System an method for harvesting electric power from a rotating tire static electricity
A technology for tires and pneumatic tires, applied in tire measurement, tire parts, tire tread/tread pattern, etc., can solve the problem of reducing tire conductivity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0036] As described in the summary of the present invention, the present invention specifically relates to a system and method for collecting electric energy in a tire structure, and also provides technical features for releasing the accumulated electric charge from the tire structure. Then, when the accumulated amount of charge collected is sufficient, it can be used to power an electronic system, where the electronic system includes, for example, electronic components that identify various tire physical parameters and radio frequency emission devices.
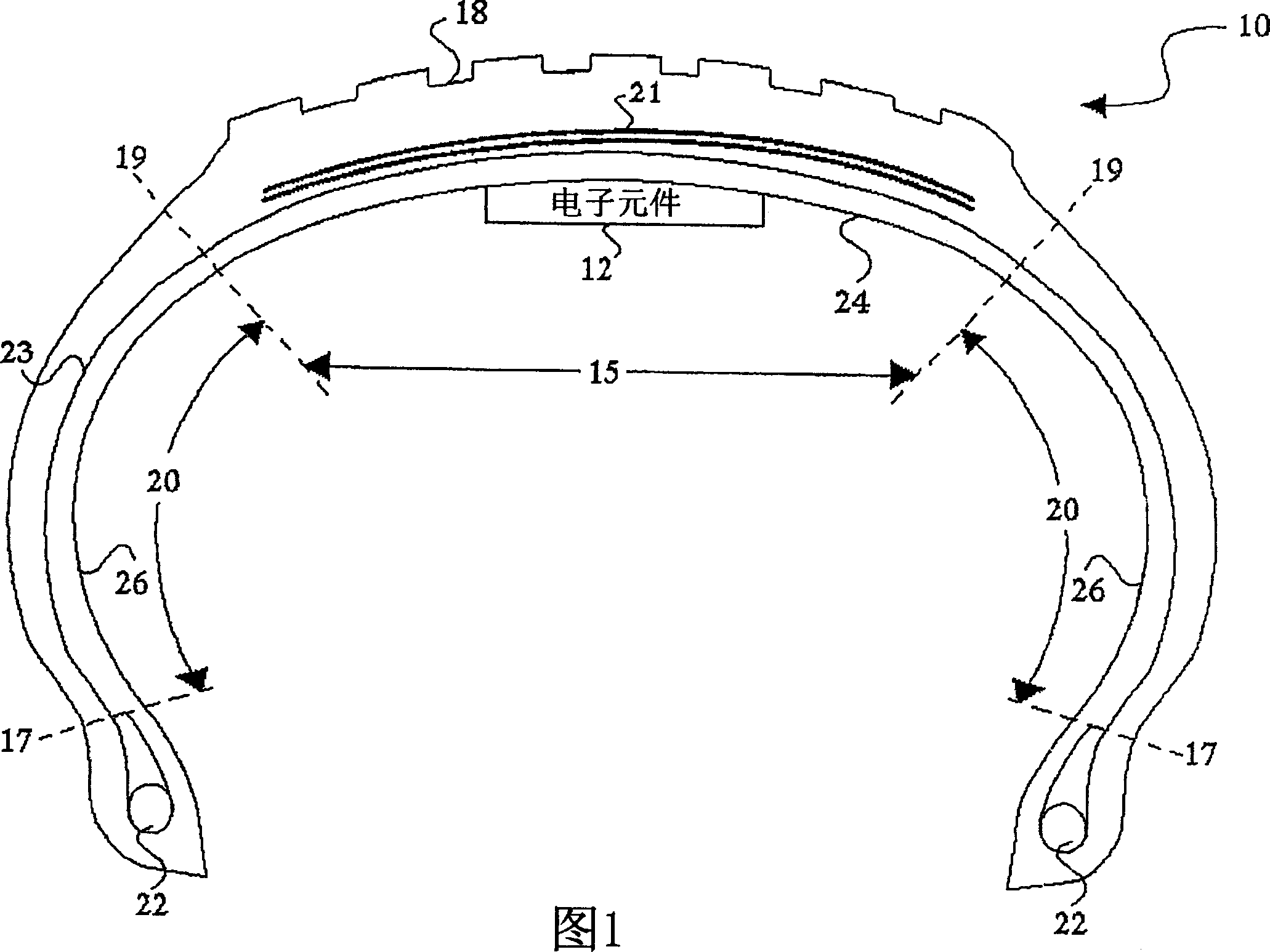
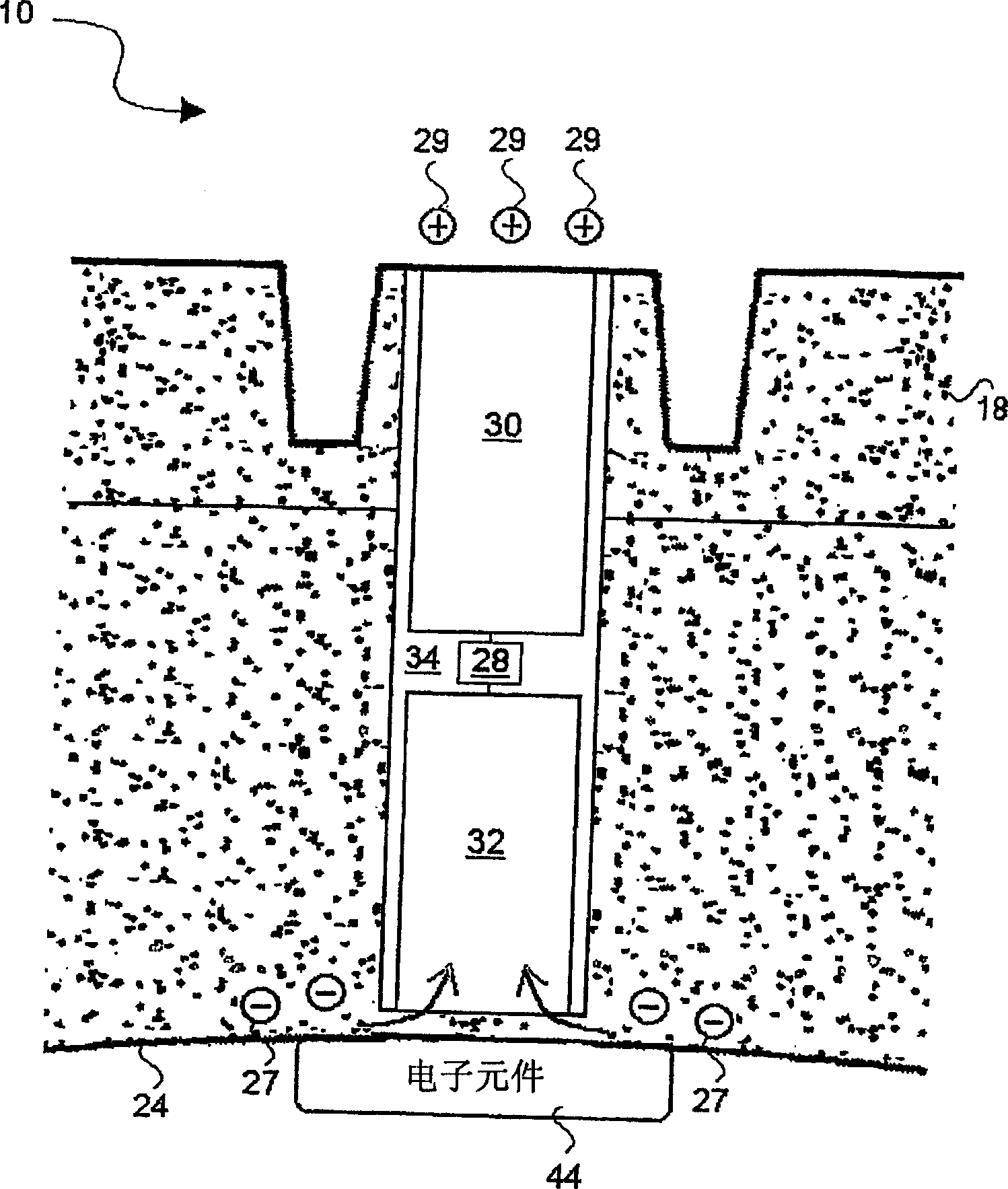
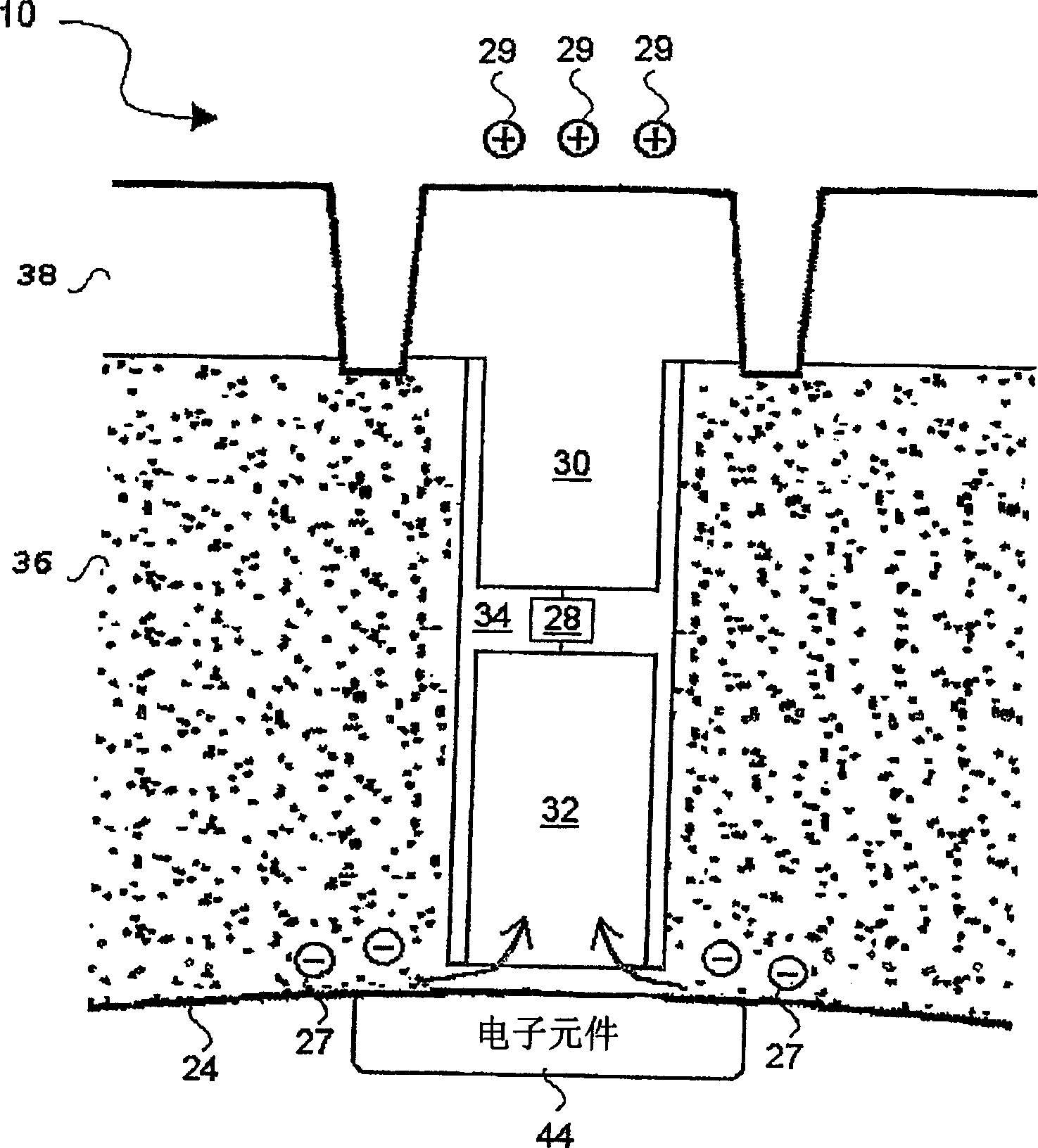
[0037] The technical feature for releasing the accumulation of static electricity from the inside of the tire structure includes a conductive material part inserted between the inner and outer surfaces of the tire structure. In Figure 1 to image 3 The technical content of this conductive material part and its connection with the tire structure is shown in. in Figure 2 to Figure 4 Shows an energy storage device and other electric...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com