Production of alpha-keto butyrate
A ketobutyric acid, microorganism technology, applied in the directions of microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problem of difficult to obtain α-ketobutyric acid accumulation and other problems
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0089] Example 1: Accumulation of α-ketobutyric acid by biotransformation of threonine in Neurospora crassa
[0090] Materials and methods
[0091] Spores of Neurospora crassa strain with ilv-3(-) genotype were purchased from Kansas Medical Center, catalog number FGSC 575, conjugation type A, and spread on agar in Erlenmeyer flasks for the preparation of the starting material. preparation. The composition of the "Horowitz" medium used for this purpose is given in Table 1 below.
[0092] Element
amount per liter
Total Salt Solution*
200ml
Glycerin (87%)
185ml
casein hydrolyzate
0.5g
Yeast extract
5g
malt extract
5g
20g
Biotin solution**
100μl
Adjust to 1000ml
pH
6.5
[0093] * total salt solution
[0094] 25g K-Tartrat (dipotassium tartrate hemihydrate, Merck)
[0096] 5gKH 2 PO 4
[0097] 2.5gMgSO 4 ×7...
Embodiment 2
[0120] Example 2: Two-step fermentation method increases the accumulation of α-ketobutyric acid
[0121] Materials and methods
[0122] The same strains, media and equipment as cited in Example 1 were used.
[0123]In the first fermentation, biomass production was achieved by inoculating a medium containing, according to the data in Example 1, fortified Vogel-salt solution, L-valine and L-isoleucine (added later threonine). The pH was 5.8 at the beginning of the fermentation, and dropped to 4.4 after 72 hours with gentle shaking (200 rpm) at 26°C.
[0124] The mycelial cells were then filtered (0.22 μm) and transferred to a different medium, phosphate buffered saline (0.1 M ). The pH was adjusted to 10 with NaOH (10N).
[0125] After a total of 110 hours of reaction at 25°C and 200 rpm, biotransformation was interrupted by filtering the medium to remove biomass and the filtrate was stored at 4°C for further analysis.
[0126] result
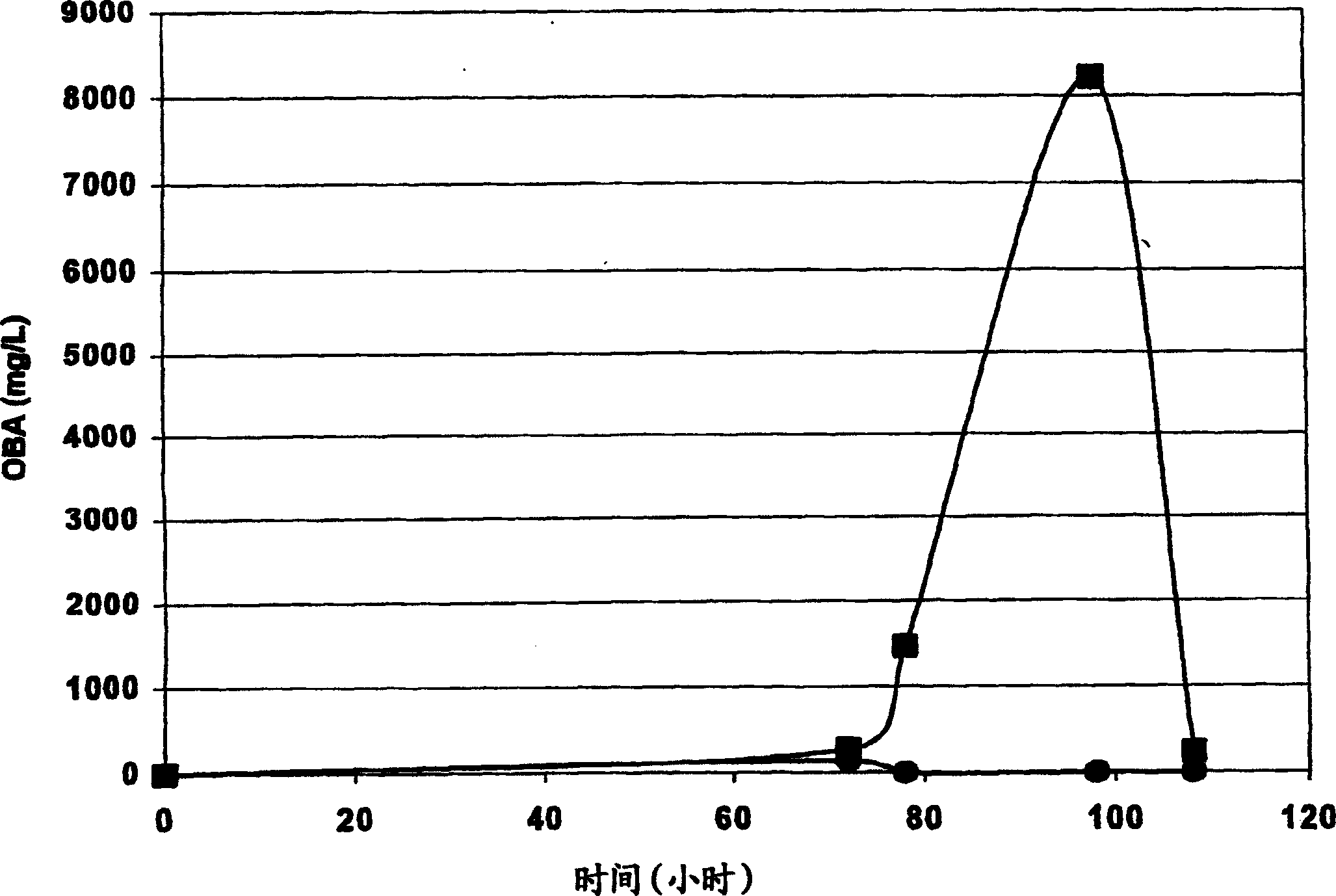
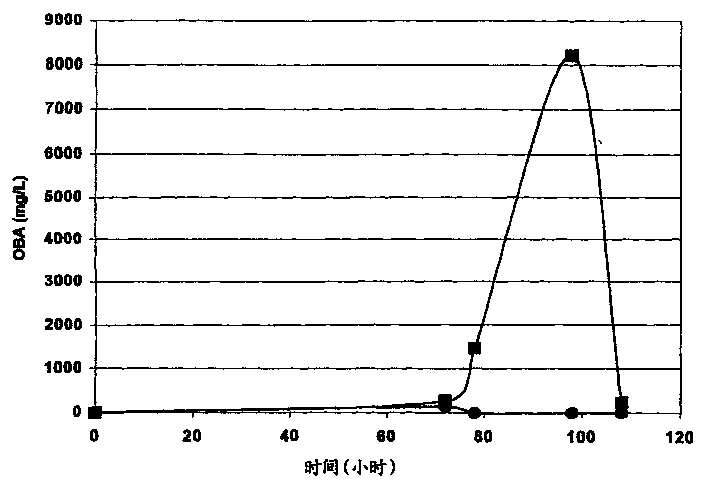
[0127] A high content of α-ketobuty...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com