Low signal-to-noise ratio inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging method
An inverse synthetic aperture and radar imaging technology, which is applied to instruments, measurement devices, and re-radiation, etc., can solve the problems of estimation result error, reduced image quality, and target image quality degradation, so as to improve efficiency and accuracy, and improve accuracy. degree of effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
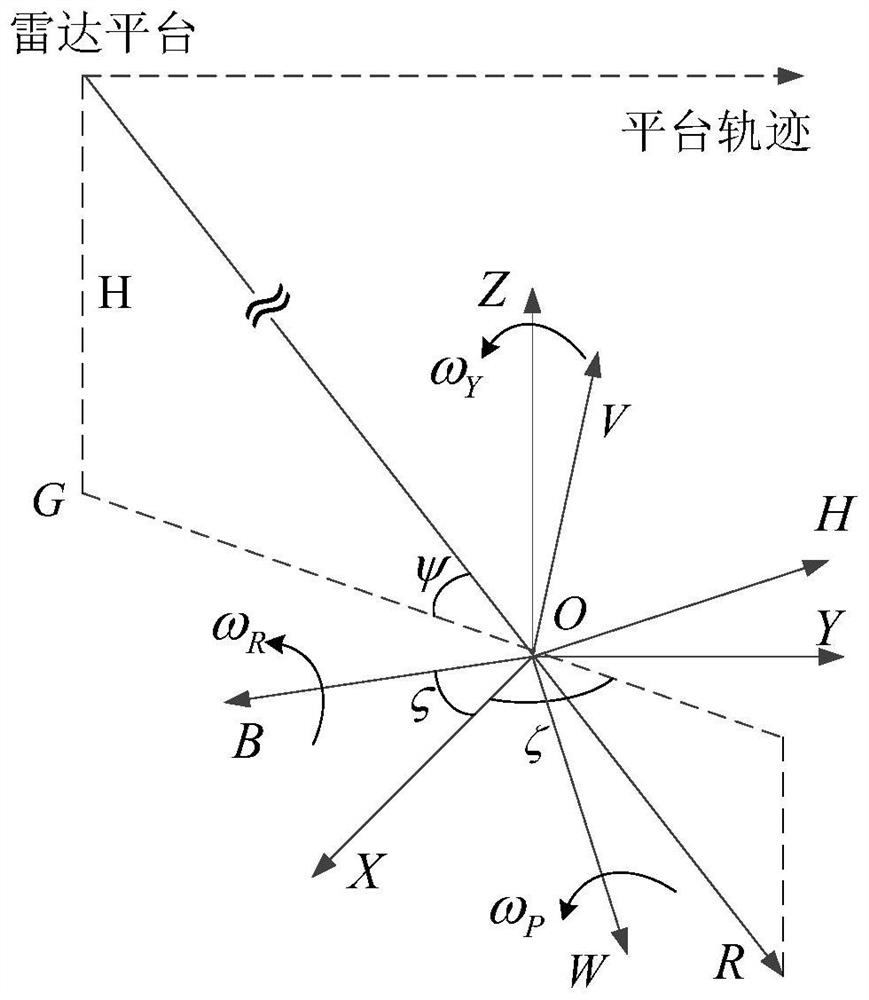
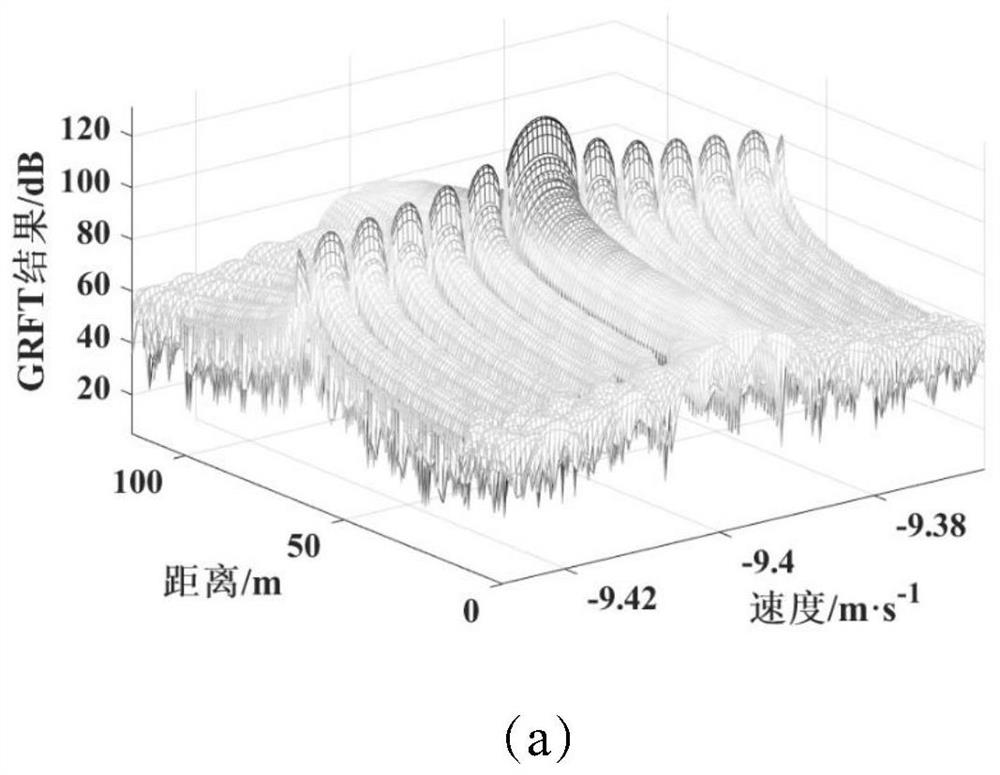
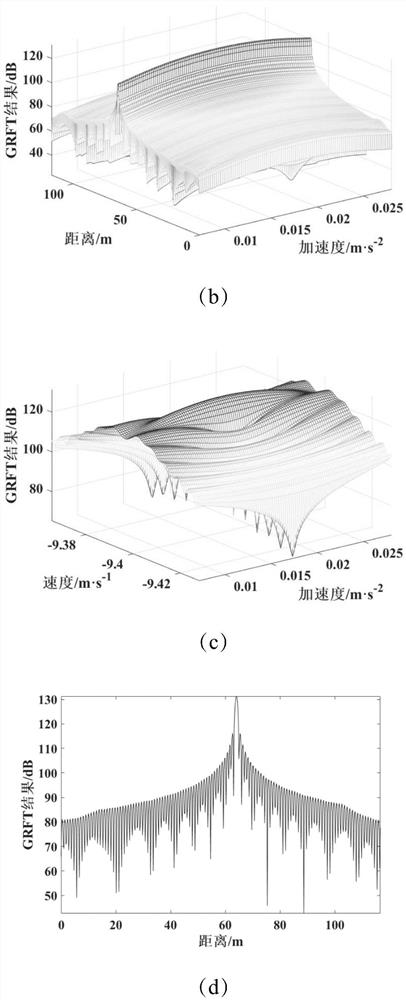
[0039] The invention provides a low signal-to-noise ratio inverse synthetic aperture radar imaging method, which uses the sidelobe learning particle swarm optimization algorithm SLL-PSO to search in the one-dimensional high-resolution range image, and uses the generalized Radon-Fourier transform GRFT Calculate the amplitude of each particle, and calculate the signal component of the scattering point corresponding to the maximum amplitude; among them, after obtaining the amplitude of multiple particles, select the particle with the largest amplitude as the global optimal particle, and then send to the global On both sides of the optimal particle, a certain number of side lobes are expanded to continue to find the particle with the largest amplitude as the new global optimal particle, and the motion parameters of the scattering points are represented by the position parameters of the new global optimal particle, and the new global optimal particle The amplitude of the optimal parti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com