Optimization method and application of global height number vertex set communication
A vertex and communication speed technology, applied in the direction of electrical digital data processing, digital computer components, multi-programming devices, etc., can solve problems such as unbalanced vertices, unbalanced graph data load, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
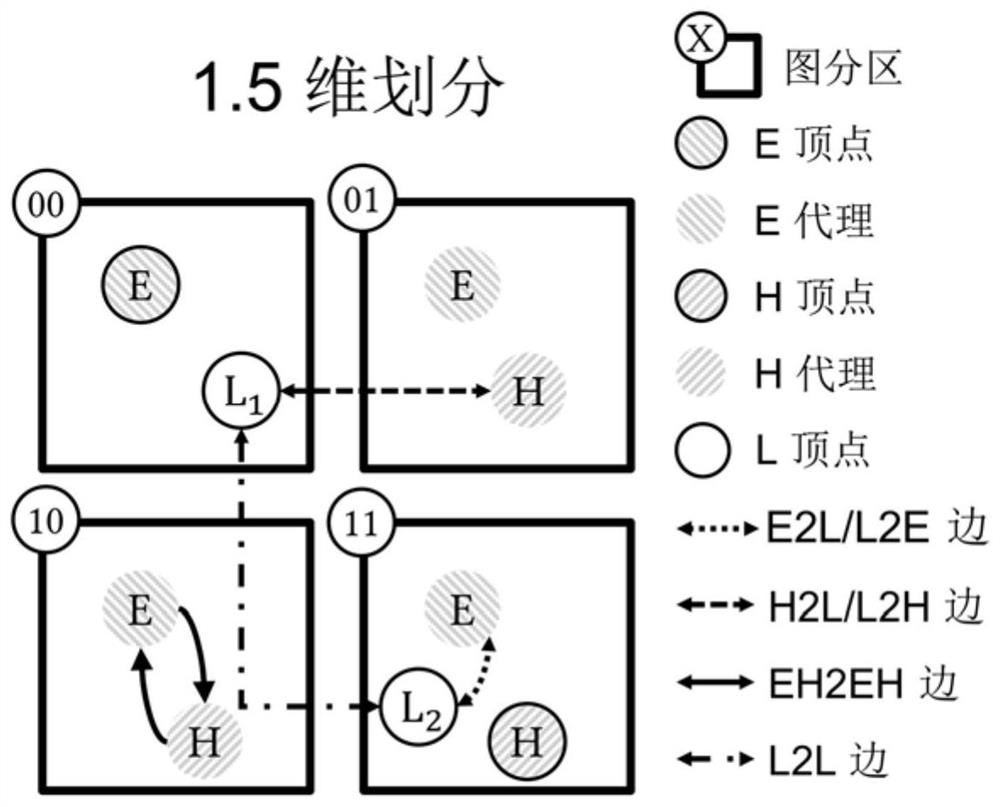
[0035] I. First embodiment: 1.5-dimensional graph division based on 3-level degree
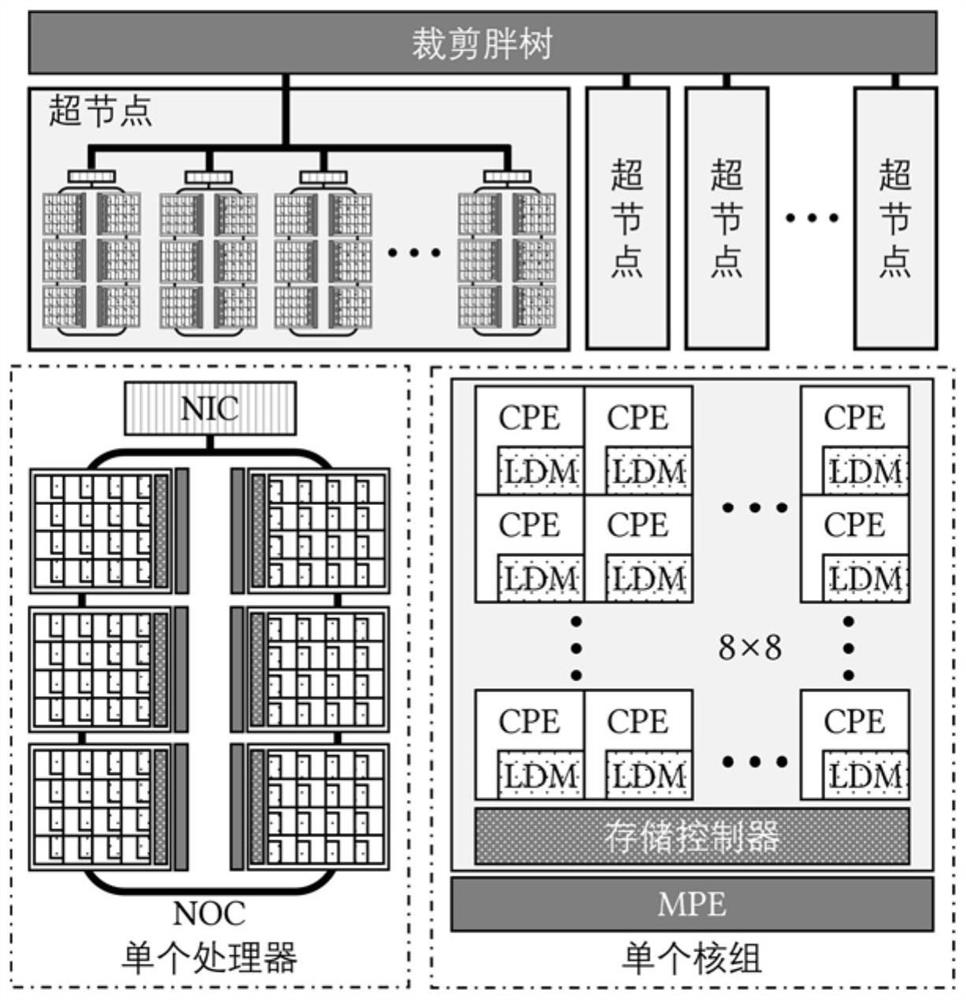
[0036] According to an embodiment of the present invention, a mixed dimension division method based on three types of degree vertices is provided, and the vertex set is divided into extreme heights (E for Extreme, for example, the degree is greater than the total number of nodes), heights (H for High , for example, the degree is greater than the number of nodes in the supernode), regular vertices (R for Regular), and sometimes R-type vertices are also called L-type vertices (L for Low, that is, a vertex with a relatively low degree); for directed graphs , then it is divided according to the in-degree and out-degree respectively, the in-degree division set and the out-degree division set are marked as Xi, Xo, where X is E, H or R. In this embodiment, at the same time, a predetermined number of nodes form a super node, and the communication between nodes within the super node is faster than the ...
no. 2 approach
[0056] II. Second Embodiment: Sub-Iterative Adaptive Direction Selection
[0057] According to an embodiment of the present invention, a sub-iteration adaptive direction selection supporting fast exit is also proposed.
[0058] In many graph algorithms, the direction in which the graph is traversed, i.e. "pushing" from source vertices to target vertices or "pulling" source vertices from target vertices, can greatly affect performance. E.g:
[0059] 1. In BFS (breadth-first search), if the “push” mode is used for the wider middle iteration, a large number of vertices will be repeatedly activated, and if the narrower head and tail iterations use the “pull” mode, the proportion of active vertices will be very high. Low results in many useless computations, requiring automatic switching between the two directions;
[0060] 2. In PageRank, the subgraphs that traverse the graph locally and reduce should use the "pull" mode to achieve optimal computing performance ("pull" is random...
no. 3 approach
[0073] III. Third Embodiment: Segmentation Subgraph Data Structure Optimization for EH Two-Dimensional Subgraphs
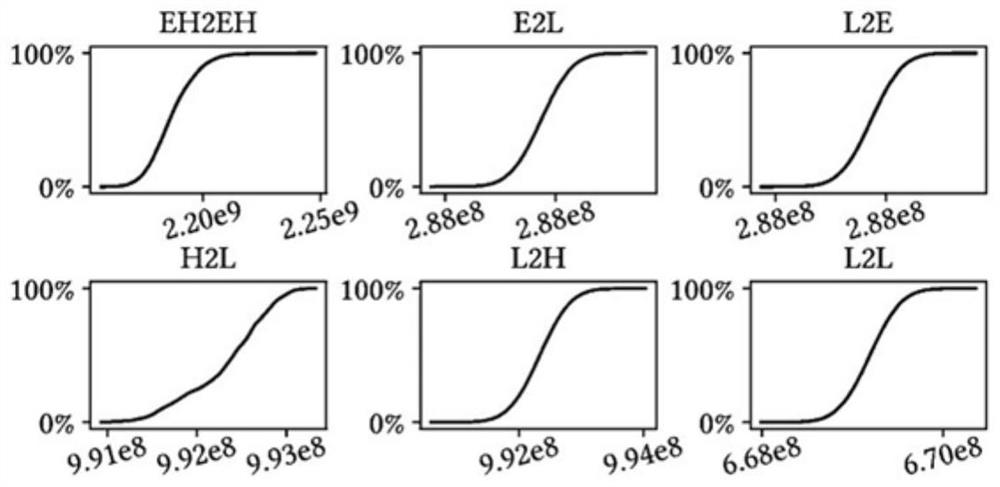
[0074] In the power-law distribution graph, it is found by simulation that the number of edges of the subgraph EHo→EHi will account for more than 60% of the whole graph, which is the most important computational optimization goal. For this sub-graph, an optimized implementation scheme is proposed by introducing a segmented sub-graph (SSG) data structure.
[0075] The Compressed Sparse Row (CSR) format is the most common storage format for graphs and sparse matrices. In this format, all adjacent edges of the same vertex are stored contiguously, supplemented by an offset array to support its indexing function. Because the range of vertices in a single large graph is too large, the spatiotemporal locality of the data accessing neighboring vertices is very poor. The following segmented subgraph method is proposed: For the subgraph (sparse matrix) of both the source v...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com