Tensioner
A technology of tensioner and shaft components, applied in belts/chains/gears, mechanical equipment, transmission devices, etc., can solve the problems of increased engine output loss, increased friction, inappropriateness, etc., to reduce output loss and stabilize amplitude. The effect of suppression, fine and stable amplitude suppression
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
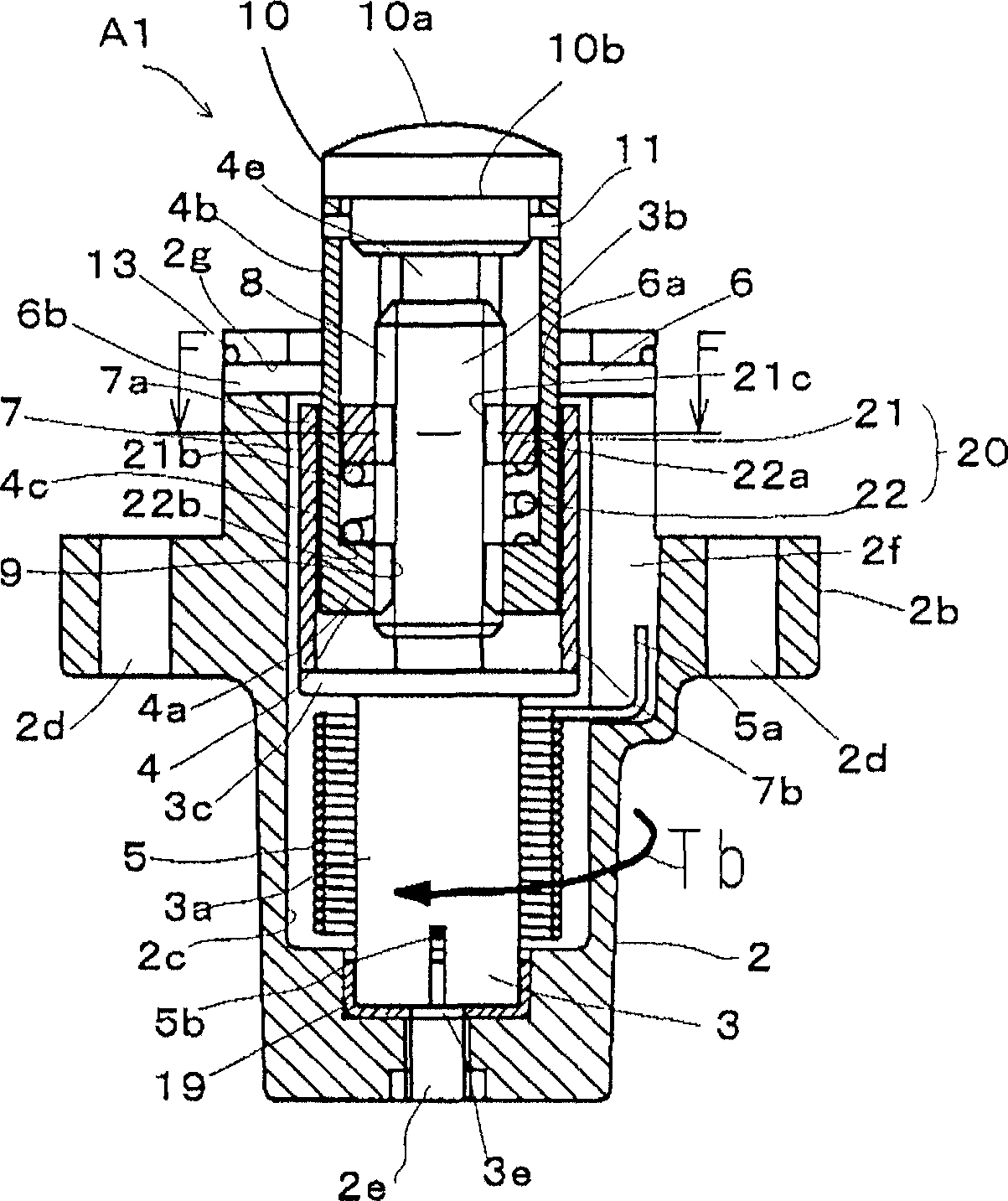
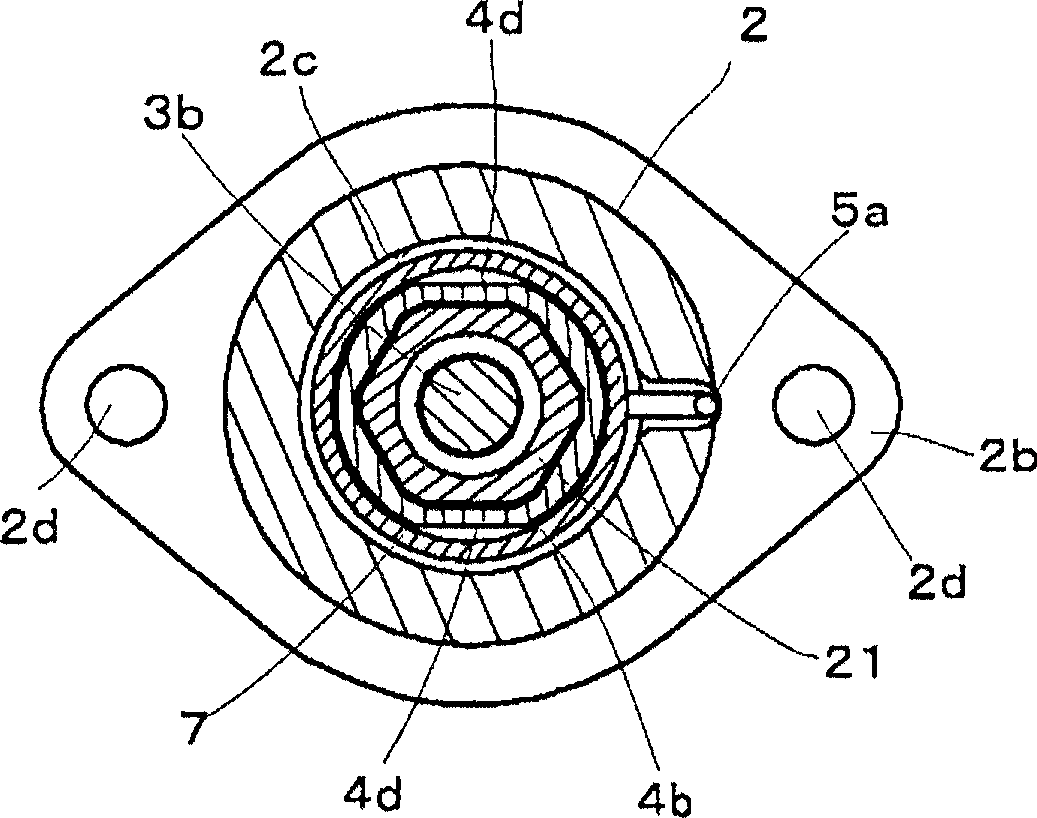
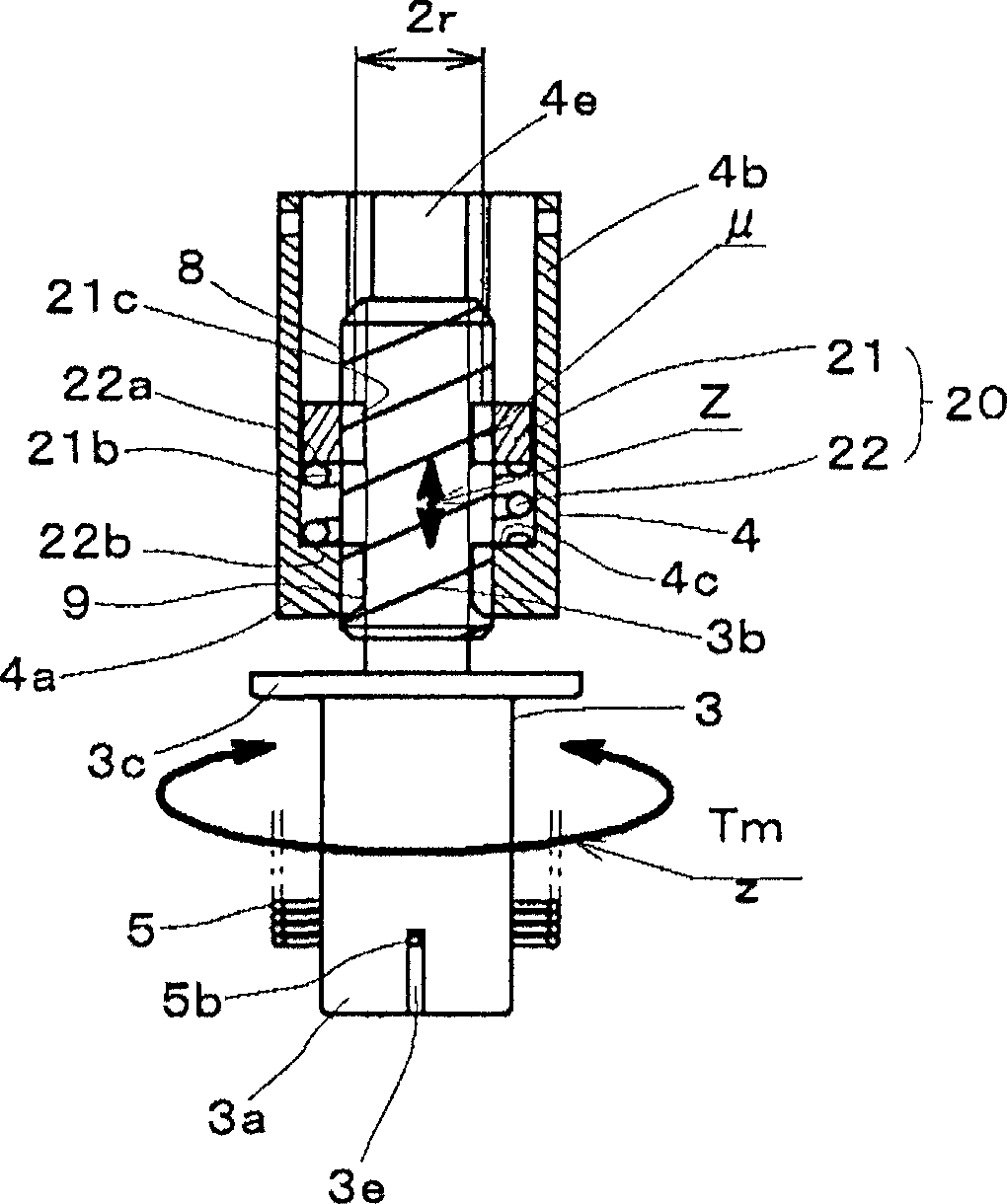
[0094] figure 1 is a longitudinal sectional view showing a tensioner A1 according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention, figure 2 yes figure 1 The F-F line section view. The tensioner A1 includes a housing 2 , a first shaft member 3 , a second shaft member 4 , a torsion spring 5 , a bearing 6 , a partition 7 and a resistance moment adding mechanism 20 .
[0095] The casing 2 is formed substantially in a bottomed cylindrical shape having a flange portion 2b in the middle of a cylindrical portion 2a. Furthermore, a storage hole 2c extending to the front end in the axial direction (propelling direction) is formed inside the cylindrical body portion 2a. The front end portion of the housing hole 2c is open, and a combination of the first shaft member 3, the second shaft member 4, the torsion spring 5, the spacer 7, and the resistance moment adding mechanism 20 is accommodated in the housing hole 2c.
[0096] The flange portion 2b of the housing 2 is used for mounting to a...
Embodiment 2
[0133] Figure 6 It is a longitudinal sectional view of the tensioner A2 of the second embodiment of the present invention.
[0134] In the second embodiment (A2), the cylindrical part 4b is cut off from the base end part 4a of the second shaft member 4 in the first embodiment (A1) to form a separate cylindrical part 41. Other configurations are similar to those of the embodiment One (A1) is the same. That is, the second shaft member 4 in the second embodiment (A2) is composed of the main member 40 and the cylindrical member 41 corresponding to the base end portion 4a of the second shaft member 4 in the first embodiment (A1) (corresponding to the claim 8 invention).
[0135] Figure 7 is a longitudinal sectional view showing the cylindrical member 41, Figure 8 is its top view.
[0136] Such as Figure 8 As shown, the cylindrical member 41 is formed into a non-circular cross-sectional shape having parallel cut portions 41c, 41d on both the inner surface and the outer sur...
Embodiment 3
[0157] Figure 15 It is a longitudinal sectional view showing the tensioner A3 of Embodiment 3 of the present invention, Figure 16 yes Figure 15 H-H line sectional view.
[0158] Such as Figure 15 As shown, compared with the above-mentioned embodiment, the tensioner A3 of this embodiment differs only in the configuration of the resistive moment adding mechanism 20, which adopts the arrangement of the second shaft member 4 and the third shaft member 21 turned upside down. The structure of other structures is basically the same as the above-mentioned embodiment. That is, the resistive torque adding mechanism 20 is configured such that the third shaft member 21 screwed to the threaded portion 3 b of the first shaft member 3 is disposed below the base end portion of the second shaft member 4 , and is connected by the connection member through the coil spring 22 . 50 is connected to the second shaft member 4 .
[0159] Figure 17 It is a longitudinal sectional view showing...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com