Hyperparallel comparison method and system
A technology of line data and table items, applied in information technology and biological engineering, biological sequence comparison in protein engineering, genetic engineering, image recognition, natural language fields, can solve the problems that do not meet biological comparison, natural language data and images Differences in data comparison requirements, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment 1
[0190] Specific embodiment 1: biological sequence hyperparallel alignment server
[0191] 1. Description of the module structure diagram
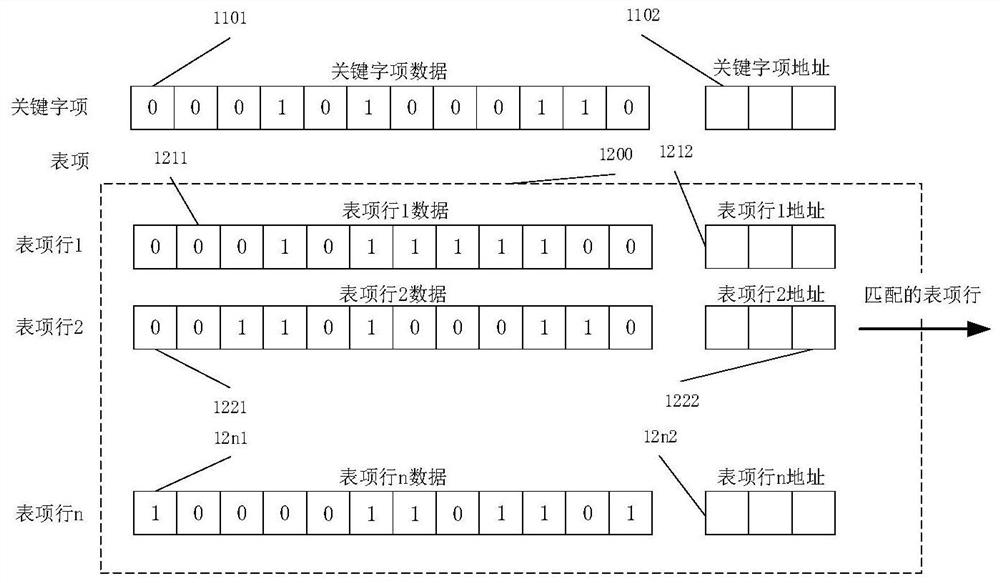
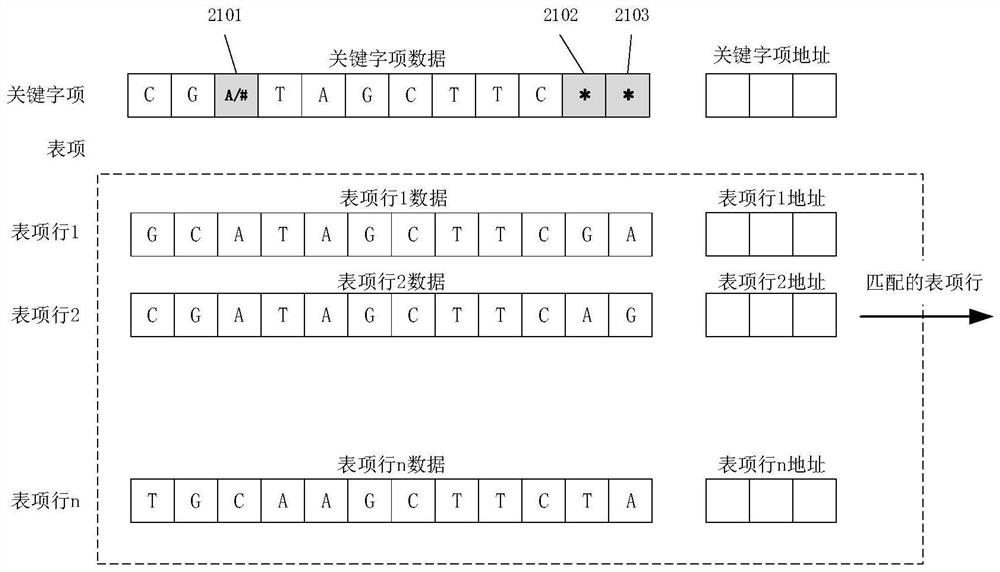
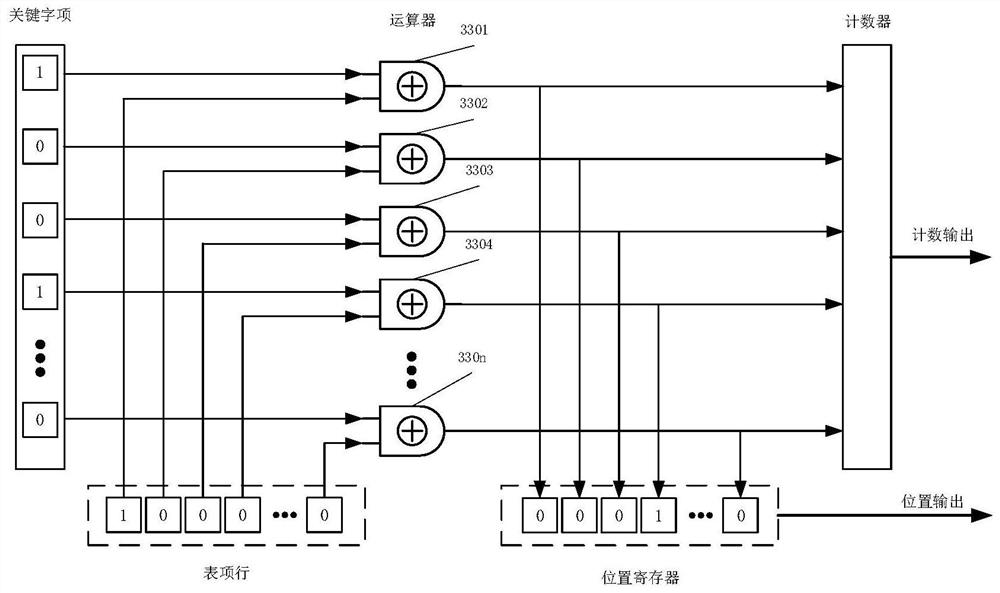
[0192] like Figure 5 It is an embodiment of the biological sequence hyperparallel alignment server of the present invention. In the figure, two comparison units are used, of which the comparison unit 1 is larger, the entry width is 256 bytes, the depth is 1M entry lines, and 1 million entry lines are compared at one time in a single cycle; the comparison unit 2 is smaller, the entry width is 64 bytes, the depth is 16, and 16 entry lines are compared at one time in a single cycle. If it is a SAM file for biological sequences, the alignment can be performed in units of bytes. In this case, such as figure 2 the logical definition of the byte-based alignment unit shown, and Figure 4 The alignment array of and Figure 5 It is also a logical definition of a byte-based comparison array; otherwise, it is a logical definition of a binary bit...
specific Embodiment 2
[0356] Specific embodiment 2: PCIE card overspeed comparison system
[0357] like Image 6 As shown, this embodiment is another application of the present invention—the PCIE card-type overspeed comparison system. The same as the previous embodiment will not be repeated here, and only the differences will be emphasized here.
[0358] 1. Use TCAM chip or FPGA to design PCIE card overspeed comparison system. The system includes: comparator array, management module, shift controller, reconfigurable logic, memory and table entry mapping and PCIE interface.
[0359] 2. The system needs to be inserted into the PCIE slot of the PC to run, and does not have the ability to run independently.
[0360] 3. The system includes a comparison unit, which adopts the built-in CPU and program design of the TCAM chip as the management module of the system.
[0361] 4. The management module of this system designs a management interface for the host PC.
[0362] 5. The entry width of this syste...
specific Embodiment 3
[0363] Specific embodiment three: general data overspeed comparison system
[0364] like Image 6 As shown, this embodiment is another application of the present invention - a general data overspeed comparison system. The same as the previous embodiment will not be repeated here, and only the differences will be emphasized here.
[0365] 1, Figure 4 The alignment array is defined using bit alignment based logic, such as figure 1 shown.
[0366] Therefore, for the step S109, the logic defines that the site adopts bits, and the alignment is based on a bit-by-bit alignment.
[0367]2. For the comparison of image data, the width of the table entry is suitable for the image size. For example, the 4K-based RGB three-primary color video image format, when each picture is 3840*2160 pixels, determine the width of the table entry to be 3840*3* 24bits=270Kbits, the entry depth is 2160*3*24bits=151875bits=152Kbits, and the entry depth can also be increased. Each entry can store mult...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com