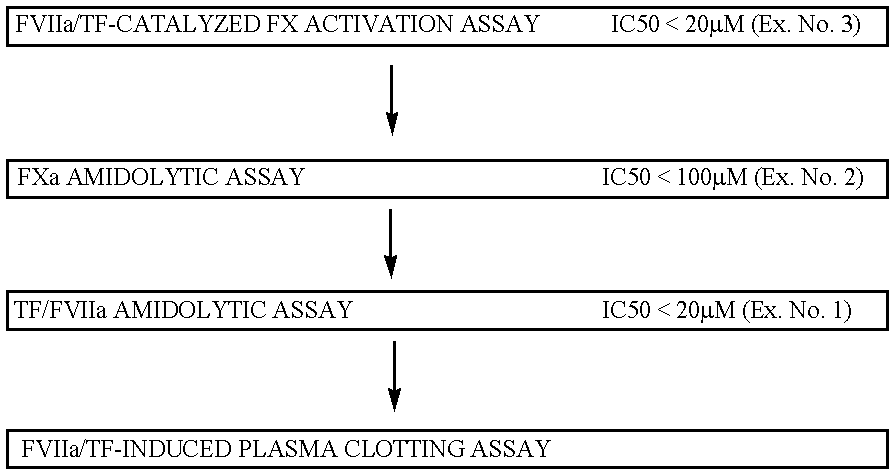
FVIIa/TF activity inhibiting compounds
InactiveUS6238878B1Inhibition of activationHinder orAntibacterial agentsAntipyreticAnticoagulantBiological activation
The invention relates to compounds inhibiting the activation of FX to FXa by TF / FVIIa. The compounds are anticoagulants. The invention also relates to a method of identifying a drug candidate.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Microfluidics devices and methods of diluting samples and reagents
InactiveUS7476361B2Low cost of reagentsShorten reaction timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEngineeringMicroanalysis
This invention relates to methods and apparatus for performing microanalytic and microsynthetic analyses and procedures. The invention provides a microsystem platform and a micromanipulation device for manipulating the platform that utilizes the centripetal force resulting from rotation of the platform to motivate fluid movement through microchannels. These assays may be performed for a variety of purposes, including but not limited to screening of drug candidate compounds, life sciences research, and clinical and molecular diagnostics. Methods specific for the apparatus of the invention for performing any of a wide variety of microanalytical or microsynthetic processes are provided.
Owner:TECAN TRADING AG
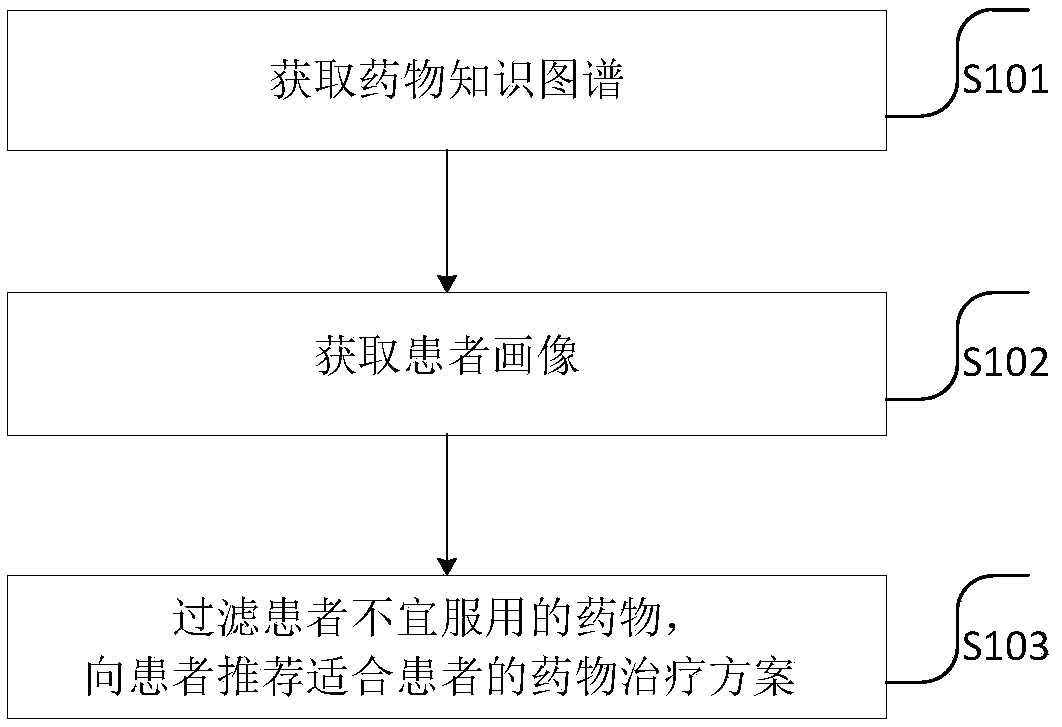
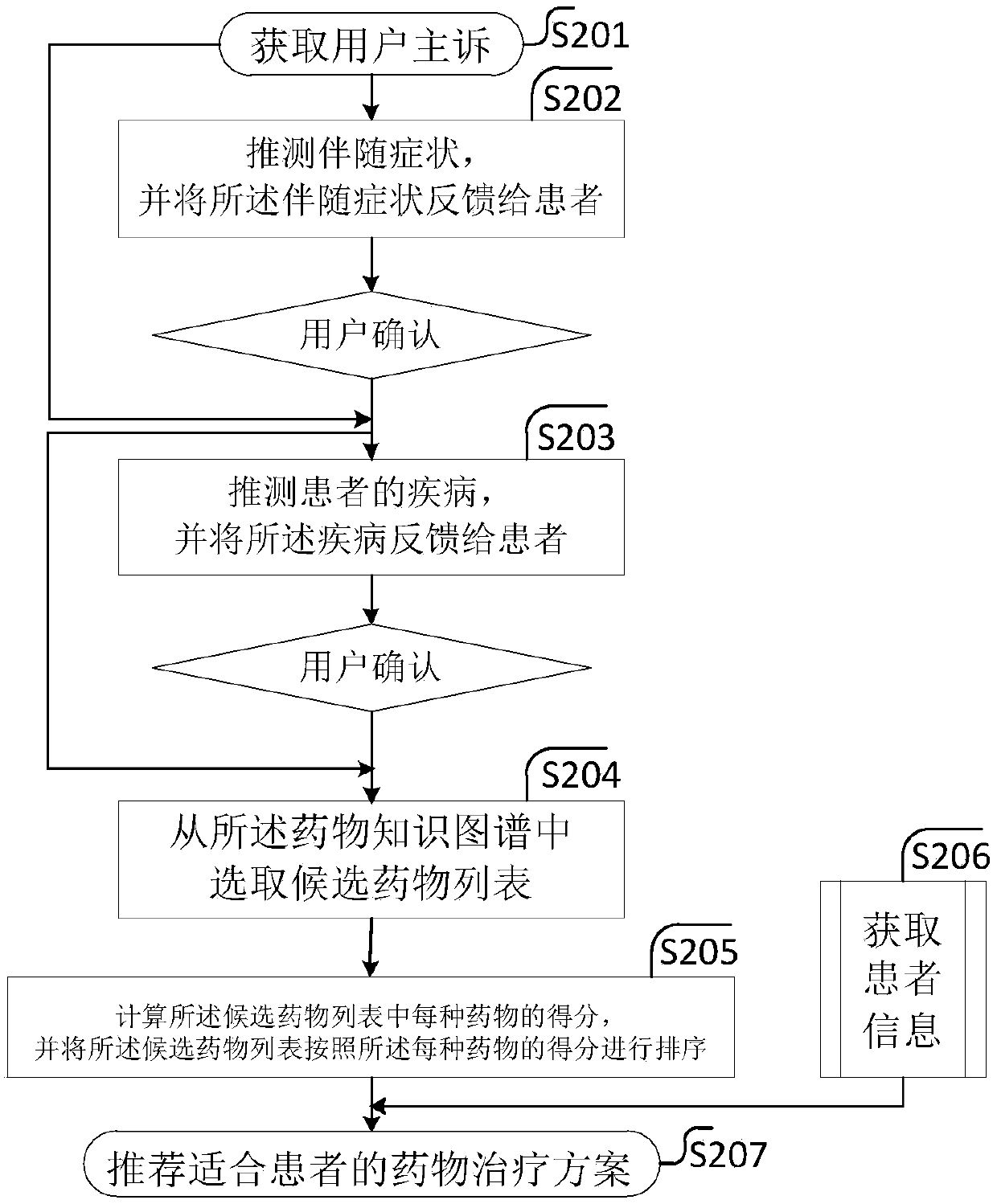
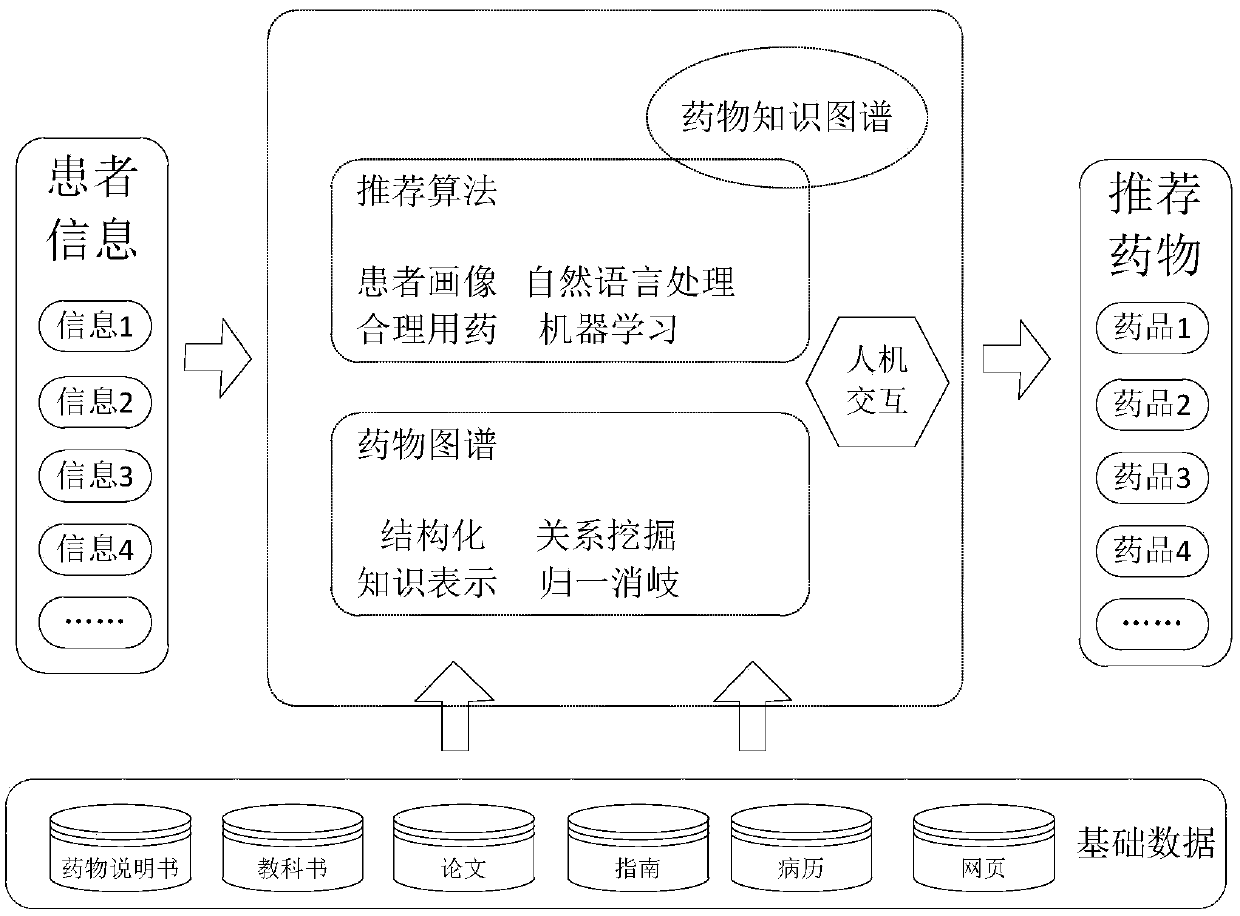
Drug recommendation method
PendingCN109102855ASolve the problem of recommending only a large list of drug candidates with fewAvoid situations where users are contraindicatedMedical data miningDrug and medicationsMedical recordClinical psychology
The invention provides a drug recommendation method. The method comprises steps that the natural language processing technology is utilized to construct a drug knowledge map; the medical record structure technology is utilized to construct a patient portrait based on the patient information, drugs that the patient should not take are filtered according to the drug knowledge map, the patient portrait and the preset recommendation algorithm, and a patient-friendly medication regimen is recommended to a patient. The method is advantaged in that problems that the user information obtained throughthe word-matching-based search method is too small and only a relatively large drug candidate list is recommended are solved, the drugs that the patient should not take are filtered according to the patient portrait and the preset recommendation algorithm, the patient can be recommended for the drugs that are more suitable for the patient, and the situation that a recommended drug is just a contraindication to the user is avoided.
Owner:北京左医科技有限公司
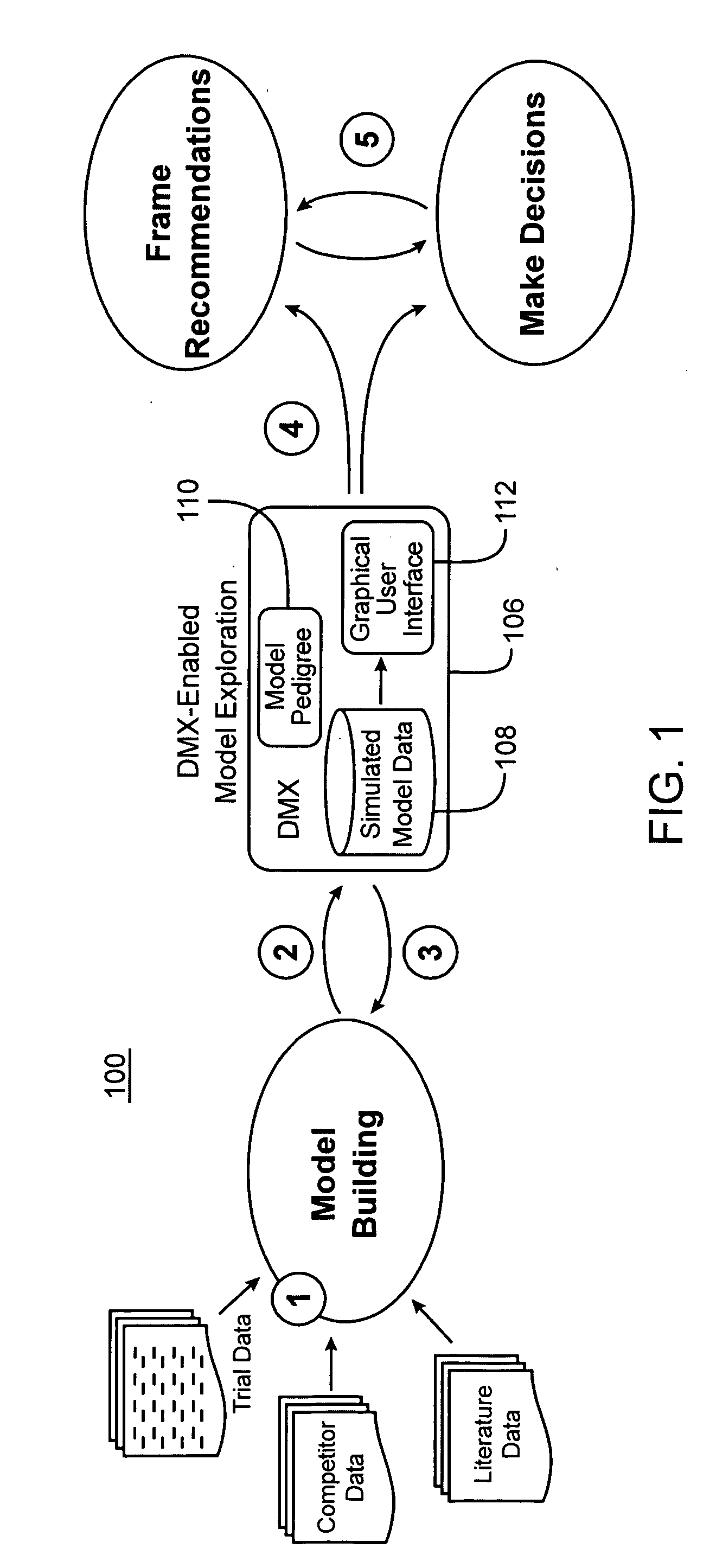
Drug model explorer
InactiveUS20050079511A1Enhanced interactionUniform and consistent evaluationMedical simulationLocal control/monitoringProbit modelInformation type
Computer systems and methods facilitate exploring results of drug candidate modeling. In one embodiment, the software is configured to receive raw data simulated by a probabilistic model of clinical safety, tolerability, and efficacy of a drug candidate. Index information is extracted from the raw data and then referenced to generate a metadata file, the structure of the metadata file explicitly reflecting a hierarchical structure of the model. The metadata file is in turn used to convert the raw data into a binary file, the metadata file explicitly identifying locations within the binary file, of treatment scenario information types and output performance information types. The metadata file is also referenced to generate an interface configured to receive inputs from a non-expert audience, and in turn present relevant subsets of the binary file in a limited number of plot and tabular formats. By standardizing presentation and manipulation of data from different models, software and methods in accordance with the present invention facilitate meaningful interaction between a non-expert audience, and the complex abstract mathematical models predicting drug behavior. The heightened audience-model interaction afforded by the present invention in turn promotes uniform and consistent evaluation of modeled data in the process of drug development.
Owner:TRIPOS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com