Photoelectric element assembly
A technology for optoelectronic components and components, applied in electrical components, electro-solid devices, circuits, etc., can solve the problems of miniaturization of substrates, lack of margin for insulation spacing, and reduction of luminous efficiency of optoelectronic components, and achieves miniaturization, optical efficiency, etc. The effect of superior utilization rate and superior light utilization efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
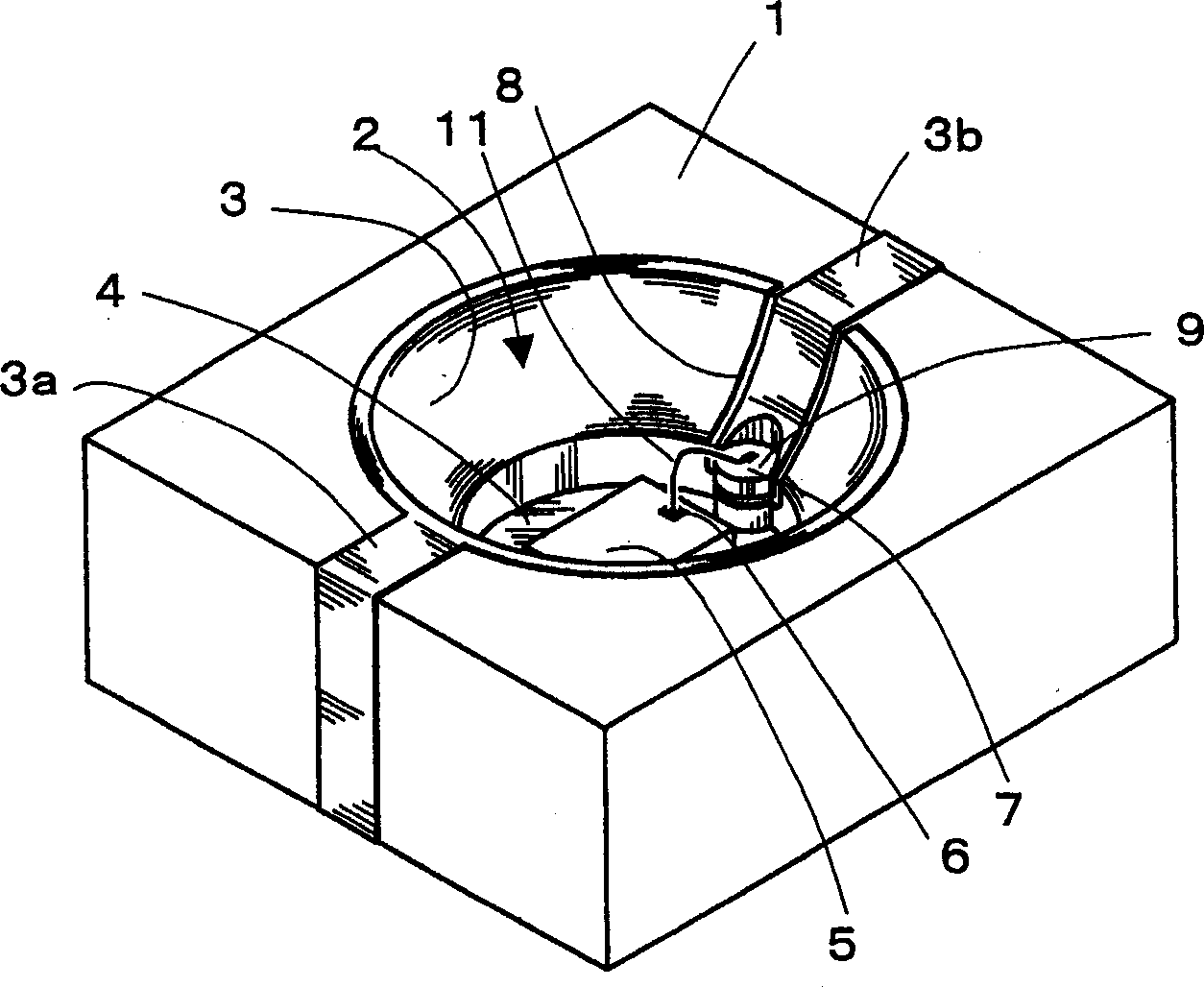
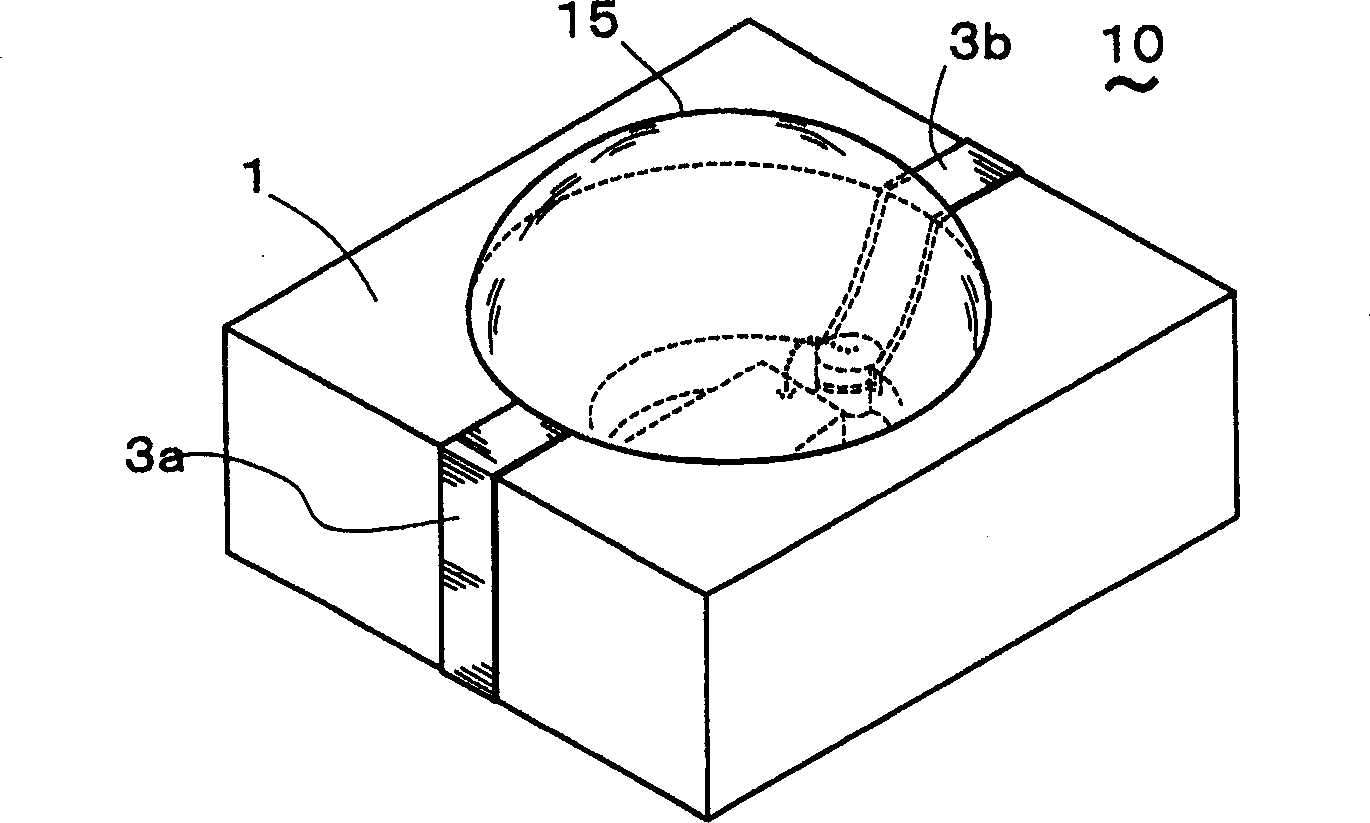
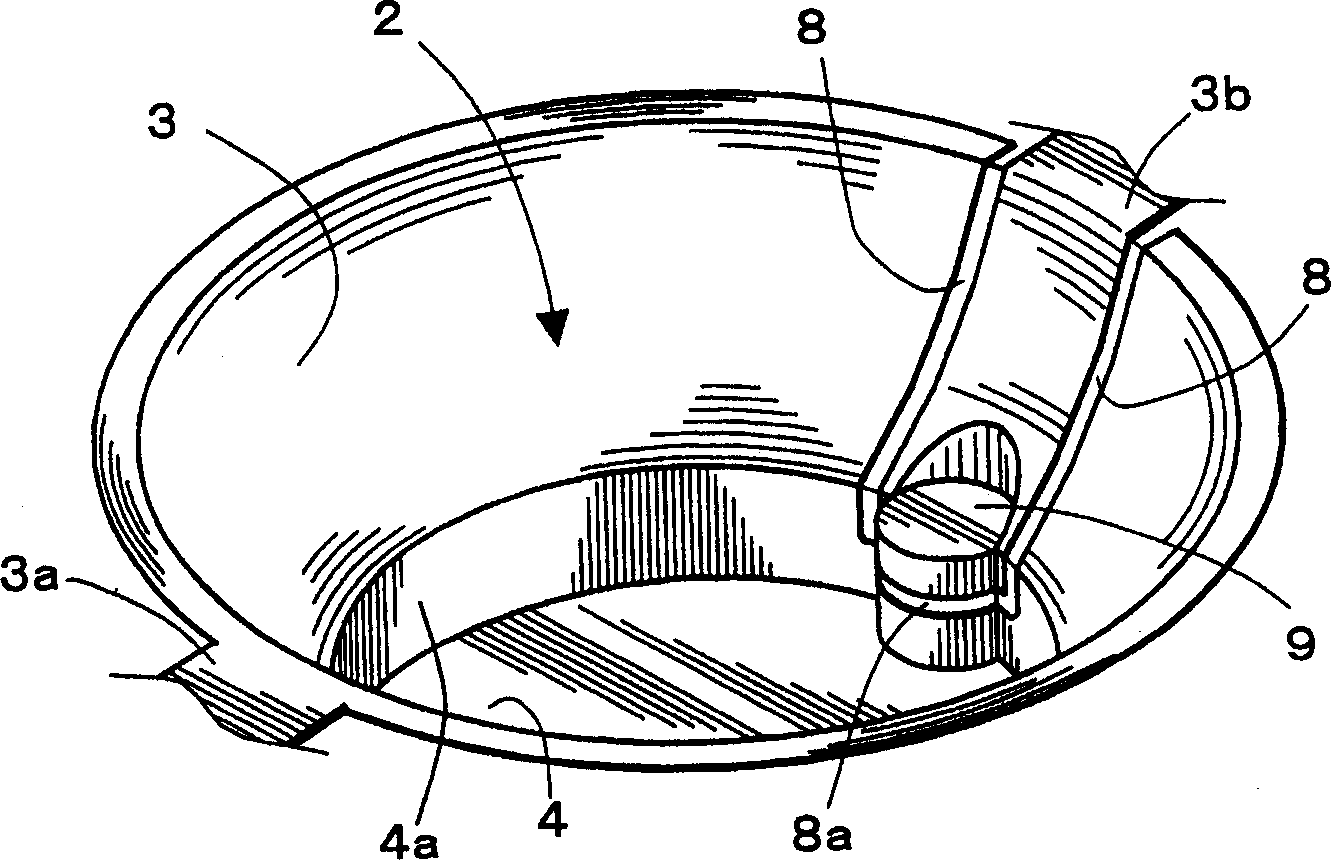
[0069] A photovoltaic element part according to an embodiment of the present invention will be described below with reference to the drawings. figure 1 Indicates the state of the photoelectric element part with the sealing resin layer removed, figure 2 Indicates the appearance of photoelectric element parts. The photoelectric element part 10 is formed by mounting the photoelectric element 5 on the bottom surface 4 of the recess 2 formed in the quadrangular circuit board 1, and is used as a light emitting / receiving device such as an optical connector. The direction of the vertical line at the approximate center of the light emitting / receiving surface of the photoelectric element 5 is defined as an optical axis. A metallized light reflection surface 3 for the photoelectric element 5 to emit / receive light is formed on the back surface including the inclined surface forming the recess 2 .
[0070] The light reflecting surface 3 is provided with an inclined surface made of, for ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Elastic coefficient | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Glass transition temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com