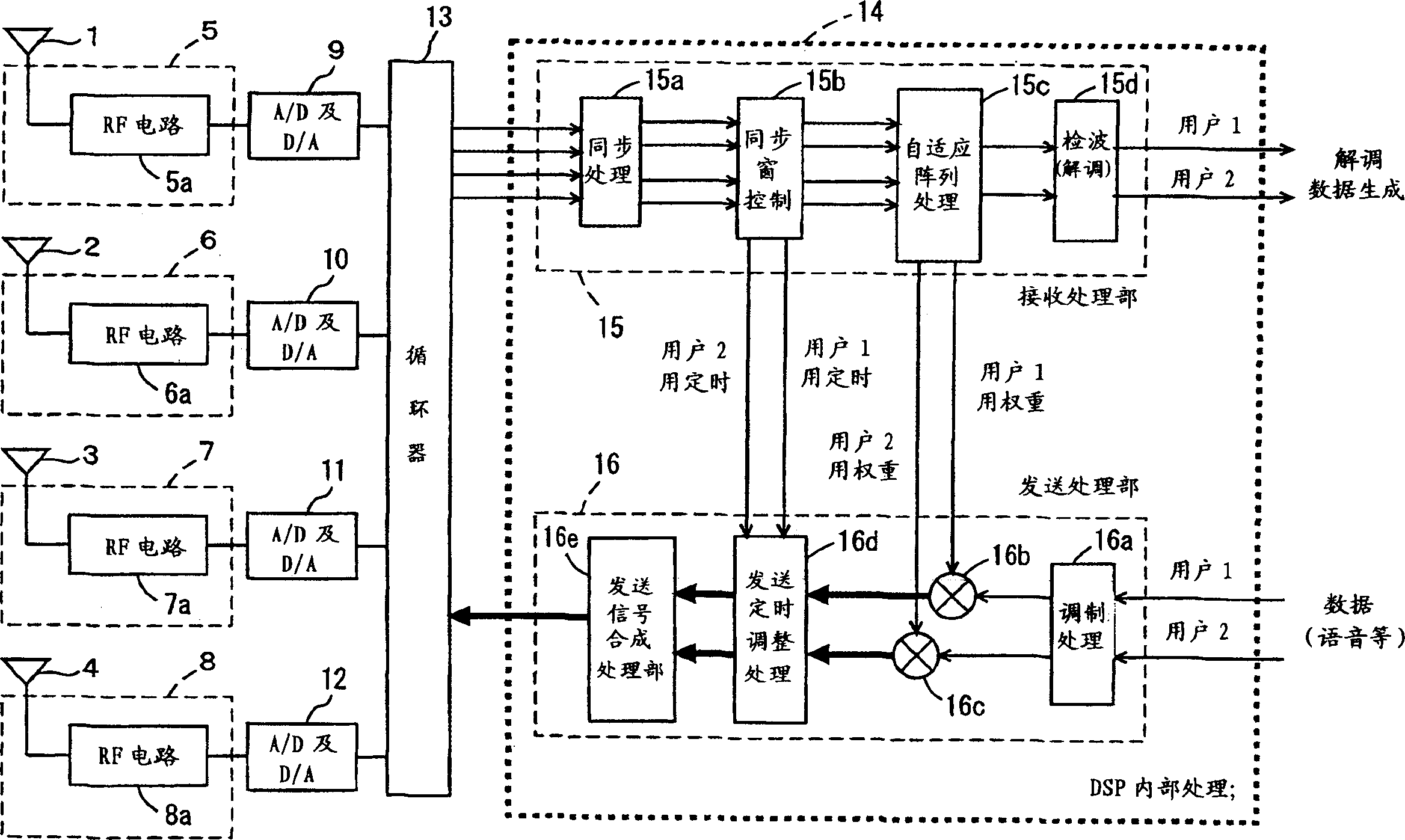
Radio base system, synchronization window control method, and synchronization window control program
A control method and base technology, applied in radio transmission systems, synchronous signal speed/phase control, diversity/multi-antenna systems, etc., and can solve problems such as interference between users, deterioration of call characteristics, and inability to identify and separate users.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach 1
[0078] Figure 4 , is a flowchart showing the synchronization window control process according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. This Embodiment 1 is meant to refer to image 3 A flowchart of the most basic processing explained.
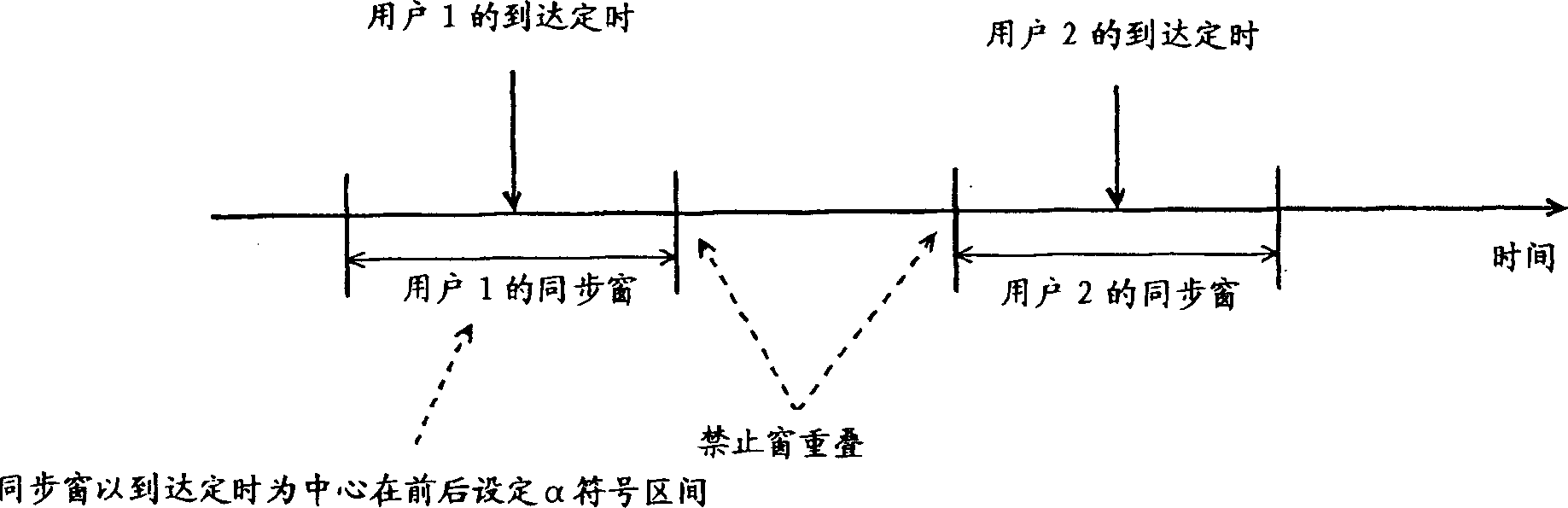
[0079] refer to Figure 4 First, in step S1, a synchronization window of the length of the preceding and following alpha symbols is set centering on the synchronization position estimated by a well-known method.
[0080] Next, in step S2, it is judged whether or not the interval between the synchronization windows of the multi-connected users is equal to or less than a predetermined threshold value 1 for preventing the synchronization windows from overlapping.
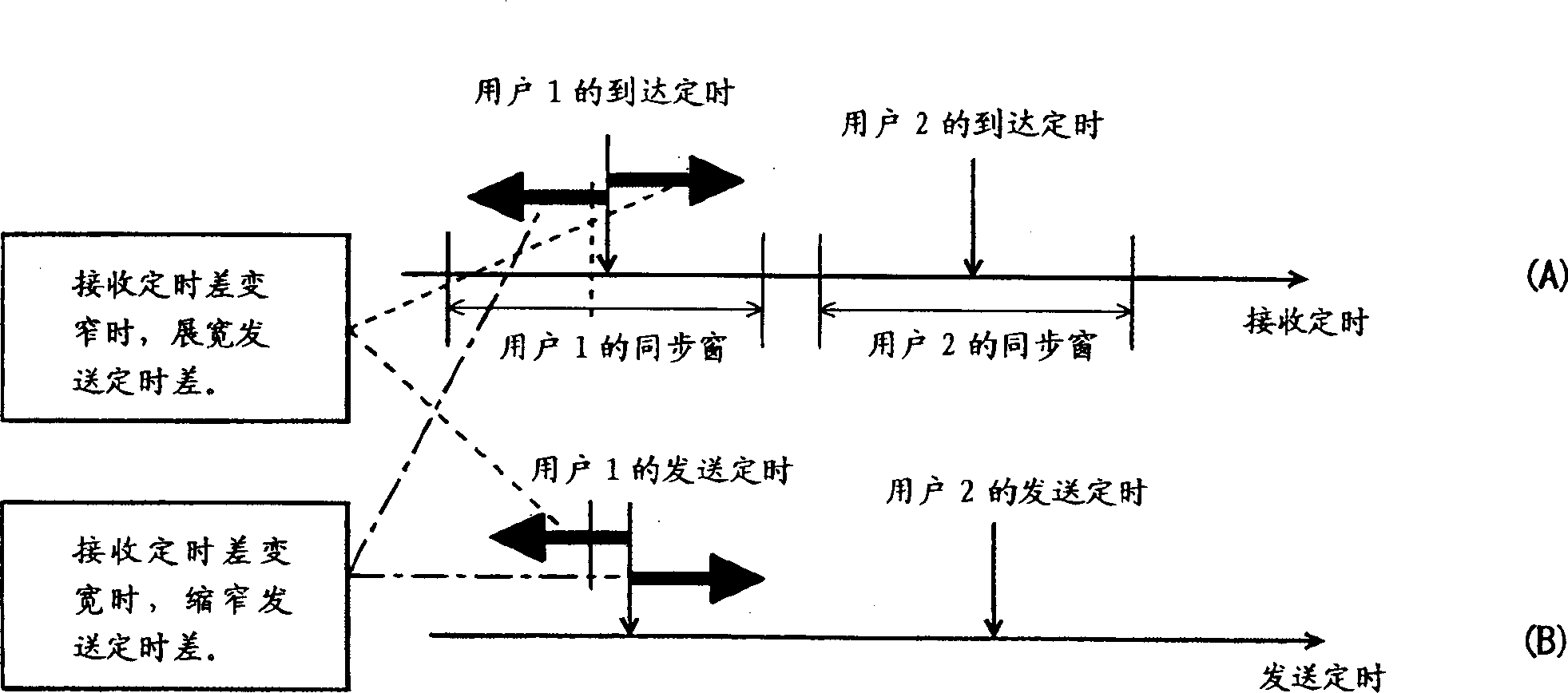
[0081] Then, if the interval is below threshold 1, proceed to step S4, as with respect to image 3 As described above, the process of widening the transmission timing difference between users is performed. In addition, the width by which the transmission timing is shifted once is s...
Embodiment approach 2
[0087] Figure 5 , is a flowchart showing the synchronization window control process according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. The processing of steps S1 to S6 in Embodiment 2 is the same as Figure 4 The processing of steps S1 to S6 in Embodiment 1 is completely the same, and the description thereof will not be repeated here.
[0088] This second embodiment differs from the first embodiment in the following points. That is, when the reception timings of multiplexed users are rapidly approaching for some reason, it is too late to widen the transmission timing difference in step S4, and as a result, synchronization windows may overlap each other. If such a situation is left unattended, there is a danger of approaching and intersecting the synchronous positions, and therefore, some kind of countermeasure must be taken.
[0089] In the second embodiment, in step S7, it is judged whether such an overlap between synchronization windows has occurred after the control of...
Embodiment approach 3
[0093] Figure 6 , is a flowchart showing synchronization window control processing according to Embodiment 3 of the present invention. This Embodiment 3, except for the following point, is the same as Figure 5 Embodiment 2 is the same.
[0094] That is, as a countermeasure when it is judged in step S7 that an overlap between synchronization windows has occurred after the control of the transmission timing, in the third embodiment, in step S9, the synchronization window is removed from the synchronization window. Handling of parts that overlap each other. In other words, in the next reception frame, even if the reception timing reaches the portion where the synchronization windows overlap with each other, it is not regarded as a synchronization position.
[0095] Therefore, according to Embodiment 3, when the synchronization windows overlap even though the transmission timing is controlled, since the next reception timing in the overlapping portion of the synchronization w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com