Optical modulator with pre-determined frequency chirp
An optical modulator and optical technology, applied in optics, nonlinear optics, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of non-intrinsic alignment of modulation electrodes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
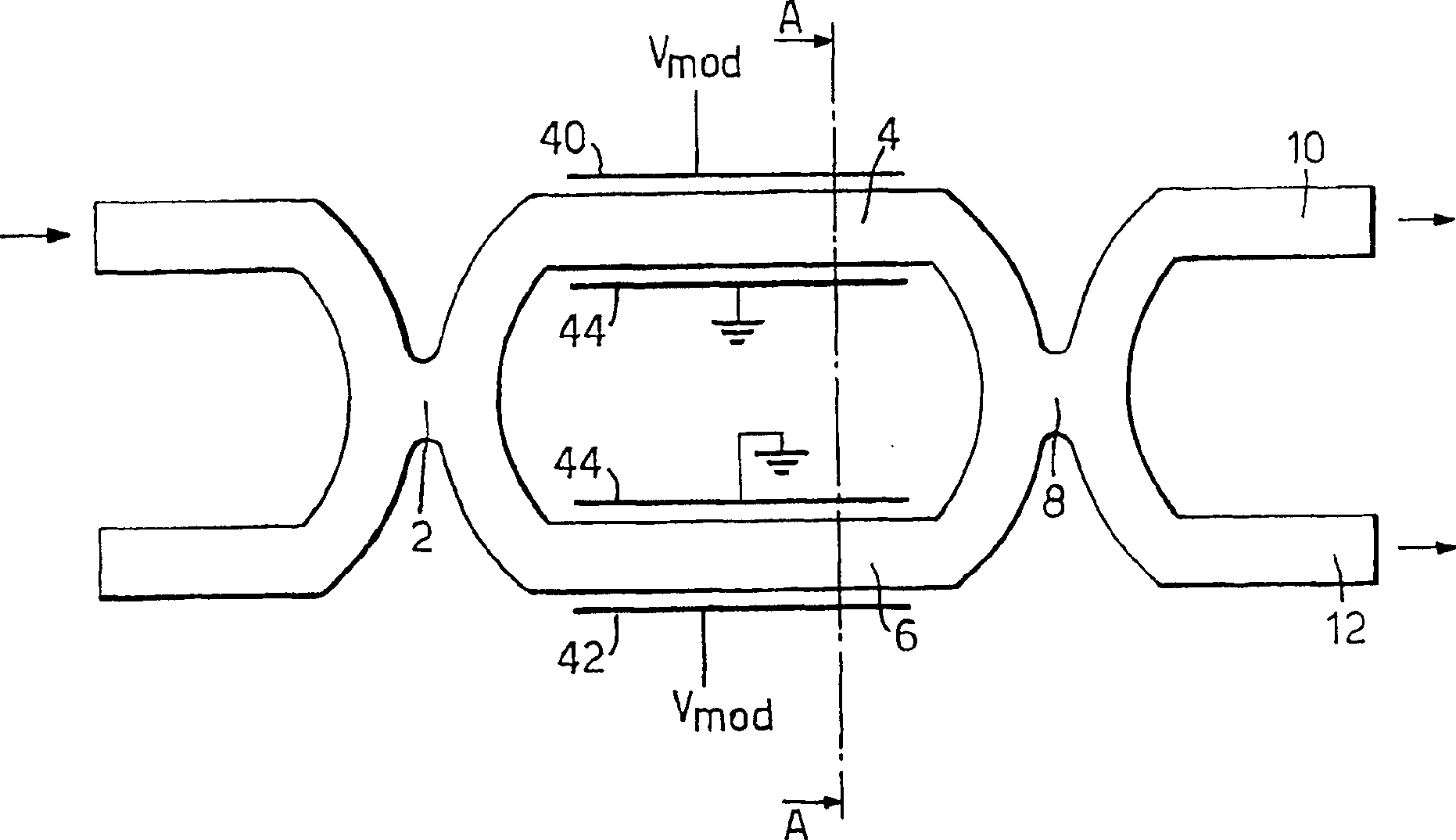
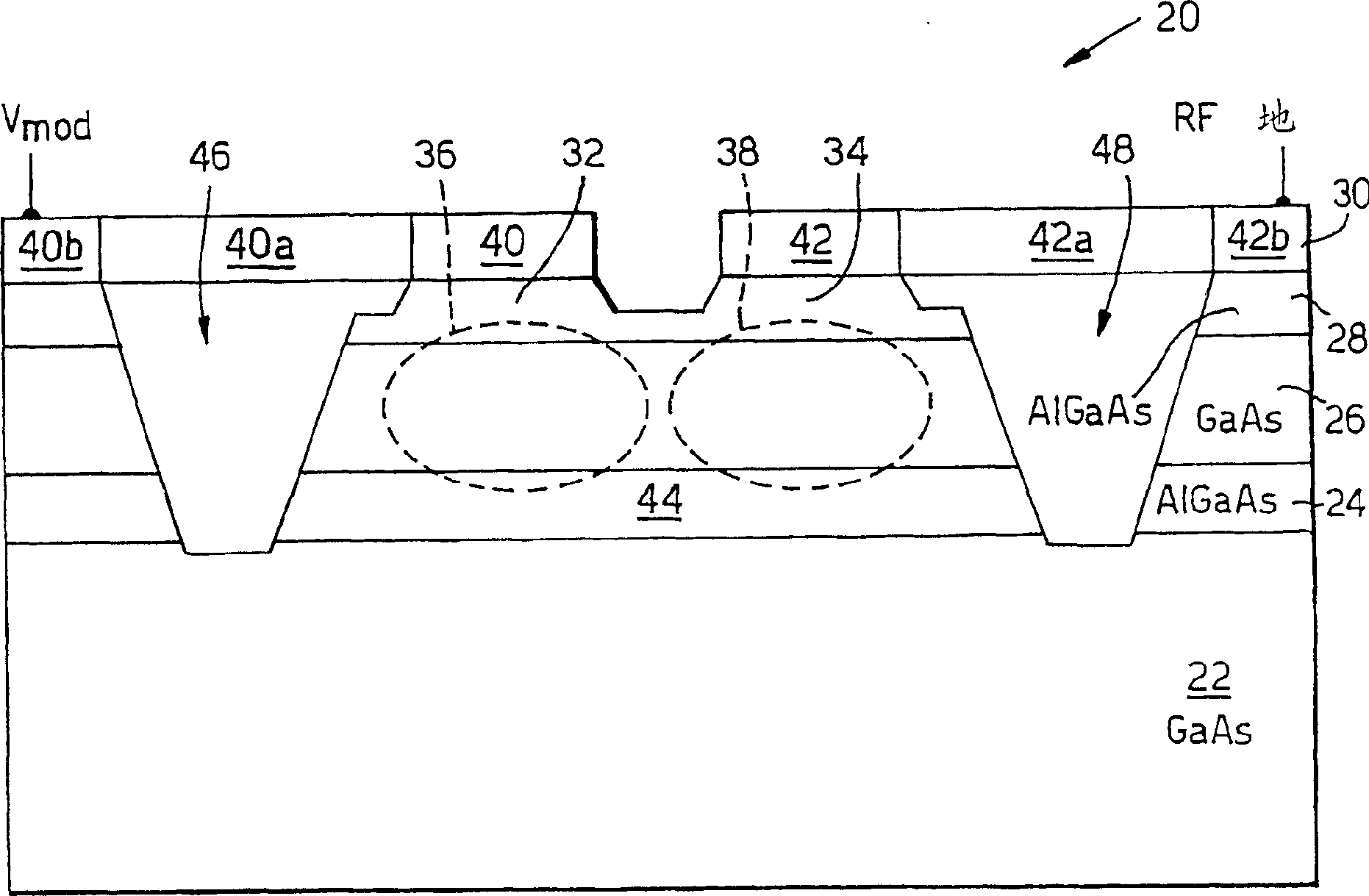
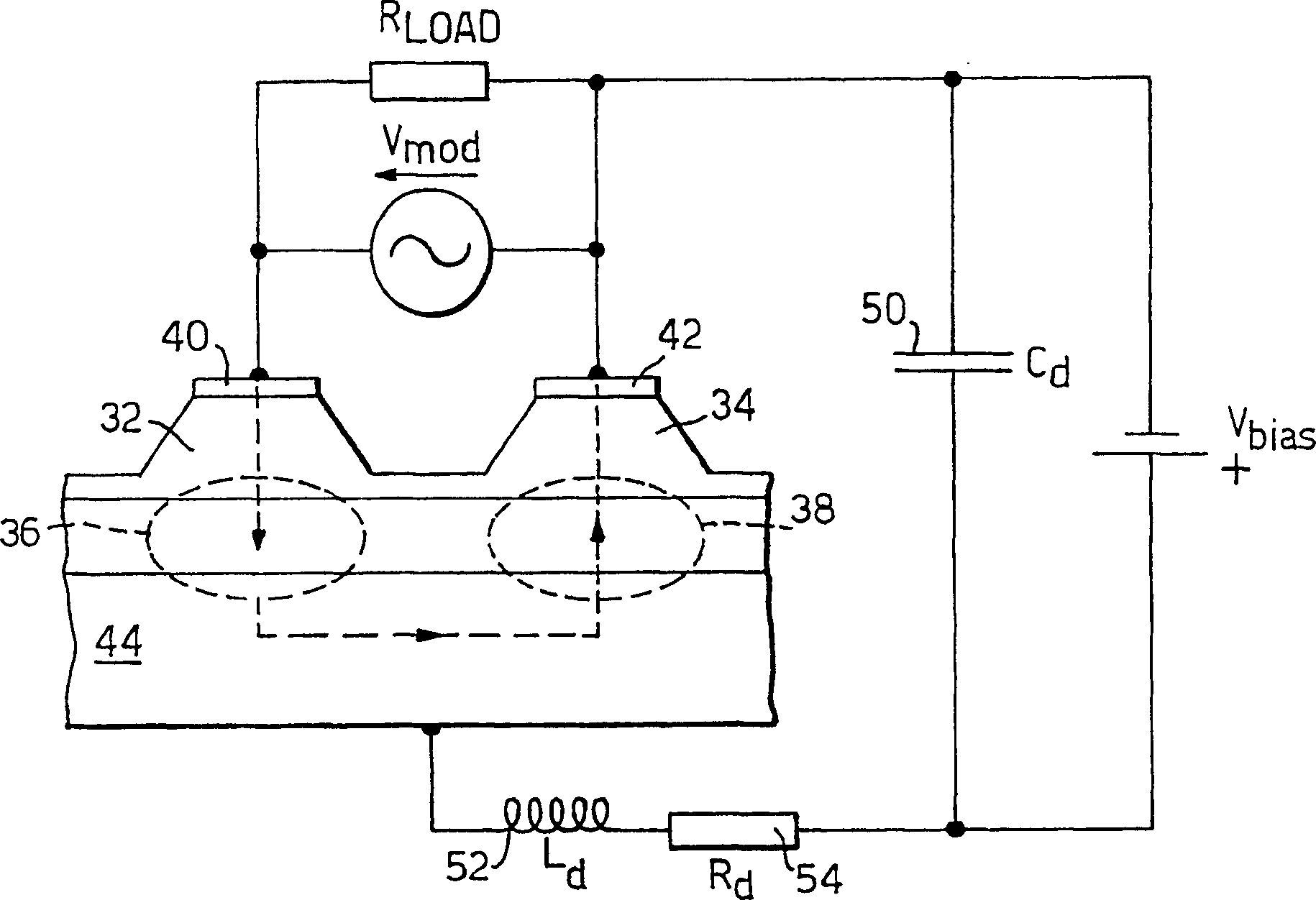
[0053] To facilitate understanding of the optical modulator of the present invention, a known Mach-Zehnder optical modulator fabricated in GaAs / AlGaAs is first described. in the attached figure 2 shown in the accompanying figure 1 The "AA" section is the end view of this modulator. The optical modulator 20 comprises, in order, an undoped (semi-insulating) gallium arsenide (GaAs) substrate 22, a conductively doped n-type aluminum gallium arsenide (AlGaAs) layer 24, a deeper undoped arsenide gallium chloride layer 26 , a deeper undoped AlGaAs layer 28 and a conductive metal layer 30 . GaAs layer 26 provides an optical waveguide medium with a contrast in refractive index between AlGaAs layers 24 and 28 , and GaAs layer 26 provides vertical confinement, thereby confining light propagating within layer 26 . The optical waveguide arm of the modulator (4, 6, see appendix figure 1 ) is defined in the GaAs layer 26, and the GaAs layer 26 is selectively etched on the two mesas (ste...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com