Antibodies against poliovirus receptor (PVR) and uses thereof
A technology of antibody and humanized antibody, which is applied in the direction of antibodies, antiviral agents, receptors/cell surface antigens/cell surface determinants, etc., and can solve problems such as reducing viability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1-N56
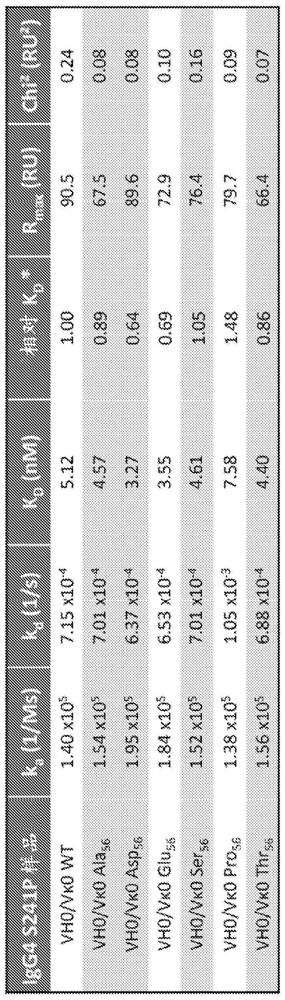
[0239] Example 1 - N56E and N56D variants have improved affinity for PVR binding
[0240]The variable region of the chimeric anti-PVR antibody 5B9 disclosed in WO2017149538 carries a deamidation sequence (asparagine-glycine) in the light chain CDR2 (WASSRHNG, SEQ ID NO: 17). Seven chimeric variants were generated by introducing a point mutation at residue asparagine N56. To assess the binding affinity of N56 substitution variants, wild-type (WT) and substitution variant IgG4 (S241P) monoclonal antibodies were immobilized on protein A capture chips. Binding of the analyte PVR conjugated to a histidine tag (PVR-HIS, Sino Cat. no. 10109-H08H) was tested. Dilution range: 5-point doubling dilution, from 50nM to 3.125nM. Conditions used: Instrument: Biacore T200 (serial number 1909913) running Biacore T200 evaluation software V2.0.1. Running buffer: HBS-P+, 300 mM NaCl, 1 mg / ml BSA. Flow rate: 30 μl / min. Association: 350s, dissociation: 800s. Regeneration: 10 mM Glycine pH 1.5...
Embodiment 2
[0241] Example 2 - N56E and N56D variants improve cross-reactivity to monkey PVR binding.
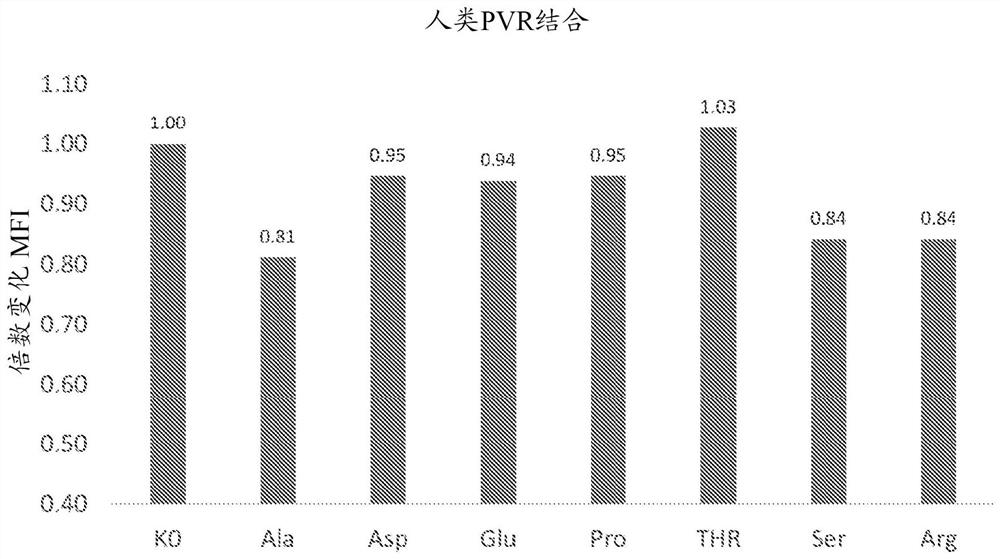
[0242] Binding of N56 substitution variant antibodies to cell-associated human PVR (protein id: Q92692) and chlorocebus PVR (African green monkey, protein id: UniProtKB-P32506) was examined. Figure 2A Relative binding of all variants added at saturating concentrations (10 ug / ml) to NCI-H1975 cells expressing human PVR is depicted. Figure 2B Relative binding of all variants added at saturating concentrations (10 ug / ml) to Vero cells expressing Vero cells PVR is depicted. For detection, goat anti-human-647 antibody (Jackson ImunomeResearch 109-606-088) was used at a 1:250 dilution. Ab cell binding was analyzed by FACS. The fold change was calculated by dividing the MFI of each variant by the MFI of the parental antibody (K0). A significant (>25%) increase in cross-reactivity was observed for the N56E and N56D variants.
Embodiment 3-N56
[0243] Example 3 - N56E and N56T variants improve NK activation
[0244] NK cells from healthy donors were incubated in the presence of selected N56 substitution variants and the target breast cancer cell line (MDA-MB-231) at an E:T ratio of 2:1 for 2 hours at 37°C. NK cell activation was measured by inducing CD107a surface expression and the fold change (Y-axis) of each variant over control IgG was calculated. All monoclonal antibodies were used at 600 pM (0.09 ug / ml). (by two-tailed student t-test, *p image 3 As shown, the N56E and N56T variants showed improved NK activation compared to KO, as manifested by increased expression of CD107a.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com