Method for designing semiconductor device
A semiconductor and device technology, applied in the field of designing semiconductor devices, can solve problems such as design restrictions on via holes and upper layer wiring, reduced design freedom, and reduced degrees of freedom
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
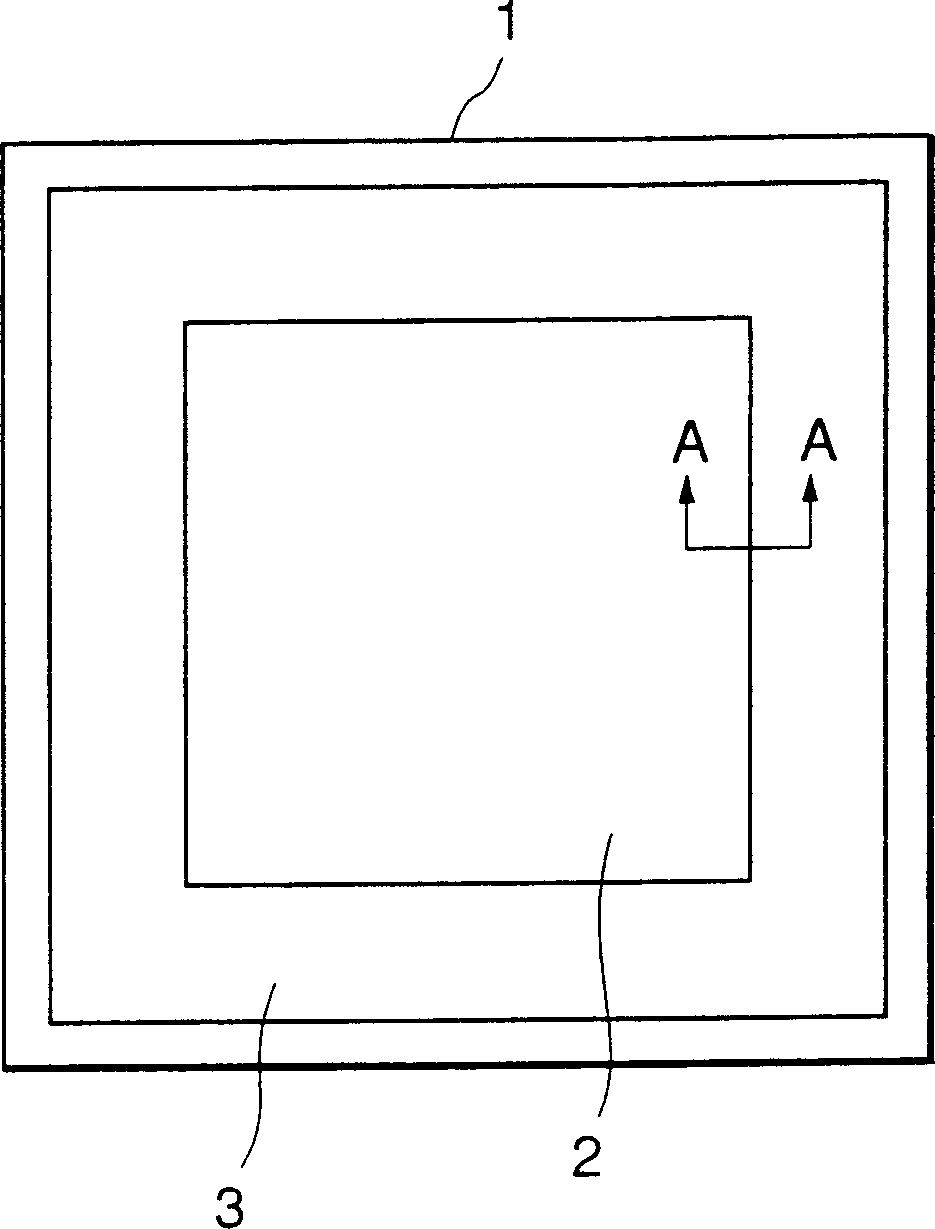
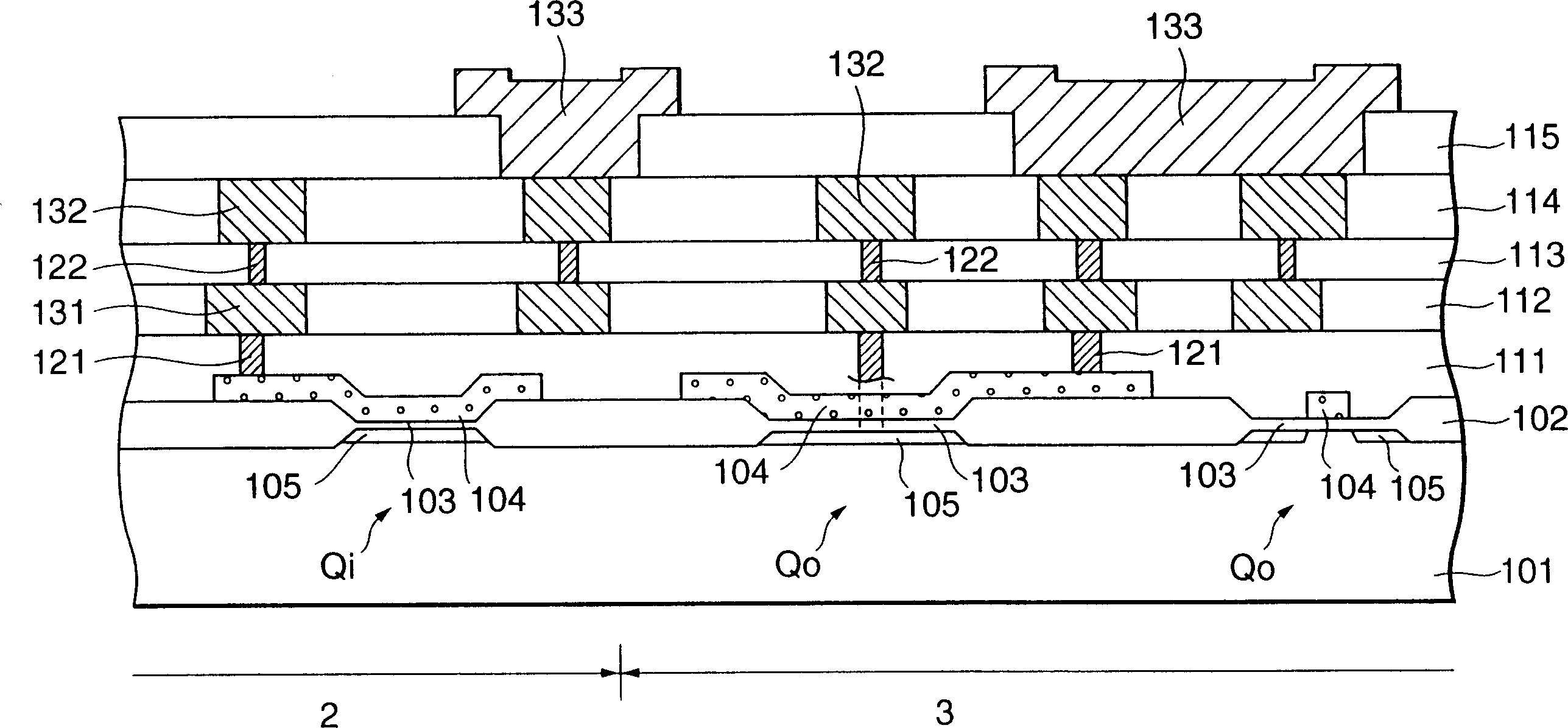
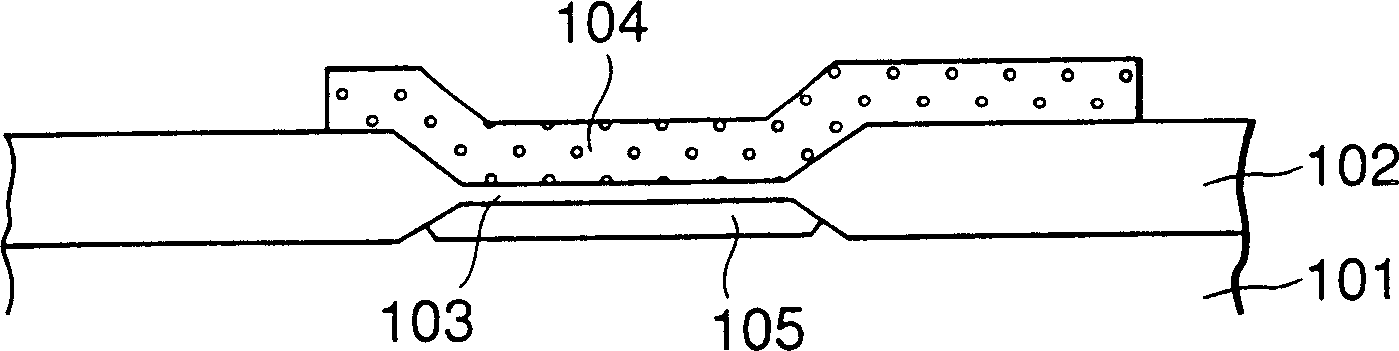
[0031] figure 1 It is a plan view diagrammatically illustrating an example structure of an embodiment of a chip in which the present invention is applied to a semiconductor device including a MOS transistor as an element. In this figure, an internal circuit 2 in which a plurality of tiny minute MOS transistors having a small gate size and constituting memory circuits, logic circuits, etc. are formed is disposed in the central area of the chip. Further, a peripheral circuit 3 in which MOS transistors having a large gate size and constituting an I / O circuit and the like are formed is disposed in a peripheral region on the chip 1 . Then, as described below, necessary circuit connections are made for the MOS transistors of the internal circuit 2 and the peripheral circuit 3 through the upper layer wiring having a layer structure. Now, peripheral circuits are also called I / O elements, or in some cases I / O buffers, and their mounting methods are not limited to figure 1 Periphe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com