Characterization method and system for in-situ statistical distribution of inclusions in steel
A technology of statistical distribution and inclusions, applied in the analysis of materials, material analysis using wave/particle radiation, measuring devices, etc., can solve the problems of long analysis period, low efficiency, and difficult process effective correlation, etc., to achieve the analysis field of view Large, complete statistical information, and intuitive evaluation results
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0073] Embodiment 1: The embodiment of this application discloses a method for characterizing the in-situ statistical distribution of inclusions in steel. The method includes the following steps.
[0074] Sampling and preparation of the sample to be tested to obtain a smooth and clean inspection surface.
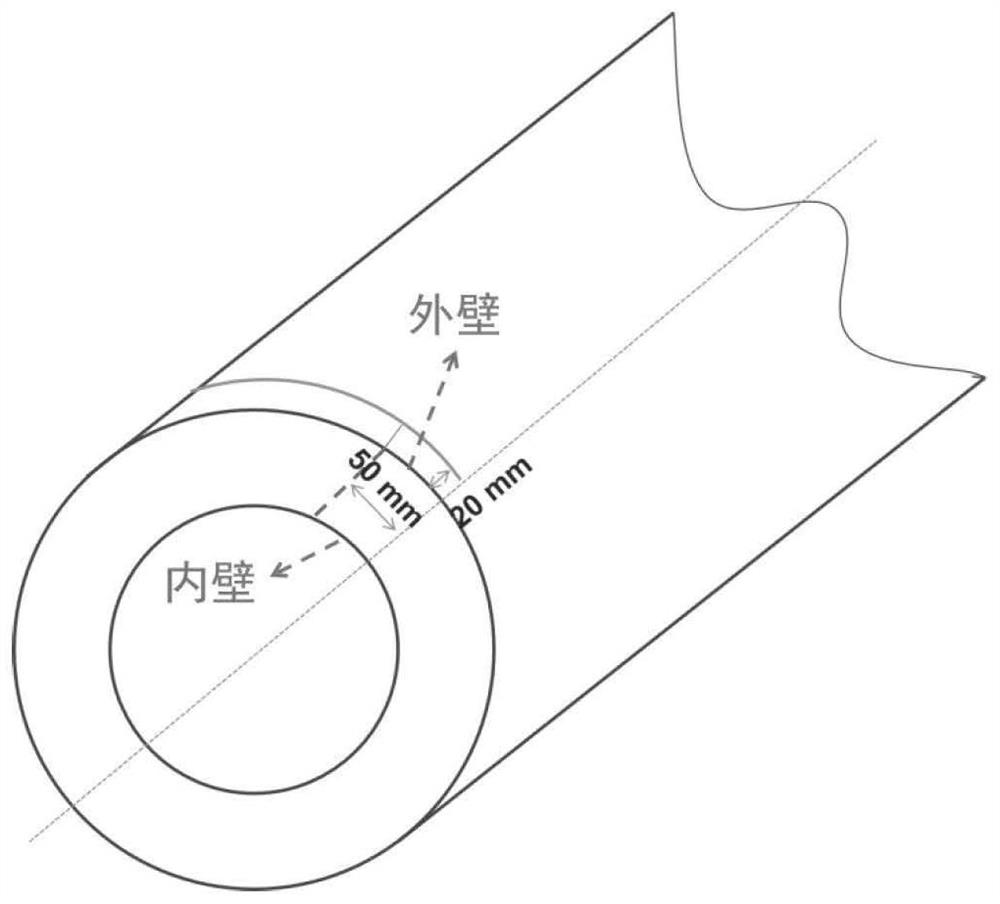
[0075] Sampling is carried out along the direction of thermal processing for steels of different processes and shapes, sampling from the center to the edge of plate-shaped, columnar, and rod-shaped samples, and sampling from the inner wall to the outer wall of tubular samples.
[0076] Rough grinding, fine grinding and polishing are carried out on the inspection surface of the test sample to obtain a smooth and clean inspection surface. The inclusions did not deform and fall off during the sample preparation process.
[0077] Paste aluminum foil on one end of the sample, and use a scanning electron microscope to evaluate the type and size range of inclusions.
[0078] Pas...
Embodiment 2
[0087] Example 2: A columnar as-cast steel is selected as the research object, and the method of the present invention is used to characterize the statistical distribution of inclusions in situ. Include the following steps:
[0088] Sampling and preparation of the sample to be tested to obtain a smooth and clean inspection surface.
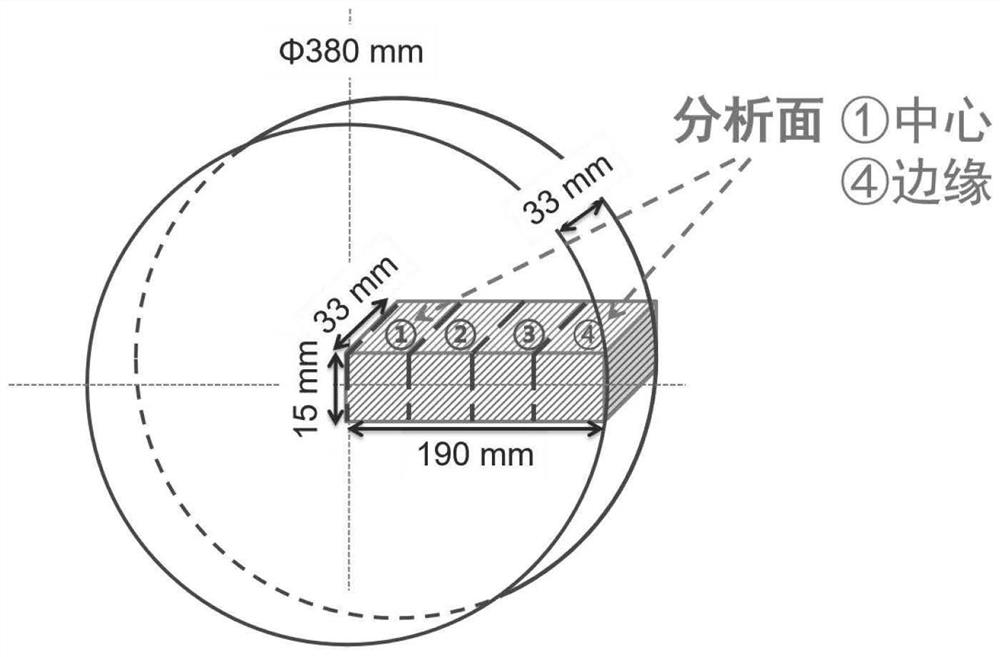
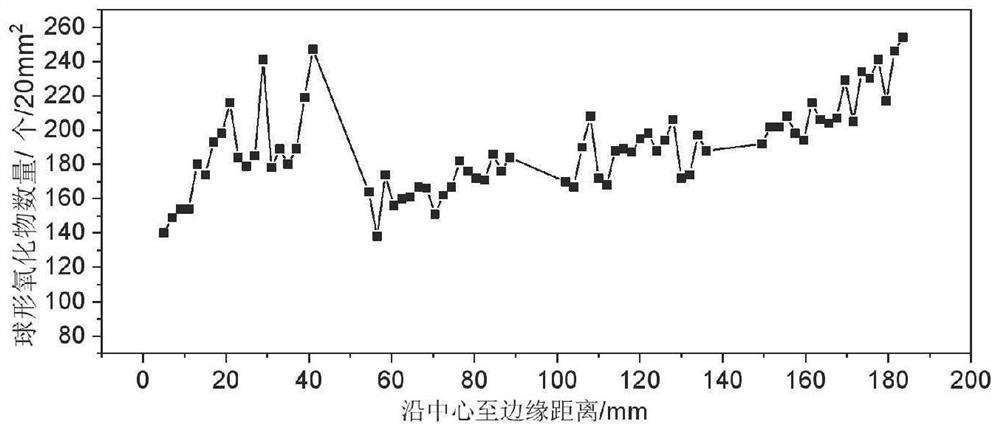
[0089] will be like figure 1 The columnar as-cast steel is sampled. Due to the large sample size, the samples were divided into four equal parts and tested one by one to obtain the distribution trend results of inclusions. After the test sample is roughly ground, finely ground and polished, a smooth and clean test surface is obtained. After observation by a metallographic microscope, the inclusions did not deform or fall off during the sample preparation process.
[0090] Paste aluminum foil on one end of the sample, and use a scanning electron microscope to evaluate the type and size range of inclusions.
[0091] Paste aluminum foil on one e...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com