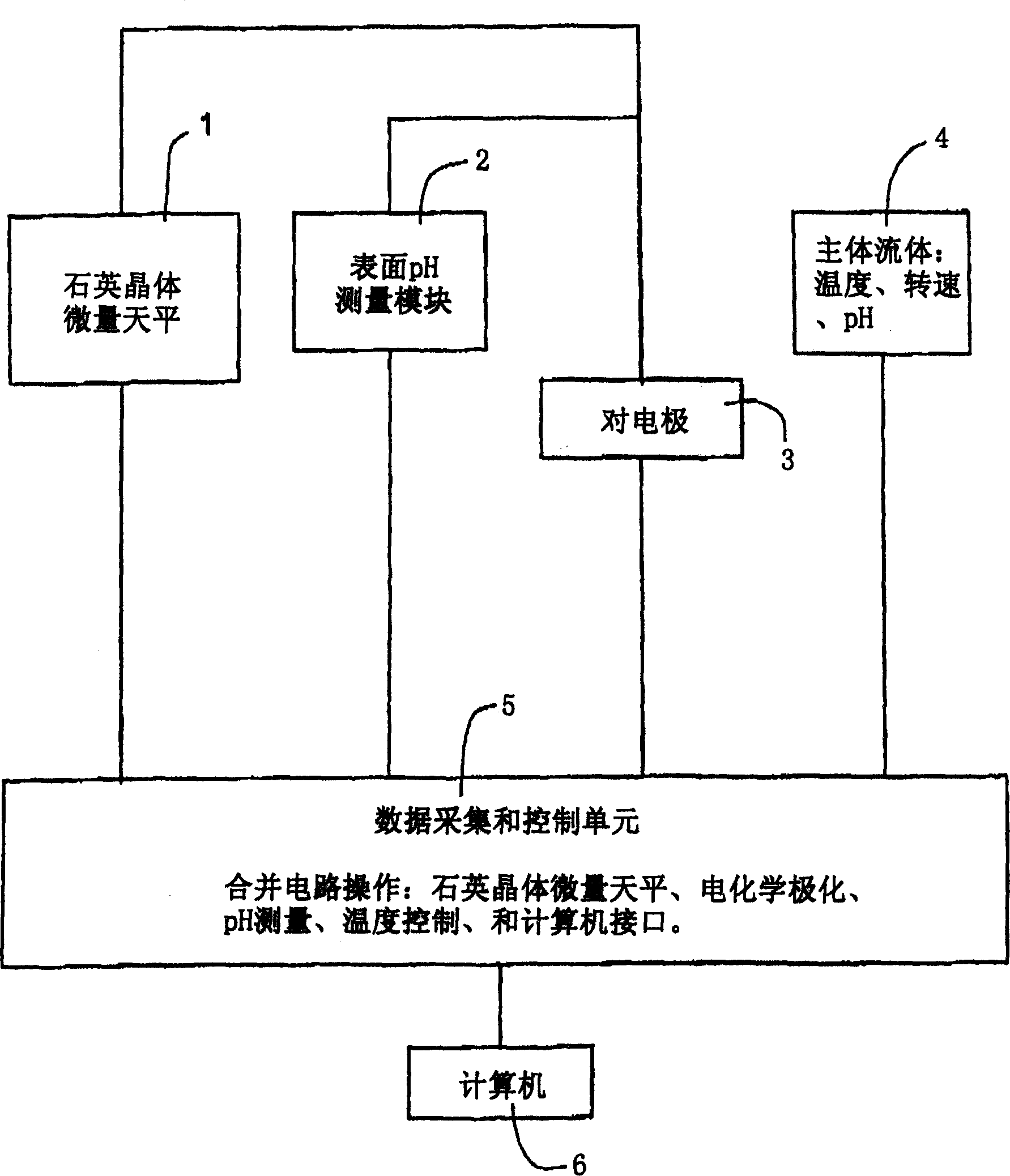
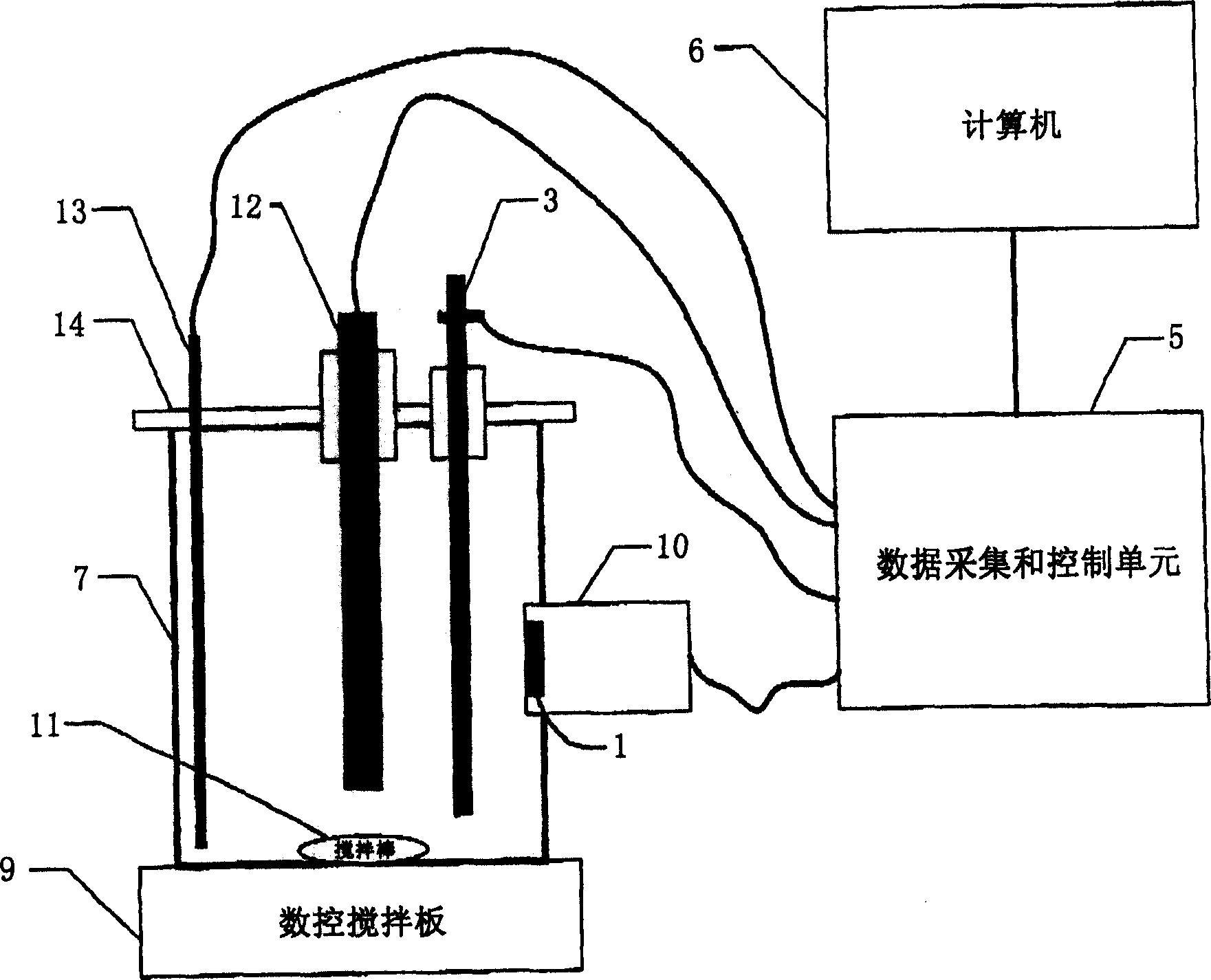
Measuring deposit forming capacity with microbalance
A technology of micro balance and measuring pool, which is applied in the direction of using material absorption and weighing, testing food, measuring devices, etc., which can solve impractical problems and achieve the effect of sensitive application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0090] Screening of Calcium Oxalate Precipitation Inhibitors in Simulated Solutions
[0091] A solution of 1 mM (128 ppm) calcium oxalate for testing was prepared as follows. Sodium oxalate (0.268g) and calcium chloride dihydrate (0.294g) were each dissolved in 35ml of 0.1N hydrochloric acid. The solutions were diluted with deionized water to about 100ml, and mixed under vigorous stirring. After dilution, the solution was diluted to 2L with deionized water. If necessary, 0.1N hydrochloric acid was added to adjust the pH value of the solution to 2.6. This solution was used as a control. A possible inhibitor is added to the remainder of the solution. The results are given in Table 2.
[0092] test solution
Embodiment 2
[0094] Mass accumulation of calcium oxalate precipitates as a function of applied current density on titanium-coated QCMs
[0095] Table 3 presents the results. A 1 mM (128 ppm) calcium oxalate test solution with a bulk pH of 2.4 was used in the test. After calcium oxalate was deposited on the surface of the QCM, a reverse current was applied (applied current density + 2.0mA / cm 2 ). It was observed that the mass of calcium oxalate decreased rapidly due to its dissolution without damage to the QCM.
[0096] table 3
[0097] Applied current density
Embodiment 3
[0099] Screening of Calcium Oxalate Precipitation Inhibitors under Acidic Conditions in Simulated Fluids
[0100] A 4 mM (128 ppm) supersaturated solution of calcium oxalate with a bulk pH of 1.8 was used in the test. Inhibitors (concentration 20 ppm on a dry weight basis) were added prior to equimolar mixing of the calcium chloride and calcium oxalate solutions. Continuous probing with a surface pH probe estimated that an applied 22mA / cm 2 The electric current raises the pH to 2.5-3.0. The results are given in Table 4.
[0101] test solution
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com