Method for pressing random noise in seismological record with low SNR
A random noise and seismic recording technology, applied in the direction of seismic signal processing, etc., can solve the problems of unpredictable random noise, difficulty in suppressing noise, dependence, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
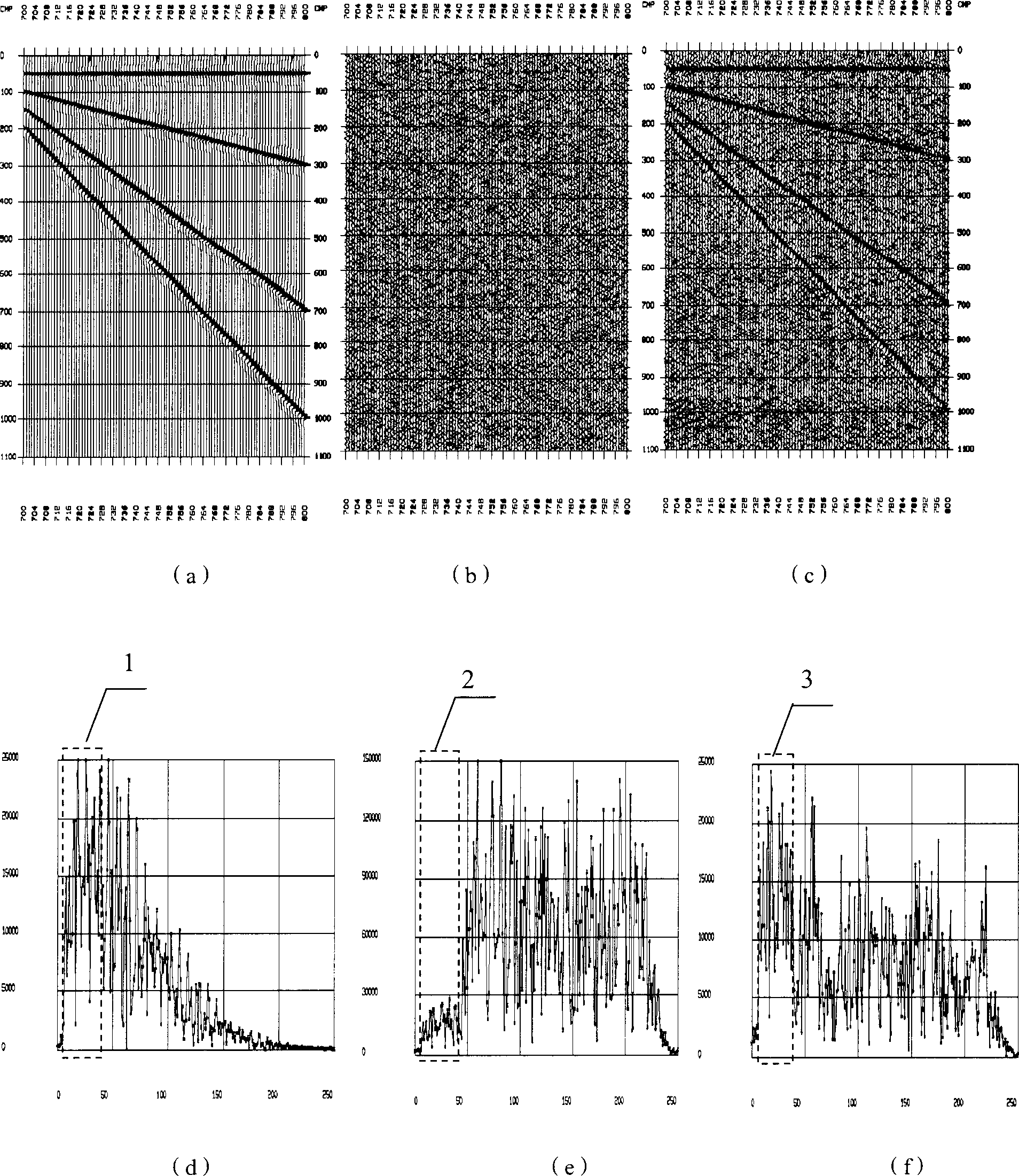
[0048] The method of extrapolating and suppressing noise in the dominant frequency band of the present invention is applied to theoretical data, figure 1 (a) is a theoretical model of high-dip strata without noise interference, in which there are four events that can be continuously tracked, including one horizontal layer and three layers with different dip angles.figure 1 (b) for figure 1 (a) Seismic trace with noise added, given by figure 1 It can be seen from (b) that due to the low signal-to-noise ratio, the effective signal is basically submerged by noise. figure 1 (d) show that figure 1 (a) its effective signals are basically concentrated in the 10-100Hz frequency band, figure 1 (e) shows that the random noise is mainly concentrated above 40Hz, and the dominant frequency band is basically 10-50Hz, which ensures that the low and middle frequency bands of the model have a higher signal-to-noise ratio, which is close to the actual seismic data.
[0049] Transform the acq...
Embodiment 2
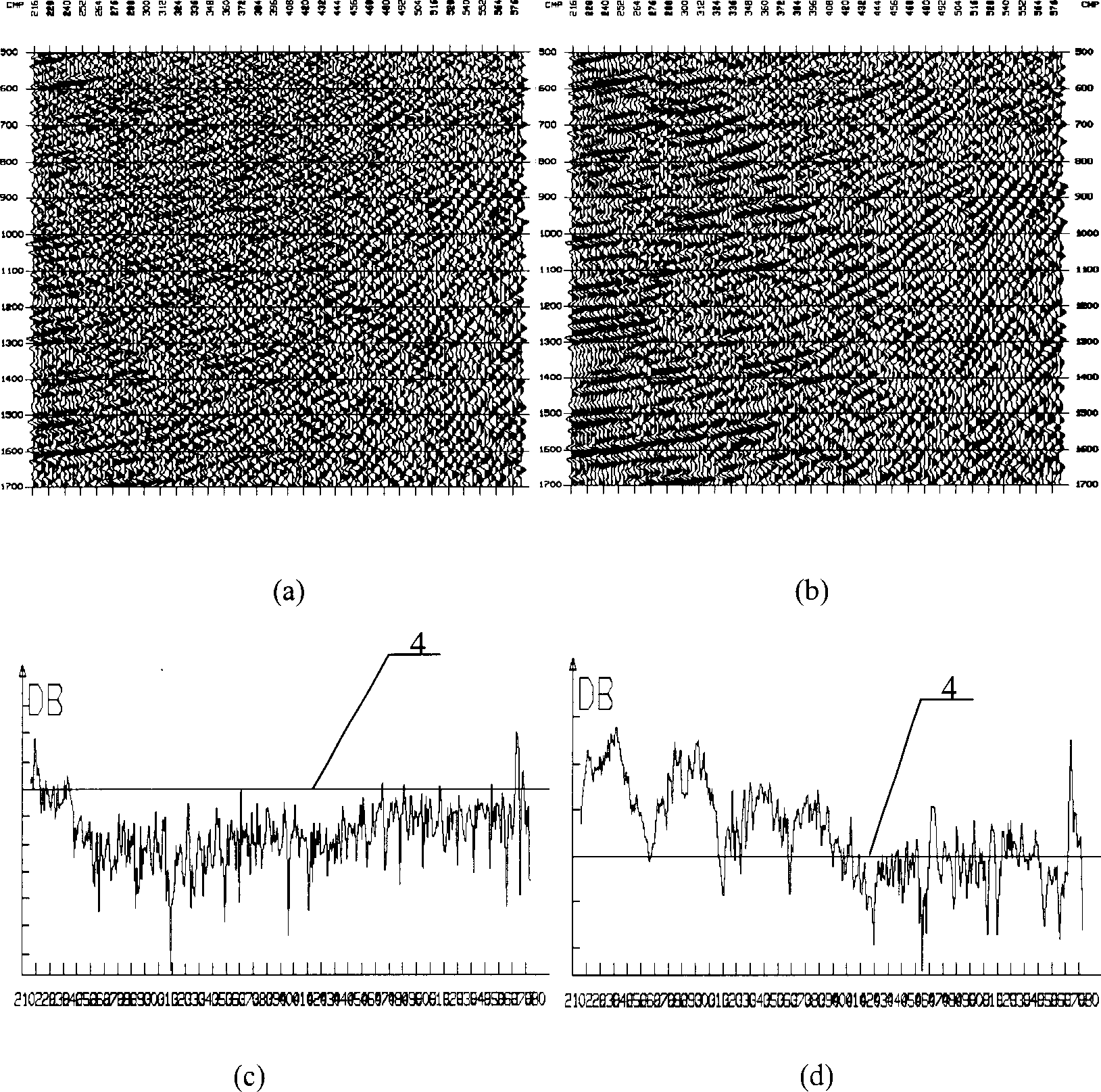
[0064] For seismic data with complex geological conditions, such as figure 2 As shown in (a), its own complexity leads to low predictability and poor regularity of seismic data. If the prediction operator is longer and the prediction range is larger, the prediction result will be more inaccurate. Therefore, at this time, the prediction operator should be appropriately selected to be shorter, but if the operator is too short, it can be seen from the prediction theory that the ability to separate noise will be weakened, so the selection of the operator length must be determined through experiments. figure 2 (a) The continuity of the event on the left section is poor, and the event on the right has a large dip angle. The operator length is selected as 5, and the dominant frequency bandwidth is 60. Adopt the method identical with embodiment 1 to predict and suppress random noise, processing result is as follows figure 2 (b), compare figure 2 (c), (d) It can be seen that the ...
Embodiment 3
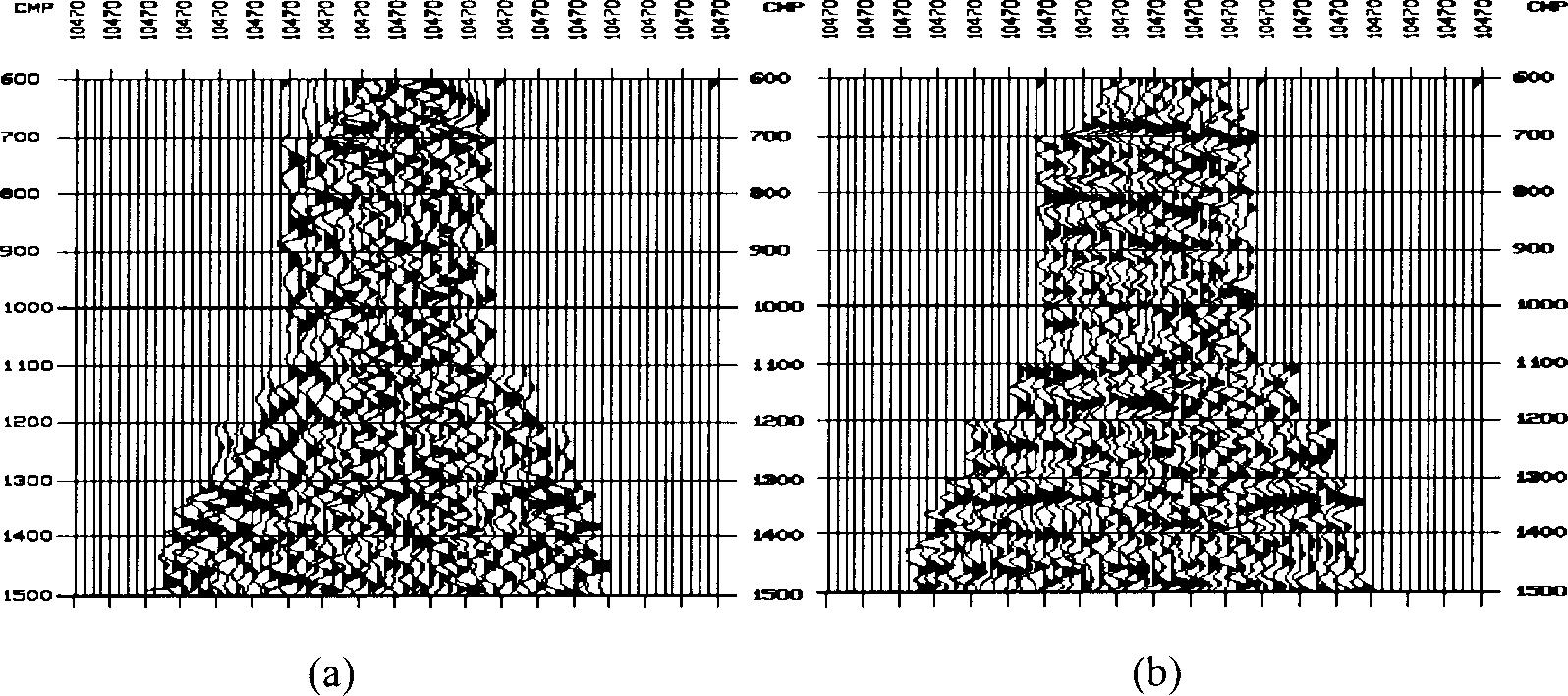
[0066] In addition to processing post-stack seismic records, the present invention can also process pre-stack seismic data, provided that it is performed after motion correction processing. image 3 (a) is a motion-corrected common reflection point gather, using the same processing method as in Example 1, image 3 (b) is the result after processing by this method. Because the event distribution on the common reflection point is hyperbolic before motion correction, the event distribution on the common reflection point is linear after motion correction. This method can predict the event in the shape of a straight line. The hyperbolic event is approached by a straight line during the prediction process. The prediction result is not particularly accurate. The longer the prediction operator is, the larger the error is, so dynamic correction must be performed before denoising .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com