Method for treating inflammatory inflammatory diseases using heat shock proteins
A heat shock protein and disease technology, applied in allergic diseases, skin diseases, sensory diseases, etc., can solve problems such as side effects and inability to fight inflammatory reactions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
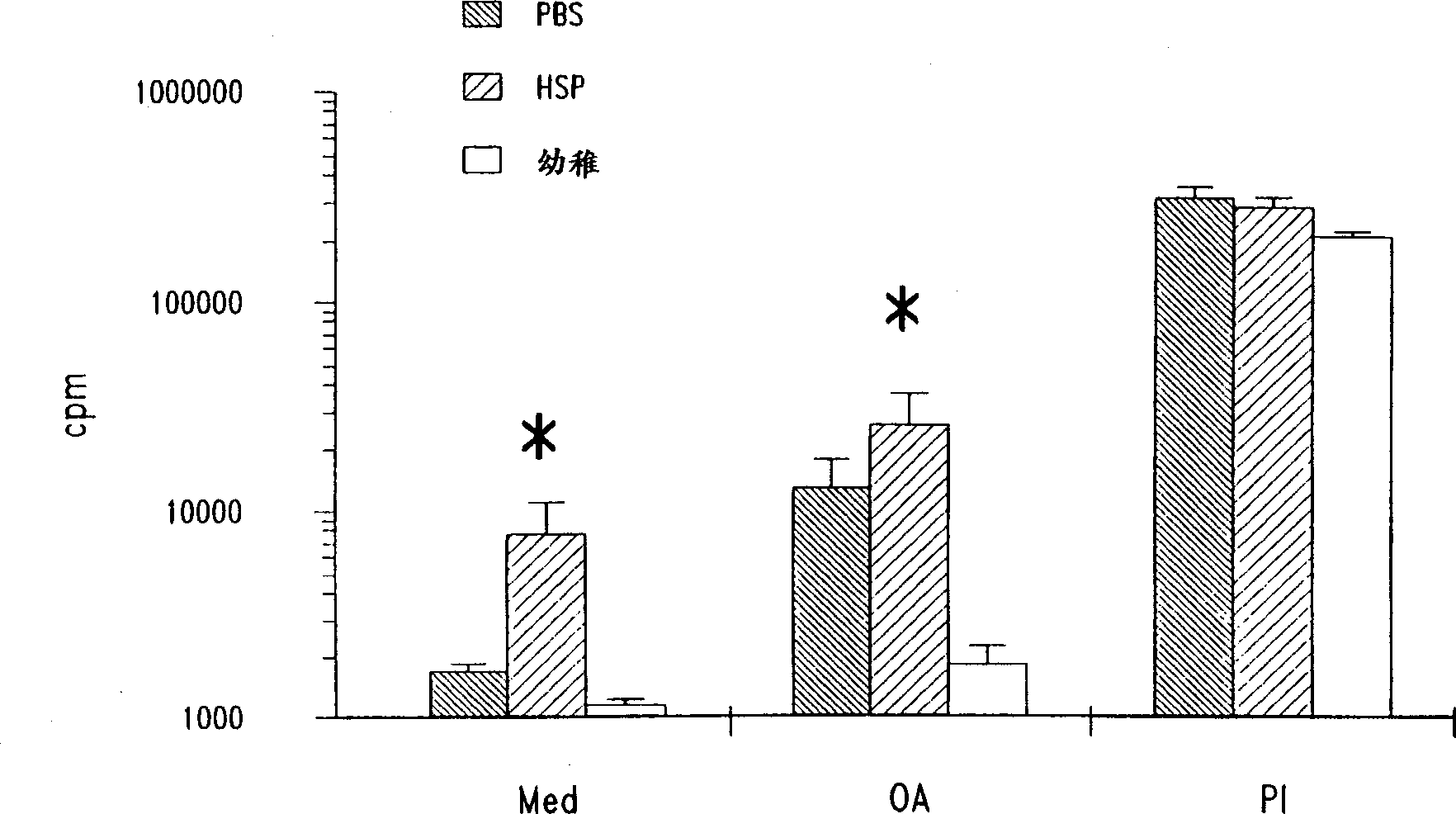
[0100] The following examples demonstrate that mycobacterial heat shock protein 65 (HSP-65) upregulates T cell proliferative responses following short-term sensitization with ovalbumin in the presence of alum in a mouse model of airway hyperresponsiveness.
[0101] Animal models of disease are invaluable for providing evidence to support a hypothesis or justify human experiments. Mice have many proteins that are greater than 90% homologous to the corresponding human proteins. For the following experiments, the inventors used an antigen-driven mouse system characterized by immune (IgE) responses, reliance on Th2-type responses, and eosinophil responses. This model is characterized by marked airway hyperresponsiveness and its progression.
[0102] Development of a universal mouse system for chronic aerobic antigen exposure (associated with profound eosinophilia and marked, persistent, and progressive airway hyperresponsiveness) provides an unprecedented opportunity to investiga...
Embodiment 2
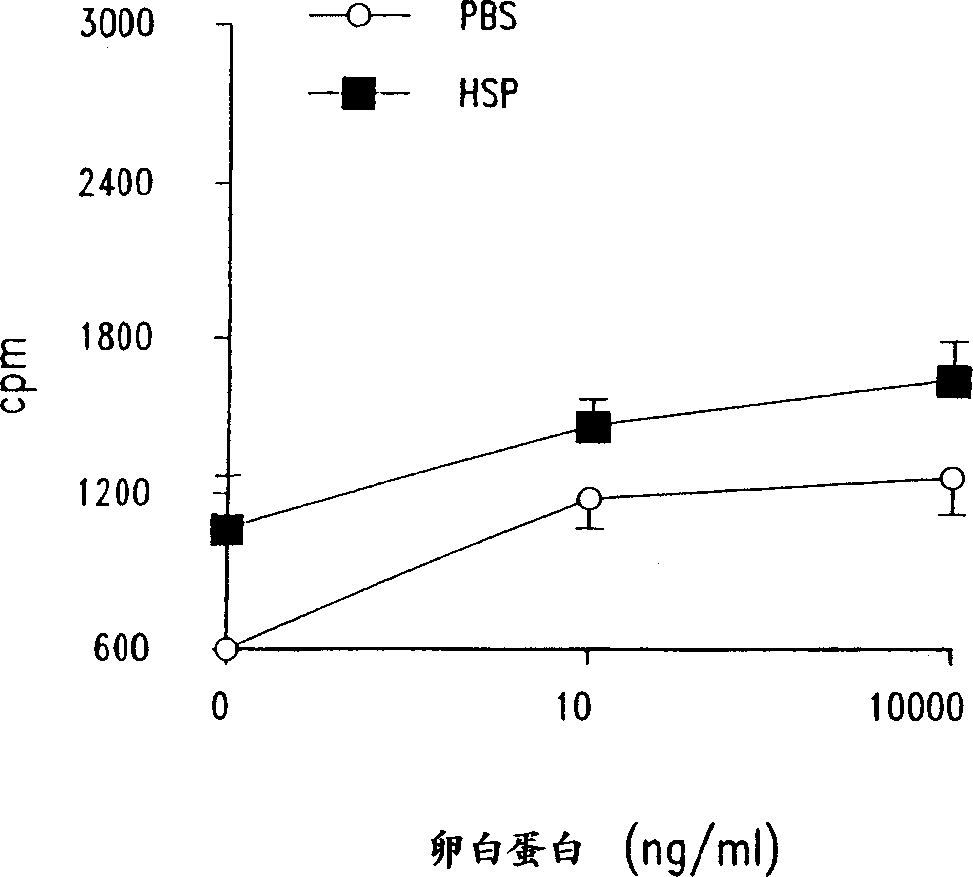
[0111] The following examples demonstrate that mycobacterial HSP-65 upregulates T cell proliferative responses in an allergic sensitized mouse model following suboptimal sensitization with ovalbumin via aerosol challenge.
[0112] Since immunization with mycobacterial HSP-65 after i.p. sensitization of mice enhanced T cell responses to OA (Example 1), the question arises that antigen-specific T cell responses are often not detected in Under conditions (ie, suboptimal sensitization with ovalbumin), will mycobacterial HSP-65 upregulate the response. In addition, the following experiments were designed to examine how short-term treatment with mycobacterial HSP-65 would affect airway responses (bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cellularity and airway response to methacholine stimulation).
[0113] Mice were exposed to OA aerosol (1%) on days 1, 2, 3 and 6 (suboptimal protocol) and received 100 μg of mycobacterial HSP-65 or PBS intravenously on days 1 and 6. It should be noted that in ...
Embodiment 3
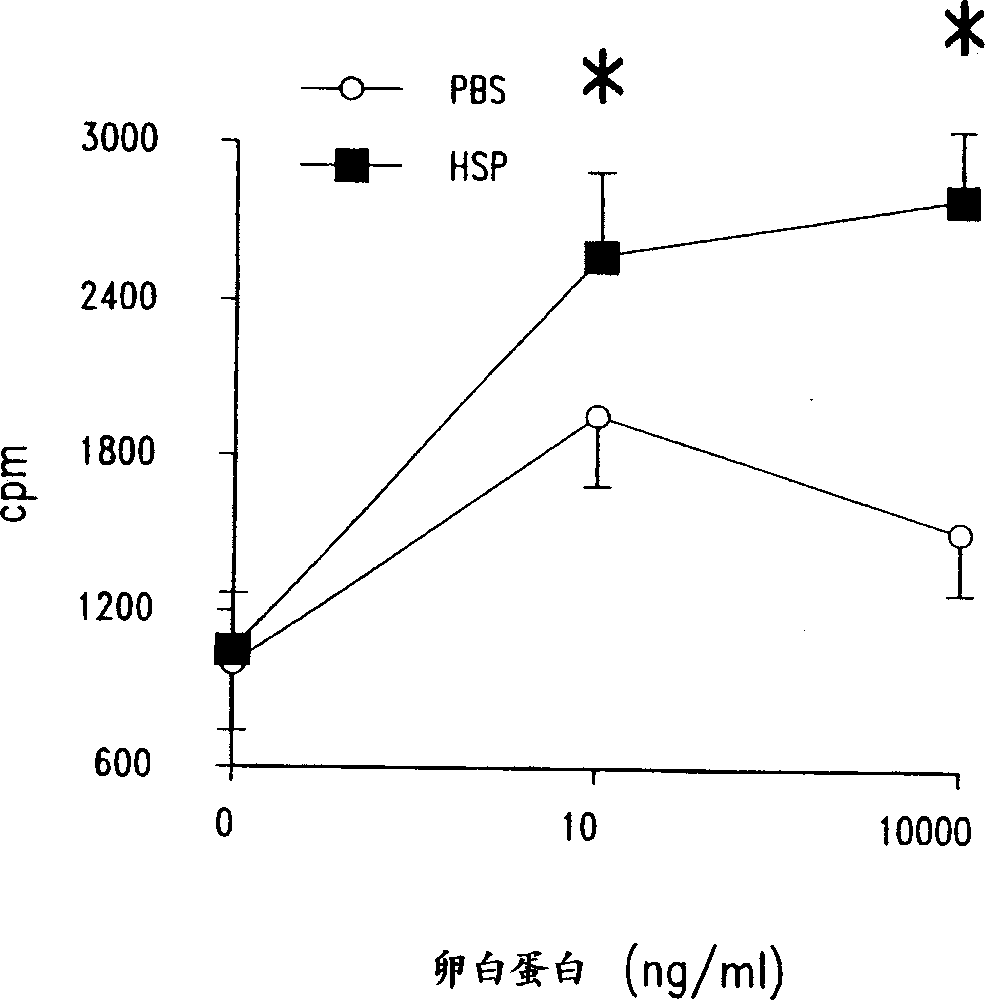
[0121] The following examples demonstrate that mycobacterial HSP-65 upregulates T cell proliferative responses in an airway hyperresponsive mouse model optimally sensitized and stimulated with ovalbumin in the presence of alum.
[0122] In the mouse model of airway hyperresponsiveness and allergic sensitization used here, it has been determined that systemic sensitization and local airway stimulation lead to airway responsiveness associated with eosinophilic inflammation of the airways Hypertension (AHR), which is a cardinal feature of asthma (see, for example, Bentley et al., 1992, Am. Res. Res. Res. 146:500-506; 213; or Dunhill et al., 1960, J. Clin. Pathol. 13:27-33; these publications are incorporated herein by reference in their entirety). To investigate the effect of mycobacterial HSP-65 treatment on these pathological changes in the airways, mice were administered intraperitoneally with 20 μg of OA in 100 μl of PBS (Phosphate Buffered Saline) (Grade V , Sigma Chemical ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com