Self-adaptive heuristic global path planning method and system for robot
A global path planning and self-adaptive technology, applied in instrumentation, surveying and navigation, comprehensive factory control, etc., can solve the problems of long planning path, low planning success rate, low effectiveness of complex obstacle maps, etc., to improve planning Excellent indicators of success rate and path length, and the effect of accurate path planning
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
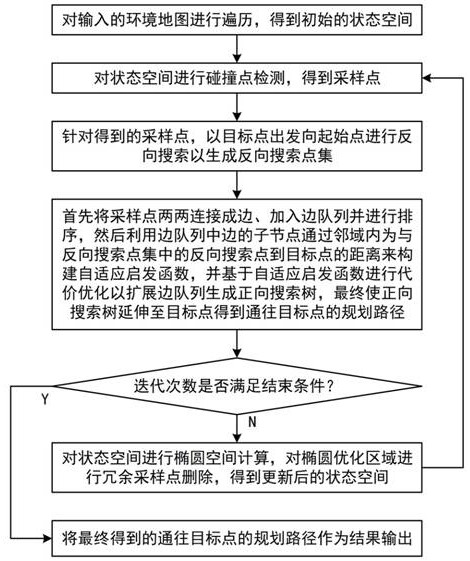
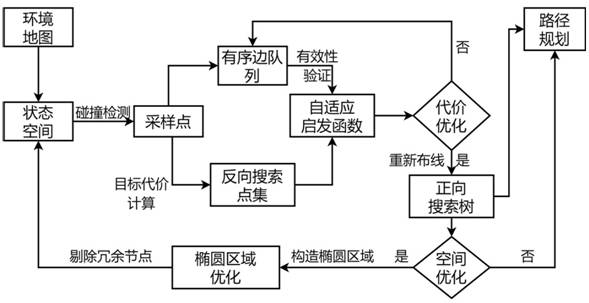
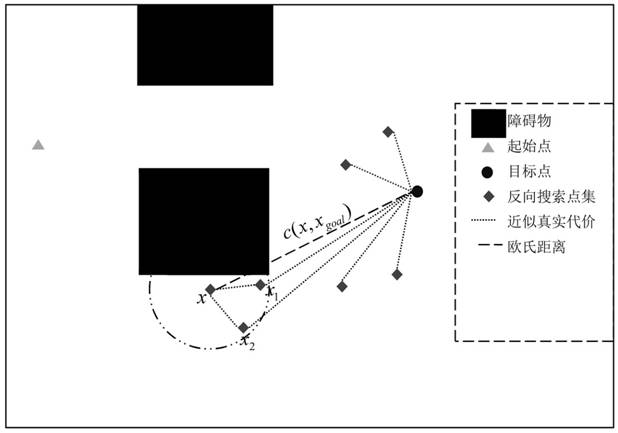
[0046] The graph theory description of the path planning problem is as follows: The input environment map for the path planning problem is a two-dimensional map, which can be expressed as: M=M 0 +M 1 , M 0 is the obstacle area, M 1 is the passable area, the state space M s Usually defined as M s =R n , n∈N, the starting point is x start ∈X, the target point is x goal ∈X, the set of sampling points X s ⊂X, where R n Represents the total set of spatial search states, each edge represents a state transition, n represents the number of map nodes, N represents the set of positive integers, and X represents the set of all nodes in the input map. Edges between sample points (nodes) can be defined as arbitrary nodes x p and x c The connections between are referred to as edges ( x p, x c ). where node x p is the parent node (closer to the starting point on the path), the node x c is a child node (closer to the destination point on the path). The forward search t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com