A femtosecond laser direct writing method for zinc oxide micro-nano patterns
A technology of micro-nano pattern and femtosecond laser, which is applied in the direction of microlithography exposure equipment, photoplate making process of pattern surface, optics, etc., can solve the problems of low manufacturing efficiency, complicated process and high production cost
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0042] Dissolve 0.5 g of zinc methacrylate into 10 g of propylene glycol monomethyl ether, add 5 mg of two-photon initiator DETC, ultrasonicate for 20 minutes to promote dissolution, and filter twice with a 0.22 μm filter to obtain a zinc-based photoresist A.
[0043] The zinc-based photoresist A was dropped onto the glass substrate, spin-coated at a speed of 500 rpm for 10 s, and then spin-coated at a speed of 2,000 rpm for 60 s to obtain a thin film of the zinc-based photoresist A.
[0044] Writing with a 780 nm femtosecond laser induces the polymerization of monomers at selected positions in the zinc-based photoresist film by changing the position of the laser focus.
[0045] After the writing was completed, it was developed in PGMEA for 40 s, and then developed in isopropanol for 5 min to obtain the inscribed pattern.
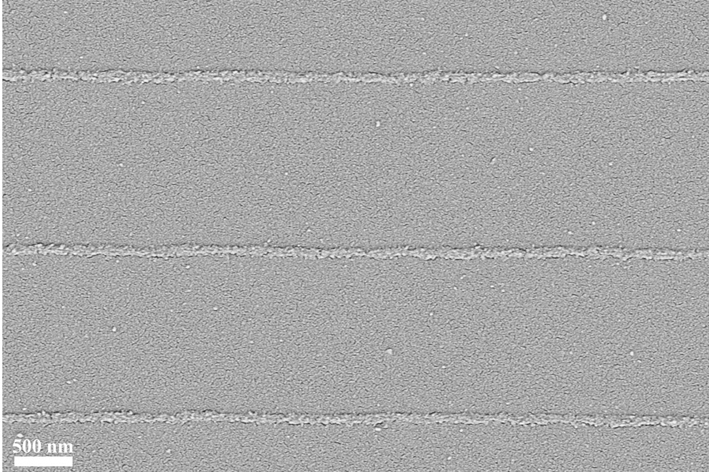
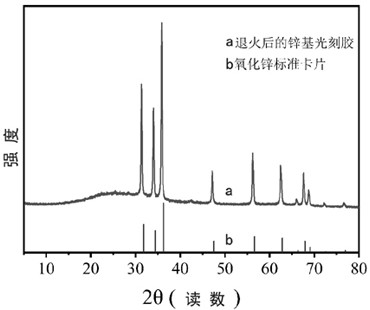
[0046] The obtained patterns were annealed in air atmosphere for 120 min, the annealing temperature was 500 ℃, the heating rate during annealing was 20 ℃ / ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Dissolve 0.75 g of zinc methacrylate into 10 g of propylene glycol monomethyl ether, add 7.5 mg of two-photon initiator DETC, ultrasonicate for 20 minutes to promote dissolution, and filter twice with a 0.22 μm filter to obtain a zinc-based photoresist B.
[0051] The zinc-based photoresist B was dropped onto the glass substrate, spin-coated at a speed of 500 rpm for 10 s, and then spin-coated at a speed of 2,000 rpm for 60 s to obtain a thin film of the zinc-based photoresist B.
[0052] Writing with a 780 nm femtosecond laser induces the polymerization of monomers at selected positions in the zinc-based photoresist film by changing the position of the laser focus.
[0053] After the writing is completed, develop in PGMEA for 2 min, and then develop in isopropanol for 5 min to obtain the inscribed pattern.
[0054] The obtained pattern was annealed in air atmosphere for 60 min, the annealing temperature was 700 ℃, the heating rate during annealing was 20 ℃ / min, and th...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Dissolve 1 g of zinc methacrylate into 10 g of propylene glycol monomethyl ether, add 10 mg of two-photon initiator DETC, ultrasonicate for 20 minutes to promote dissolution, and filter twice with a 0.22 μm filter to obtain a zinc-based photoresist C.
[0058] The zinc-based photoresist C was dropped onto the glass substrate, spin-coated at a speed of 500 rpm for 10 s, and then spin-coated at a speed of 2,000 rpm for 60 s to obtain a thin film of the zinc-based photoresist C.
[0059] Writing with a 780 nm femtosecond laser induces the polymerization of monomers at selected positions in the zinc-based photoresist film by changing the position of the laser focus.
[0060] After the writing is completed, develop it in PGMEA for 1 min, and then develop it in isopropanol for 5 min to obtain the written pattern.
[0061] The obtained pattern was annealed in air atmosphere for 30 min, the annealing temperature was 1000 ℃, the heating rate during annealing was 20 ℃ / min, and t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com