Radio apparatus and adaptive array processing method
A wireless device and array processing technology, applied in radio transmission systems, polarization/direction diversity, diversity/multi-antenna systems, etc., can solve problems such as inability to remove interference and gain drop
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
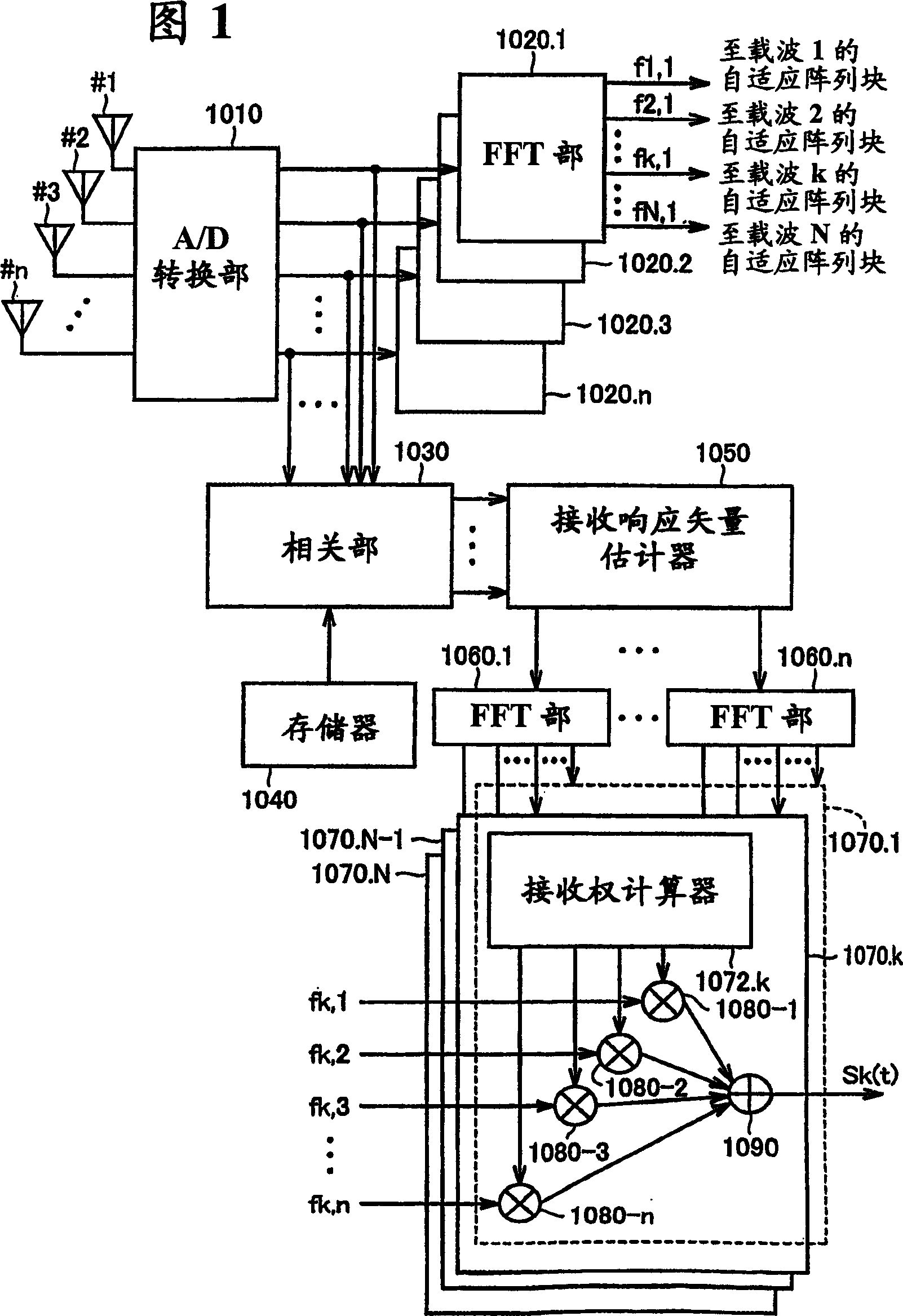
[0153] FIG. 1 is a schematic block diagram showing the configuration of an adaptive array base station 1000 according to an embodiment of the present invention. The adaptive array base station 1000 of the present invention transmits and receives signals having directionality through adaptive array processing between mobile stations such as user terminals. However, as will be understood from the following description, the adaptive array base station 1000 may also transmit and receive signals with mobile stations by using space division multiplexing.
[0154]Referring to Fig. 1, the adaptive array base station 1000 is provided with: an array antenna composed of n (n: natural number) antennas; receiving signals from array antennas #1 to #n, performing detection or A / D conversion of analog / digital conversion Part 1010; set for each antenna, and receive the output from the A / D conversion part 1010 to separate and extract n FFT parts 1020.1~1020.n of the signals of the respective ca...
Embodiment 2
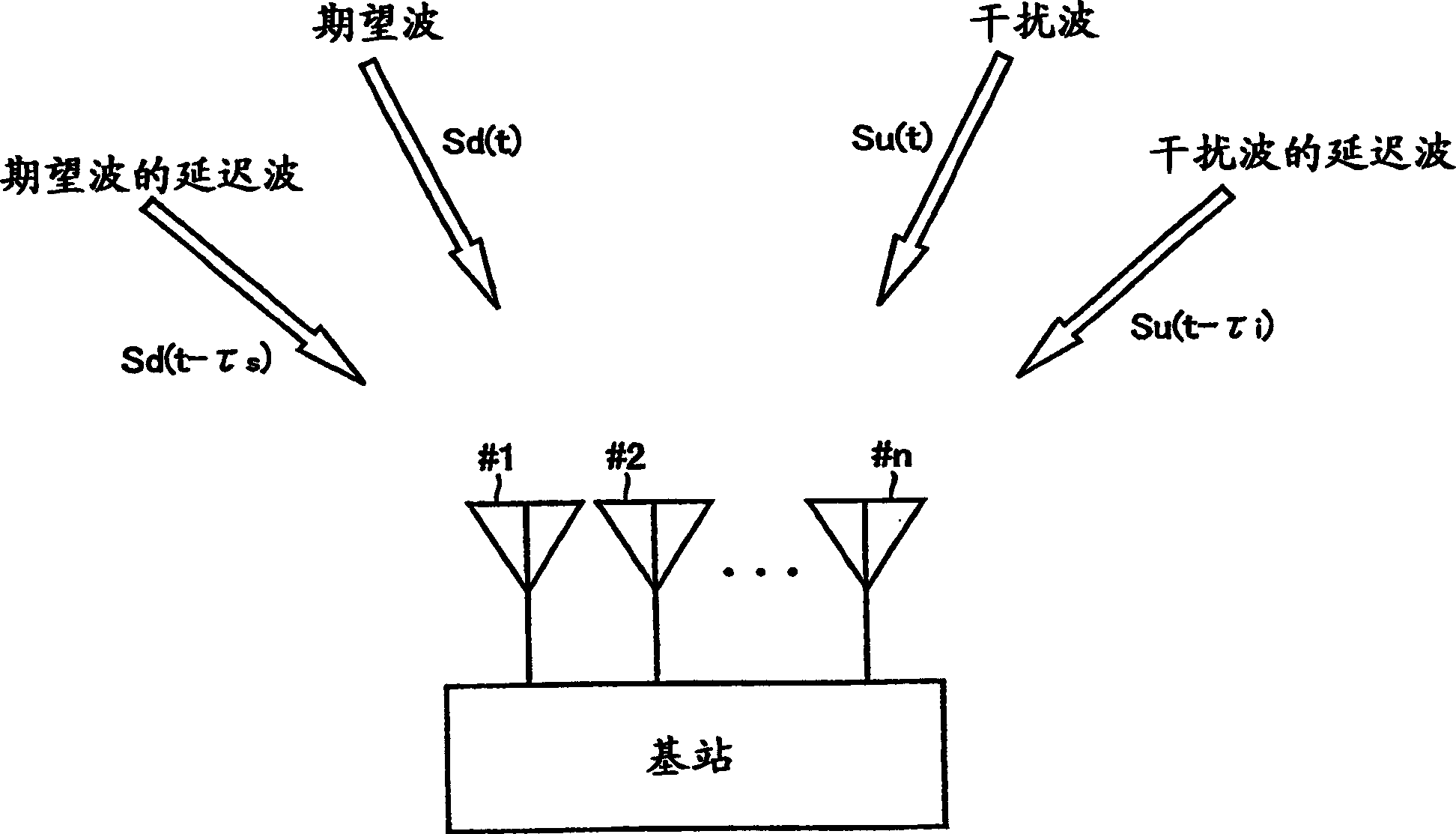
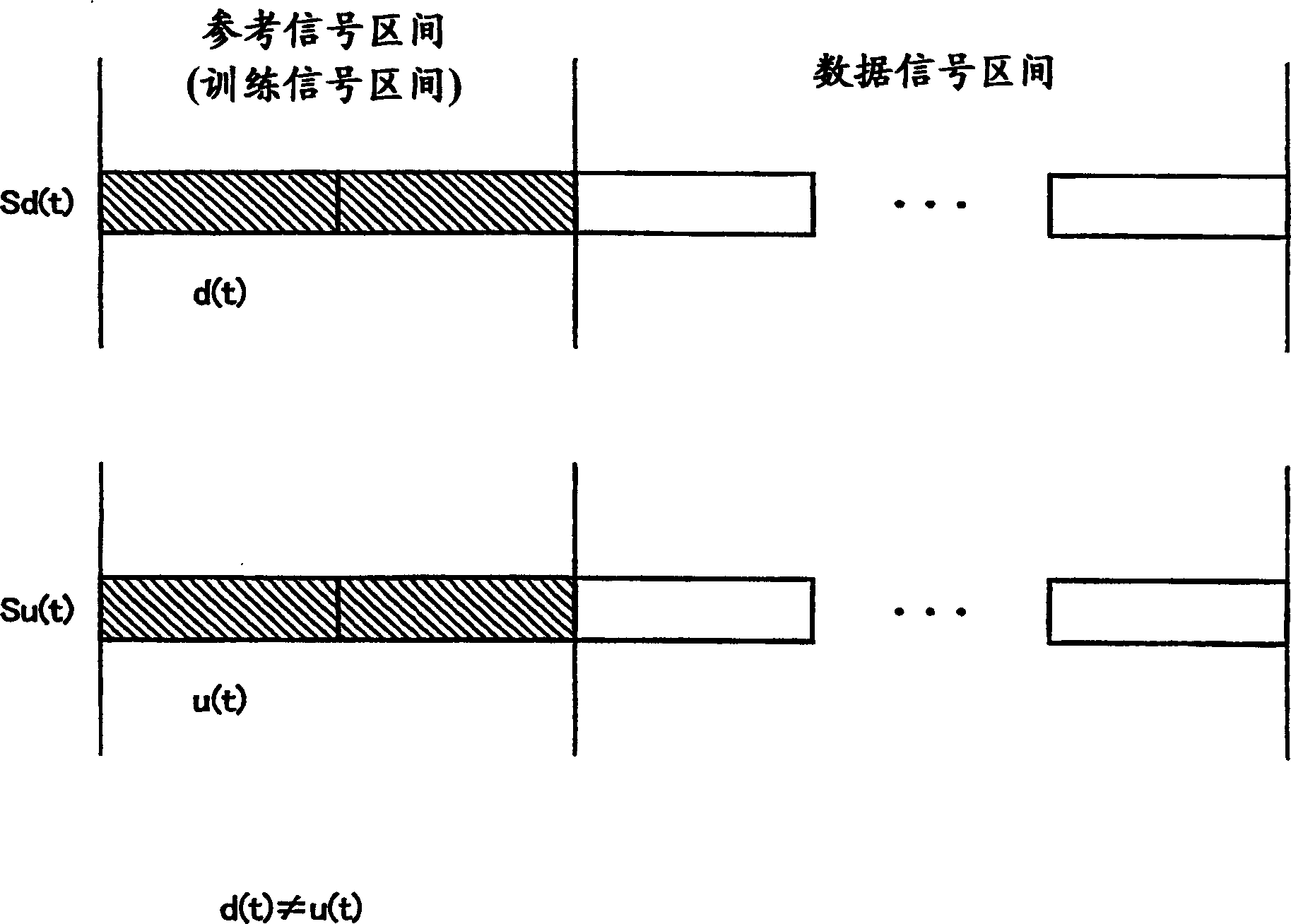
[0285] In Embodiment 1, as the operation of reception response vector estimator 1050, the complex response of the desired signal and the complex response of the interference signal are obtained by the method described in equations (22) to (26).
[0286] However, when there is no overlap between the reference signal interval of the desired signal and the reference signal interval of the interference signal, the methods described in equations (22) to (26) cannot be directly used as they are.
[0287] In Embodiment 2, a method of deriving the complex response of the desired signal and the complex response of the interference signal that can be used even in such a case will be described.
[0288] (estimate of expected signal response)
[0289] When finding the complex response of the desired signal, the evaluation function J provided by the following equation (35) is used 2 . In addition, unless otherwise specified, the code|symbol in the following formula is the same as formula...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com