Parachute avoidance method for Mars lander based on parachute drop point offline analysis
An off-line analysis and parachute technology, applied in the direction of aerospace vehicles, aerospace vehicle landing devices, aircraft, etc., can solve the problem of covering landers, achieve conservative and reliable results, and reduce evasive maneuvering energy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
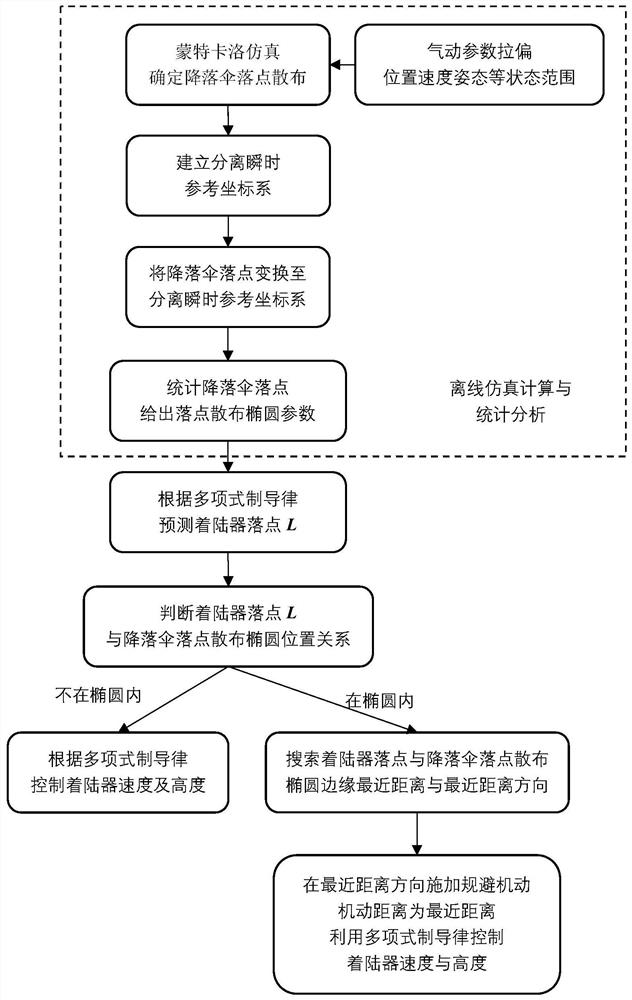
[0063] Specific implementation mode one: refer to figure 1 Specifically illustrate this embodiment, the method for avoiding the parachute of the Mars lander based on the off-line analysis of the parachute landing point described in this embodiment includes:
[0064] Step 1: Use the Monte Carlo simulation method to determine the parachute landing point p for n times of simulation by offline simulation on the ground before the landing mission is implemented i , where the subscript i=1,2,…,n, indicates the landing point result corresponding to the i-th simulation, and indicates that when Mars enters the ground coordinate system Σ m Down;
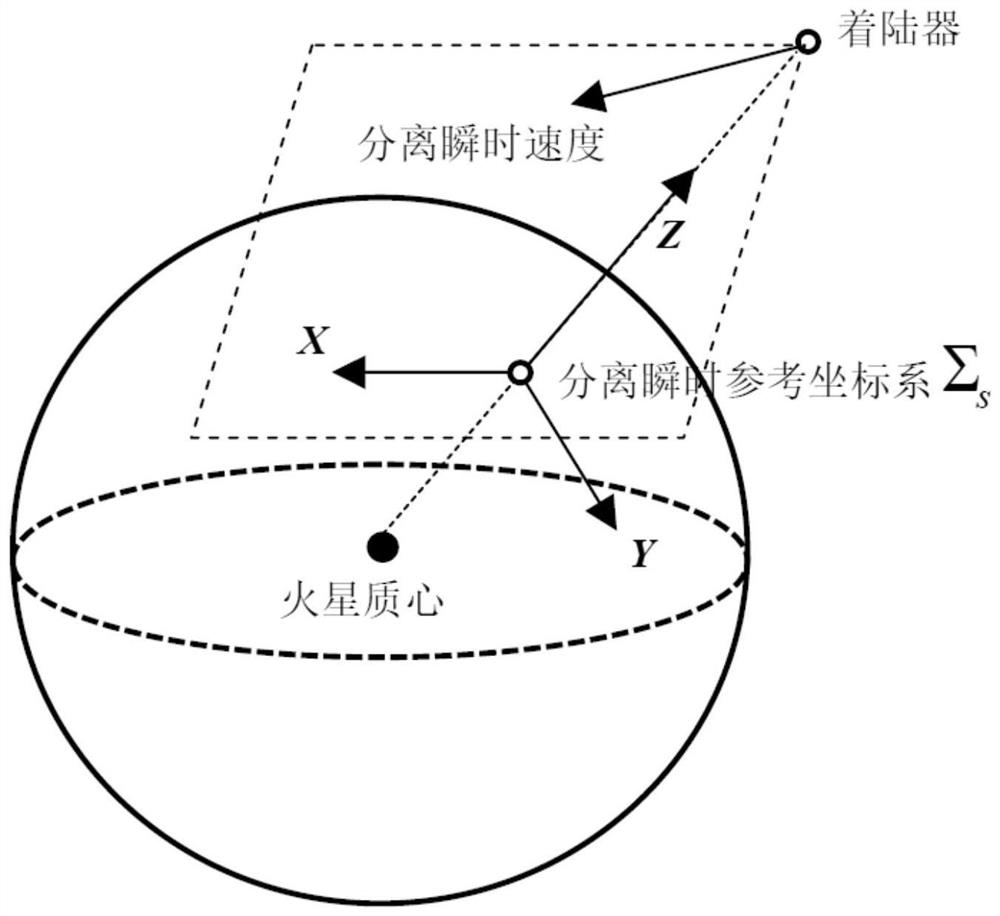
[0065] Step 2: Construct the separated instantaneous reference coordinate system Σ s , drop the parachute in step 1 to point p i Transform to Σ s in, expressed as
[0066] Step 3: Count the mean value of n times of simulated landing points and the covariance matrix σ s , giving the separated instantaneous reference frame Σ s The stat...
Embodiment
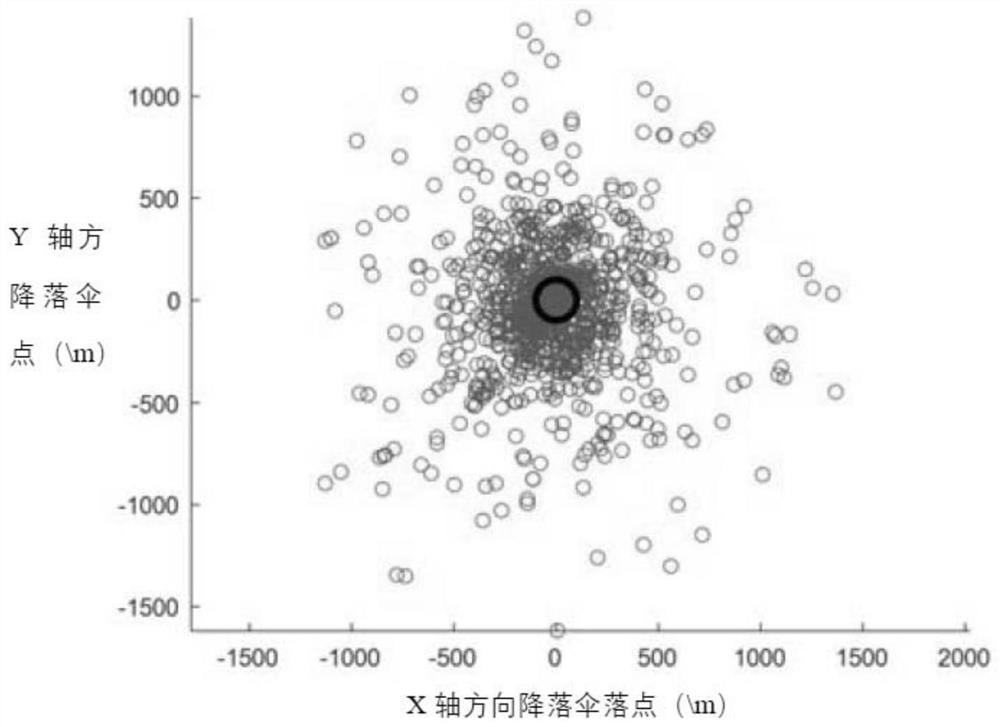
[0149] In order to verify the parachute evasive maneuvering strategy provided by the present invention, 1020 Monte Carlo simulations have been carried out, and the distribution of the parachute landing points under the instantaneous reference coordinate system after the evasive maneuver is applied is as follows: Figure 6 shown. The simulation results show that the number of trajectories with the distance between the parachute back cover assembly and the landing point of the lander is less than 100m, and the probability of the landing point distance being less than 100m is only 0.29%. Among the 1020 trajectories, 99.73% of the relative distances between the landing points are greater than 90.74m. The minimum distance is 68.73m, and the statistical histogram of the relative distance of the landing point is as follows Figure 7 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com