Method of predicting branch transfers
A transfer prediction and branch prediction technology, applied in program control design, instrumentation, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve problems such as low accuracy rate, low hit rate of double value predictor, complex hybrid predictor, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
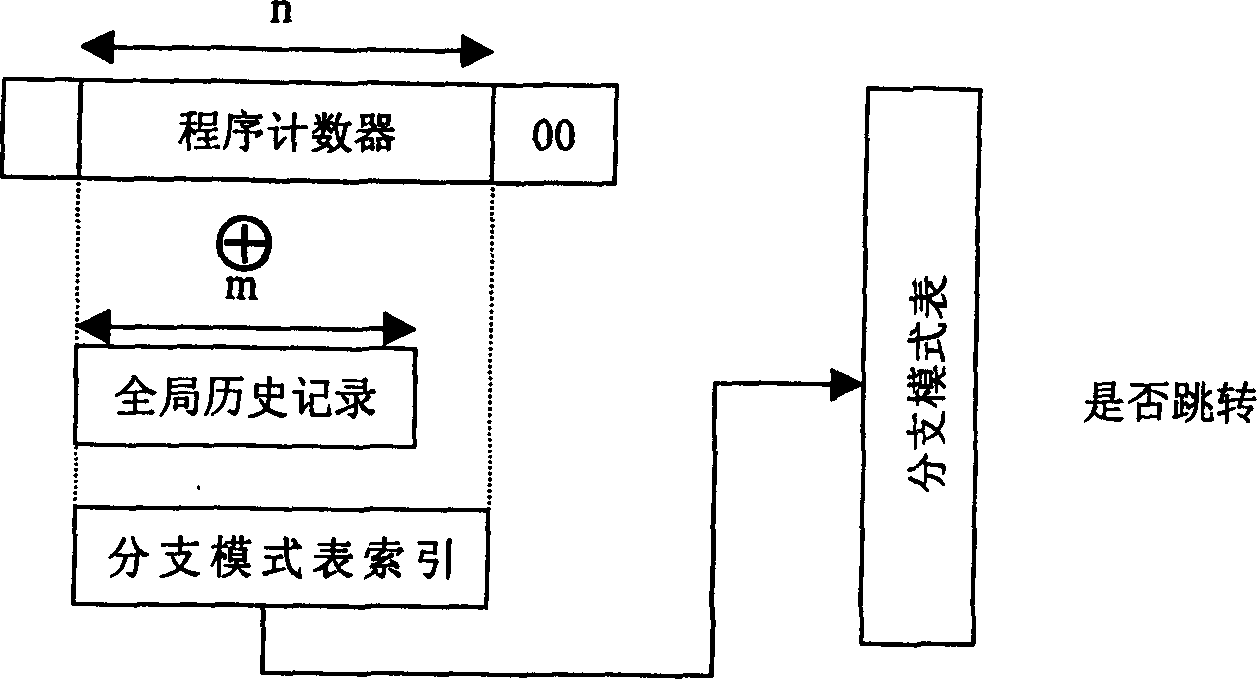
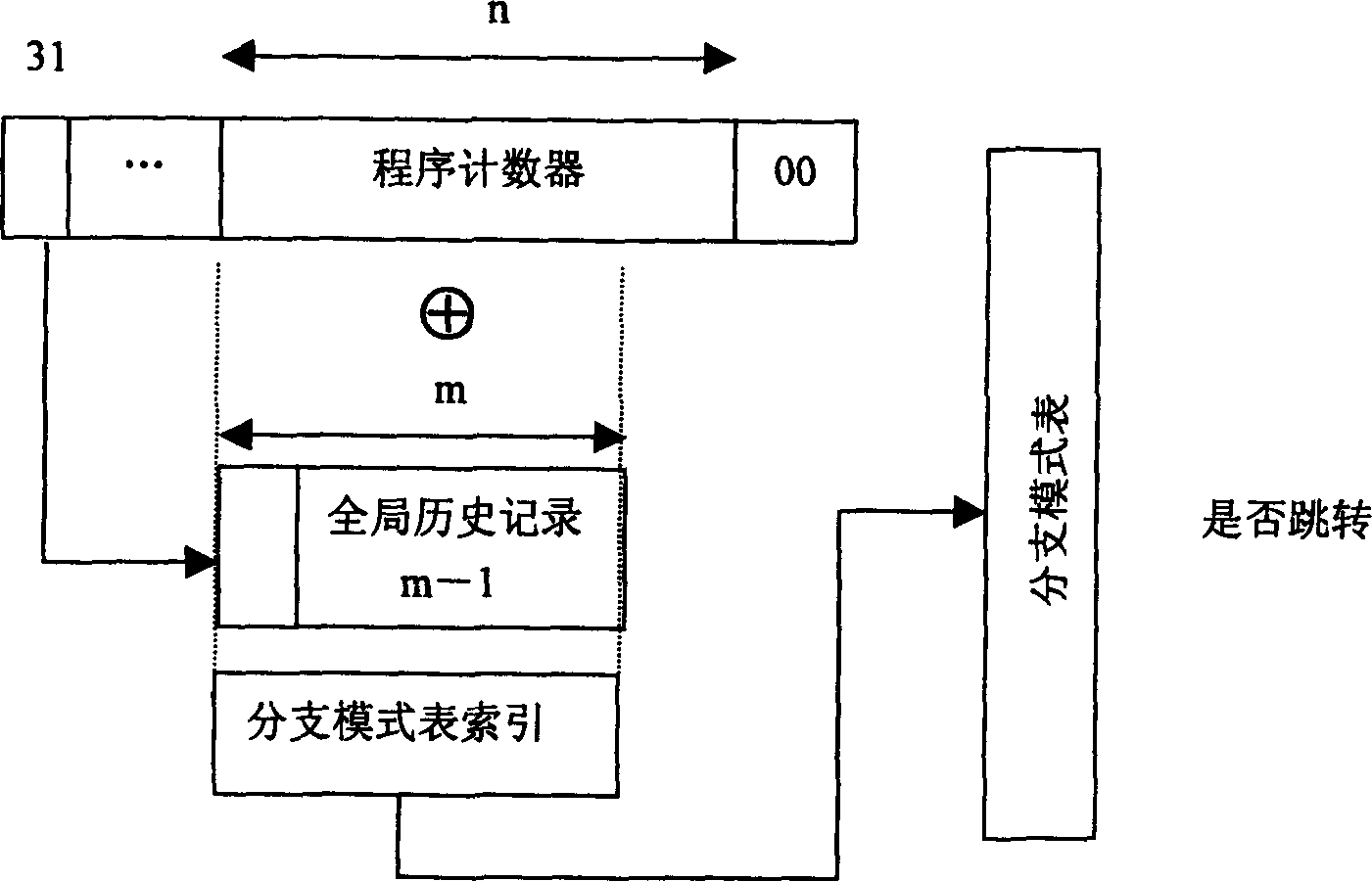
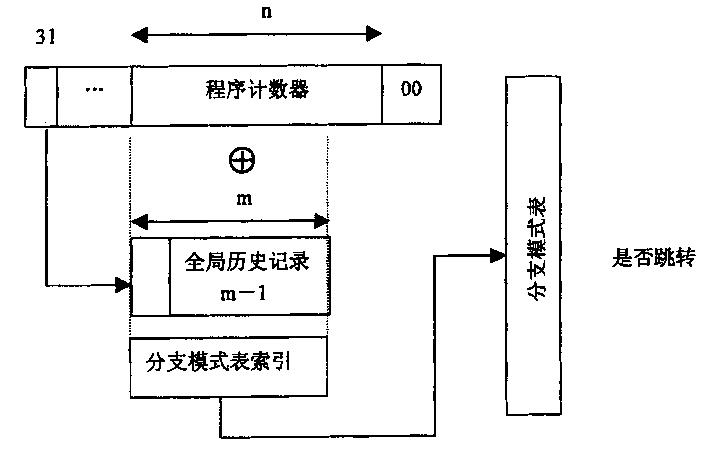
[0022] Please refer to figure 2 , a branch transfer prediction method of the present invention, comprising the following steps:
[0023] a) When the system encounters a branch transfer instruction, obtain the count value of the current instruction from the program counter PC, and obtain the history record from the global history record table;
[0024] b) Utilize the strict control of the operating system on the system space and the user space, use the program counter PC and the historical records obtained in the aforementioned step a) to splice into new global records;
[0025] c) The new global record obtained in the preceding steps replaces the global history record in the traditional global history prediction method, and cooperates with the program counter PC to perform branch prediction.
[0026] Use bits in the PC that contain important information (such as figure 2 PC 31) in , replacing the high bit in the original global history record, and splicing with the remaini...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com