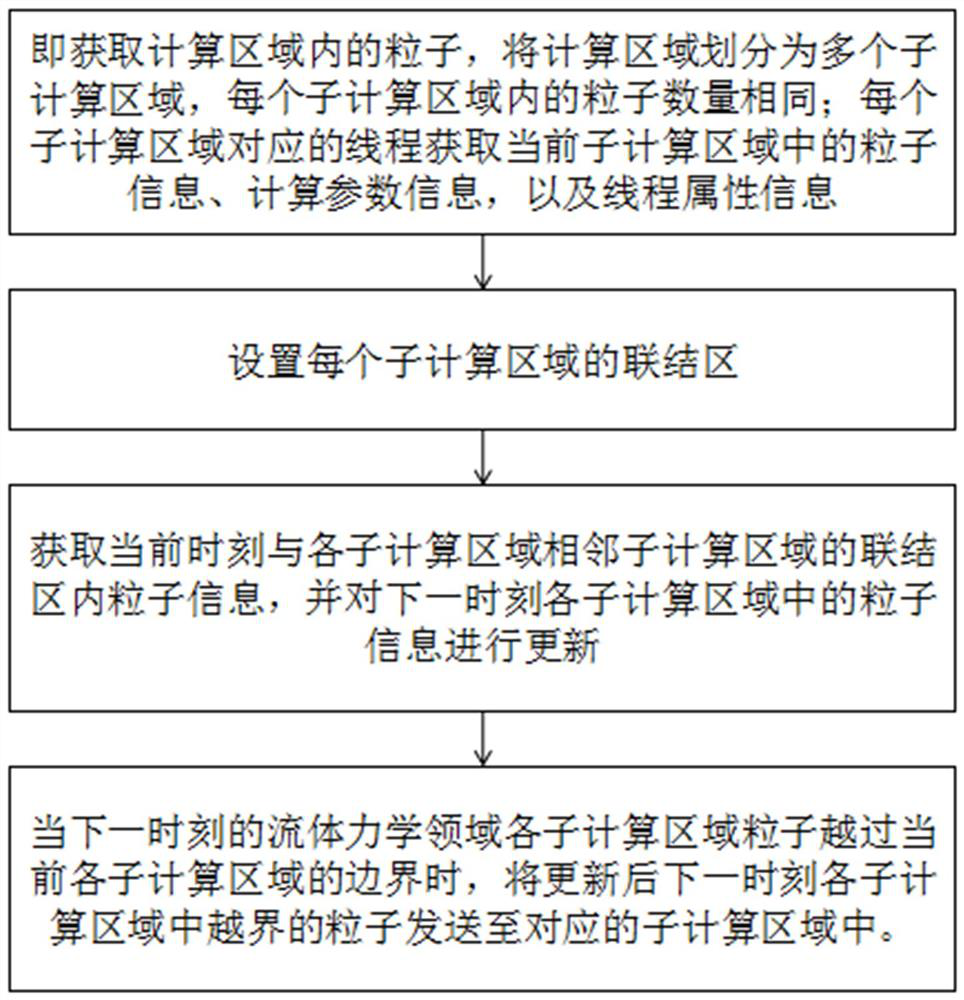
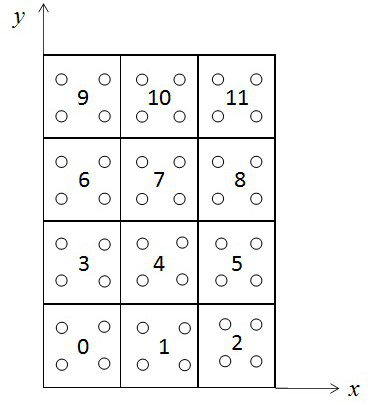
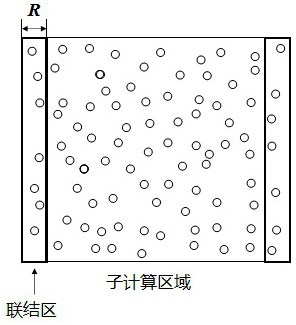
Parallel method suitable for Lagrange particle class numerical simulation
A Lagrange-type, numerical simulation technology, applied in the field of fluid mechanics, can solve problems such as inability to handle large-scale computing problems, difficult problems of tens of millions of particles, and large hardware constraints, so as to improve computing efficiency and Effects of memory supply, reduction of information interaction consumption, and improvement of engineering application capabilities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0047] The following description provides many different embodiments, or examples, for implementing various features of the invention. The elements and arrangements described in the following specific examples are only used to express the present invention in a concise manner, and are only used as examples rather than limiting the present invention.
[0048] Aspects of the invention will be described more fully hereinafter with reference to the accompanying drawings. This invention may, however, be embodied in many different forms and should not be construed as limited to any specific structure or function presented throughout this invention. Rather, these aspects are provided so that this disclosure will be thorough and complete, and will fully convey the scope of the invention to those skilled in the art. Based on the teachings herein one skilled in the art will appreciate that the scope of the invention is intended to encompass any aspect disclosed herein, whether implemen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com