On-orbit autonomous earth shadow calculation method and system for geostationary orbit satellite
A technology of geostationary orbit and calculation method, which is applied in the field of overall space vehicle technology and experiment and testing, can solve problems such as unexplained calculation-related content, and achieve the effects of avoiding satellite energy crisis, simplifying the calculation process, and reducing the amount of calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
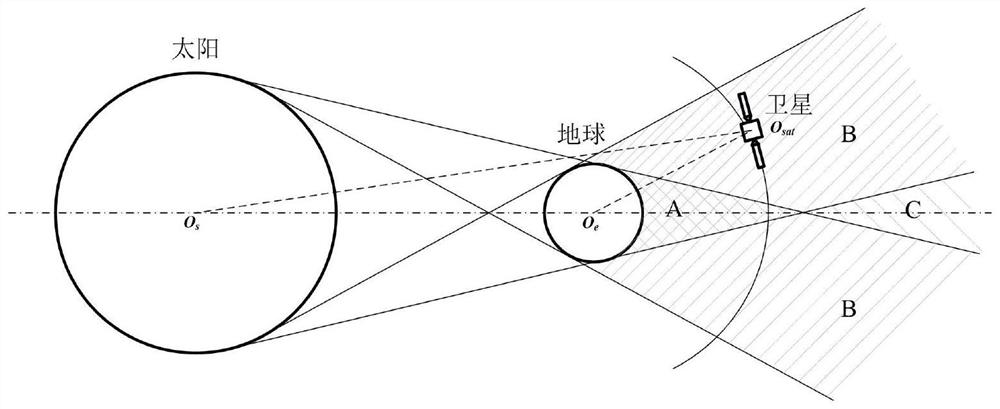
[0074] A method for calculating an autonomous geography shadow of a geostationary orbit satellite on-orbit according to the present invention, comprising:
[0075] Step S1: Calculate the radius of the disk in the shadow area according to the opening angle of the sun disk and the disk opening angle of the earth;
[0076] Step S2: Calculate the cumulative seconds relative to GMT at midnight of the satellite according to the longitude of the sub-satellite point at the fixed-point position of the satellite;
[0077] Step S3: Calculate the sun altitude angle at midnight according to the accumulated seconds of the satellite at midnight relative to GMT;
[0078] Step S4: Calculate the angle that the sun crosses during the earth shadow period according to the radius of the disk of the earth shadow area and the altitude angle of the sun at midnight;
[0079] Step S5: Calculate the duration of the satellite earth shadow, the time when the satellite enters and exit the shadow, and deter...
Embodiment 2
[0130] Embodiment 2 is a preferred example of Embodiment 1
[0131] A method for calculating an autonomous geography shadow of a geostationary orbit satellite on-orbit according to the present invention, comprising:
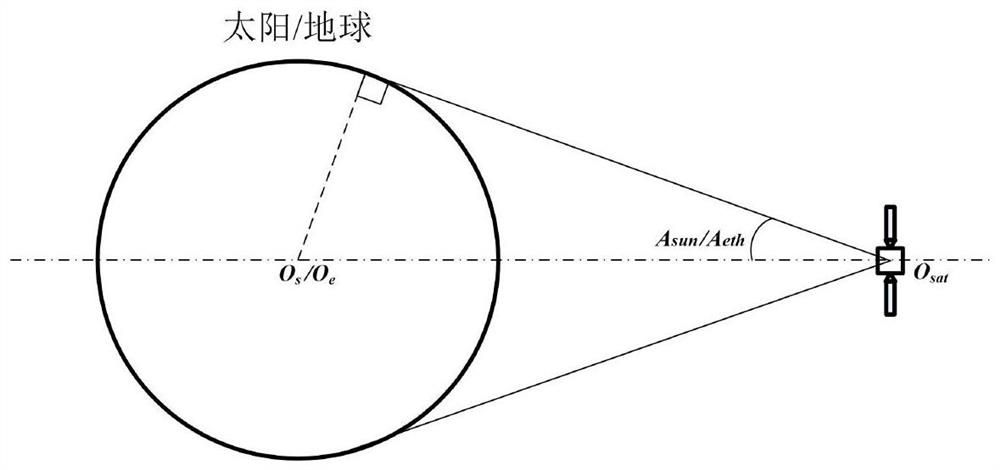
[0132] Step S1: Calculate the opening angle of the solar disk according to the average radius of the sun and the average distance between the earth and the sun.
[0133] Step S2: Calculate the opening angle of the earth disk according to the average radius of the earth and the average distance between the stars and the earth.
[0134] Step S3: Calculate the Greenwich time at midnight at the fixed-point position of the satellite.
[0135] Step S4: Calculate the sun altitude angle at midnight.
[0136] Step S5: Calculate the duration of the satellite earth shadow.
[0137] Step S6 : Calculate the time of the satellite entering and leaving the shadow and determine the shadow area.
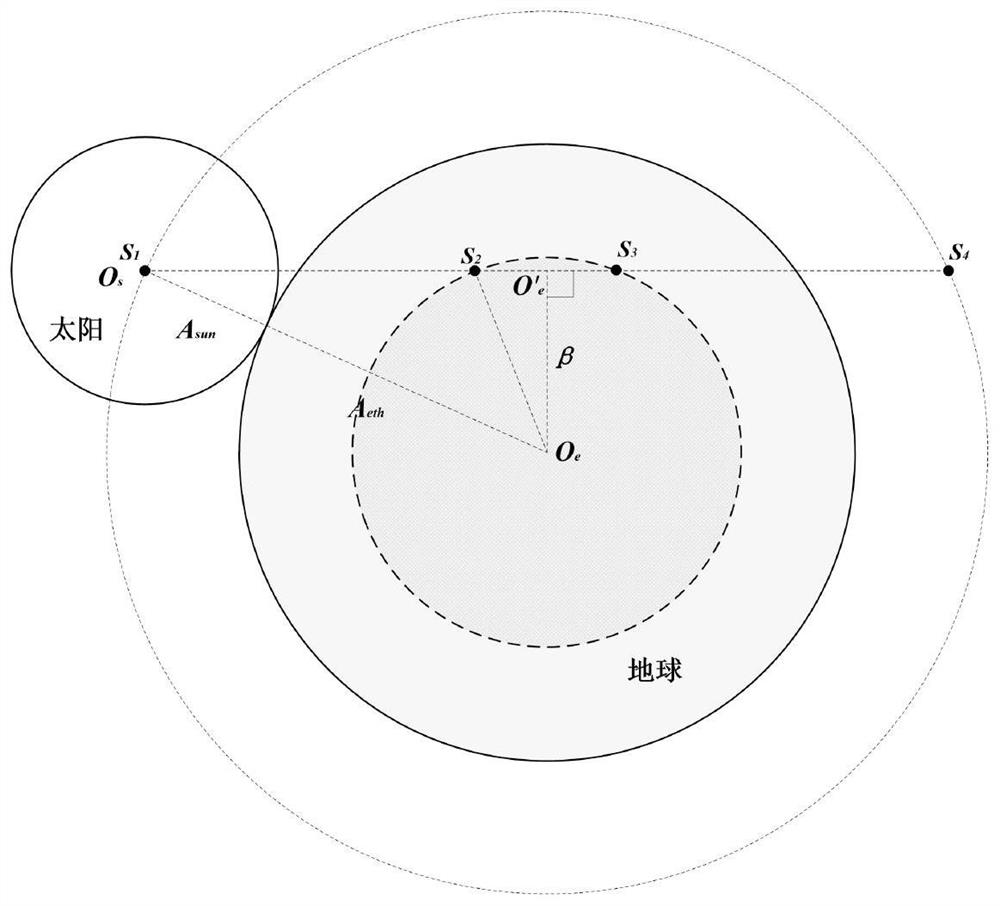
[0138] Specifically, the step S1 includes the following steps: according to the ...
Embodiment 3
[0160] Embodiment 3 is a preferred example of Embodiment 1 and / or Embodiment 2
[0161] The present invention provides a method for calculating the on-orbit autonomous ground shadow of a stationary orbit satellite, comprising the following steps:
[0162] Step 1: Calculate the opening angle of the solar disk according to the average radius of the sun and the average distance between the earth and the sun;
[0163] Step 2: Calculate the opening angle of the Earth's disk according to the Earth's average radius and the average star-to-earth distance;
[0164] Step 3: Calculate the Greenwich Mean Time at midnight at the fixed-point position of the satellite;
[0165] Step 4: Calculate the sun altitude angle at midnight;
[0166] Step 5: Calculate the duration of satellite earth shadow;
[0167] Step 6: Calculate the satellite entry and exit time and judge the shadow area.
[0168] Specifically, as described in step 1, the opening angle of the sun disk is the opening angle of t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com