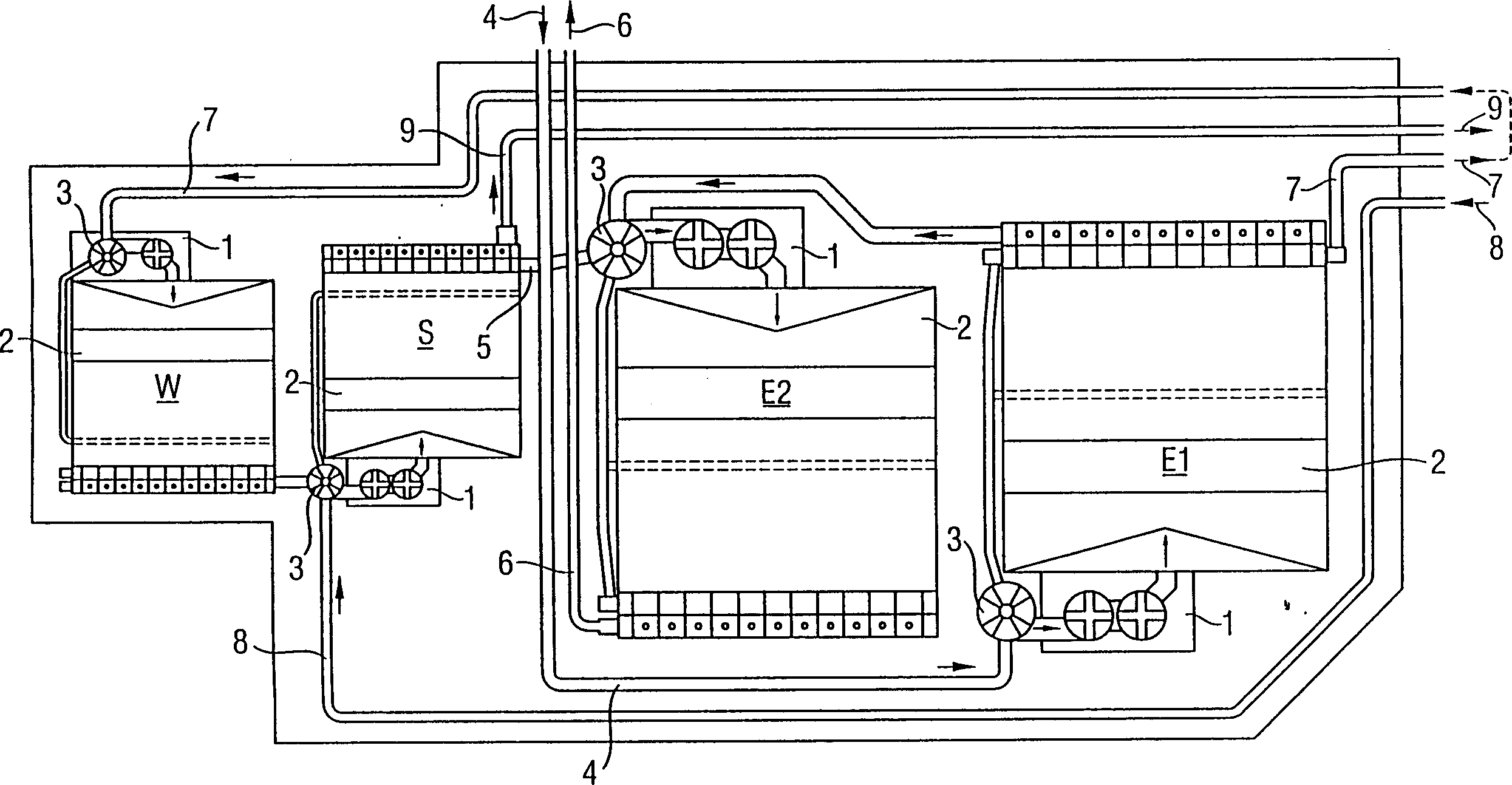
A method for extracting copper from an aqueous solution
An aqueous solution and extraction technology, applied in the field of copper extraction, can solve problems such as viscosity increase, disturbance of aqueous solution and extraction solution dispersion, aqueous solution damage, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0034] A series of experiments have been carried out which show that when the viscosity of the organic phase is increased by increasing the extractant content during copper extraction according to the invention, the separation of the organic phase and the aqueous solution from each other is facilitated. Table 1 shows the composition of the extract and the results obtained.
[0035] An aqueous solution is prepared using ion-exchanged water, copper sulfate and sulfuric acid. The solution had a copper content of 2 g / l, a sulfuric acid content of 52 g / l and a pH of 1.8. The extract was prepared by mixing different ratios of extractants (commercially available) shown in the above table and kerosene solution D70 (commercially available) as a diluent. The mixing and contacting of the extract and the copper sulfate solution (aqueous solution) was carried out at room temperature with an O / A phase ratio of 1.0, thereby obtaining the copper content values of the solutions in the table...
Embodiment 2
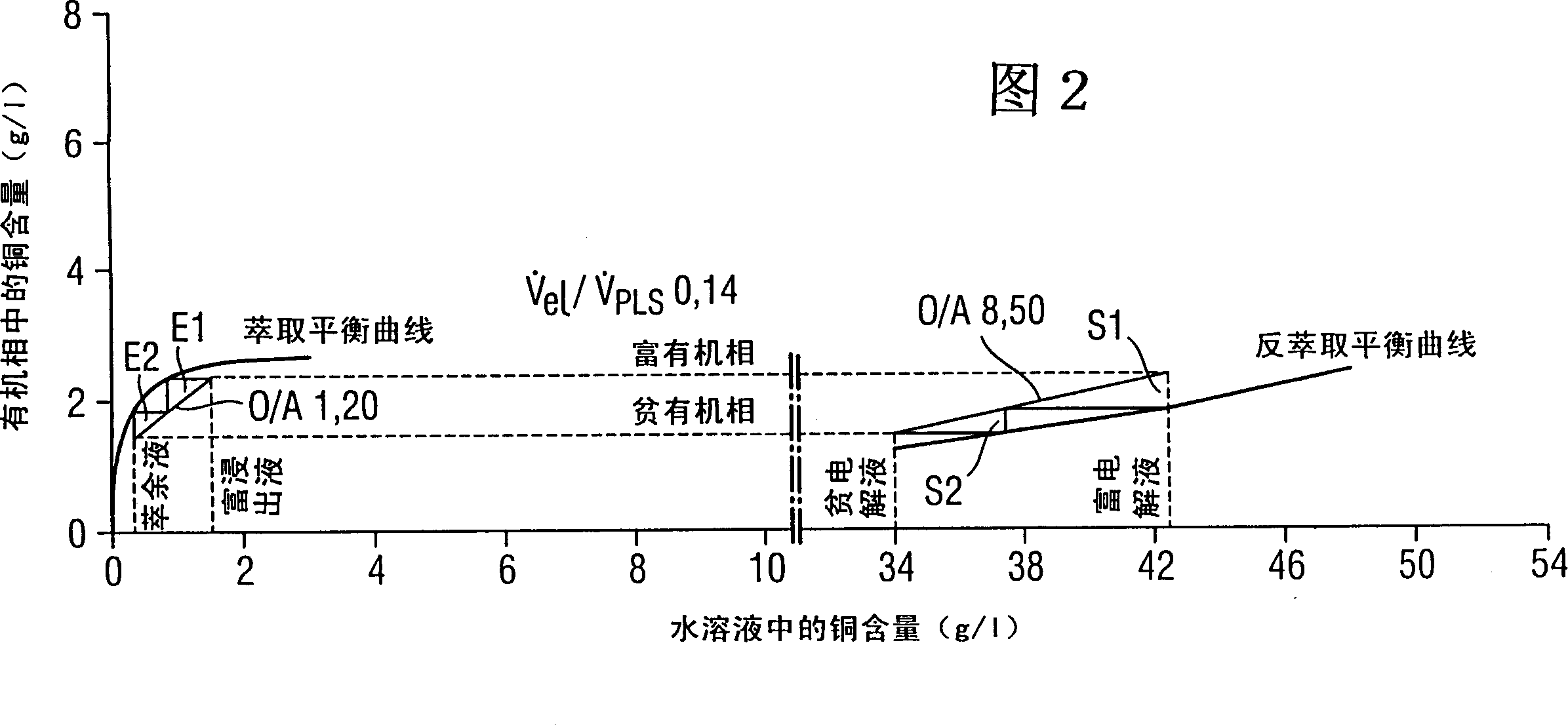
[0041] The aqueous solution was prepared to have a copper content of 1.5 g / l, a sulfuric acid content of 50 g / l, and a pH of 1.8. The following three extracts were also prepared.
[0042] 1.Acorga M 5640 5.0% by volume
[0043] D70 95% by volume
[0044] 2.Acorga M 5640 15.0% by volume
[0045] D70 85% by volume
[0046] 3. Acorga M 5640 25.0% by volume
[0047] D70 75% by volume
[0048] The above-mentioned first solution represents the extraction solution in the prior art.
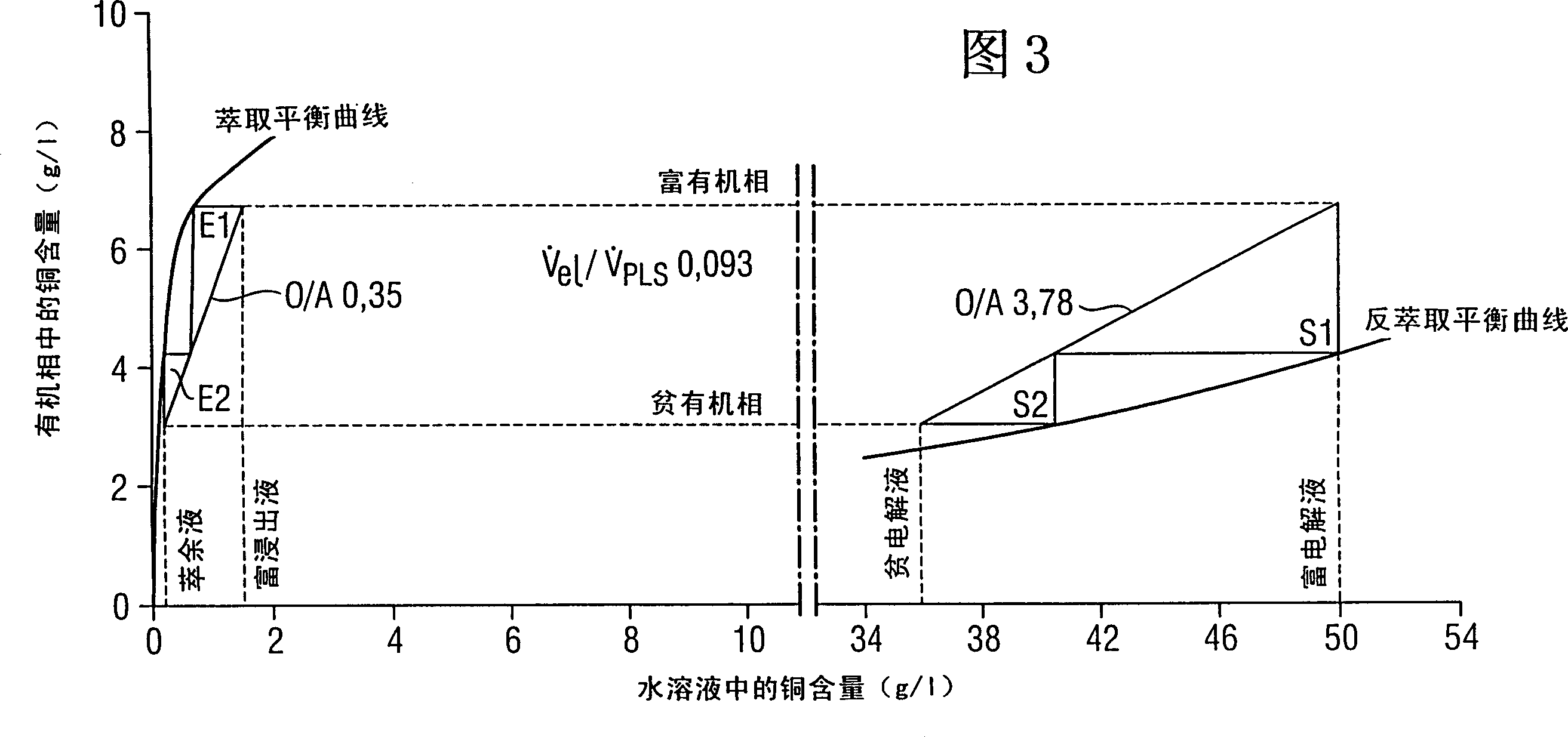
[0049] The extraction equilibrium curve EEQ and stripping equilibrium curve SEQ as shown in Figures 2, 3 and 4 are determined for the above-mentioned extract and aqueous solution using methods used by experts in the field. Figure 2 illustrates the prior art, Figures 3 and 4 illustrate the method according to the invention. Next, extraction calculations were performed for a copper extraction process with two extraction stages operating under the countercurrent principle and two stripping stag...
Embodiment 3
[0059] In this example, the performance values according to the prior art are shown in FIG. 5 and the performance values according to the method according to the invention are shown in FIGS. 6 and 7 , based on the provided stage calculations. These again show that the inventive method facilitates a considerable reduction in the size of the device. The copper content in the aqueous solution is 3 g / l, ie still a dilute solution. The normal solution is given first in the table at 8.5% by volume of extractant, followed by 15 and 25% by volume according to the invention (as in the examples above). Used extractant and diluent are identical with embodiment 2. The temperature of the extract is 18 degrees Celsius.
[0060] quantity
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com