Preparation of nanoparticles with targeting or photo-thermal function based on polytannic acid modification technology
A polytannic acid and nanoparticle technology, applied in the field of medicine, can solve problems such as poor water solubility, lack of specific selectivity, and clinical application constraints, and achieve the effects of stable performance, simple operation, and safe and non-toxic raw materials
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Example Embodiment
[0032] Example 1 Preparation of Nanoparticles with Photothermal Function Based on Polytannic Acid Modification Technology
[0033] 1) Preparation of PNCs
[0034]First, add 3 mL of dichloromethane to 6 mg of paclitaxel and 24 mg of surfactant poloxamer (F127), dissolve them completely, and transfer them to an eggplant-shaped flask. The solvent was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain a thin film of paclitaxel and F127 mixture. Then add 6 mL of deionized water for 3 hours of hydration. After paclitaxel was precipitated in the form of crystals, ultrasonic crushing was performed using an ultrasonic cell disruptor in an ice-water bath (power: 150W; frequency: 2s on, 2s off; duration: 15min) to obtain nano-scale paclitaxel nanosuspension. Finally, the precipitate was collected by centrifugation (14000rpm, 15min) to obtain purified PNC.
[0035] 2) Preparation of PNC-pTA
[0036] The purified PNC prepared in 1) was dispersed into 1.5 mL of N-biglycine buffer solution (10 mM, ...
Example Embodiment
[0037] Example 2 Preparation of nanoparticles with tumor targeting function based on polytannic acid modification technology
[0038] 1) Preparation of PNCs
[0039] First, add 3 mL of dichloromethane to 6 mg of paclitaxel and 24 mg of surfactant poloxamer (F127), dissolve them completely, and transfer them to an eggplant-shaped flask. The solvent was removed by rotary evaporation to obtain a thin film of paclitaxel and F127 mixture. Then add 6 mL of deionized water for 3 hours of hydration. After paclitaxel was precipitated in the form of crystals, ultrasonic crushing was performed using an ultrasonic cell disruptor in an ice-water bath (power: 150W; frequency: 2s on, 2s off; duration: 15min) to obtain nano-scale paclitaxel nanosuspension. Finally, the precipitate was collected by centrifugation (14000rpm, 15min) to obtain purified PNC.
[0040] 2) Preparation of PNC-pTA
[0041] The purified PNC prepared in 1) was dispersed into 1.5 mL of N-biglycine buffer solution (10 ...
Example Embodiment
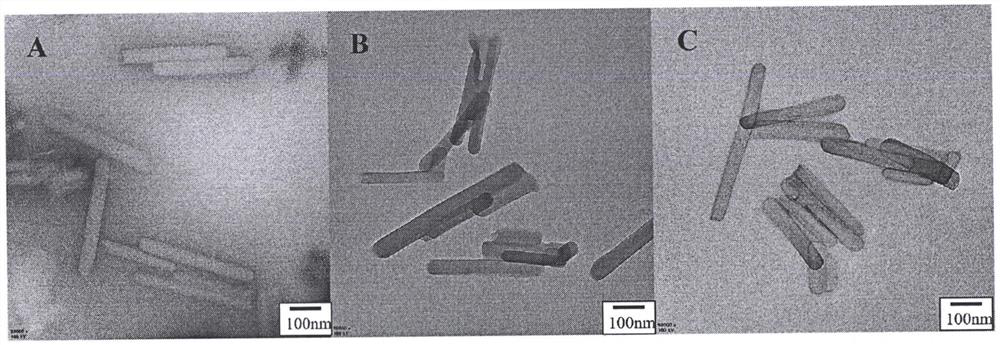
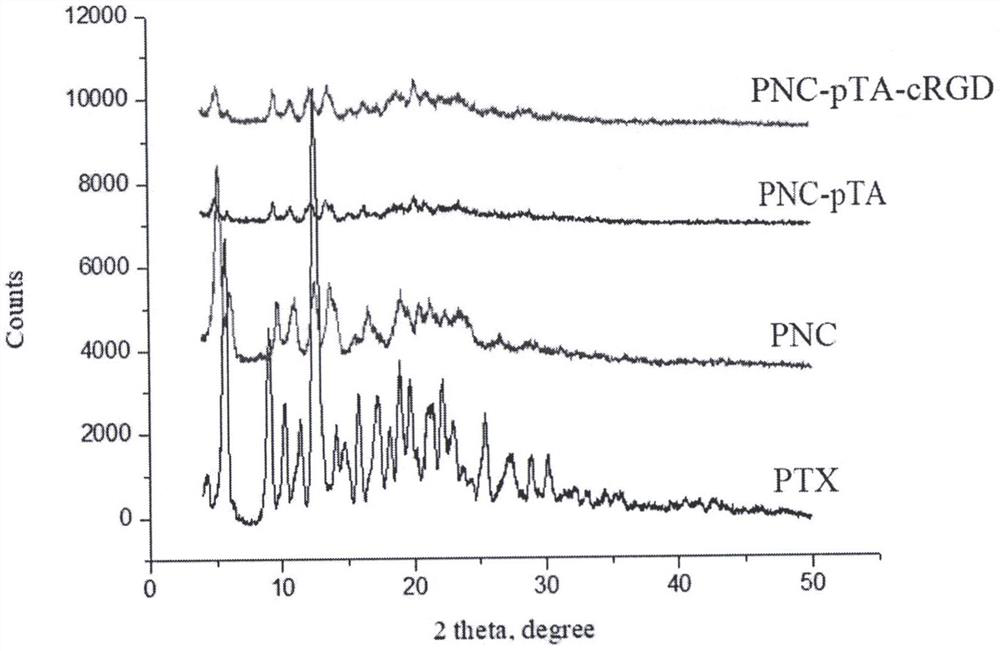
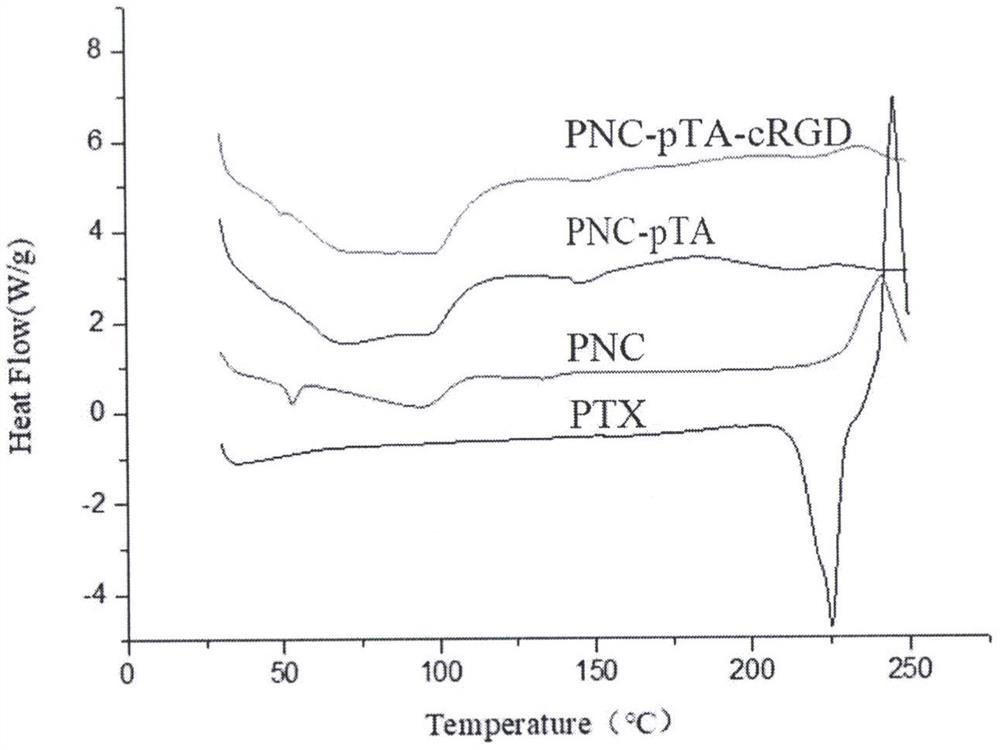
[0044] Example 3 Zeta potential characterization of nanoparticles
[0045] In this example, the PNC and PNC-pTA prepared in Example 1 and the PNC-pTA-cRGD prepared in Example 2 were morphologically characterized as follows:
[0046] Disperse 1-2 drops of PNC, PNC-pTA and PNC-pTA-cRGD suspensions in 1mL phosphate buffer solution (10mM, pH=7.4), and use the Malvern laser particle size analyzer to investigate the Zeta potential of each nanoparticle . Measured in parallel three times. The surface potential of PNC is -1.66±0.27mV, which is close to electrical neutrality. After coating pTA, the potential drops to -26.23±0.59mV, which proves that pTA has been coated. The specific results are shown in Table 1.
[0047] Table 1 Zeta potential measurement results of different samples (n=3)
[0048]
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap