Method for producing Mn-Zn ferrite
一种制造方法、铁氧体的技术,应用在电感/变压器/磁铁制造、化学仪器和方法、建筑构件在现场的制备等方向,能够解决应用不合适、没有考量饱和磁通密度、不能发挥变压器、电抗器用铁心性能等问题,达到损耗低的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0066] Fe will be used as the main component raw material 2 o 3 The powder, MnO powder, ZnO powder, and NiO powder were wet-mixed according to the composition shown in FIG. 1 , and then calcined at the temperature shown in FIG. 1 for 2 hours.
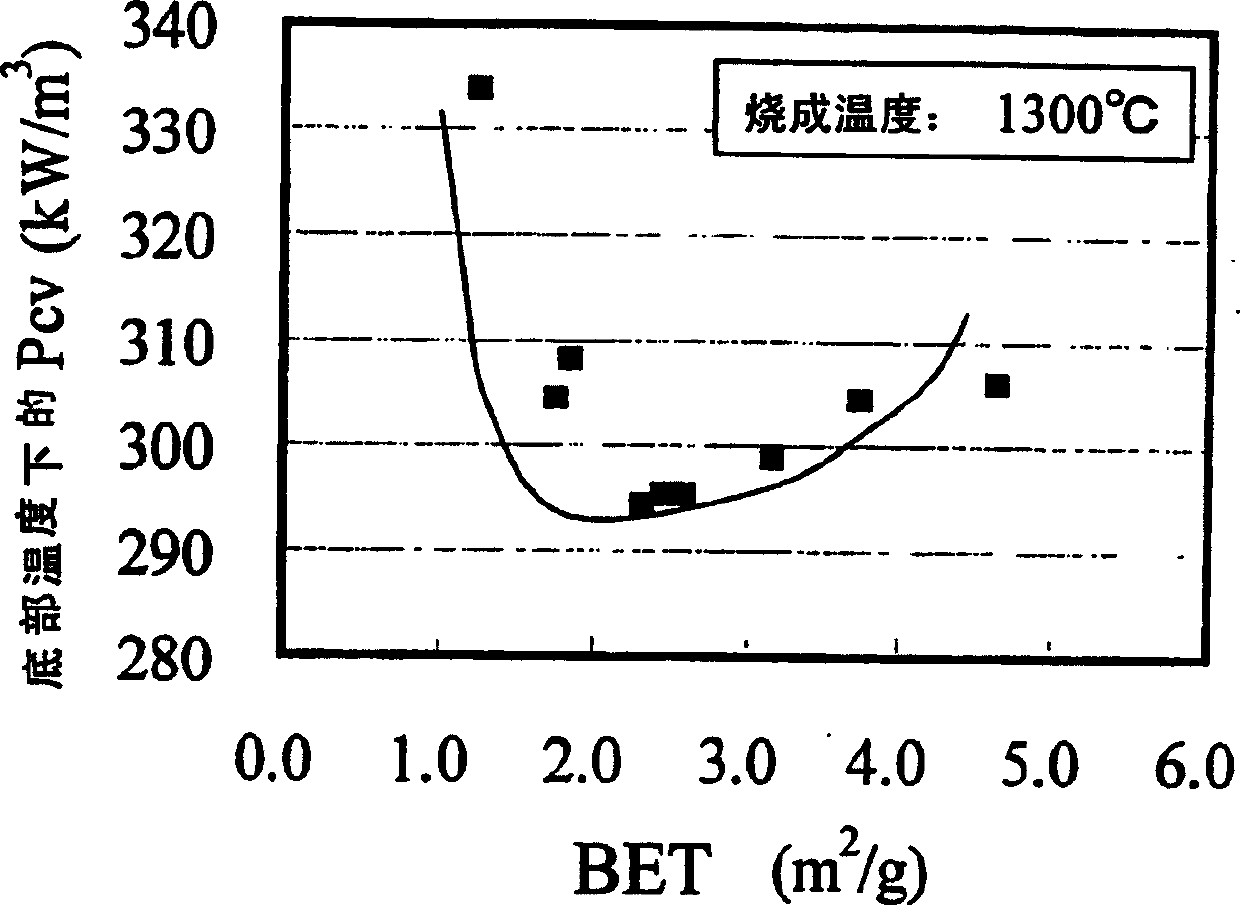
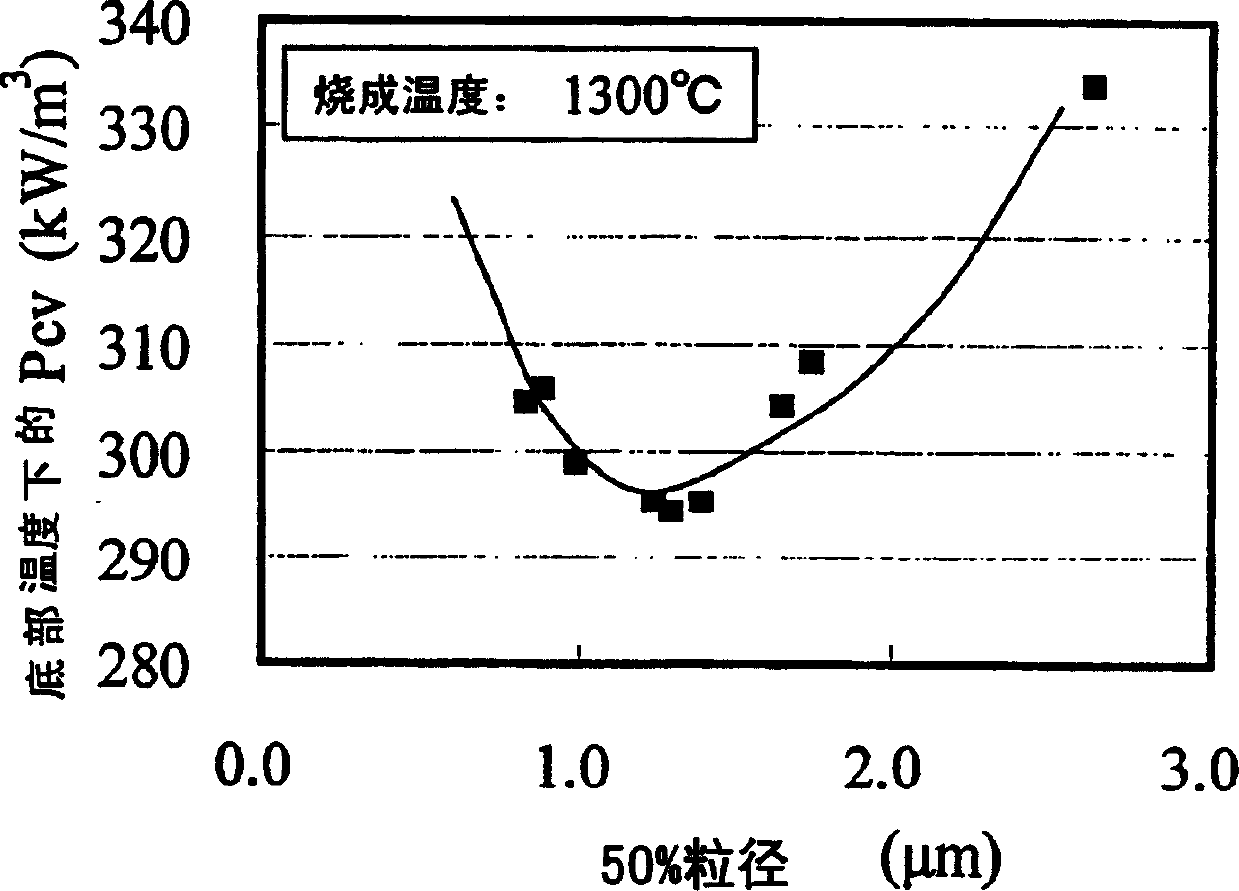
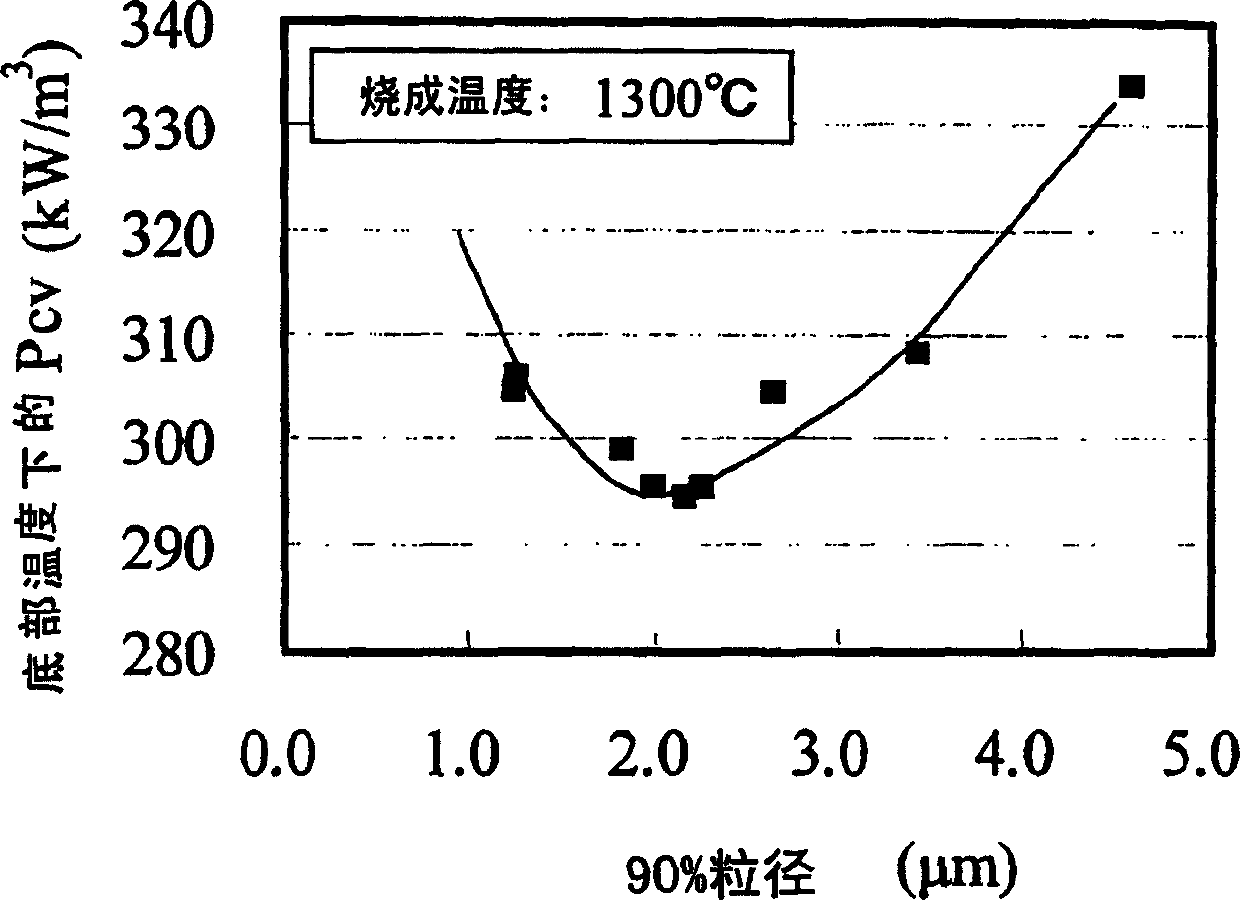
[0067] Next, the calcined product of the main component raw material and the sub component raw material are mixed. As a secondary component raw material, SiO is used 2 Powder, CaCO 3 Powder, Nb 2 o 5 Powder, ZrO 2 Powder and Co 3 o 4 powder. The raw materials of the subcomponents are added to the calcined product of the main component raw materials, and mixed while pulverizing. The specific surface area (BET), 50% particle diameter, and 90% particle diameter of the pulverized mixed powder were measured, and the results are shown in FIG. 1 .
[0068] From Fig. 1, it can be confirmed that the lower the calcining temperature and the longer the pulverization time, the larger the specific surface area of the powder....
Embodiment 2
[0076] The set composition and firing conditions are shown in Fig. 15, and only SiO is added as the first subcomponent 2 and CaCO 3 , In addition, MnZn ferrite was produced in the same manner as in Example 1, and the characteristics were measured in the same manner as in Example 1. The results are shown in FIG. 15 . In addition, the powder properties before firing are as follows:
[0077] BET: 2.5~4.0m 2 / g
[0078] 50% particle size: 0.7~1.5μm
[0079] 90% particle size: 1.0~4.0μm
[0080] Also, Pcv in Fig. 15 represents the loss at the bottom temperature, and B.Temp. represents the bottom temperature.
[0081] As shown in Figure 15, the Fe 2 o 3 When it is as little as 53.5 mol%, the saturation magnetic flux density (Bs) decreases. On the other hand, in Fe 2 o 3 As much as 57.5 mol%, the loss increases.
[0082] Next, when ZnO is as little as 4.5 mol%, the loss increases, while when ZnO is as much as 11 mol%, the saturation magnetic flux densi...
Embodiment 3
[0086] Except for the types and contents of the subcomponents set in FIGS. 16 and 17 , MnZn ferrite was produced in the same manner as in Example 1, and the characteristics were measured in the same manner as in Example 1. The results are shown in FIGS. 16 and 17 . The powder properties before firing are as follows:
[0087] BET: 2.5~4.0m 2 / g
[0088] 50% particle size: 0.7~1.5μm
[0089] 90% particle size: 1.0~4.0μm
[0090] In addition, Pcv at RT in FIG. 17 represents loss at 25°C, Pcv at 100°C represents loss at 100°C, and ΔPcv represents loss at 25°C-loss at 100°C.
[0091] As shown in FIG. 16 , by adding the second subcomponent and the third subcomponent, the saturation magnetic flux density (Bs) can be increased and the loss can be reduced. However, adding too much will decrease the saturation magnetic flux density (Bs) or increase the loss, so it is desirable to add within an appropriate range.
[0092] In addition, as shown in FIG. 17 , by adding a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com